Oral Anatomy midterm
1/203
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
204 Terms
Anatomy
The scientific study of the shape and structure of the human body
Physiology
The scientific study of how the human body functions
anatomical position
human body standing in an upright position, eyes facing forward, feet parallel and close together, arms at the sides of the body with the palms facing forward
sagittal (lateral) plane
divides body into left and right
mid-sagittal plane
divides the body into equal left and right halves
AKA: Midline or median plane
transverse (horizontal) plane
divides the body into superior and inferior parts
Perpendicular to sagittal plane
frontal plane (coronal plane)
divides body into anterior (Front) and posterior (Back) sides
Anterior (ventral)
Toward the front of the body
Posterior (dorsal)
toward the back
Superior (cranial)
above
Inferior (caudal)
below
Medial
toward the midline
Lateral
away from the midline
Left or right
Internal
Toward the center of the body
External
Toward the periphery (outside)
Proximal
Closer to the midline
Cells
Basic unit of life
Differentiation
The specialized function of a cell
stem cells
Immature/Unspecialized cells located in bone marrow
Tissues
Groups of cells with a common structure and function.
Body system
group of organs that work together to perform a specific function
How many body systems are there?
10
- Skeletal
- Muscular
- Cardiovascular/Lymphatic and immune
- Nervous
- Respiratory
- Digestive
- Urinary
- Integumentary
- Endocrine
- Reproductive
skeletal system
Protects and supports body organs and provides a framework the muscles use to support movement. Made up of bones and joints
Muscular System
Holding body erect and movement
cardiovascular/lymphatic and immune system
Heart and defense against disease
nervous system
response or sends a message
respiratory system
Transports oxygen, excretes carbon dioxide
digestive system
Digestion, absorption, and excretion
uriary system
Elimination of urine
integumentary system
Protection of body regulation of temperature
endocrine system
Integration of bodily function and growth
reproductive system
Production of a new life
What are the 3 layers of bone
Periosteum, compact, and cancellous
Periosteum
First layer of bone, thin layer of connective tissue with nerve and blood vessels, contains osteoblasts
Osteoblasts
bone forming cells
Compact bone
dense, hard layers of bone tissue that lie underneath the periosteum
AKA cortical bone
Cancellous bone and marrow
Inside the bone forming a honeycomb shape
AKA trabecular bone
Joints
where two bones meet in such a way to permit motion
3 types of muscle tissue
Striated - Voluntary
Smooth - involuntary
Cardiac - walls of the heart
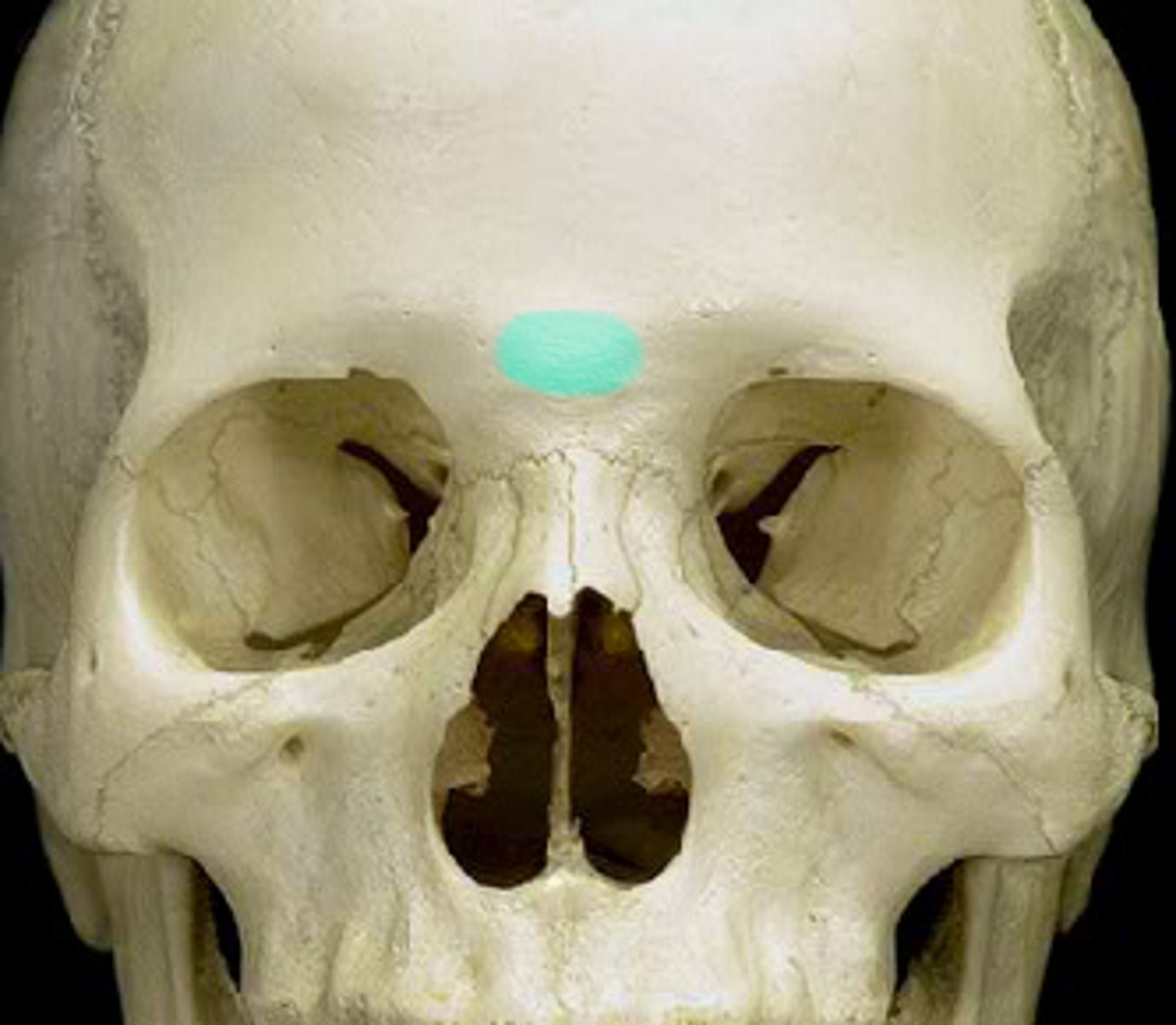
Glabella
the flattened area between the eyebrows
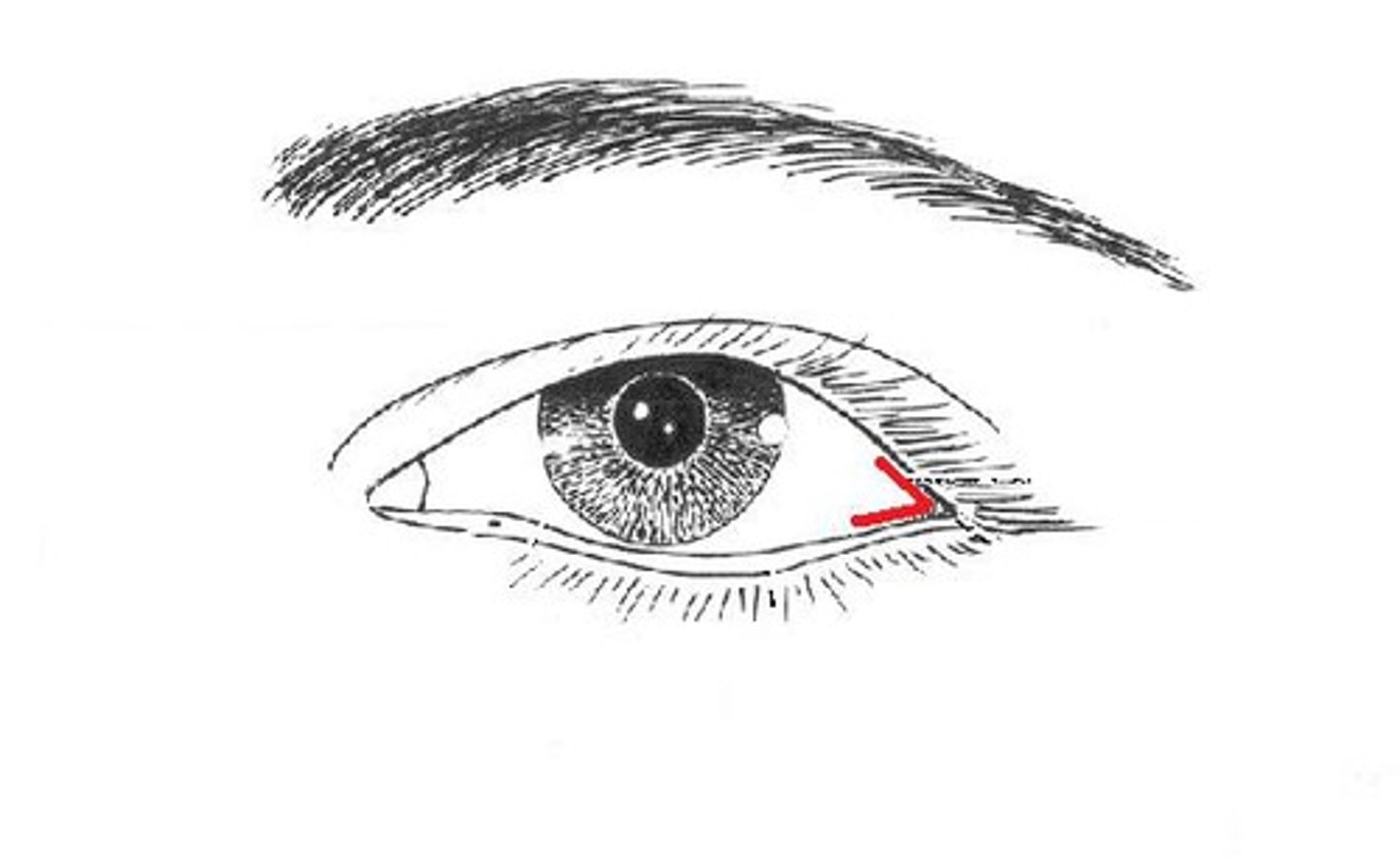
