Biochemistry Exam 1
1/126
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
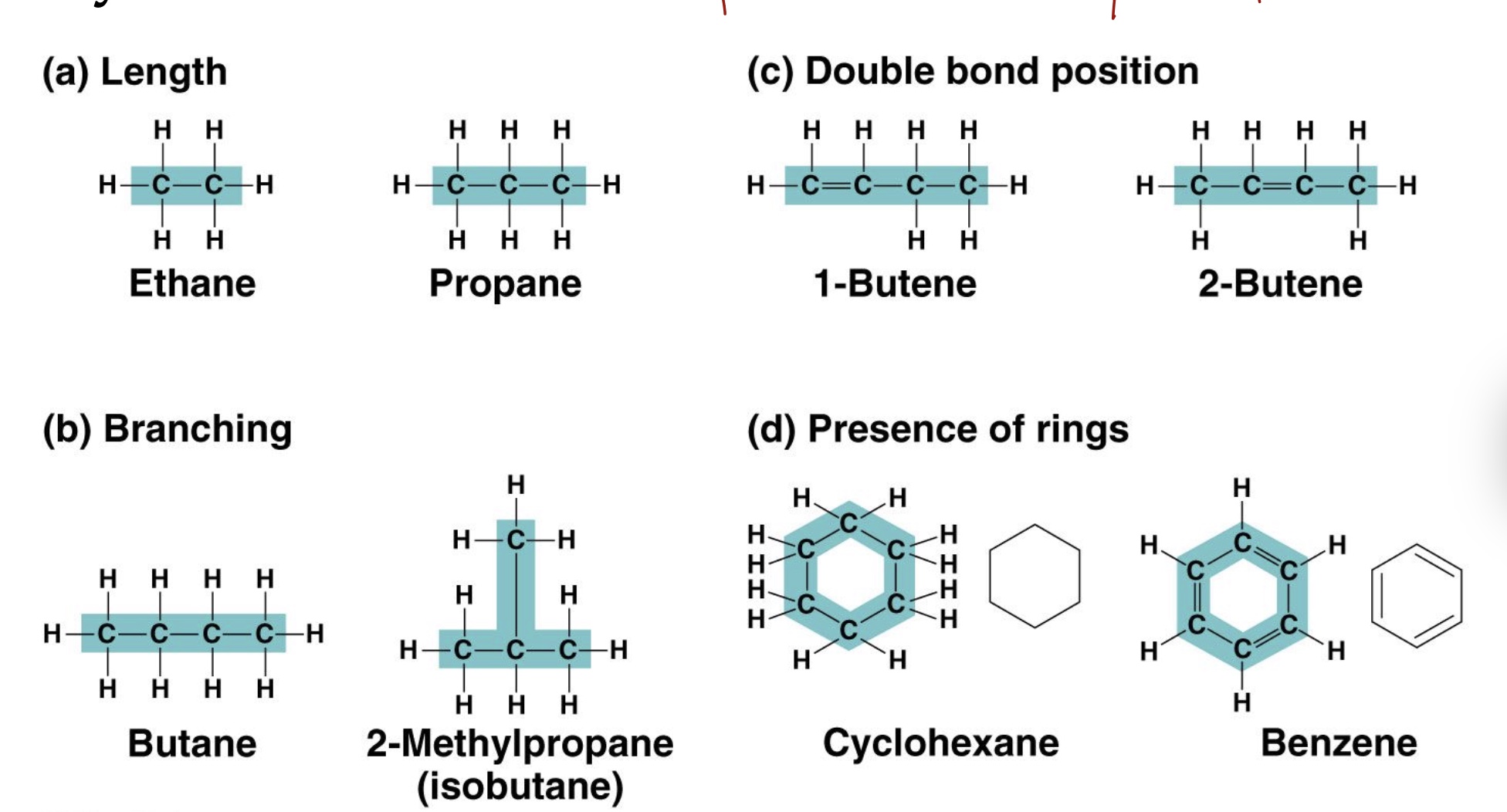
A carbon atom has outer shell electrons and can establish ___ bonds with itself and other molecules/atoms. hydrocarbon are ___ and _____
4, covalent. Hydrocarbons are nonpolar and hydrophobic
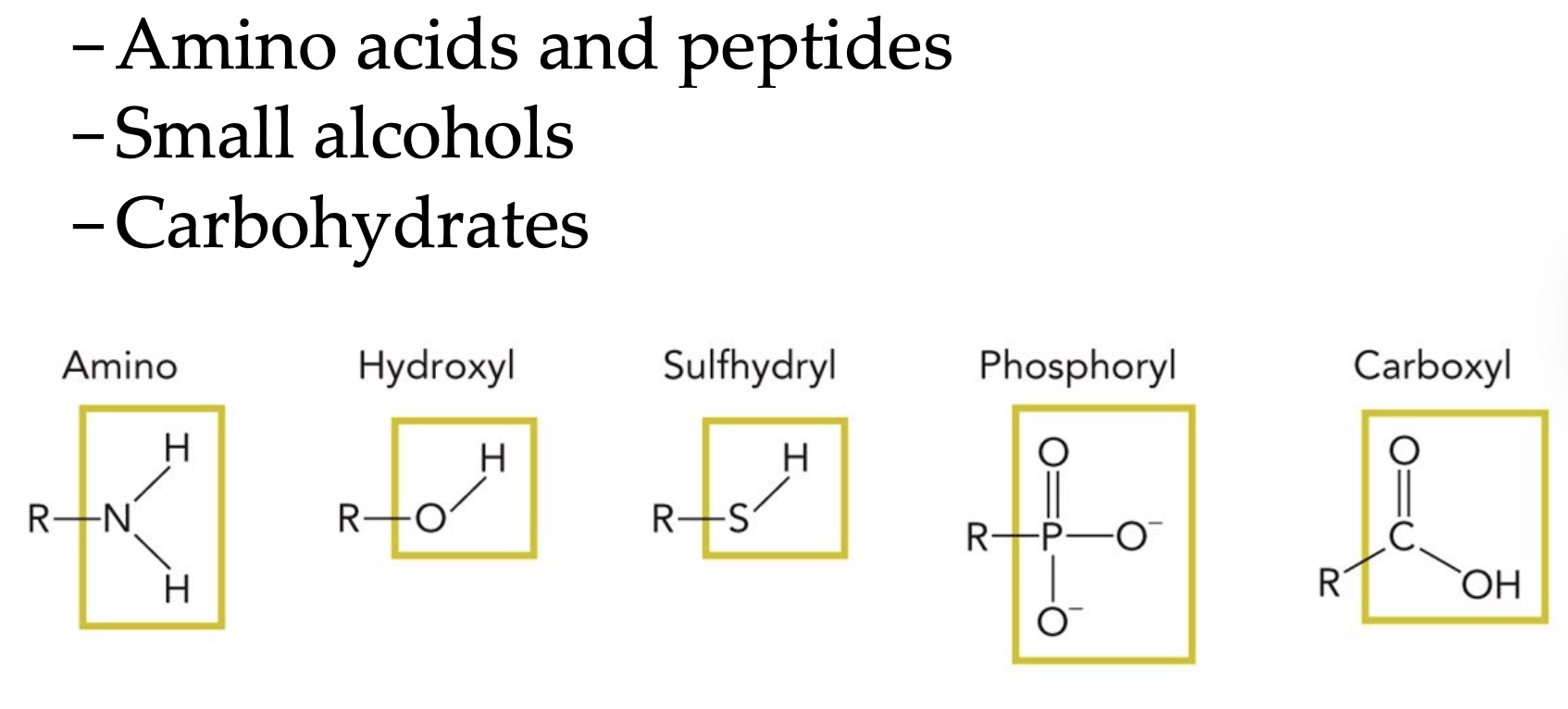
Amino
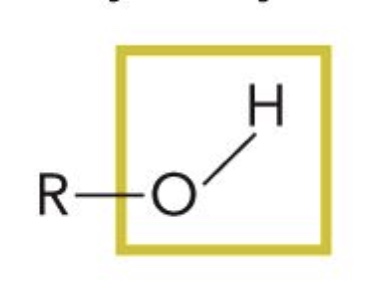
Hydroxyl
