Info Tech Exam 1.2
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What is attribute data and what types of geospatial data have it?
It provides characteristics about spatial data beyond location
What makes something spatial data?
if it references location for its basis
What are some reasons we need to use GIS’s?
GIS is easy to manipulate
good for large data points
easy to share
Uses of attribute data
to symbolize map features
select features
serve as variables for analysis
Rows
records
columns
attributes
single symbol
categories
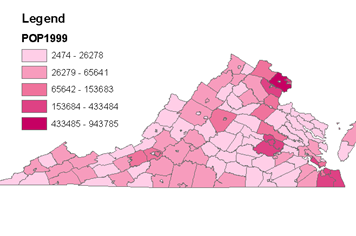
quantified
the ways ArcMap assigns breaks to continuous data and why you might use them
So you can take out the data you don’t need
Makes data easier to manipulate
You can select data based on:
filter
query
interactive selection
Reasons to select features:
perform calculations on just selected features
highlight for visualization
create dataset from selected data
Once you have a selection you can:
add
remove
select from
switch
clear your selection
(TYPE=”UH”) OR (TYPE=”LP”)
Select all with that are either type UH or type LP
(TYPE=”UH”) AND (AGE<30)
select all that are both type UH and less than 30 years old
Interactive select
click on the selection you want
Select by location
select by intersection, distance from, touching…
Raster
features depicted by contents of grid cells
pixelated up close
better for land cover
good for large datasets
worse for having a loss of small info
Vector
features defined by coordinate pairs
high resolution up close
better for buildings and roads
does not lose clarity up close
larger data set
Files in a shapefile
shapename.shp
shapename.dbf
shapename.shx
common files extension for raster
.tif
.bmp
Common file extension for vector
.shp
Nominal
think names
no numeric meaning or relative ranking
may use numeric codes
Ordinal
labels or categories
but ranking is meaningful
difference between categories might not be consistent
1rst, 2nd, 3rd,…
very good, moderate, poor
Interval
numerical values
zero is not absolute
ratios not always meaningful
time and temperature
pH
Ratio
zero is absolute
zero doesn’t change with units
ratios meaningful
Integer
whole number
short/long
float
has a decimal
single/double
DEM
digital elevation model
DRG
Digital raster graphic
Components of a map
North Arrow
Scale Bar
Bounding Box
Legend
Title
All projections
distort the earth
Geographic coordinate system
angular units (not distance) (degrees, minutes, seconds)
doesn’t involve a projection
latitude, longitude, parallel, meridian
Projection coordinate system
projection of the earth onto a plane
cartesian coordinates (x,y)
distance units (meters, feet,…)
mathematically defined
Angular
degrees, minutes, seconds
Cartesian
(x,y)
Common coordinate systems:
geographic
state plane
utm
Datum
represents assumptions about the shape of the earth
Why is UTM accurate at smaller scales?
Split into zones - zones matter
It minimizes distortion by doing this
Why do states use different projections for their state plane coordinate systems?
To minimize error
states may be broken up into zones
choose different projections based on shape
Projections
there will always be distortion
UTM scale
good at small scale
Geographic scale
good at big picture
State Plan scale
good at state scale
Where to find Coordinate system
in metadata
Dataframe
complete maps to themselves
Layers
different sets of data and displayed within the data frame
projected into the coordinate system of the dataframe
Layer coordinate systems
can be different but it is better if they are the same if you are calculating area and/or distance
When projection isn’t defined
you just have to figure it out
can still use data
How GPS receivers determine their location
read the differences in times sent by different satellites to triangulate its location.
3 components of GPS
satellites
control (monitor, orbits and clock)
and GPS receiver
common sources of GPS error
Ionospheric Delay
Clock Errors
Multipath Error
WAAS
keeps track of error and lets your GPS unit know
corrects clock error
Differential correction
using a base station with known location to test error
used to correct all error types
How many satellites do you need to get your position in 3d?
4
Accuracy
closeness of a measured value to a standard or known value
measure of bias
how close the test is to the true value
Precision
measure of exactness
how close the tests are to each other
How to measure area in arcmap
In attribute table, right click then calculate geometry
Standard Deviation
measure of the distribution of data
lower values means they are closer together
doesn’t use a true value
measure of preciseness
Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE)
uses difference from true value rather than just the mean
lower means closer to true value
How RMSE is calculated
(Observed- actual value) squared
Add together and divide by n – average
Take square root
Bias
Metric related to the systematic accuracy of the data
Not just random error