lateral canthus of the eye
outer corner where the upper and lower eyelids meet
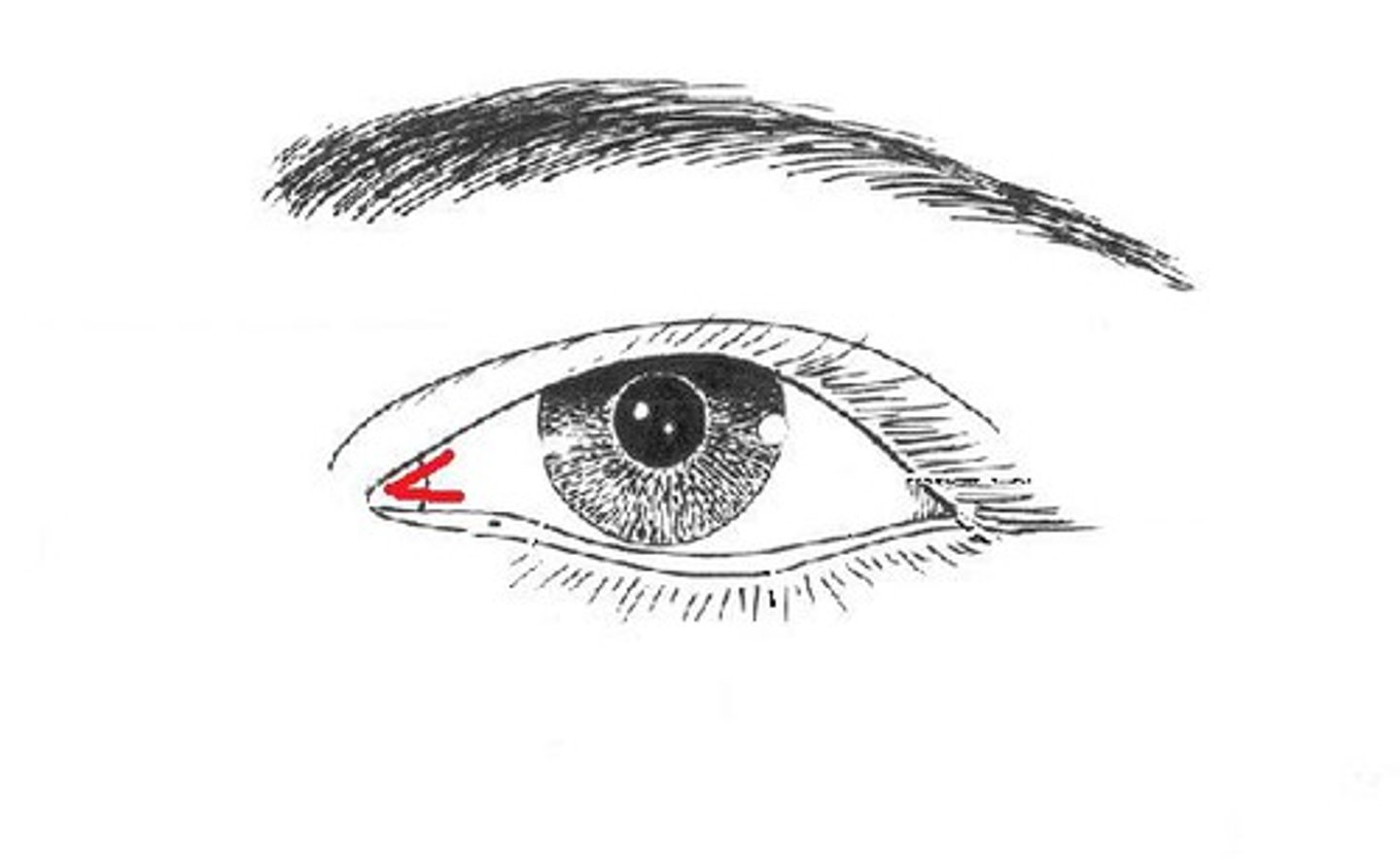
medial canthus of the eye
inner corner of eye where the upper and lower lids meet
Ala
Winglike tip of the outer side of each nostril
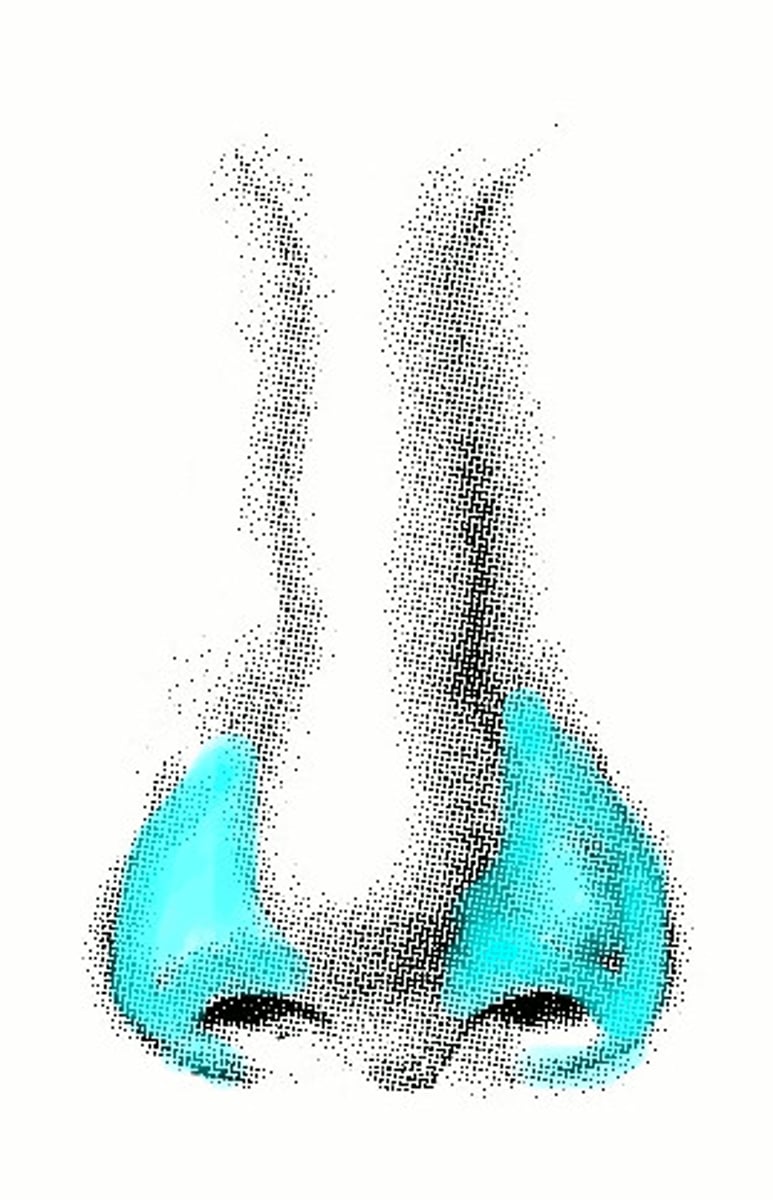
root and bridge of nose
area between the eyes
Septum of the nose
divides nasal cavity into left and right
Anterior Naris
nostril
apex
the highest point, tip
Philtrum
Rectangular area from under the nose to the midline of the upper lip
Tubercle of lip
Thicker area on upper lip at termination of philtrum

vermillion border
line around the lips
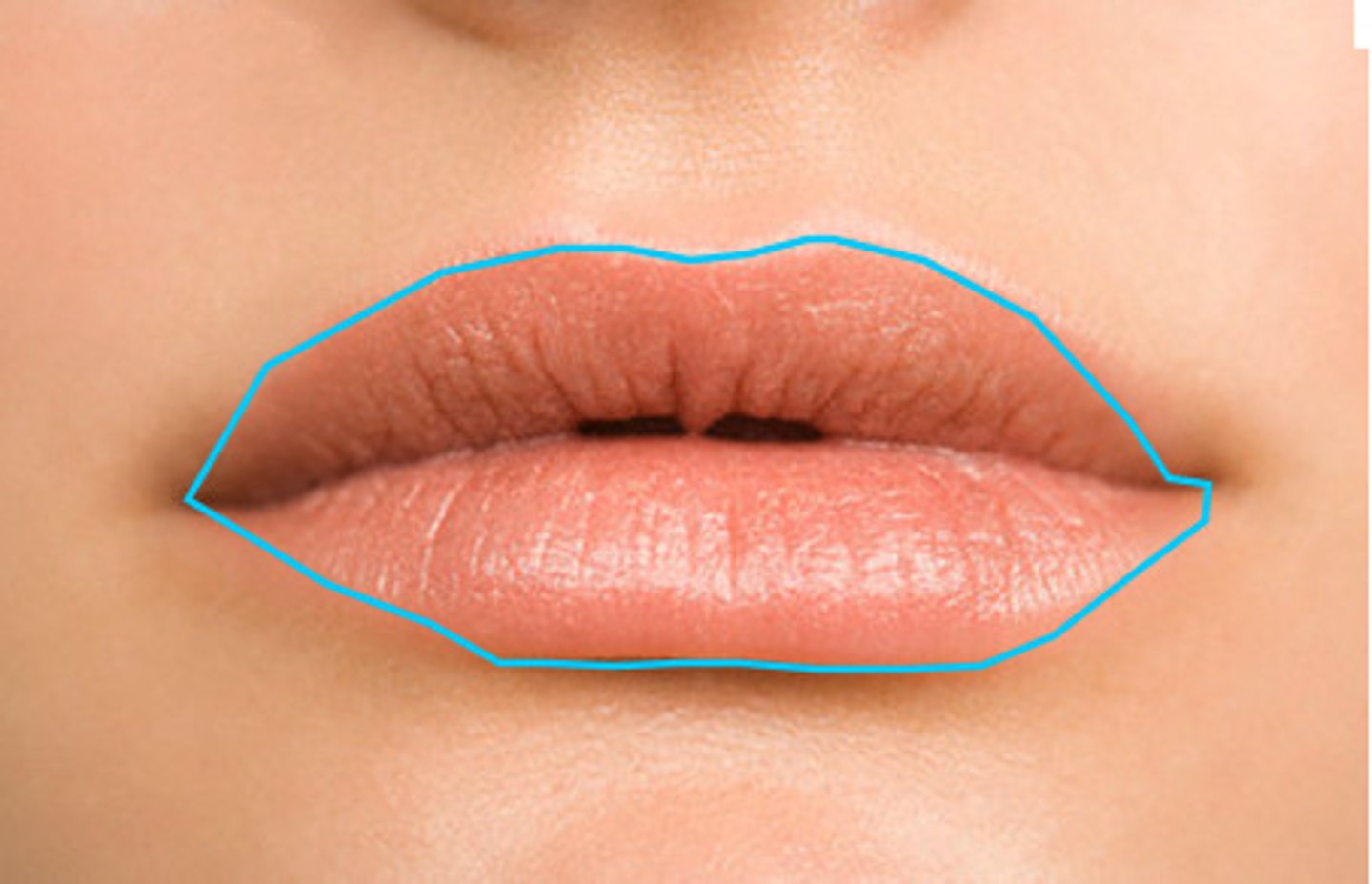
Labiomental groove
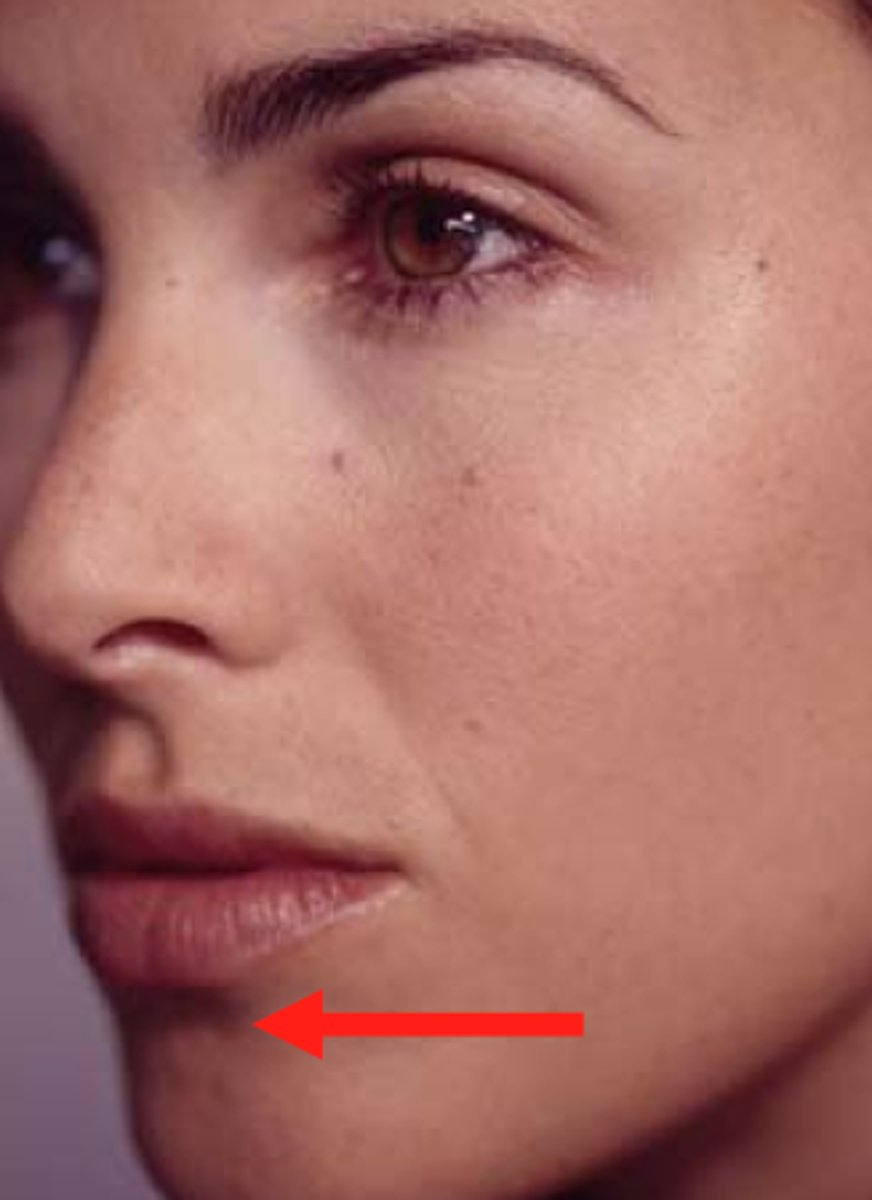
horizontal groove between lower lip and chin

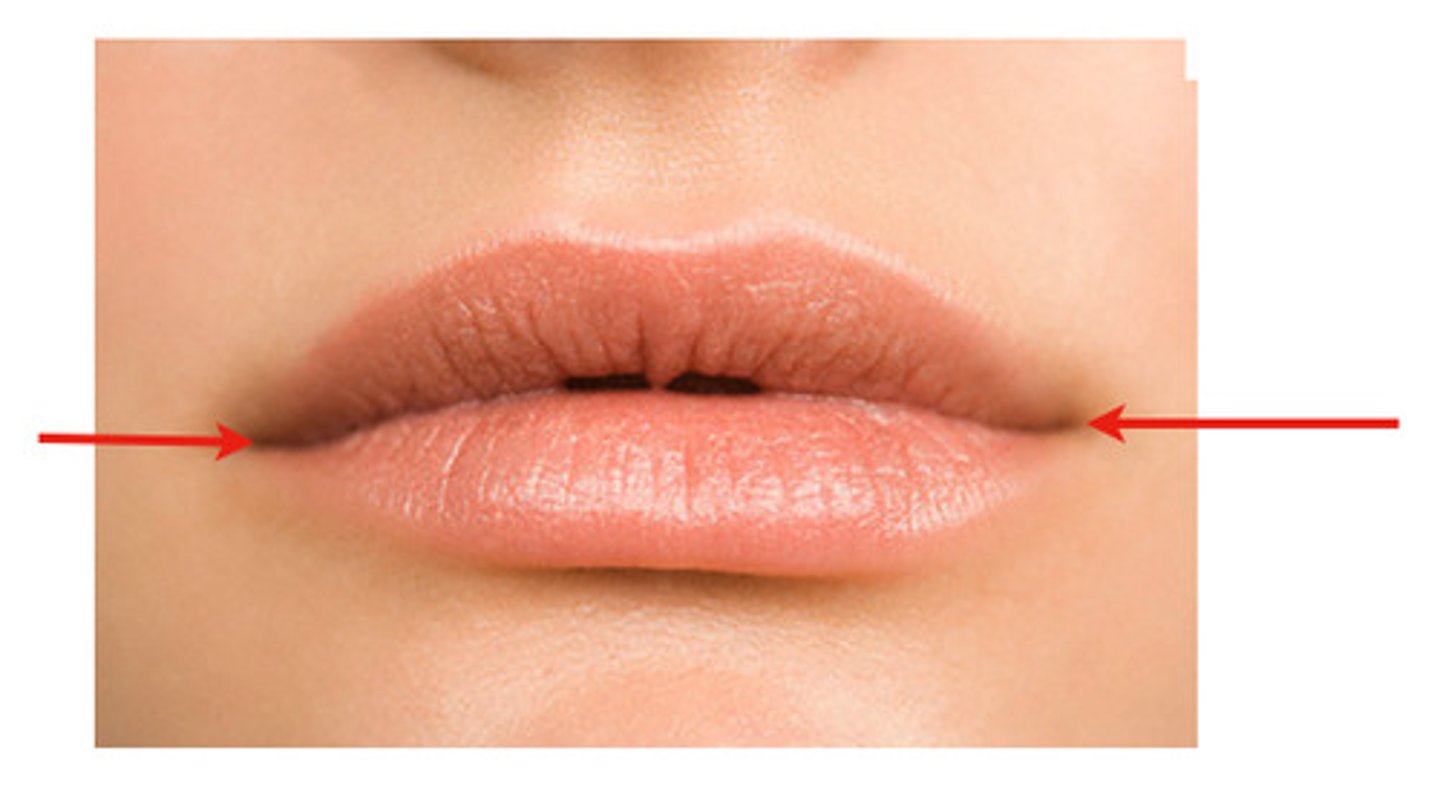
Labial commissure
corners of the mouth

Auricle
external portion of the ear
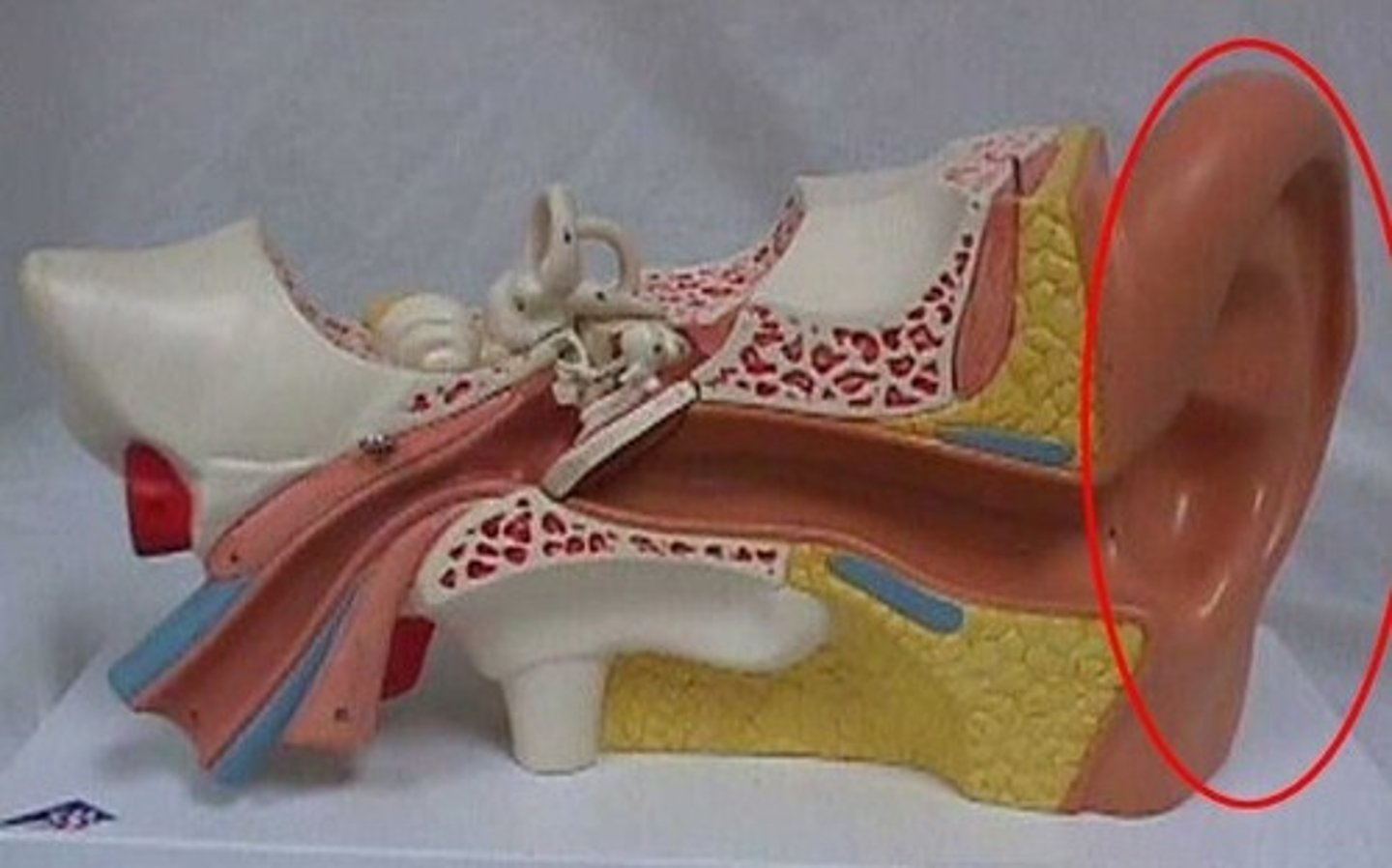
Tragus of the ear
Cartilage projection anterior to the external opening of the ear
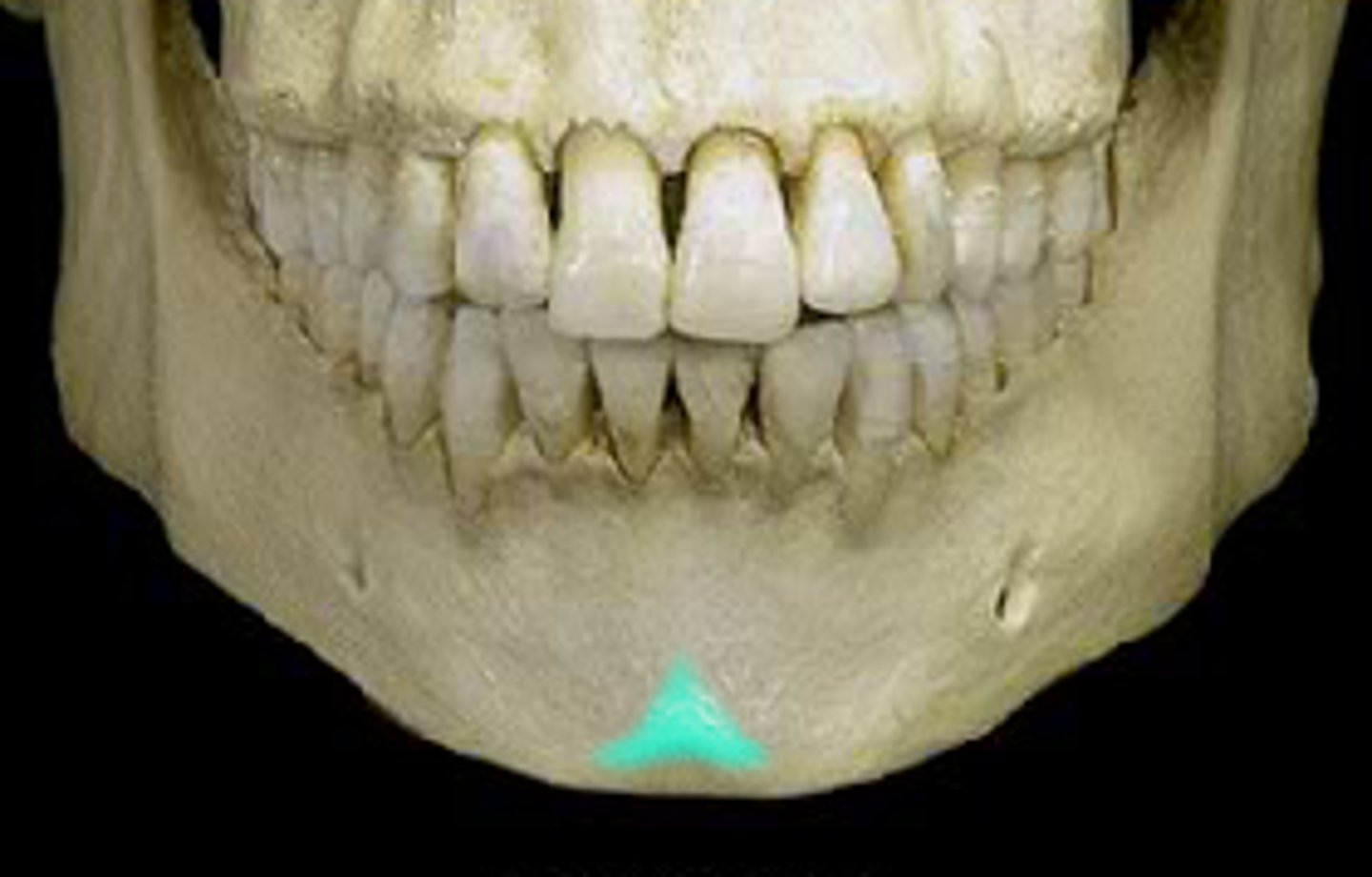
mental protuberance of mandible
point of chin
ramus of mandible
vertical part of mandible
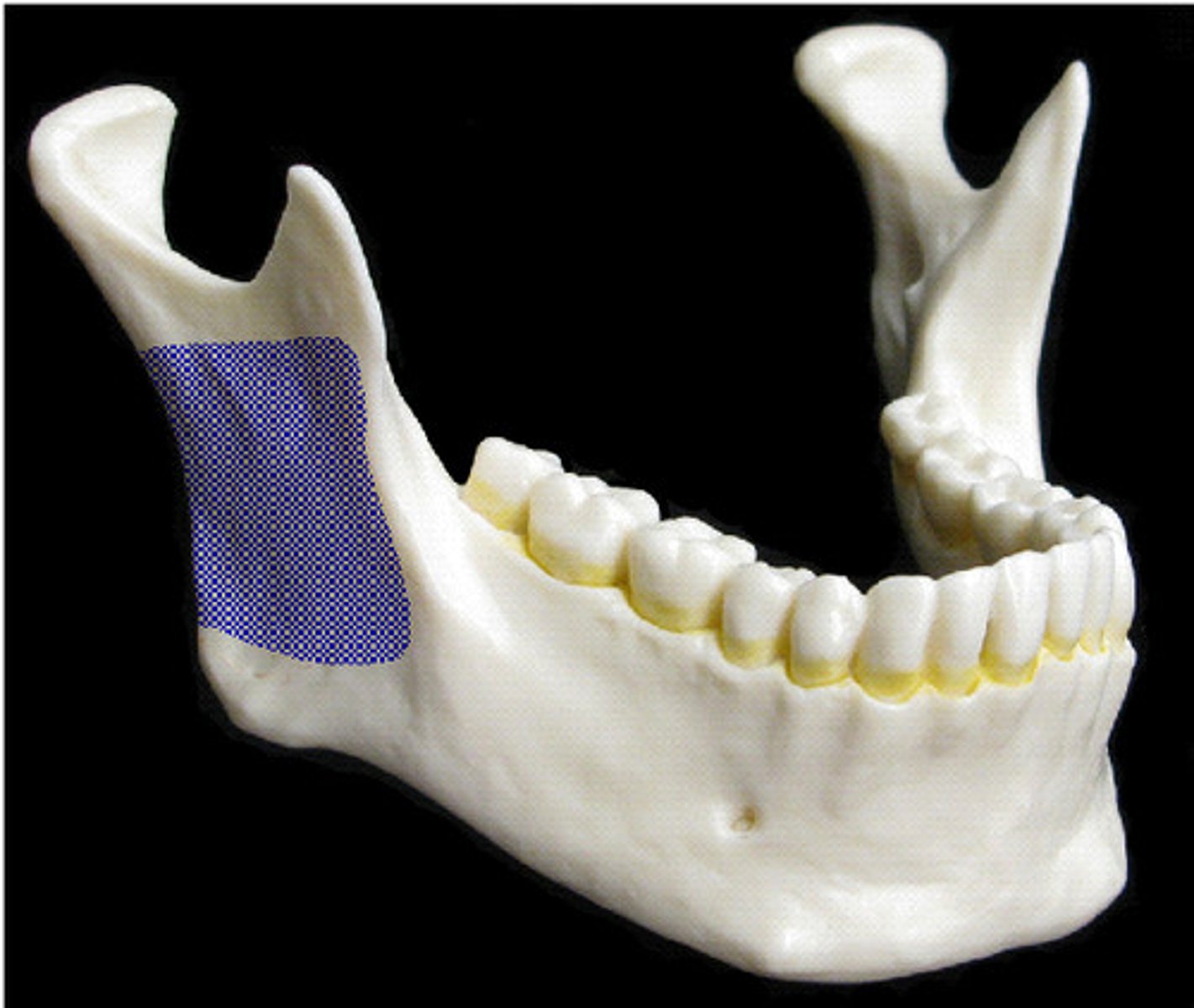
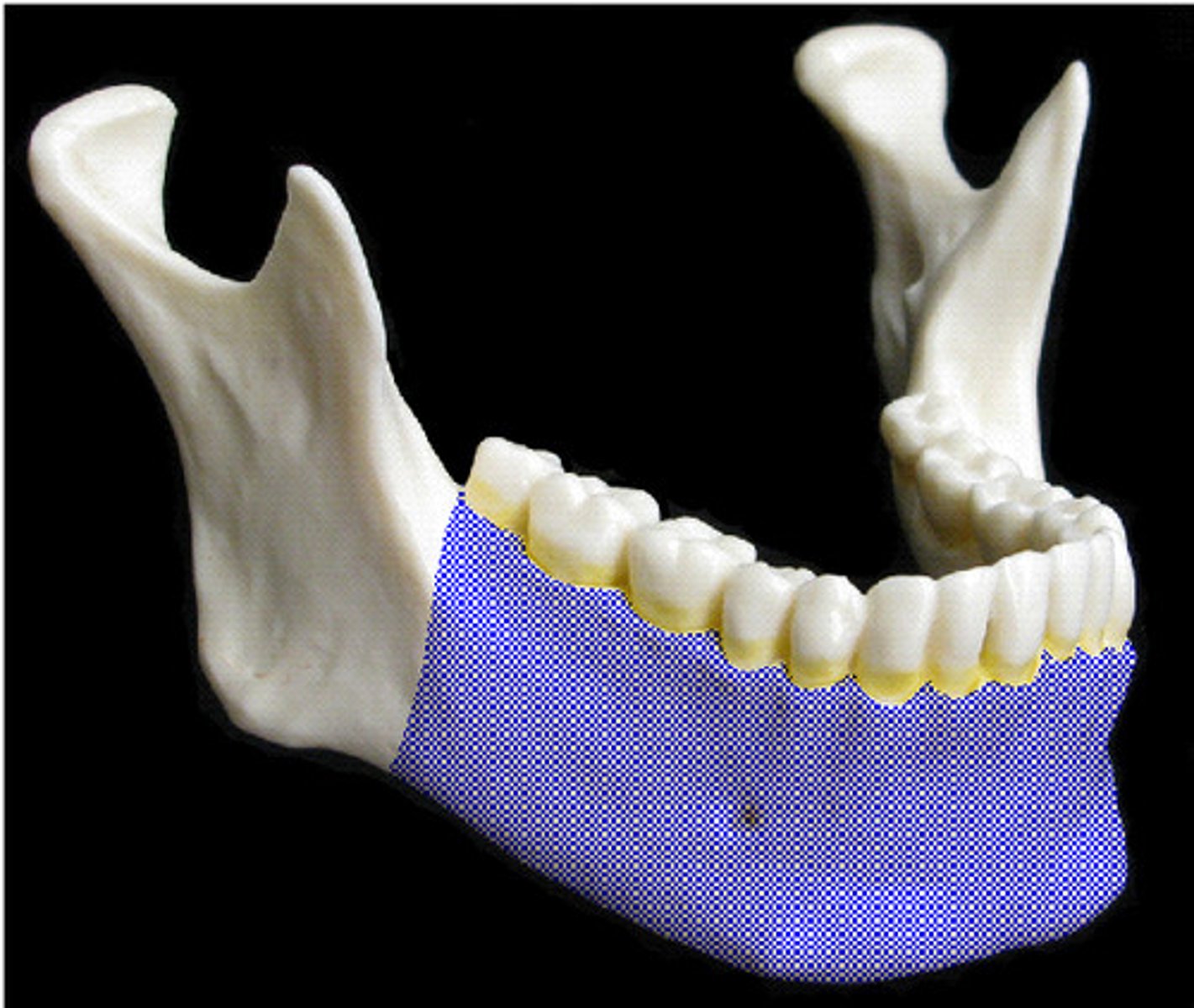
body of mandible
horizontal portion of the mandible
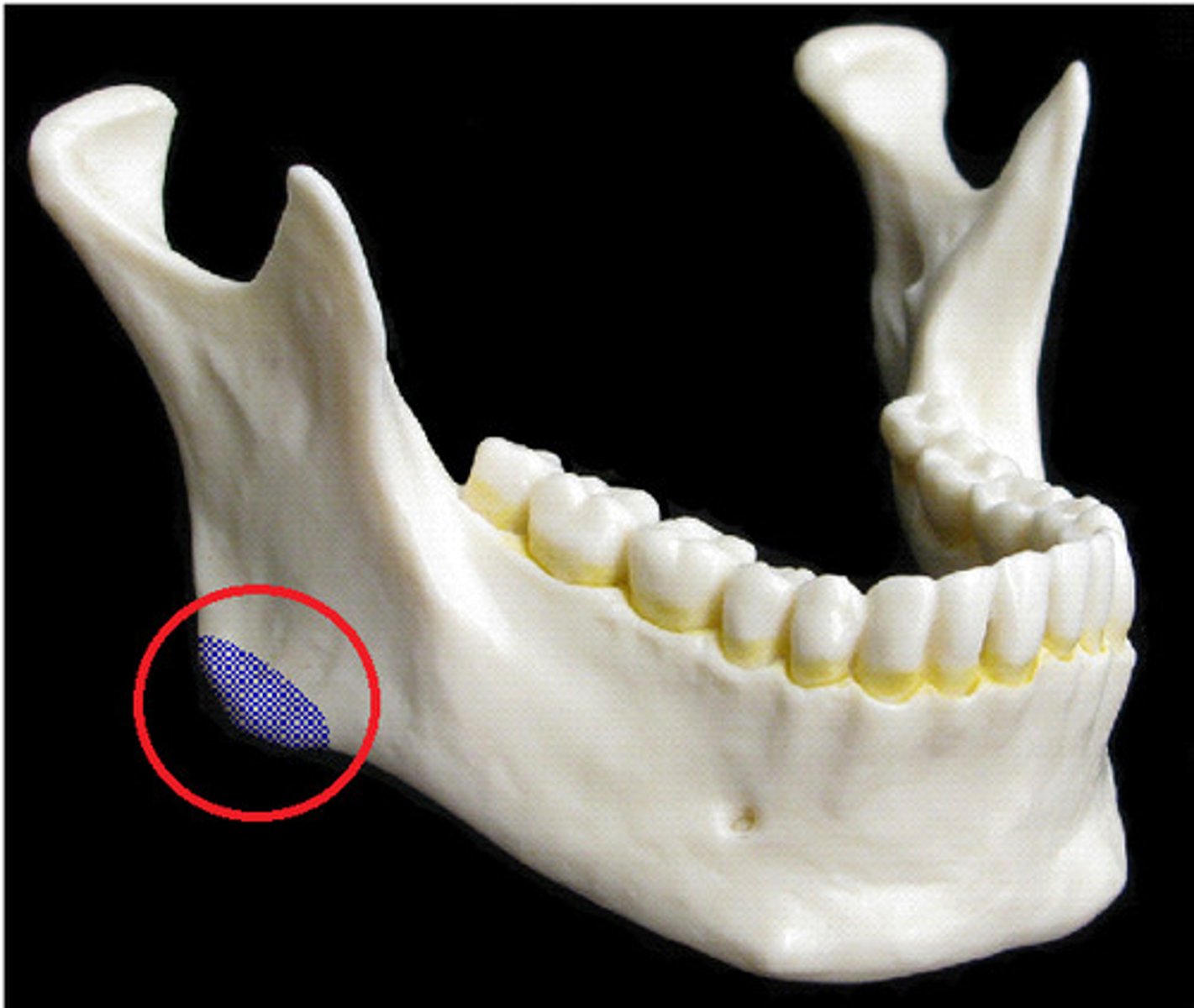
angle of mandible
Point at the lower border of the body of the mandible where it turns up onto the ramus.