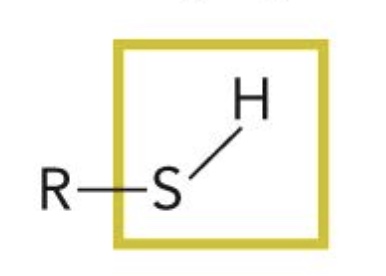
Sulfhydryl
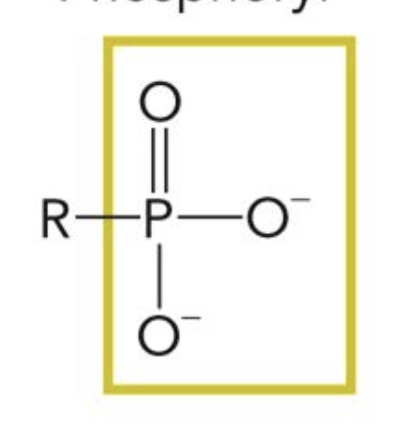
Phosphoryl
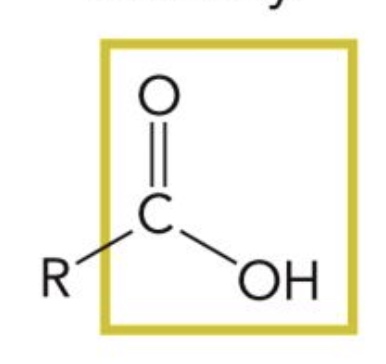
Carboxyl
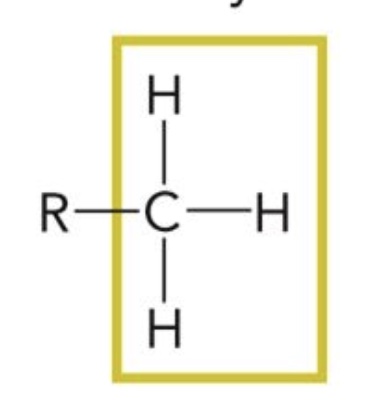
Methyl
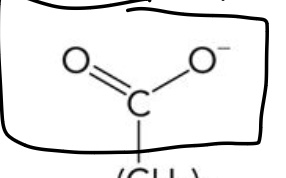
Carboxylate
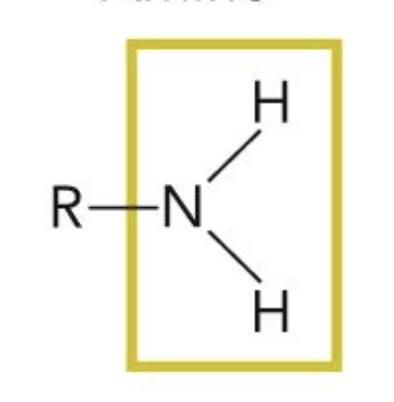
Amines are characterized by nitrogen joined to at least one ____ group.
Alkyl
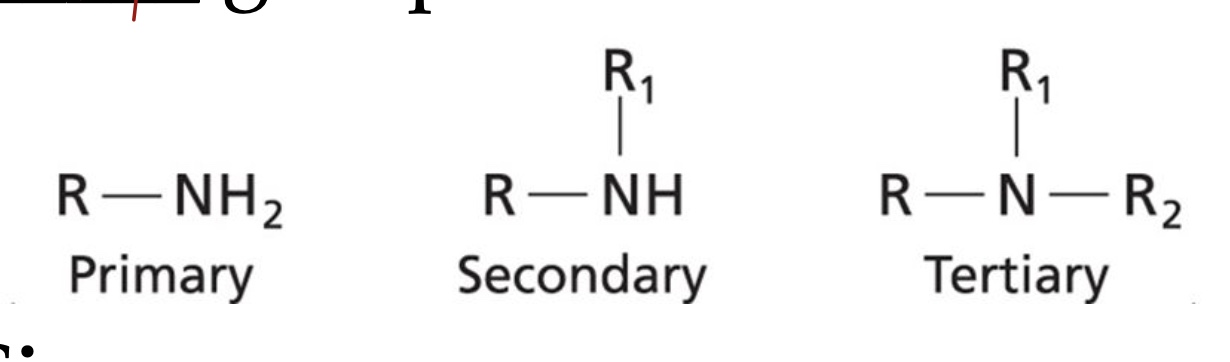
