Chapter 8 Xray Production
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
only FINAL review higlights
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Chapter 8
What is Characteristic Radiation?
Projectile electron collides with inner-shell electron, removed from target atoms = ionized
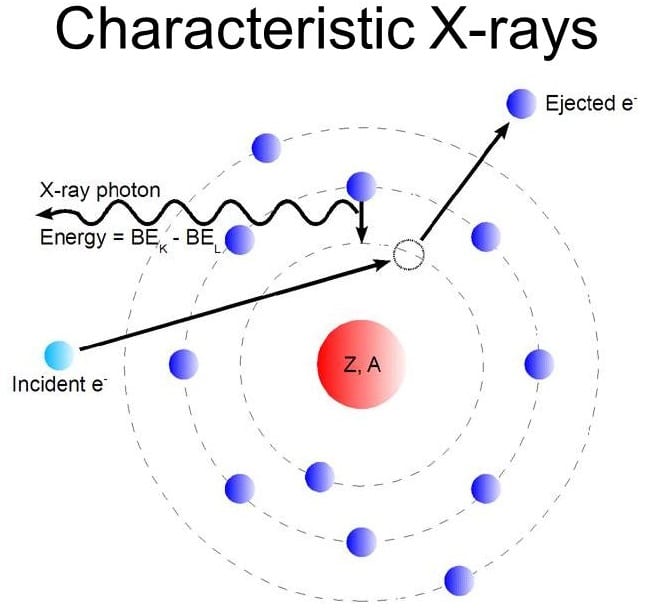
What fills the inner shell vacancy (characteristic)? and what is produced?
Outer shell; x-ray emission
What does each photon have?
Has specific energy equal to the difference in binding energies of two shells involved
Projectile Electron=
Photoelectron
Which shell = characteristic x-ray? with what energy?
Only K Shell
with at least 69 keV = Diagnostic radiograph
higher atomic # of target = ?
increased energy
What is Brems Xrays?
Projectile electron passes nucleus of target atom, slows down, changed course and leaves with reduction KE
Which interactions happen in the tube?
Characteristic and Bremsstrahlung
What is lost in Brems X-rays?
energy lost
What do most X-rays = ?
Brems (diagnostic Range)
<69 kVp = what type of interaction?
Brems X-rays
over 69 kVp = Which interaction?
Characteristic and/or Brems
X-ray Emission Spectrum
illustrated relative number of x-rays at each energy levels, from 0 - 100 keV

aka Characteristic Xray
discrete, Specified Spectrum
Characteristic Xray Spectrum binding energy
= 69keV (limited energies)
Mono energetic
one energy
Poly energetic
many energies
Factors that affect size and position of x-ray spectrum
mAs
kVp
added filtration
target material
voltage waveform
mAs
Change in mAs is DIRECTLY PROPORTIONAL to change in amplitude of spectrum
Examples of mAs increase
if doubled 200 mA to 400 mA = twice the # of projectile electrons (from cathode to anode) = mAs doubled but energy is the same
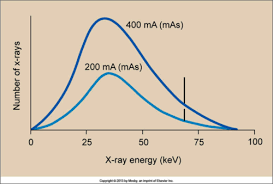
increase in mAs = ?
increase in amplitude
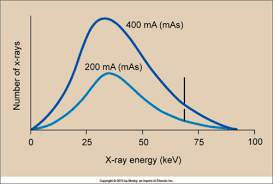
increase in quantity =
NO change in quality
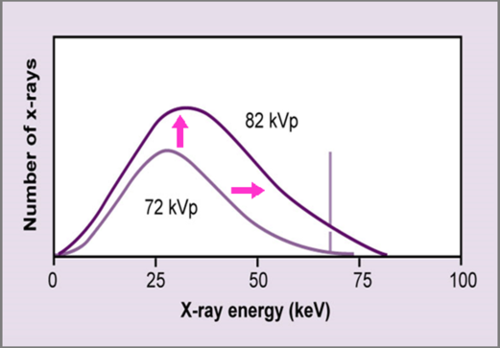
kVp increase
When kVp is increased = amplitude of spectrum increased BUT also more high energy emitted
kVp High Energy =
higher potential for multiple penetrability
increase both energy and quality
Increase voltage ripple =
Decrease quantity and decrease in quality
The shift of the characteristic x-ray spectrum to higher energy will occur because of
an increased in atomic number
Useful characteristic x-rays are produced in tungsten
by ionization of a k-shell electron
Characteristic x-ray
are characteristic of target Z
Brems radiation is produced by
a conversion of projectile electron kinetic energy to electromagnetic energy
If an average radiographic technique is used
most x-rays are bremsstrahlung
In bremsstrahlung x-ray production
the projectile electron is from the cathode
When Brems X-ray is produced
a projectile electron will lose enegry
The wavelength of an x-ray
becomes longer as projectile electron kinetic energy is reduced
An increase in mAs will
increase the number of bremsstrahlung x-rays
The area under the curve of the x-ray emission spectrum us representative of
the total number of x-rays
Normally the x-ray emission spectrum contaisn
both characteristic and bremsstrahlung x-rays
The characteristic x-ray emission spectrum principally depends on which of the following?
target material
The x-ray emission spectrum that represents several energy levels comes from
the x-rays emitted from the tube
Both the shape and position of the characteristic x-ray emission spectrum
correspond to target electron binding energies
Characteristic radiation is produced when
a vacancy in an electron orbit is filled
The x-ray emission spectrum is a plot of
the number of x-rays versus energy
The amplitude of the brems x-ray emissiono spectrum
has max value at an energy approx one third of the kVp
On s general x-ray emissiong spectrum, what 2 items are affected?
Quantity and Quality
Most of the x-rays produced at the target are
Bremsstrahlung
In order to construct an x-ray emission spectrum, one must know the
number of x-rays at each energy intervals
The wavelength of an x-ray is
inversely proportional to its energy
Minimum wavelength is related to
the KE of the Projectile Electron
The region of the x-ray emission spectrum associated with minimum wavelength
highest-energy brems x-ray
To calculate minimum x-ray wavelength, one must know the value of
kVp
Chapter 9