vestibule
Space between the teeth and the inner mucosal lining of the lips and cheeks
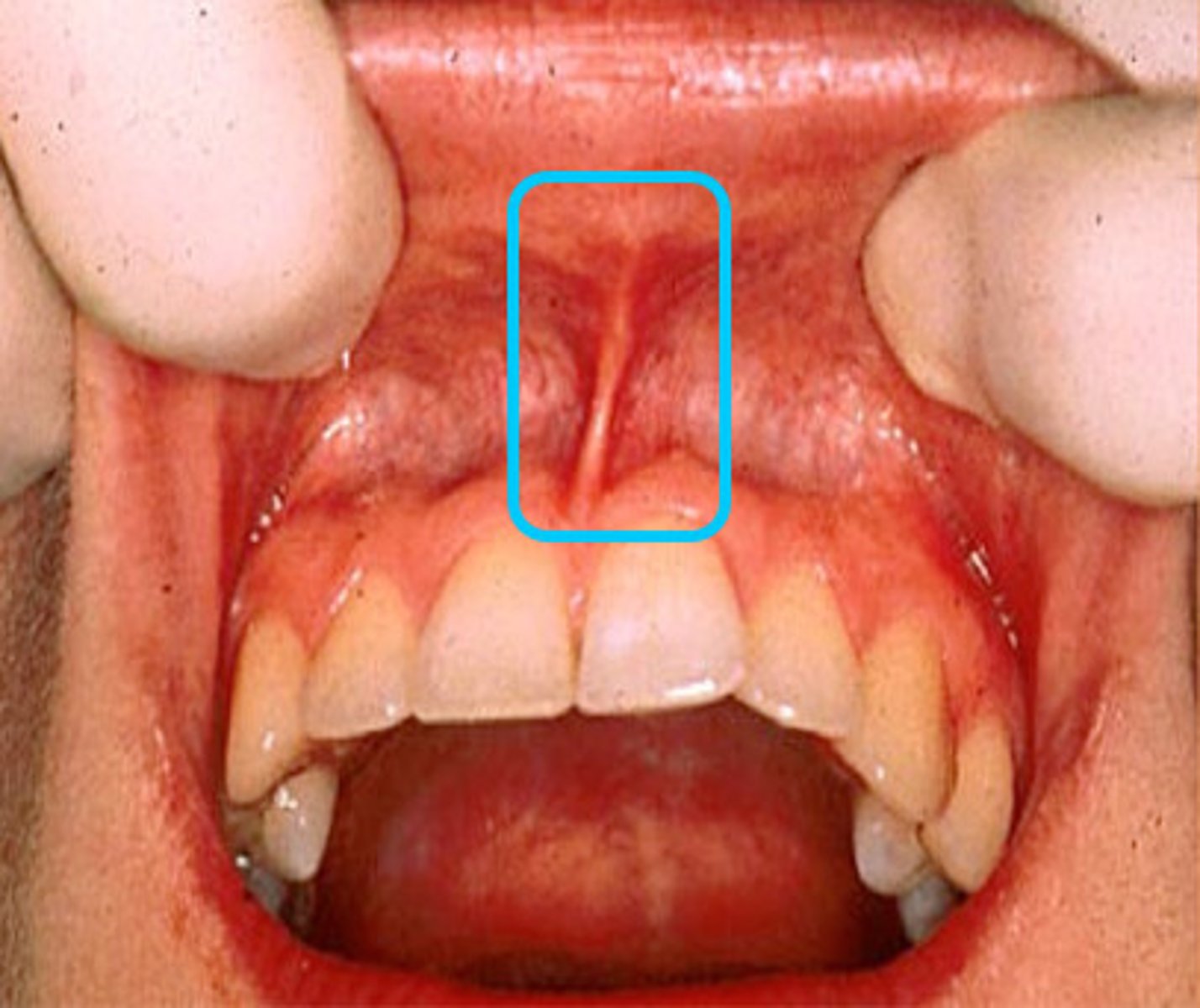
Labial frenum
Band of tissue that passes from the facial oral mucosa at the midline of the arch to the midline of the inner surface of the lip
buccal frenum
lateral boundary of the vestibule, bonds of fibrous tissue holding cheek in place
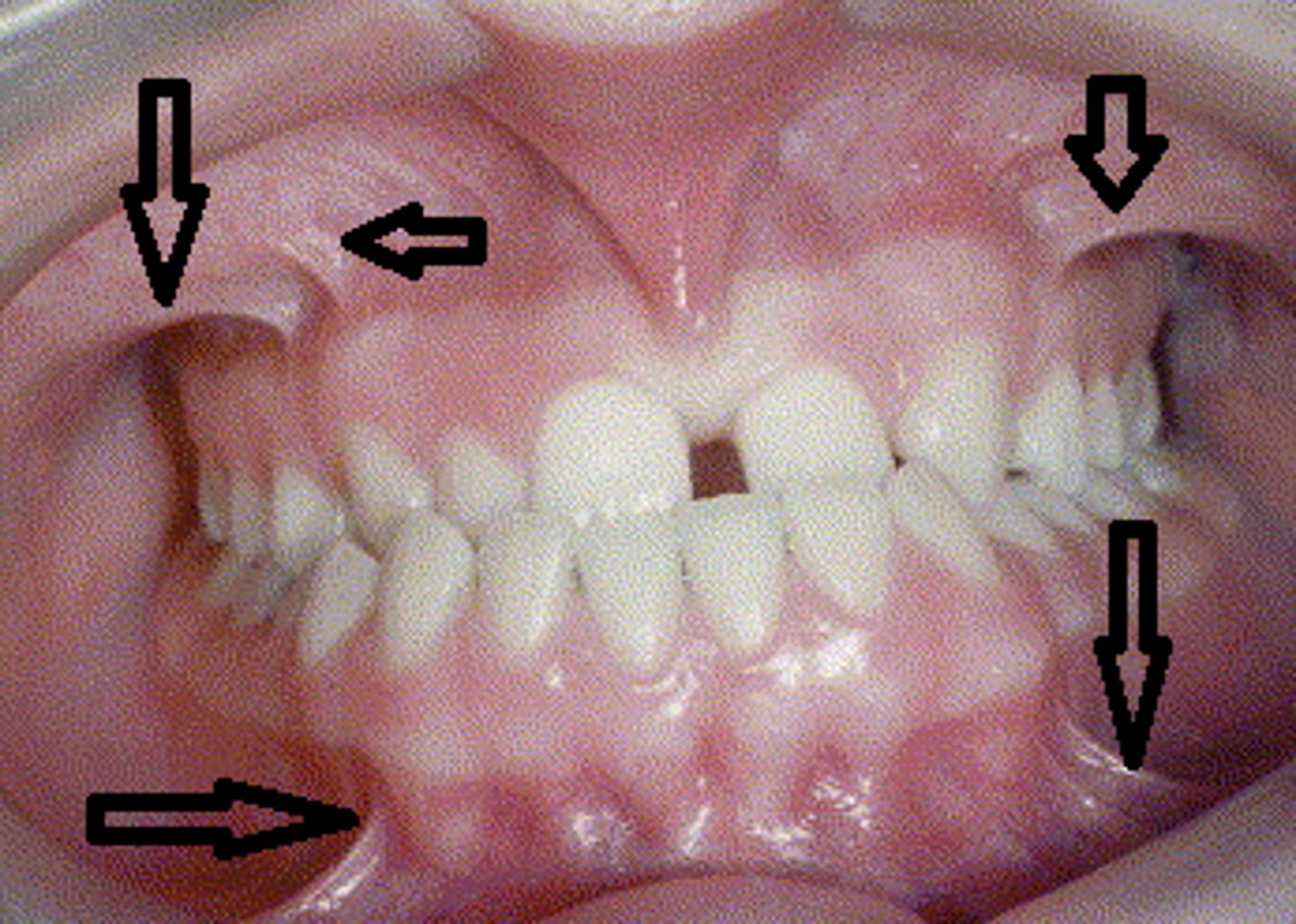
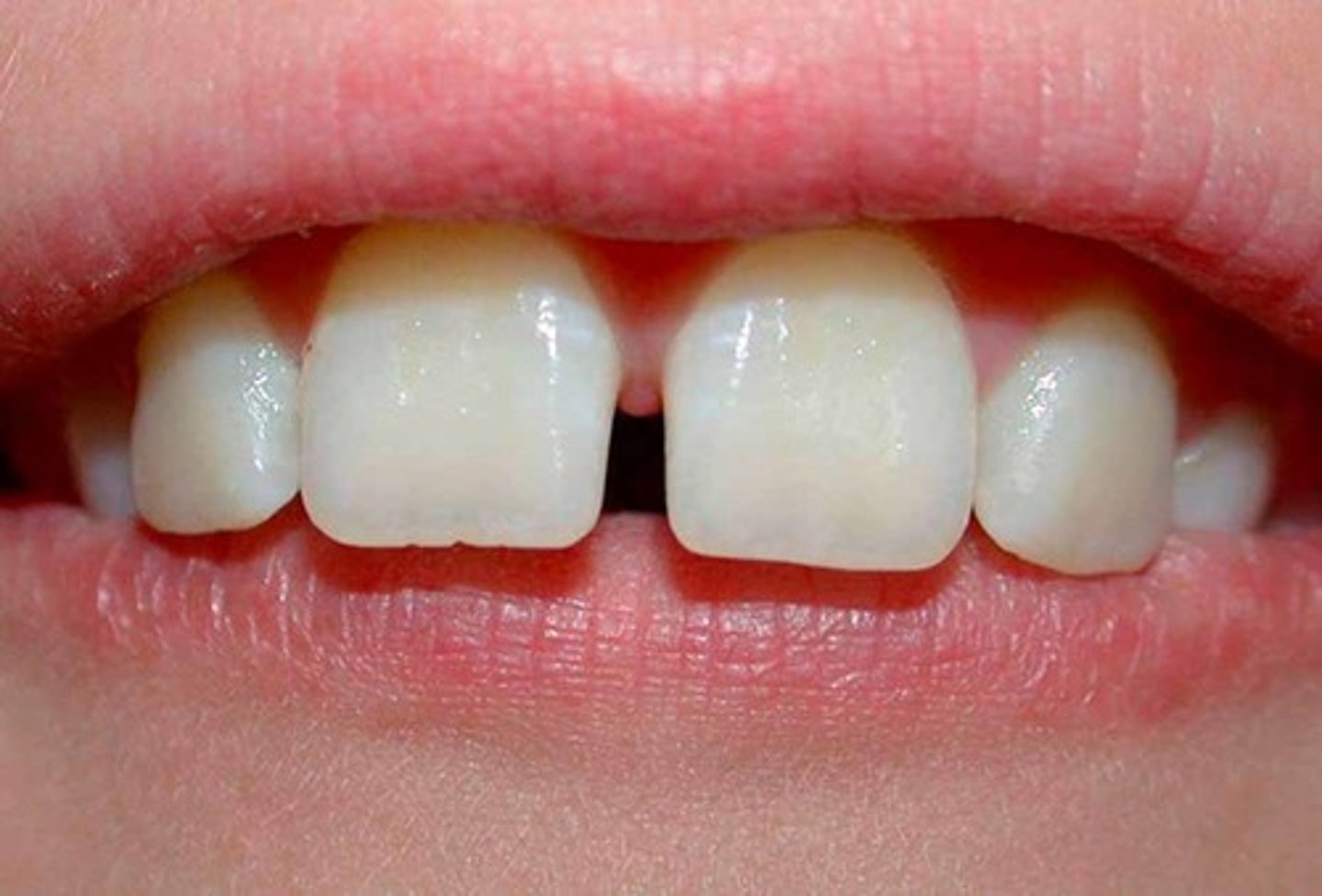
Diastema
A space between two teeth
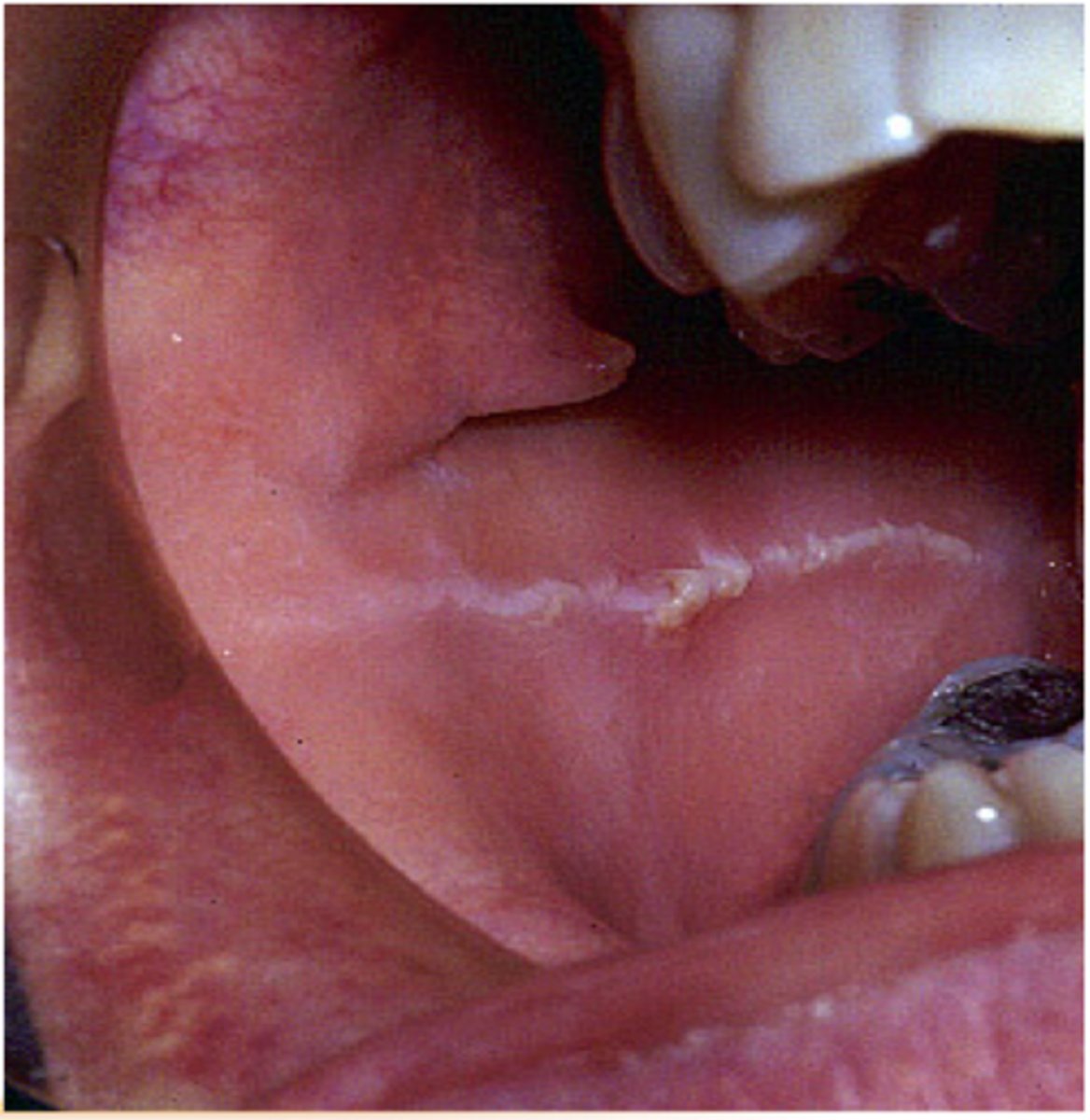
Linea Alba Buccalis
white line running posteriorly on each side at the level where the upper and lower teeth come together
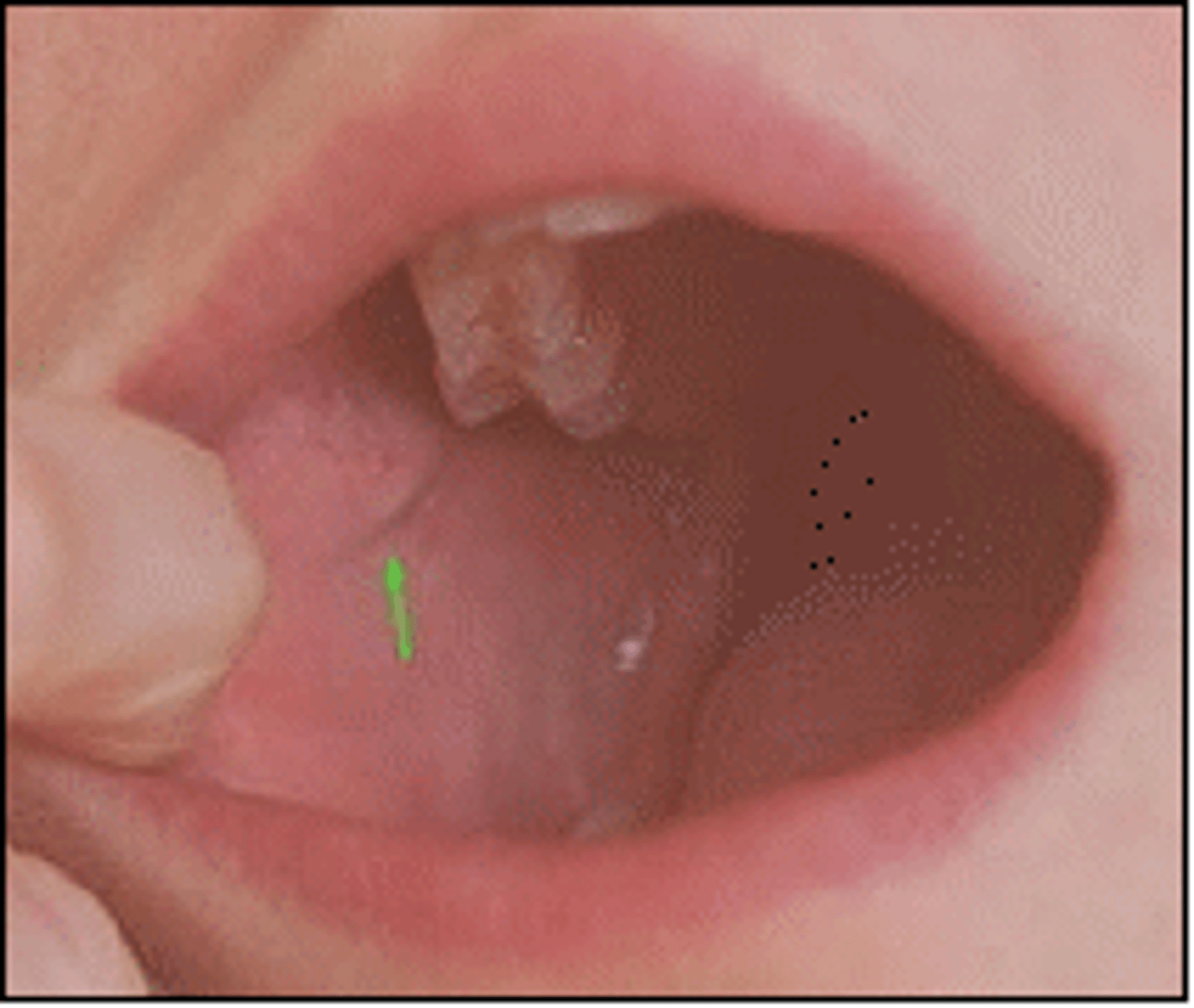
Stenson's duct
The excretory duct of the parotid gland