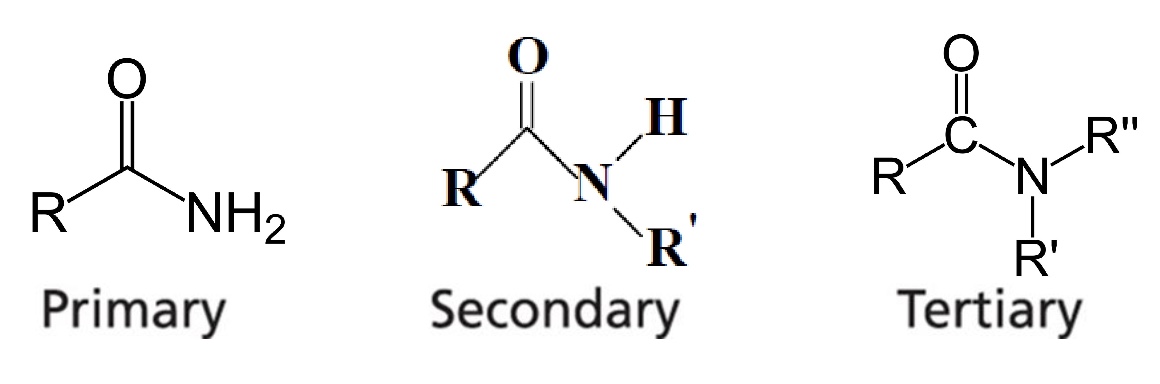
An amide has a ____ group between the nitrogen and R.
Carbonyl
Functional groups contain electronegative atoms (__, ___, ___). They are usually ____ or ___.
O, N, S. charged or Polar
Functional groups make organic molecule _______. They create multifunctional molecules that increase functional ______.
Amphipathic, diversity.
