Inorganic
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
What is the mass of the electron?
m = 1/1836 of a proton
How to figure out intensity?
(amplitude)²
What is the wavefunction?
Consists of a radial and an angular component - mathematical function describing the behaviour of an electron
What are the solutions to the SE called
Wave functions, 3D stationary waves
What is “phi”²?
Refers to “intensity”, so “phi”² is the probability of finding the electron at the point.
Give equation for wavefunction split into two parts
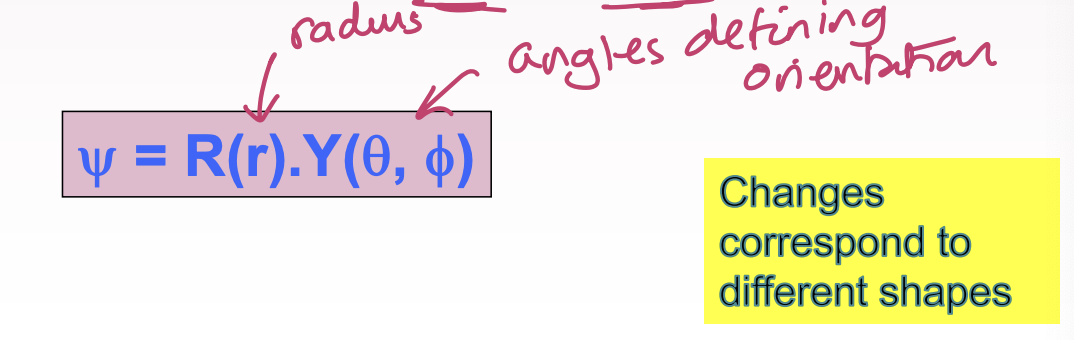
What does the radial part of the wavefunction R(r) depend only on?
Radial distance between the nucleus and the electron, depends on quantum numbers n and l
What does R(r) not contain information about?
No information on direction or orientation
What does the angular part Y(theta, phi) depend on?
The direction/orientation, quantum numbers l and mL
What does the angular part not depend on?
The distance
What values can “n” take?
Any value from 1 to infinity
What is the description of the Principal Quantum number?
Orbital size quantum number
What values can l take?
Any value from 0 → (n-1)
What is the description for the Angular Momentum Quantum number?
Orbital shape quantum nunmber
What values can ml take?
Any values from -l to +l, (e.g. -l, -l +1, 0, l-1, l)
What is the description of the Magnetic Quantum number?
Orbital orientation quantum number
What occurs at a node?
Zero electron density
Give formula for number of nodes relating to n?
No. nodes = n-1
How to find the number of angular nodes?
= l
How to find the number of radial nodes?
n - l -1
What does the Radial Part of the wavefunction tell us about in general?
Orbital size
What value of phi is at the nuclues for s orbitals?
Non-zero
What value of phi is at the nucleus for p orbitals?
phi = 0
Give definition of radial node
Spherical surfaces where the sign of phi changes from positive to negative → zero electron density
How can you get the probability of finding an electron at a point?
Plot of graph of phi² vs r
What is the plot of 4pi.r².phi² vs r called?
The radial distribution function (r.d.f) or radial probability function
What is the value of the r.d.f for all orbitals when r=0?
0
What sign can phi be?
+, - or 0
What are 3 similarities for polyelectric atoms vs monoelectronic atoms?
Same quantum numbers found
Same angular functions, so same shape and types of orbitals e.g. 1s, 2s, 2p
Radial functions are similar
What are 3 differences for polyelectric atoms vs monoelectronic atoms?
They are contracted to smaller radii, i.e. orbitals shrink due to increaisng nuclear charge
Energies are lower
Importantly, energies now depend on l as well as n
What does the Pauli exclusion principle state?
No two electrons in the same atom may have the same set of four quantum numbers
What is the Aufbau Principle?
Electrons go into the lowest energy orbitals available.
What is Hund’s rule?
For a set of degenerate orbitals, electrons will start by going one into each with spins alligned or parallel
What does the penetration describe?
The proximity that an e- can approach the nucleus
What are the valence electrons?
Those with the higehst energies (highest value of n) - involbed directly in chemistry and bonding
What are core electrons?