hard palate
roof of the mouth
Rugae
ridges on the hard palate
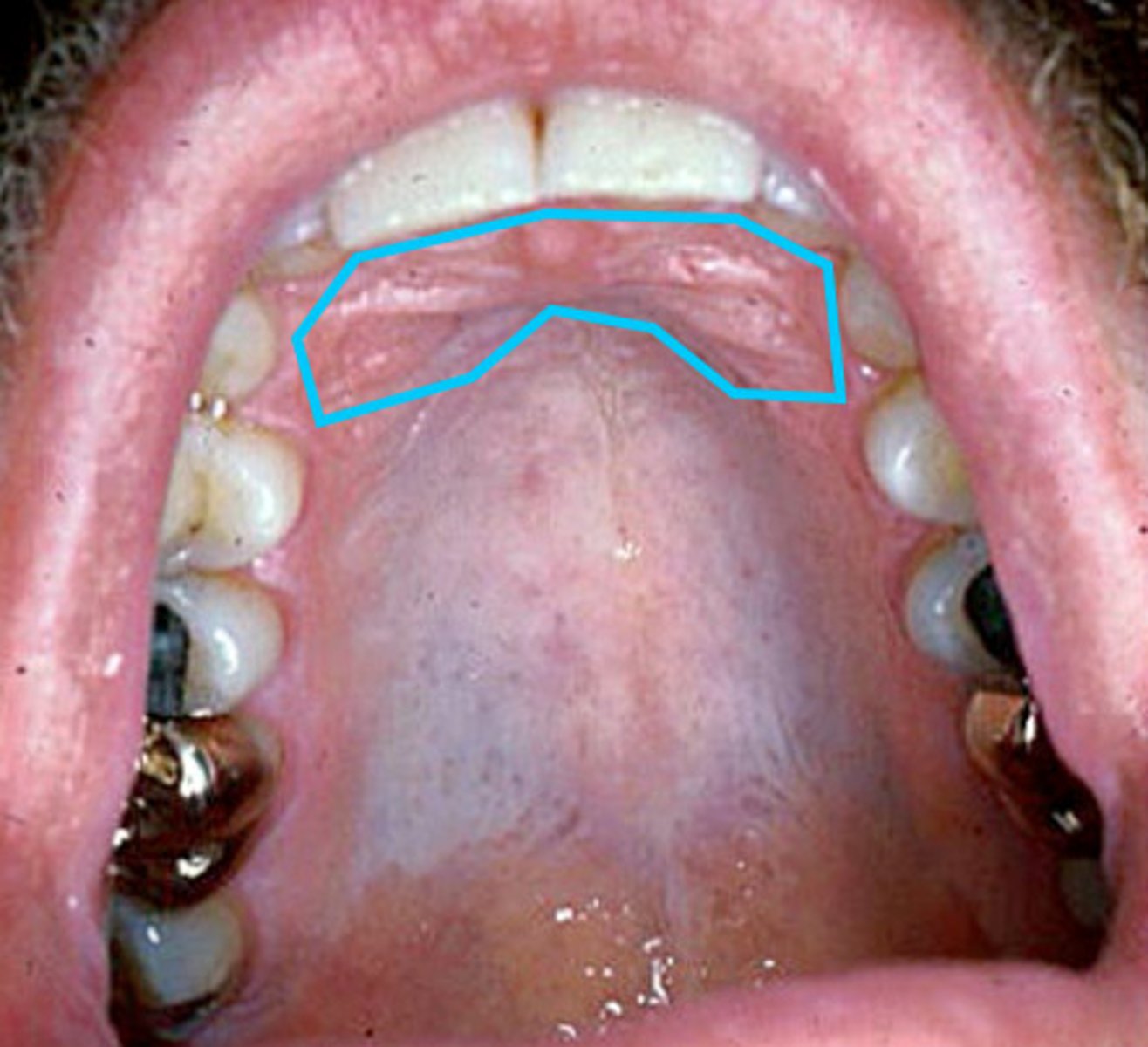
Incisive papilla
Pear-shaped pad of tissue that covers the incisive foramen
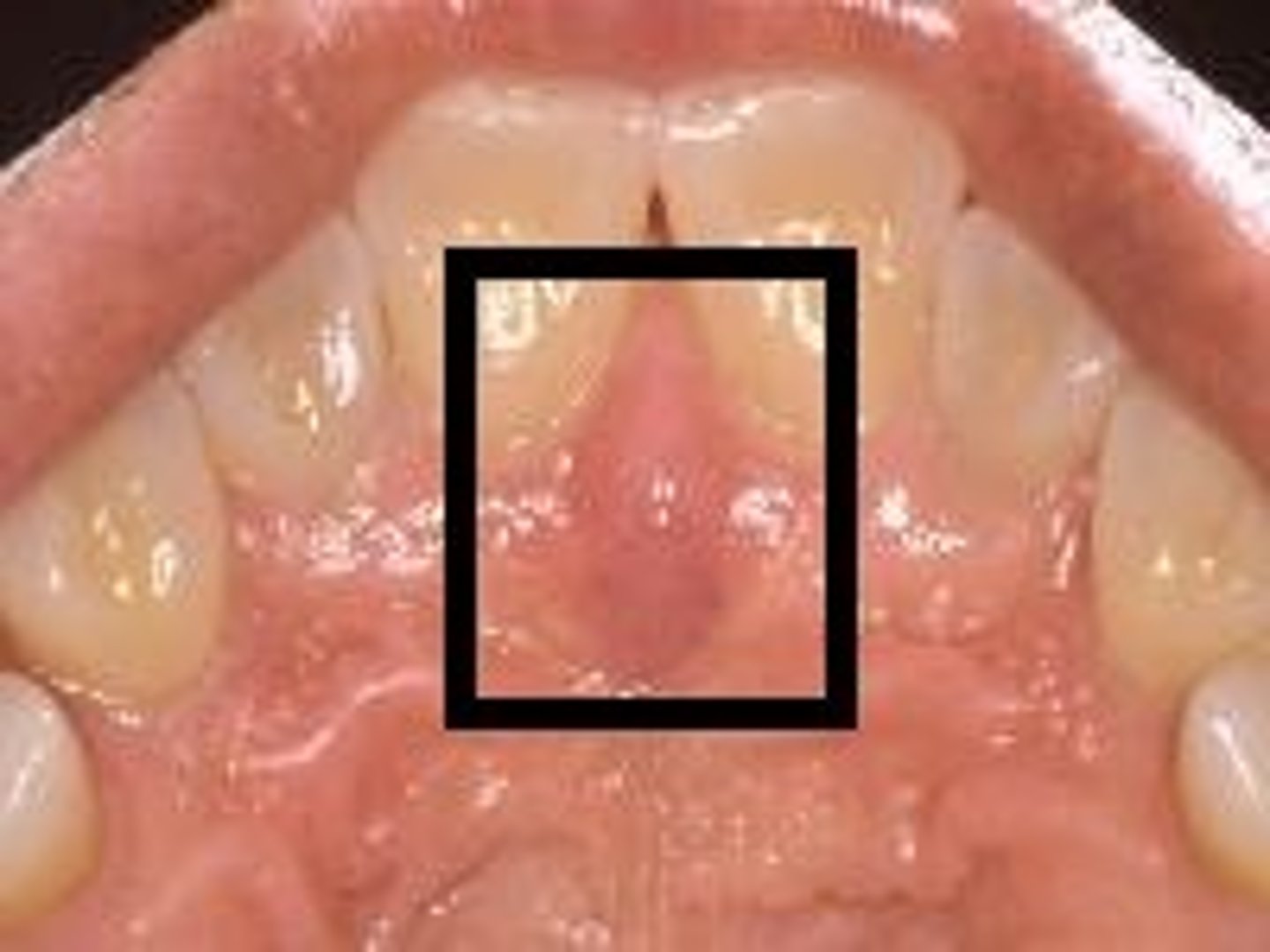
soft palate
posterior portion, not supported by bone
uvula
soft tissue hanging from the middle of the soft palate
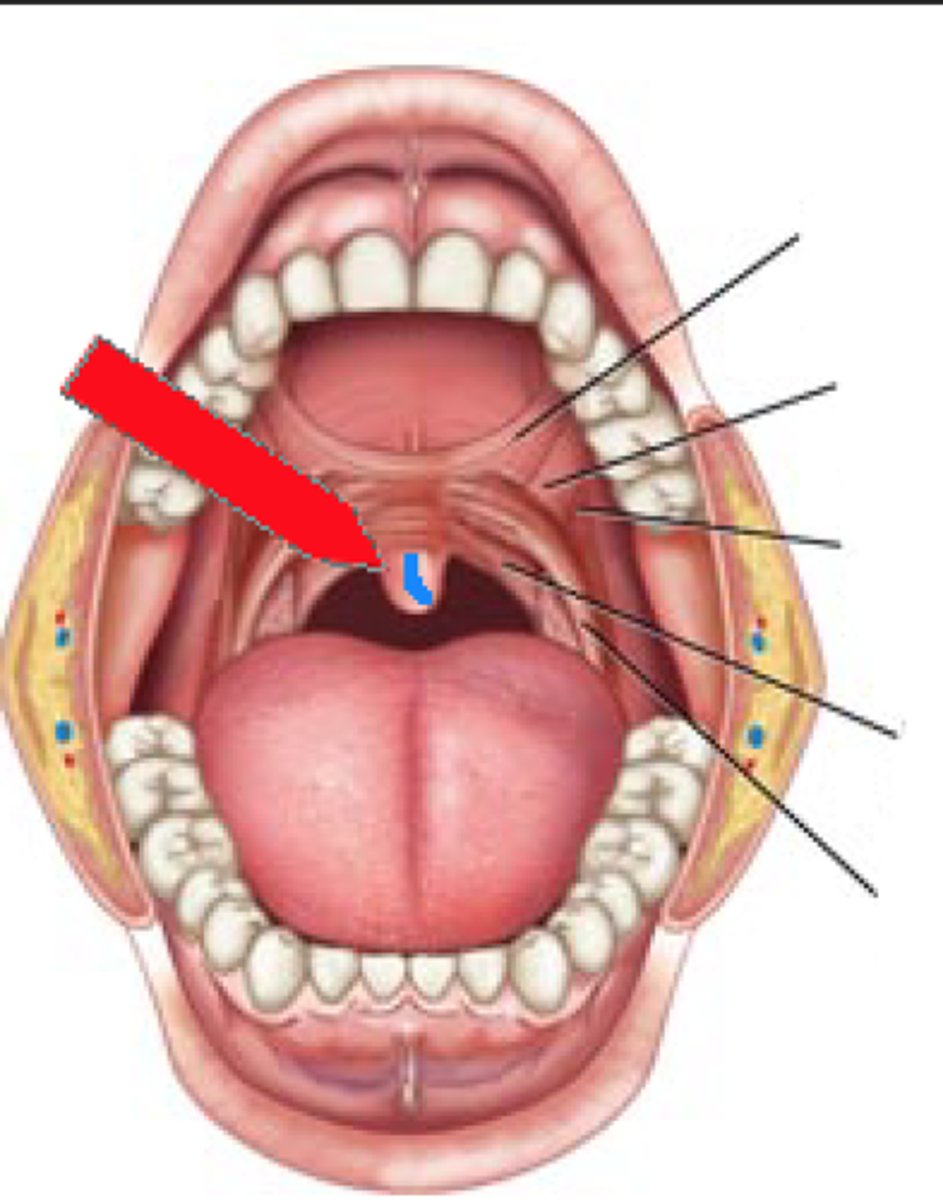
palatine tonsils
located on the left and right sides of the throat in the area that is visible through the mouth
torus palatinus
a bony protuberance in the midline of the hard palate
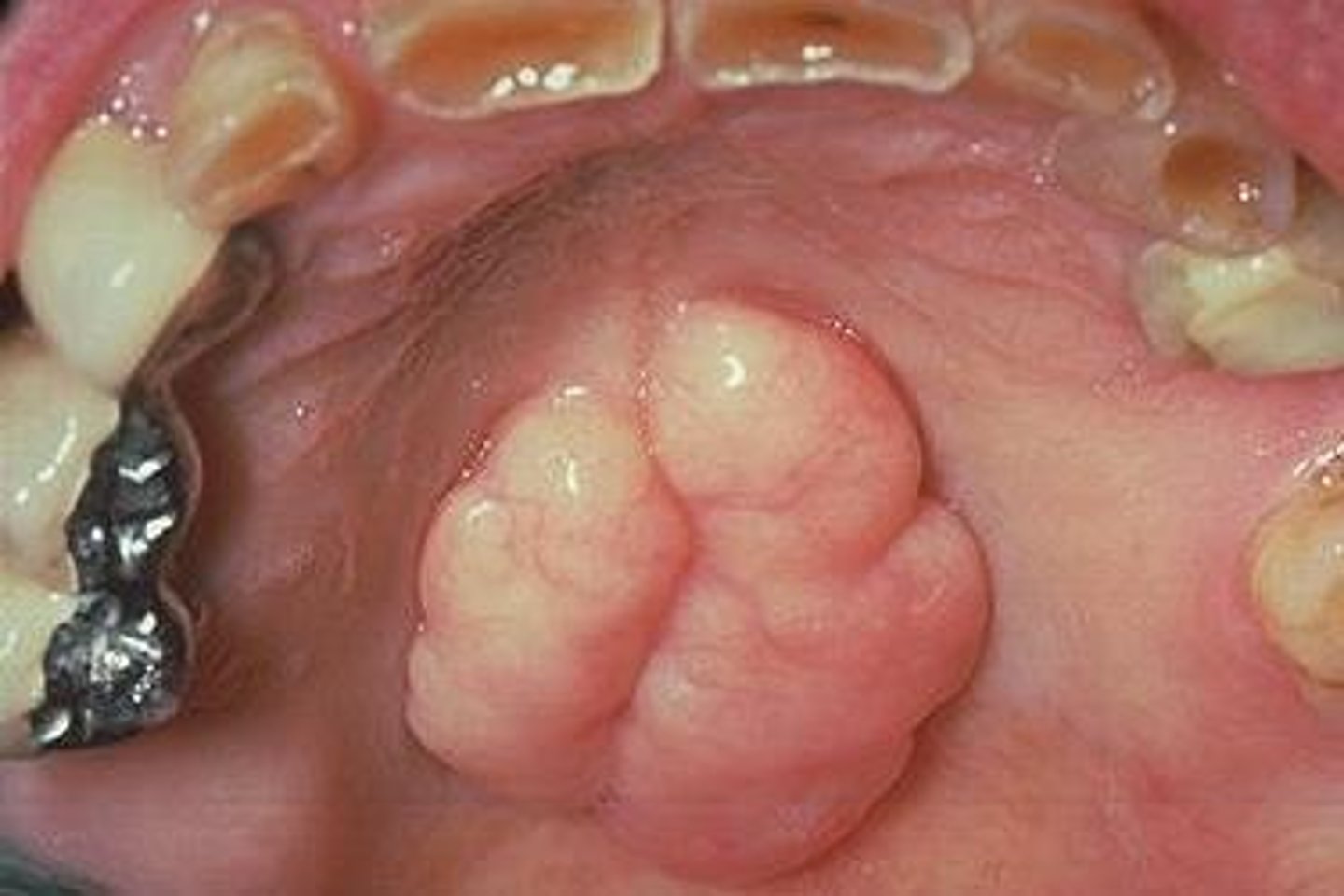
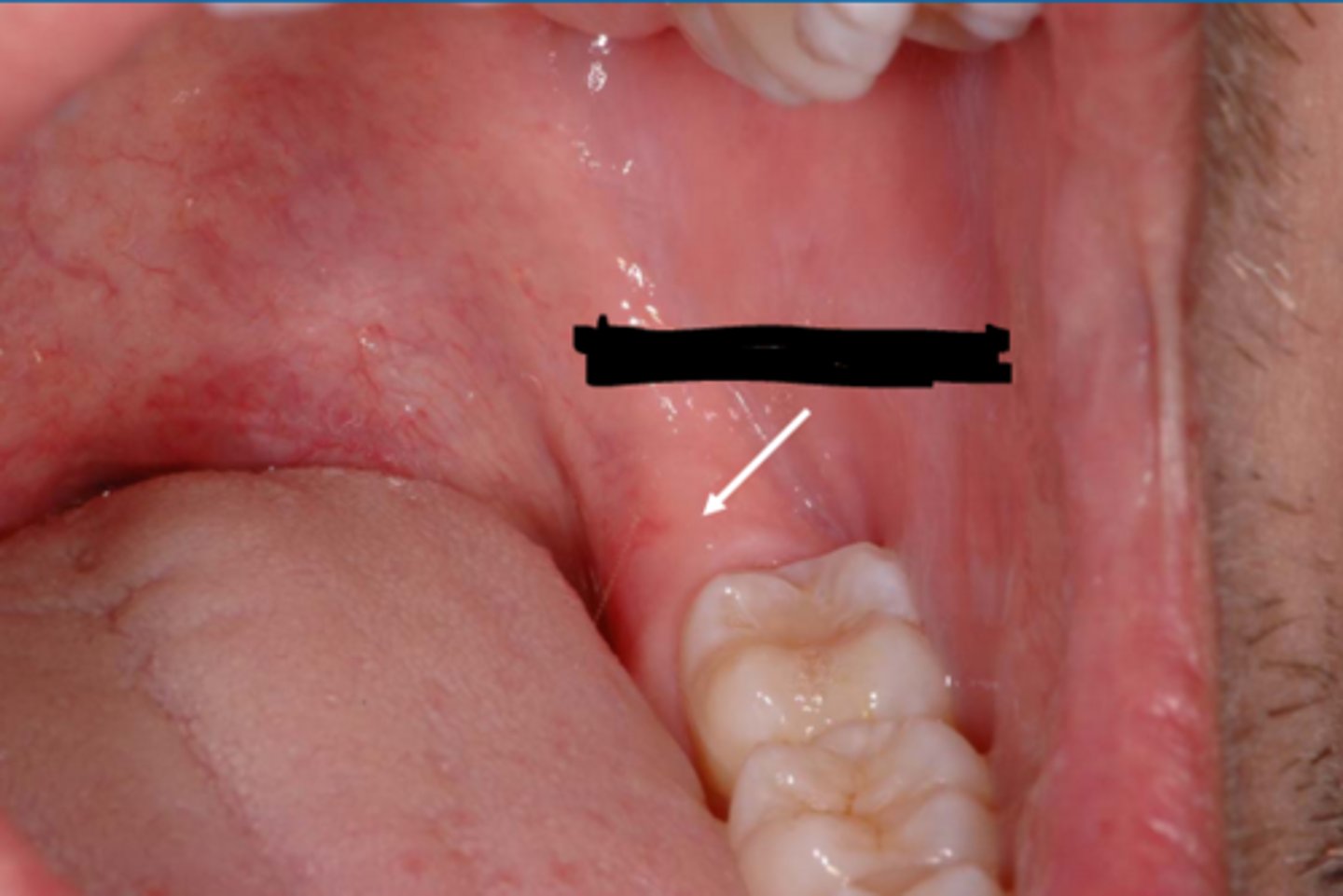
retromolar pad
pad of tissue behind the last molar on the mandible.