Functional groups provide sites for intra- and intermolecular interaction: _____. ______.
Hydrogen bonding and ionic interaction
Amphipathic
Hydrophobic region (hydrocarbon) and hydrophilic region (functional group)
Covalent bonds
Formed by atoms sharing their valence electrons to completely fill each atom's outermost shell.
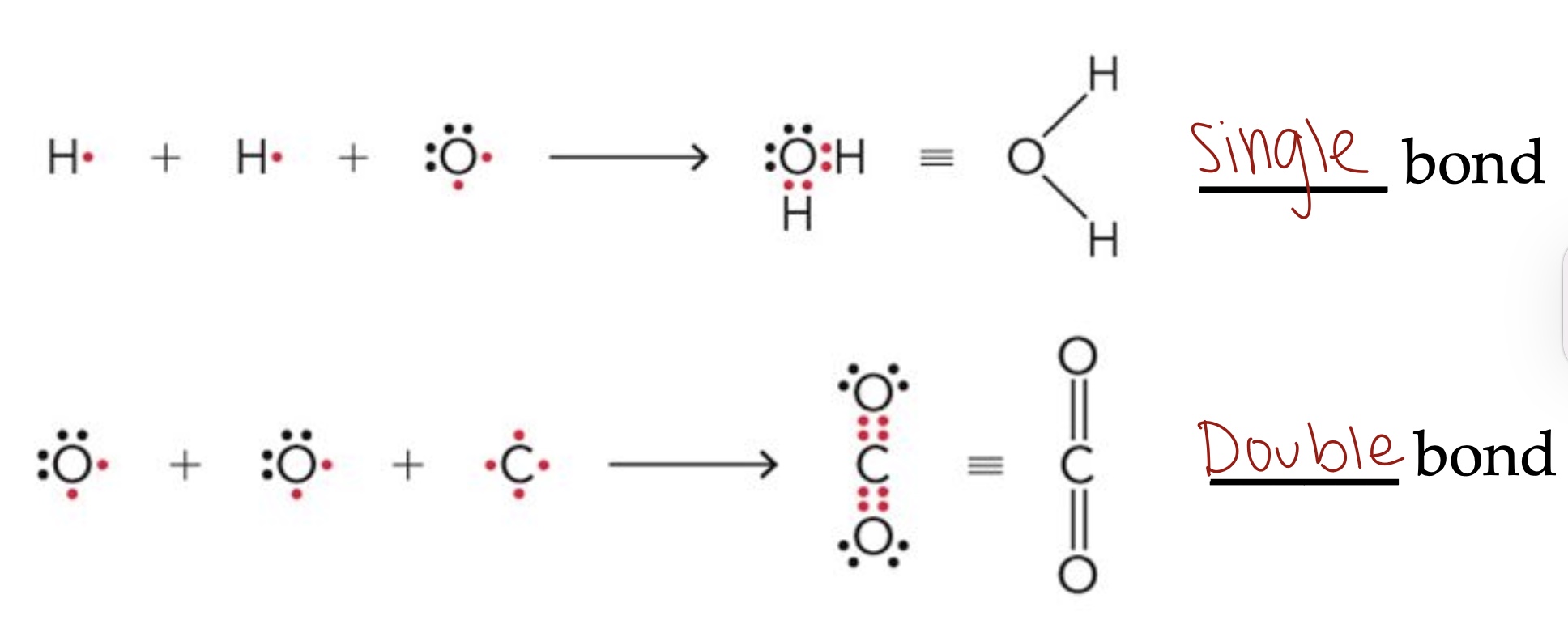
Covalent bonds can be polar or nonpolar. What does this mean?