Electrons with lower values of n, sitting in completely filled orbital groups act as a less-than-complete shield of nuclear charge
Why are 2s and 2p energies not degenerate?
1s orbital less effectively shields an electron in 2s orbital than in 2p. Zeff experienced by electron in 2s>2p
Give formul a for calculated Zeff
Zeff = Z - S where Z is atomic number and S = shielding constant
For s and p outer electrons, what are the contributions to the shielding constant S from the other electrons?
0 for any electrons with a higher n
0.35 from every other electron with the same n
0.85 from every electron with n one less than out chosen atom
1 from every electron with lower values of n
For d and f outer electrons, what are the contributions to the shielding constant S from the other electrons?
0.35 for electrons within the same group (e.g. nd)
1.00 for all electrons in lower groups (to the left)
What are the values for IE and EA for inert gases?
High IE and low EA
What is special for d orbitals in terms of penetration?
They do not penetrate
What are the conditions for covalent bonding to occur?
Ionic bonding must be unfavourable. This means the energies of the electrons to be shared must be similar on both atoms.
What happens to the potential energy as the distance between the nuclei decreases?
Decreases because of the electron-nucleus attraction.
What does paramagnetic mean?
Form of magnetism that occurs in an applied magnetic field. This means it is attracted into the magentic field. (it has unapired e-)
What does diamagnetic mean?
(no unpaired e-) Not attracted into the magnetic field
How do we represent the wavefunctions for molecular orbitals?
As combinatioins of the wavefunctions for the individual atomic orbitals.
What oribtal occurs when there is constructive and then destructive interference?
Constructive - bonding orbital
Destructive - antibonding
What happens to the e- density in the internuclear region in a bonding orbital?
It is enhanced
What happens to the e- density in the internuclear region in an antibonding orbital?
Density is excluded from the internuclear region
Where does a nodal plane occur in molecular orbitals?
In antibonding orbitals, which is perpendicular to the internuclear axis
What does delta(E1) and delta(E2) indicate in a molecular orbital diagram, and how are they related?
delta(E1) indicates the extent to which the bonding orbital is lowered in energy
delta(E2), the extent to which the antibonding is raised.
In general, delta(E2)>delta(E1) by a small amount
What types of orbitals are seen in MO diagram of H2 and describe their symmetry
Sigma orbitals, and they are cylindrically symmetric with respect to the internuclear axis
Give formula for bond order and state what the value of bond order denotes
BO = (Nb - Na)/2
0 = no bond
1 = single bond
2 = double bond
3 = triple bond
Hwo many nodal planes are present in sigma-orbitals formed from p orbitals?
The same number as in the atomic orbitals for bonding.
The same number + 1 for antibonding
Why is the sigma(2p) and pi(2p) orbitals swapped in the MO diagram for B, C, and N?
Previously we made an oversimplification where we ignored s-p mixing. As Zeff increases (B→F) the energy separation between 2s and 2p increases considerably. For BCN, 2s and 2p are close in energy and therefore mix to an appreciable extent.
How do the s and pz orbitals therefore mix in B, C, N?
s and pz orbitals hybridize to give two sp hybrid orbitals on each atom
Why is the energy of the pi-orbitals not changed in energy?
As they are not involved in hybridization
What happens in terms of the position of the upper and lower molecular orbital when two orbitals with different energies overlap
Lower molecular orbital is cmoposed of the lower atomic orbital and vice versa
What does HOMO stand for?
Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital
What does LUMO stand for?
Lowest unoccupied Molecular Orbital
Why are the pi electrons in CO polarized towards oxygen?
Because the pi-bonding orbitals are closer in energy to the oxygen 2p than the carbon 2p, so spend proportionally more of their time close to the oxygen atom.
What 3 shapes can triatomic molecules form?
Bent, Linear, or Cyclic
What are the principal shapes for H3+ an H3- respectively?
Triangular(D3h) and Linear (D(infinity)h)
What are two rules of thumb regarding HOMO and LUMO?
A molecule adopts the structure that best stabilises the HOMO. If the HOMO is unperturbed by the sturctural change under consideration, then the occupied MO lying closest to it governs the geometric preference.
Molecules tend to adopt the geometry that maximises the HOMO-LUMO gap