Dorsum
Top side of the tongue
filiform papillae of tongue
abundant, fine, and hair-like covering about 2/3 of the dorsal surface
NO TASTE BUDS
fungiform papillae
Mushroom-like protuberances often containing taste buds and located on the sides and tip of the tongue.
circumvallate papillae
v-shaped row of circular raised papillae, located in the back of the tongue
CONTAINS TASTEBUDS
Lateral surface (tongue)
sides of tongue
Foliate Papillae (Tongue)
on side walls of tongue; contain taste buds
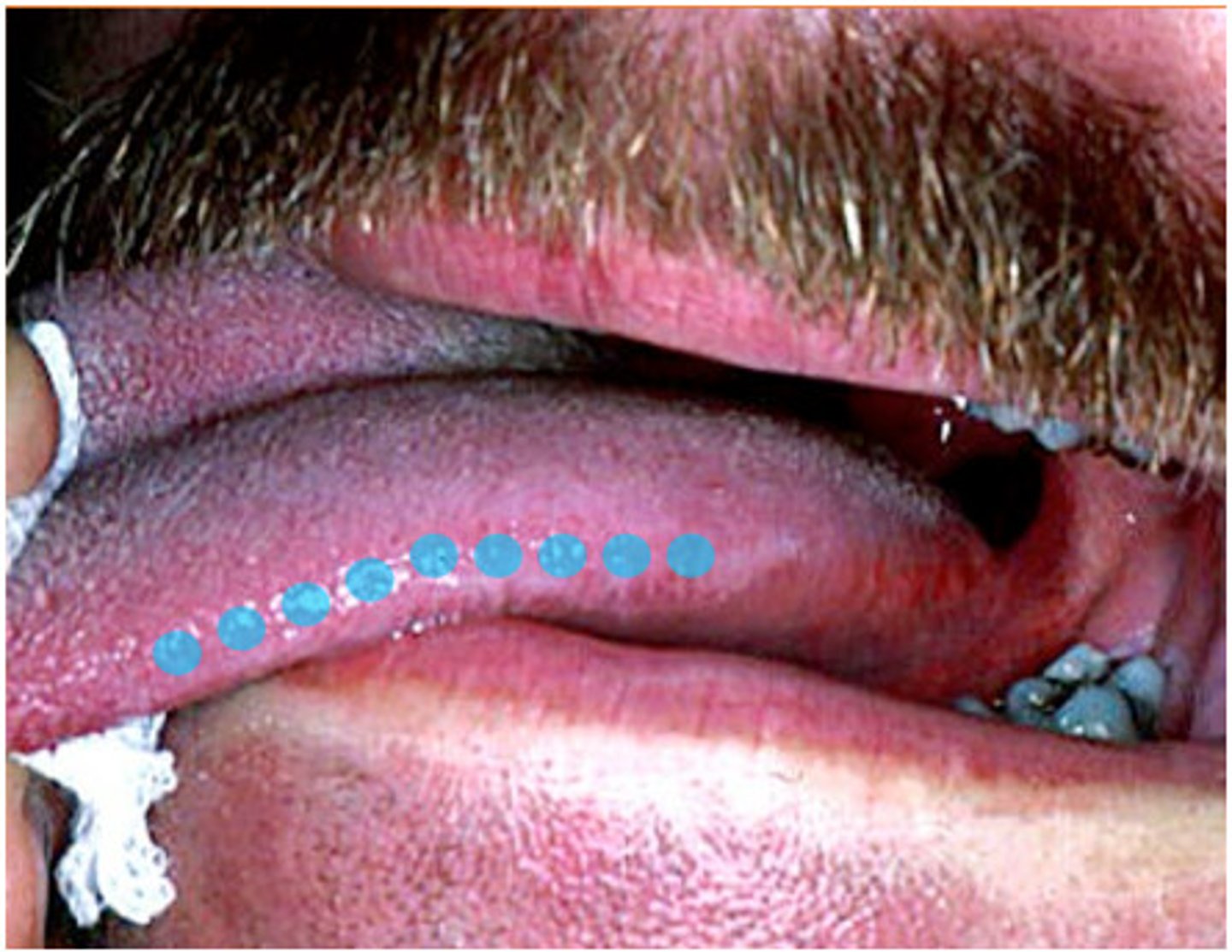
Ventral surface of tongue
Bottom surface of the tongue
Lingual vein/artery
also called ranine vein
Lingual Frenum
fold of skin in center of underside of tongue
ankyloglossia
tongue-tied
Wharton's duct
submandibular duct
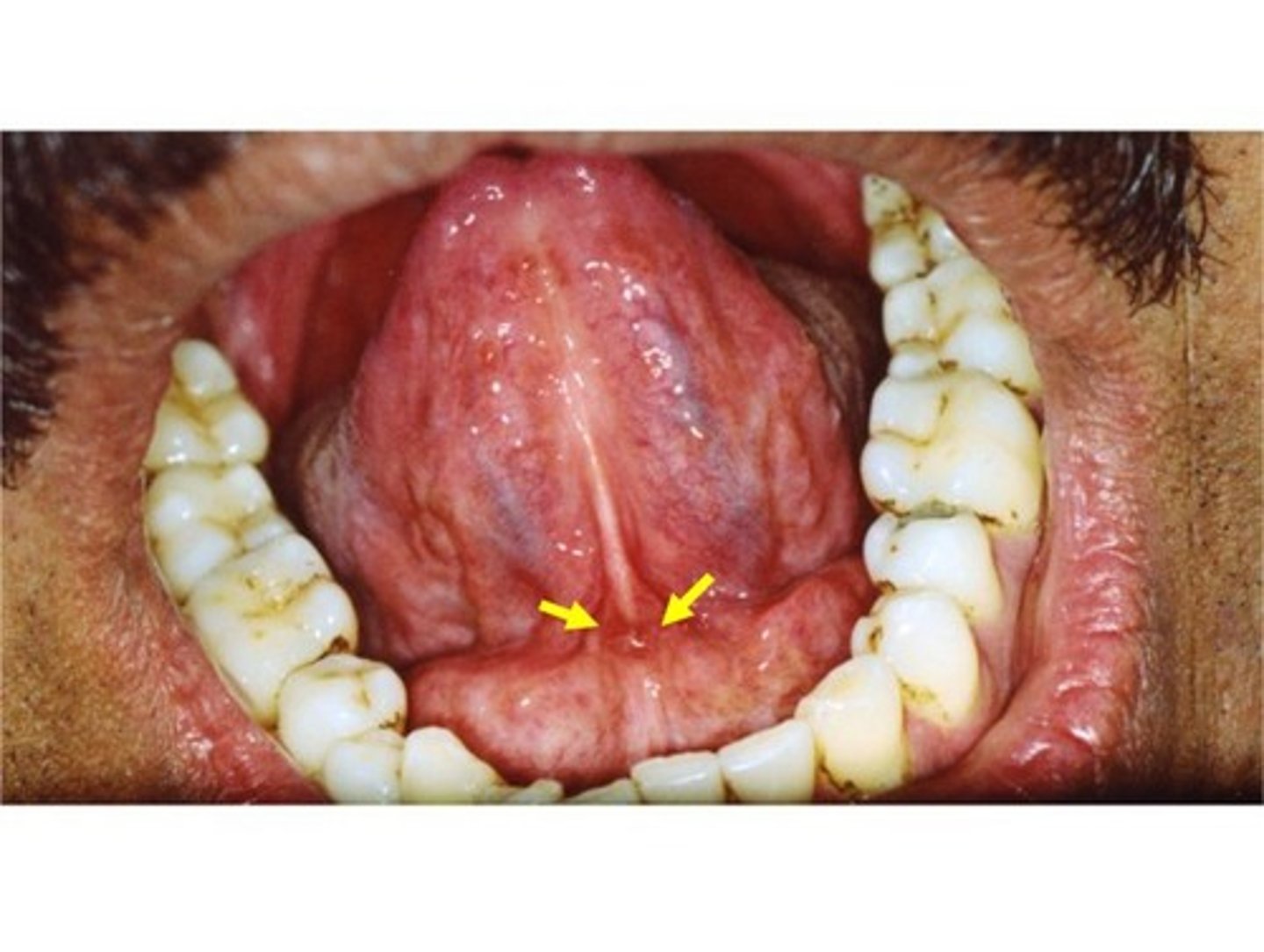
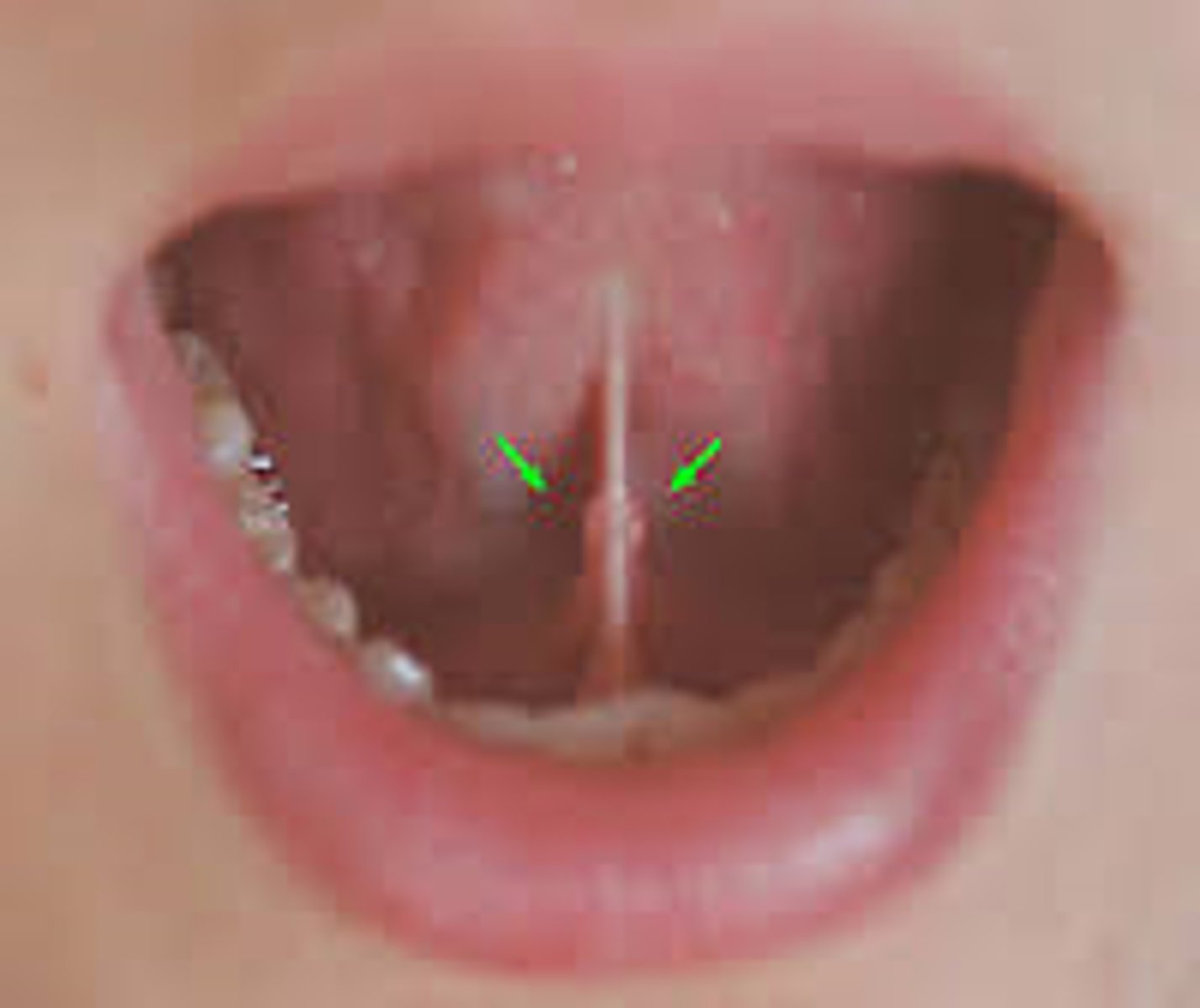
sublingual caruncle
small papilla at the anterior end of each sublingual fold contains the duct openings from both the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands
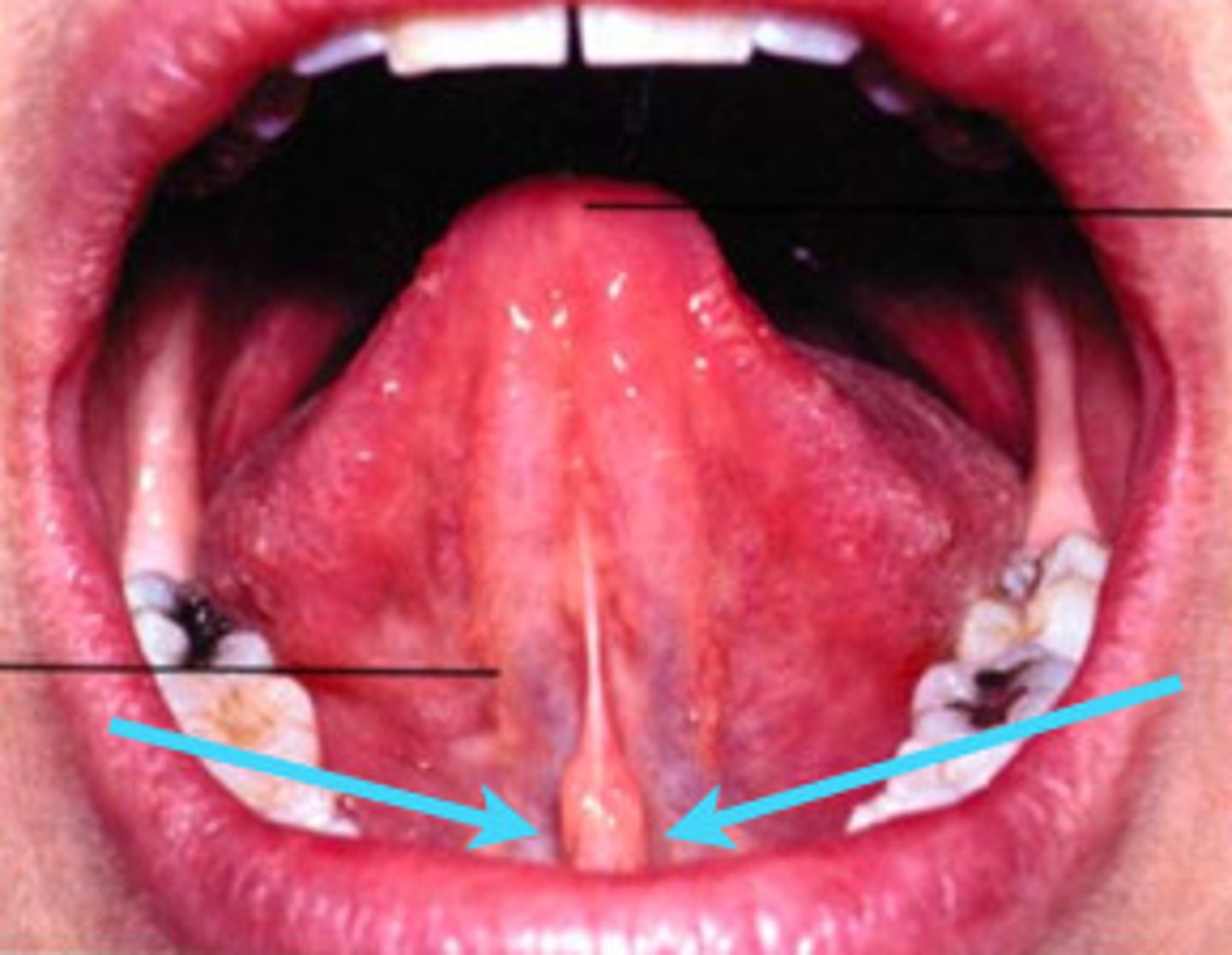
sublingual fold
fold of tissue extending anteriorly on each side from the 1st molar to the lingual frenum, duct of submandibular gland lies below.