Covalent bonds can be either polar or nonpolar depending on whether the atoms share the electrons equally or not.
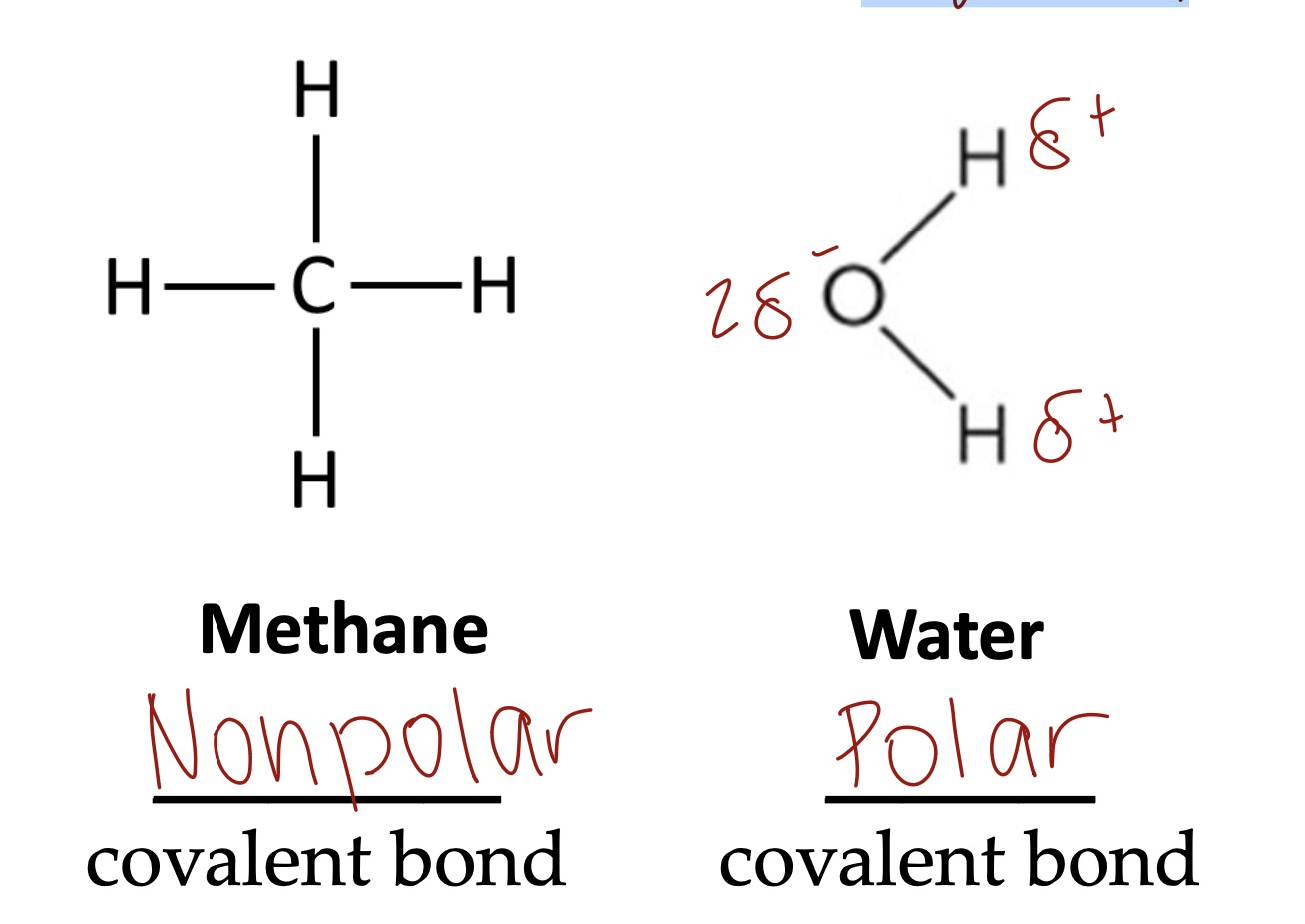
If the bond is nonpolar covalent, the electronegativity difference is ___ and if it is polar, the difference is ____.
