Categorical and Propositional Logic
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts and definitions from the lecture notes on categorical and propositional logic.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Categorical Proposition
A simple proposition that asserts the relationship between two classes of objects or concepts.
Subject
The term being predicated in relation to another category or concept.
Predicate
The term that predicates (defines/describes) the subject.
Universal Affirmative
Form A: A categorical proposition stating that all members of a subject class are included in a predicate class.
Universal Negative
Form E: A categorical proposition stating that no members of a subject class are included in a predicate class.
Particular Affirmative
Form I: A categorical proposition stating that some members of a subject class are included in a predicate class.
Particular Negative
Form O: A categorical proposition stating that some members of a subject class are not included in a predicate class.
Quantity
The extent to which the subject class refers to all or some members in a categorical proposition.
Quality
The affirmative or negative character of a proposition.
Copula
A linking verb ('are' or 'are not') that connects the subject and predicate.
Existential Import
The concept that the truth value of a proposition depends on the existence of the things to which it refers.
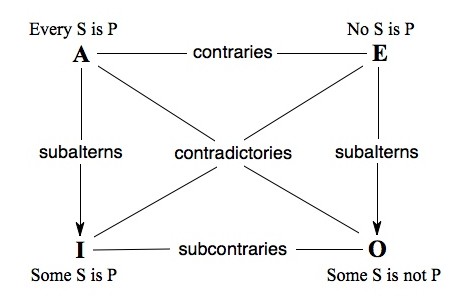
Contradictories
Propositions that cannot both be true or both be false.
two propositions never share the same truth value.
Contraries
Pairs of propositions that cannot both be true but can both be false.
A and E can’t both be true but may both be false.
Subcontraries
Pairs of propositions that cannot both be false but can both be true.
I and O can’t both be false but may both be true
Subalterns
The relationship between a universal proposition and its corresponding particular proposition.
Categorical Syllogism
A deductive argument consisting of two premises and a conclusion, each being categorical propositions.
Major Term
The predicate in the conclusion of a categorical syllogism.
Minor Term
The subject in the conclusion of a categorical syllogism.
Middle Term
The term that connects the major and minor terms, appearing in both premises.
Mood and Figure
The mood is symbolized by the propositional forms, while the figure is determined by the position of the middle term in premises.
Propositional Logic
The logic of compound statements that focuses on propositions as its primary components.
Truth Functions
The relationships that determine the truth value of a compound statement based on its simple propositions.
Tautology
A statement that is always necessarily true.
Self-Contradiction
A statement that is always necessarily false.
Logical Equivalence
Two statements that have the same truth value in every scenario but not necessarily the same phrasing.
Square of Opposition
A graphical representation to highlight relationships between standard-form categorical propositions that differ in quality, quantity, or both.
Universal statements have a truth value, even if their subject class is empty.
Universal statements lack existential import: they can be framed as If-then statements.
Particular statements inherently have existential import.