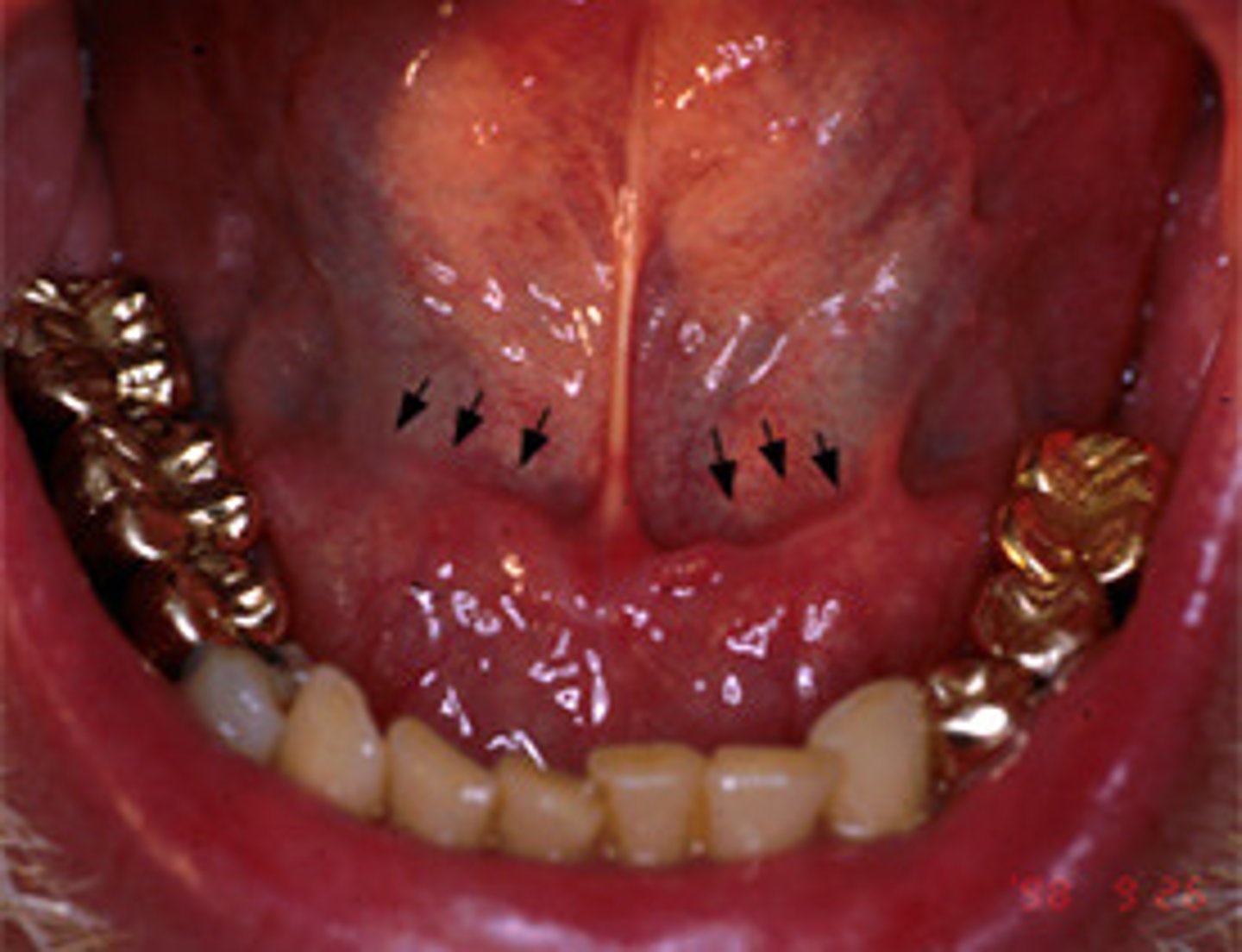
mandibular tori
Bony growths along the lingual aspect of the mandible
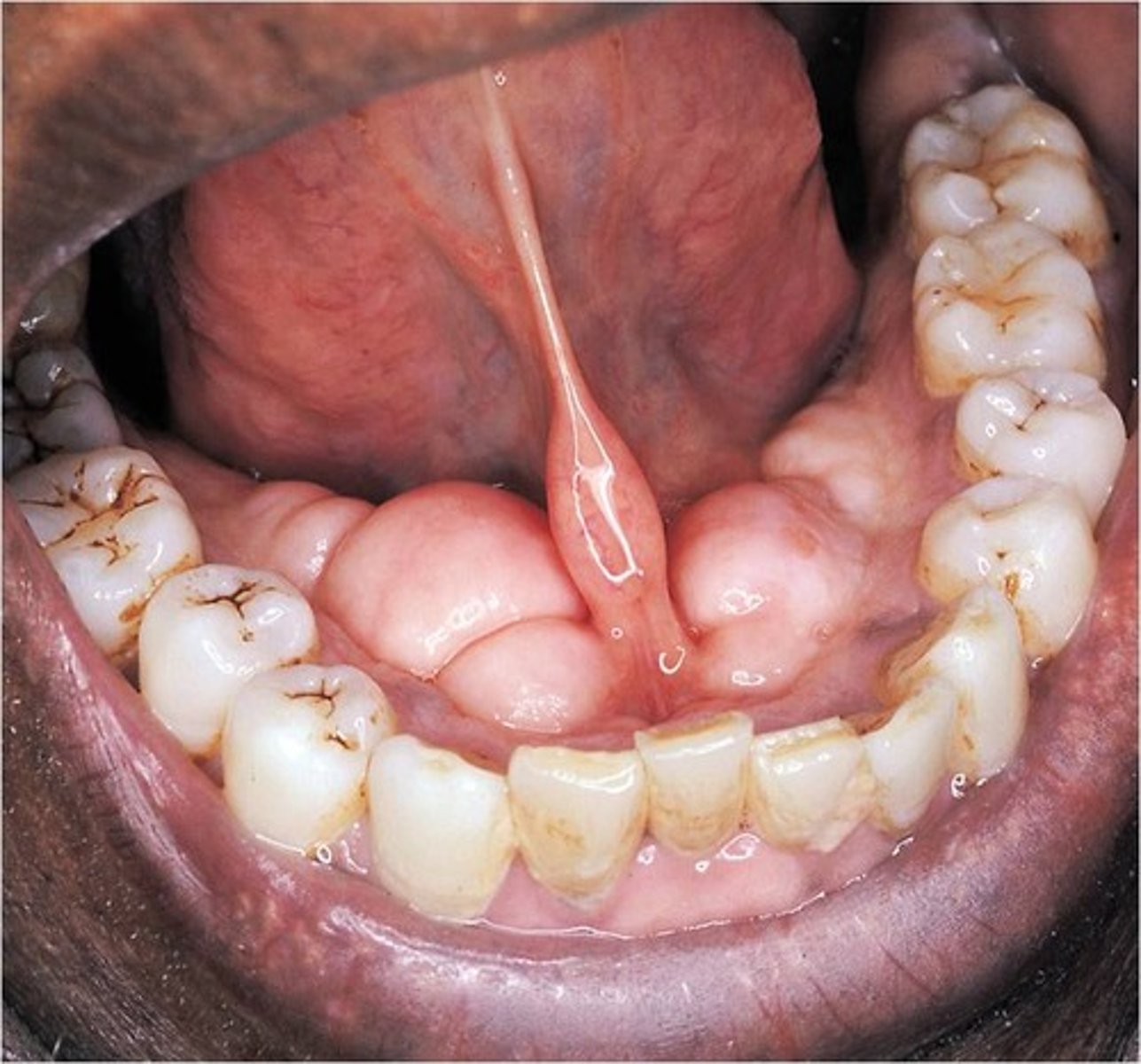
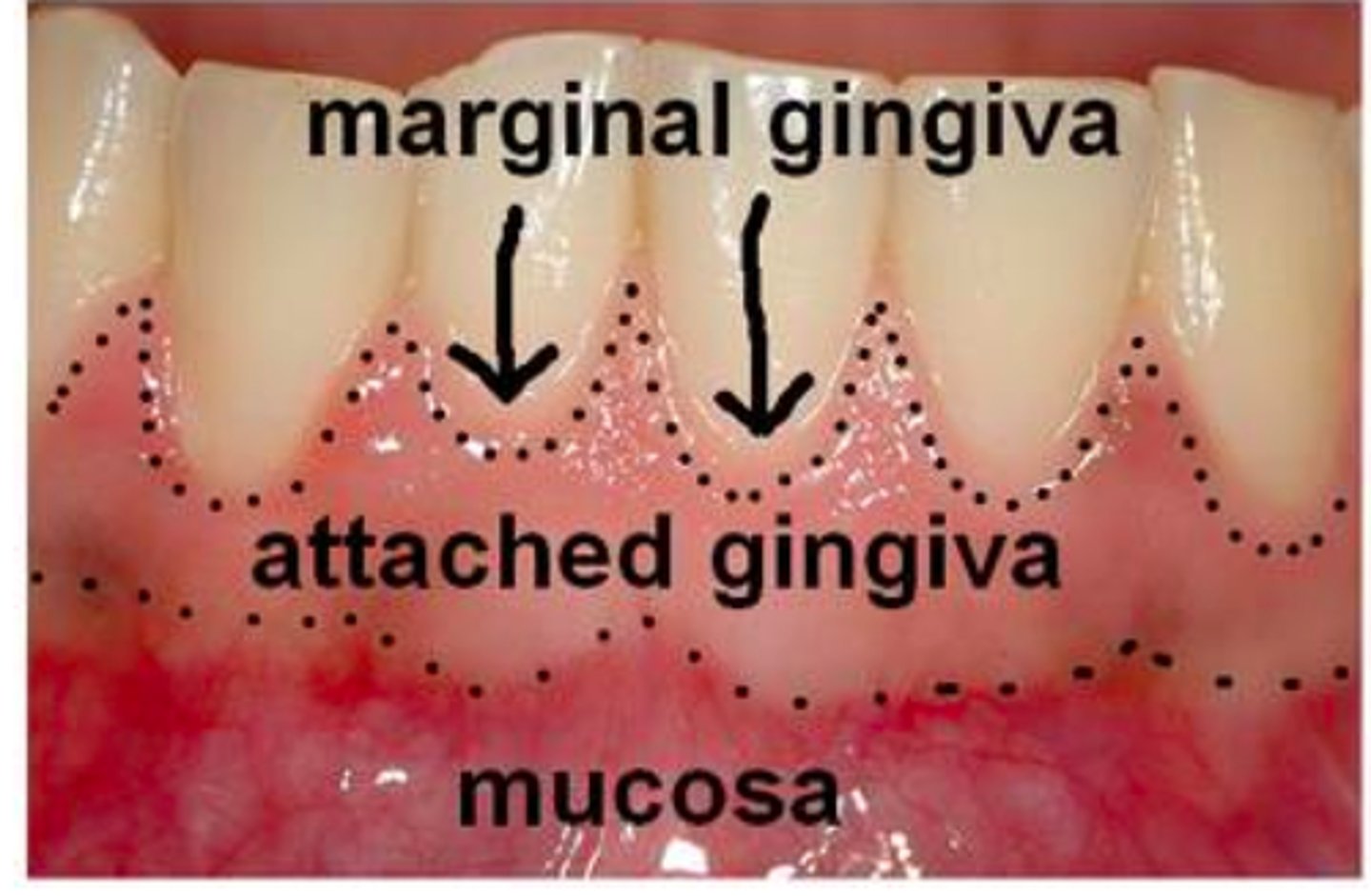
free/unattached gingiva
border of the gingiva surrounding each tooth, not attached
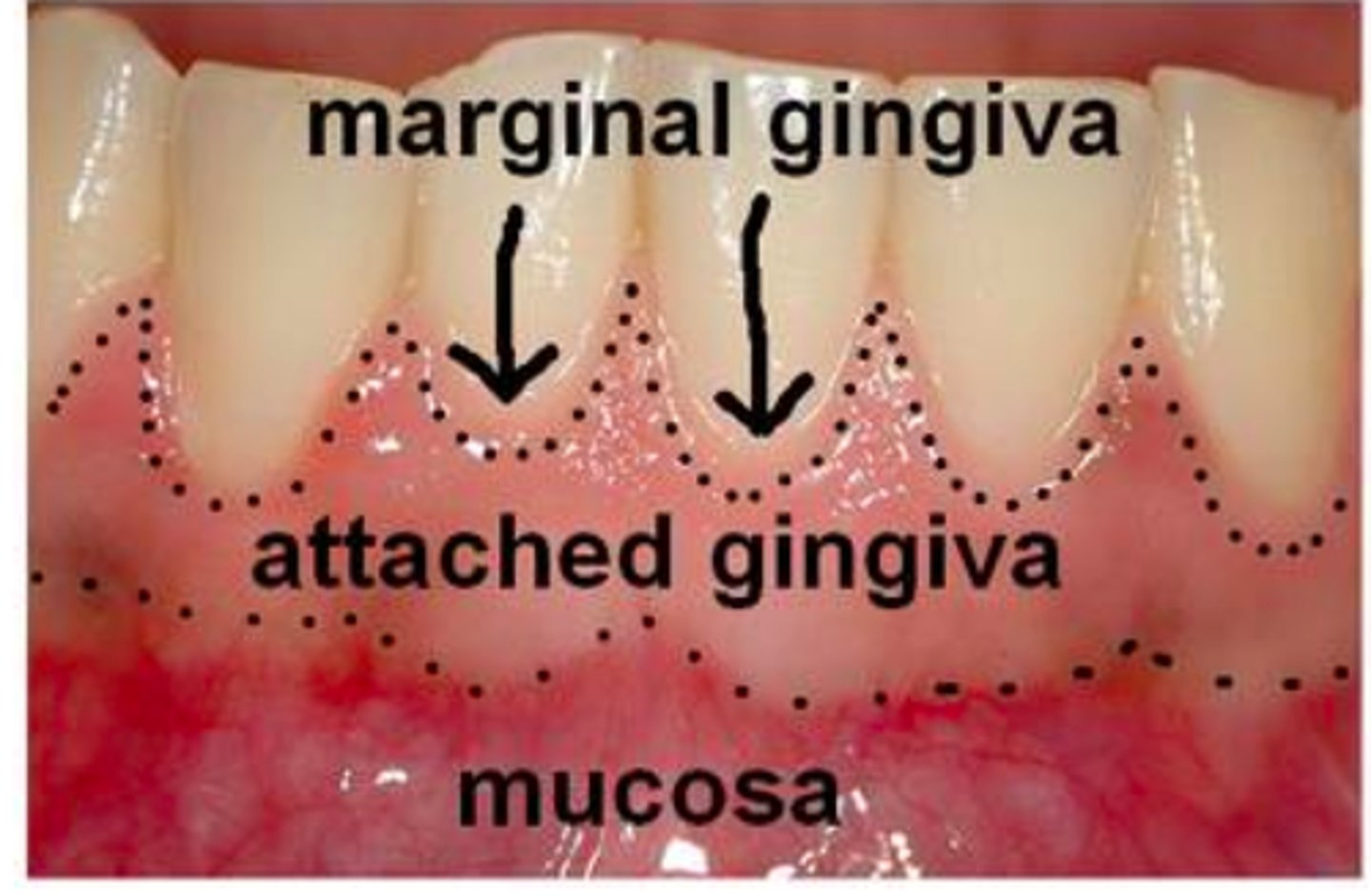
marginal gingiva
highest point of free gingiva
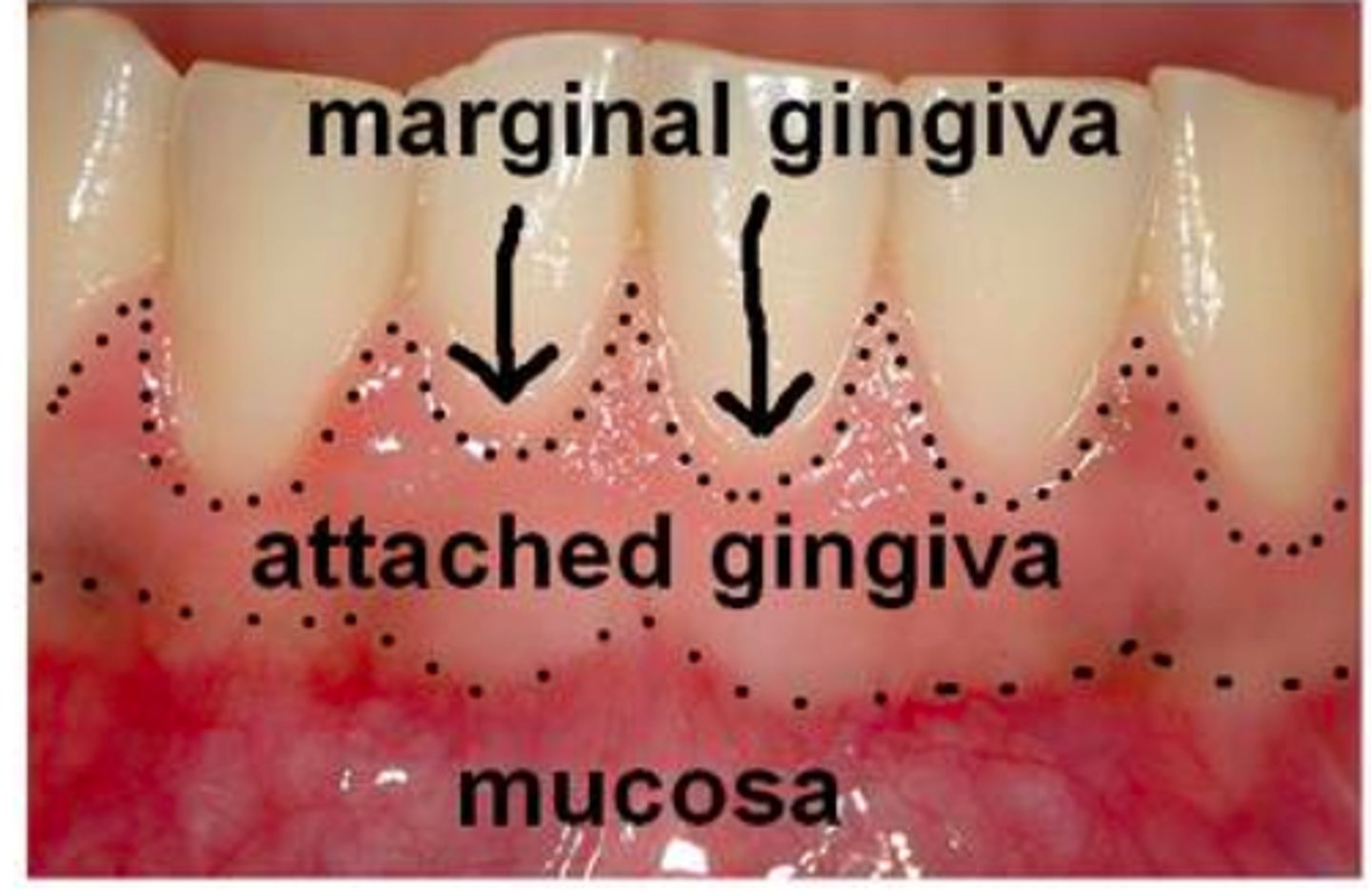
attatched gingiva
Firmly bound to the underlying alveolar bone.