<0.5 is nonpolar, >0.5 is polar.
Common polar covalent bonds:
C-O
O-H
N-H
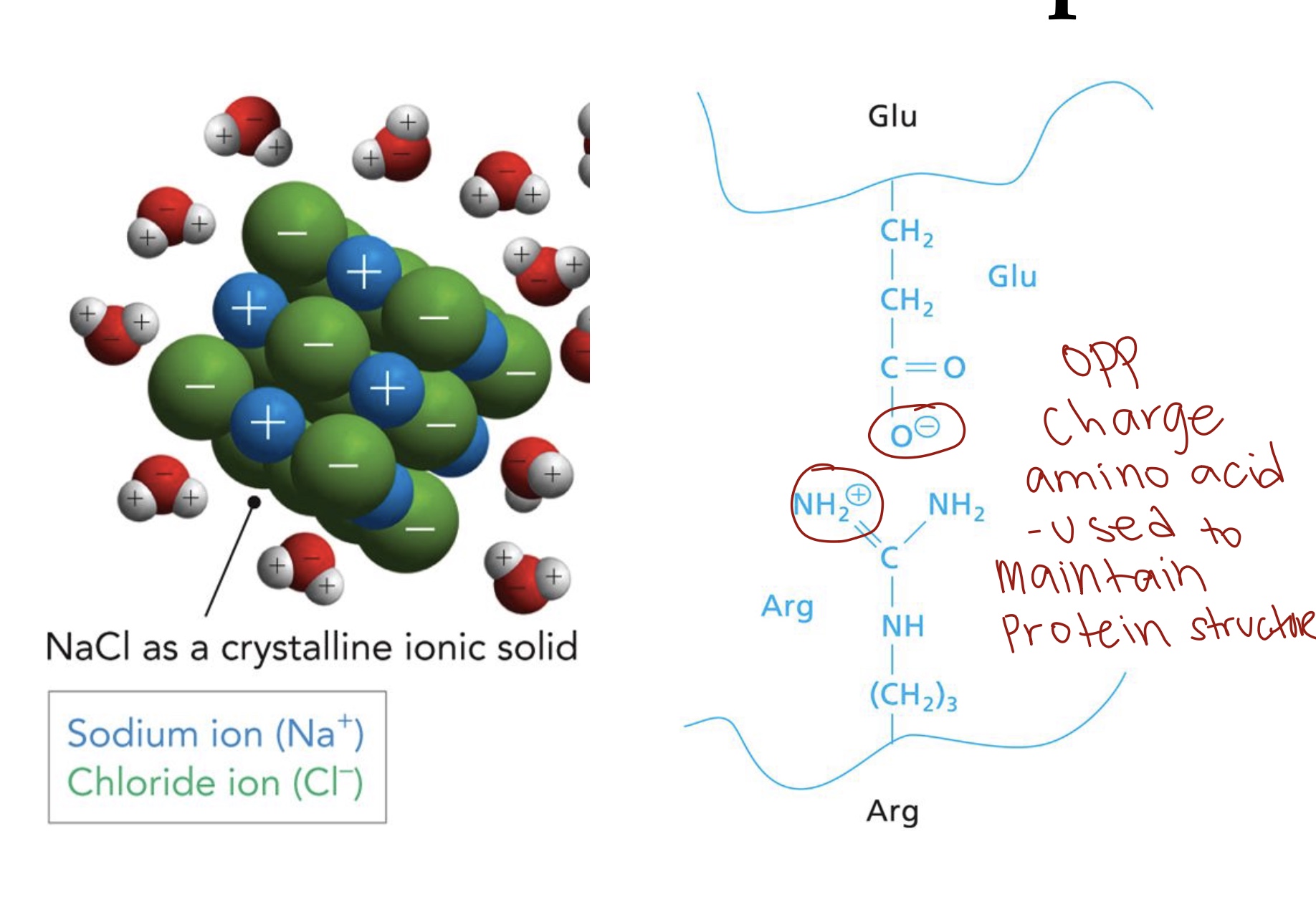
Ionic Interactions
“Charge-Charge”/ Salt bridge. These interactions occur between opposite charged atoms or groups. Electronegativity difference is >2
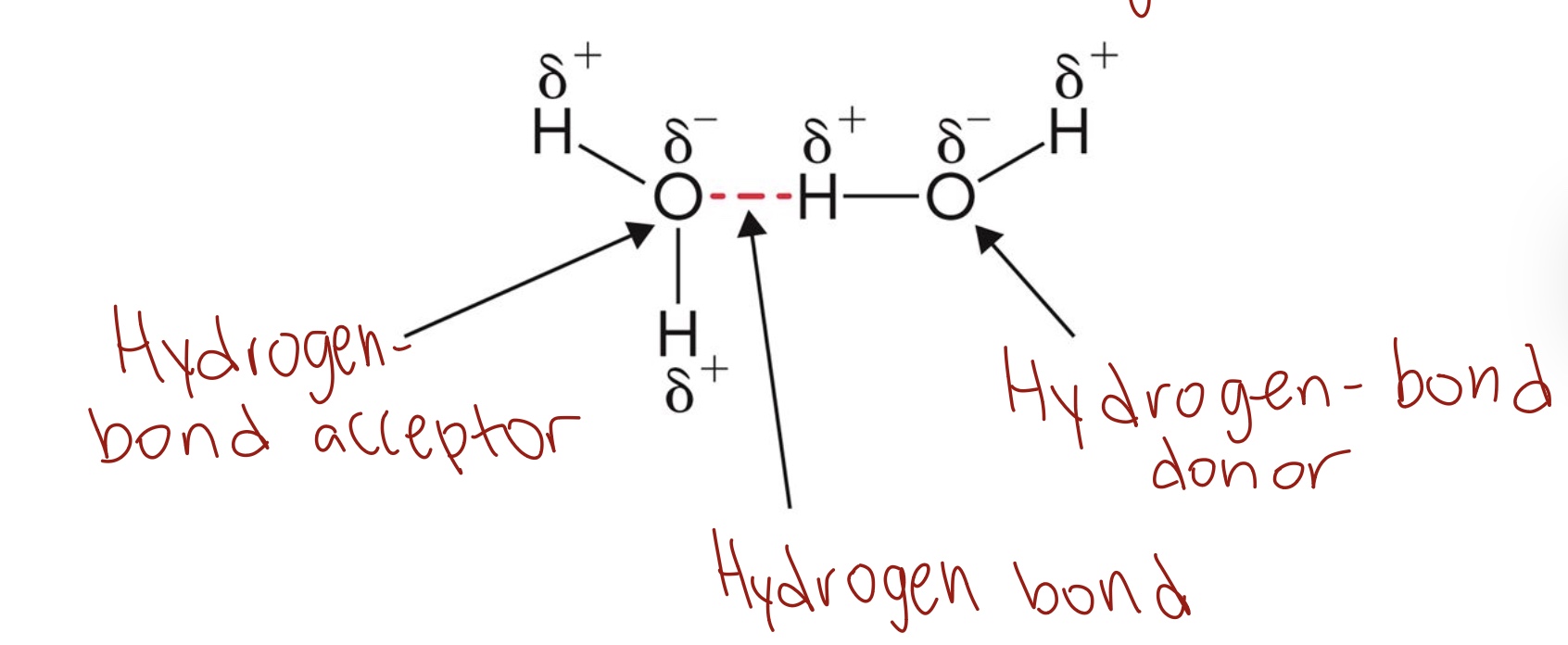
Hydrogen bonds
Hydrogen bonds form when a hydrogen that is covalently bonded to an electronegative atom is in proximity to another electronegative atom.