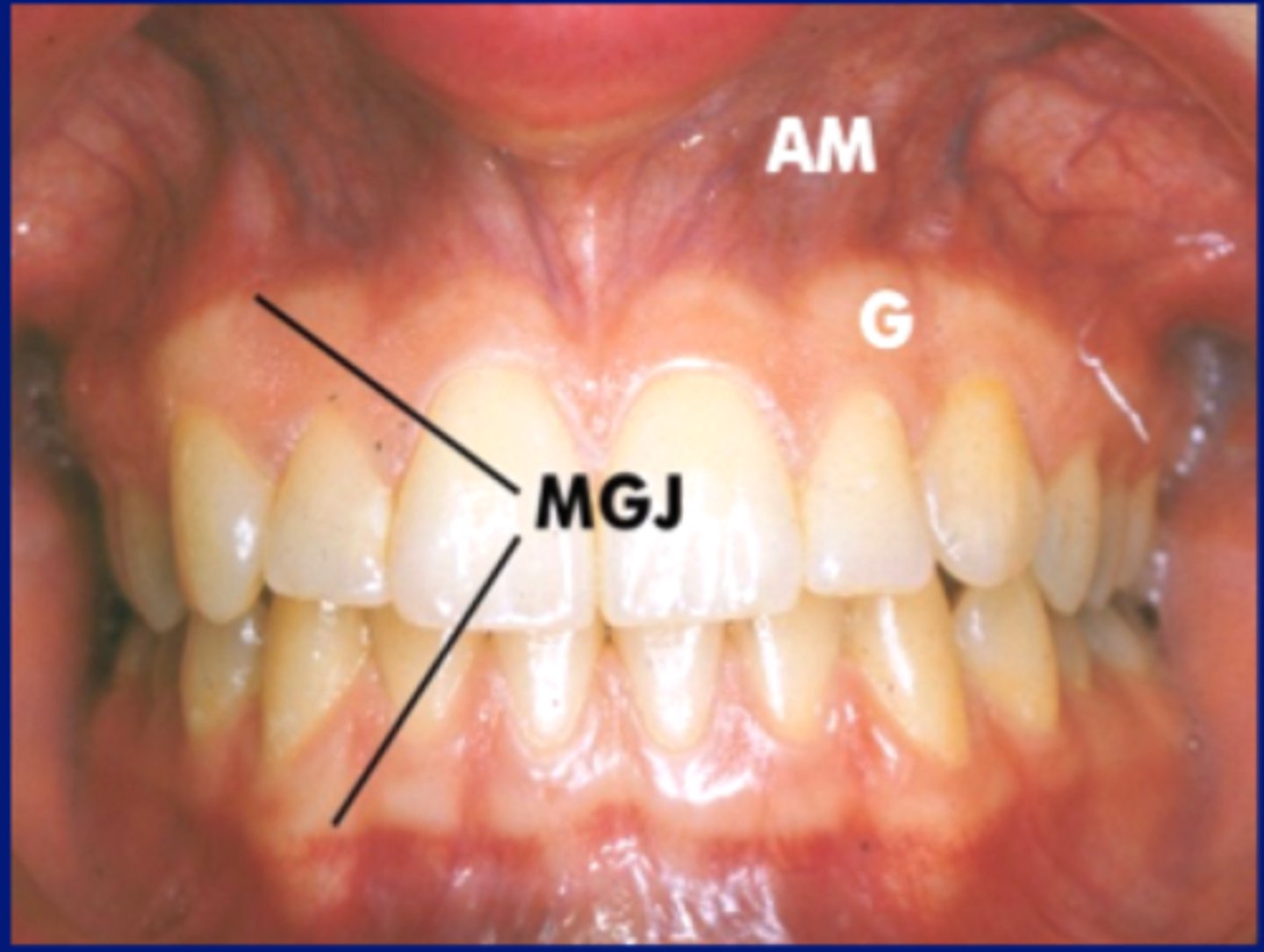
Mucogingival Junction (MGJ)
line where the attached gingiva meets the alveolar mucosa
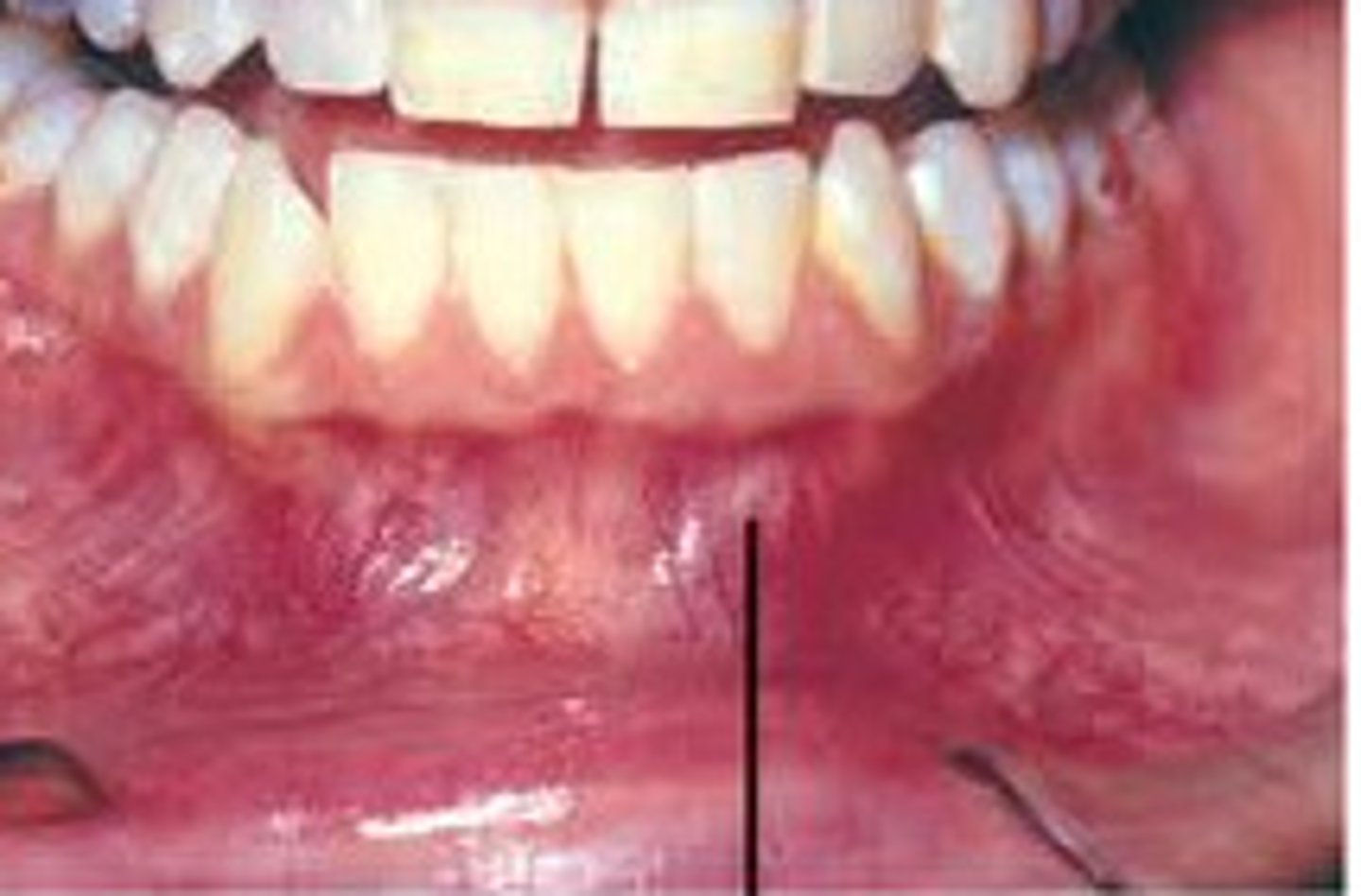
alveolar mucosa
a darker pink or red in color beyond the attached gingiva, non-attached gingiva highly vascularized.
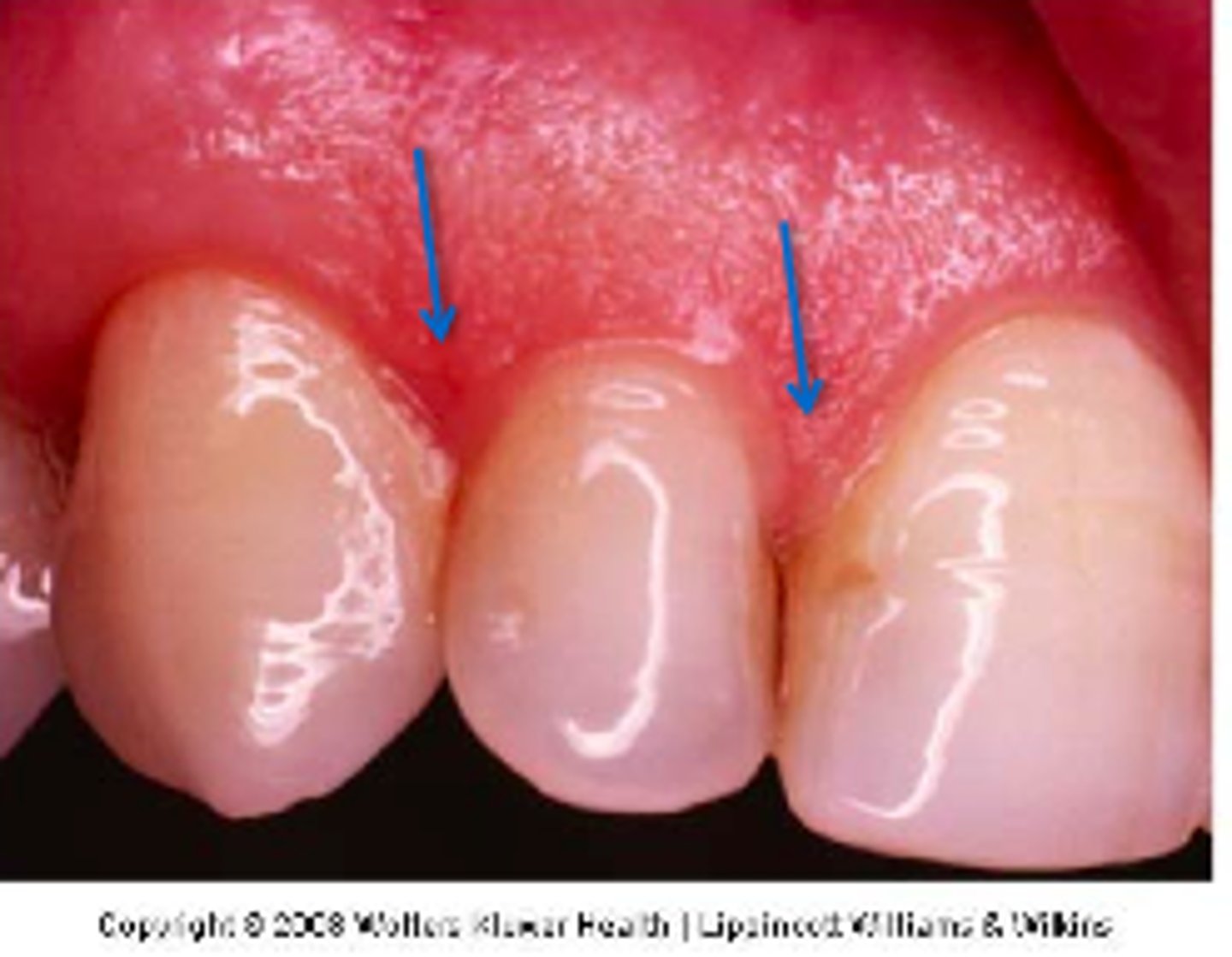
Interdental papilla
Triangular shaped unattached gingiva (fills space between teeth)
Dentition
Natural teeth in the dental arch
primary dentition
The first set of 20 primary teeth (baby teeth)
Mixed dentition
A mixture of permanent teeth and primary teeth that occurs until all primary teeth have been lost, usually between the ages of 6 and 12.
permanent dentition
The set of 32 secondary teeth
maxillary arch
upper jaw
mandibular arch
lower jaw
occlusion
The natural contact of the maxillary and mandibular teeth in all positions
Sextants (six segments)
- Maxillary right posterior
- Maxillary anterior
- Maxillary left posterior
- Mandibular right posterior
- Mandibular anterior
- Mandibular left posterior