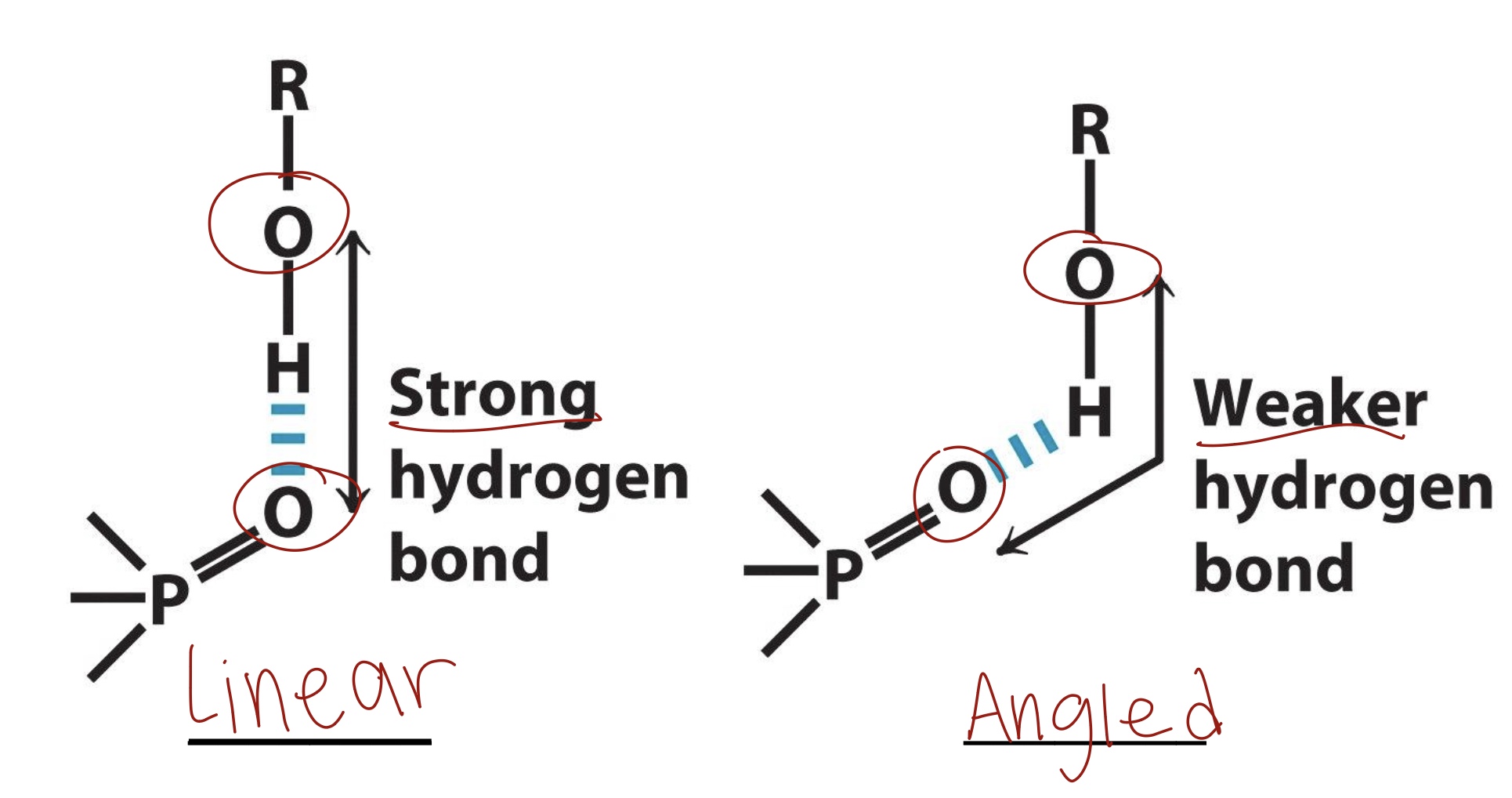
Strongest types of hydrogen bond are in what type of alignment?
Linear
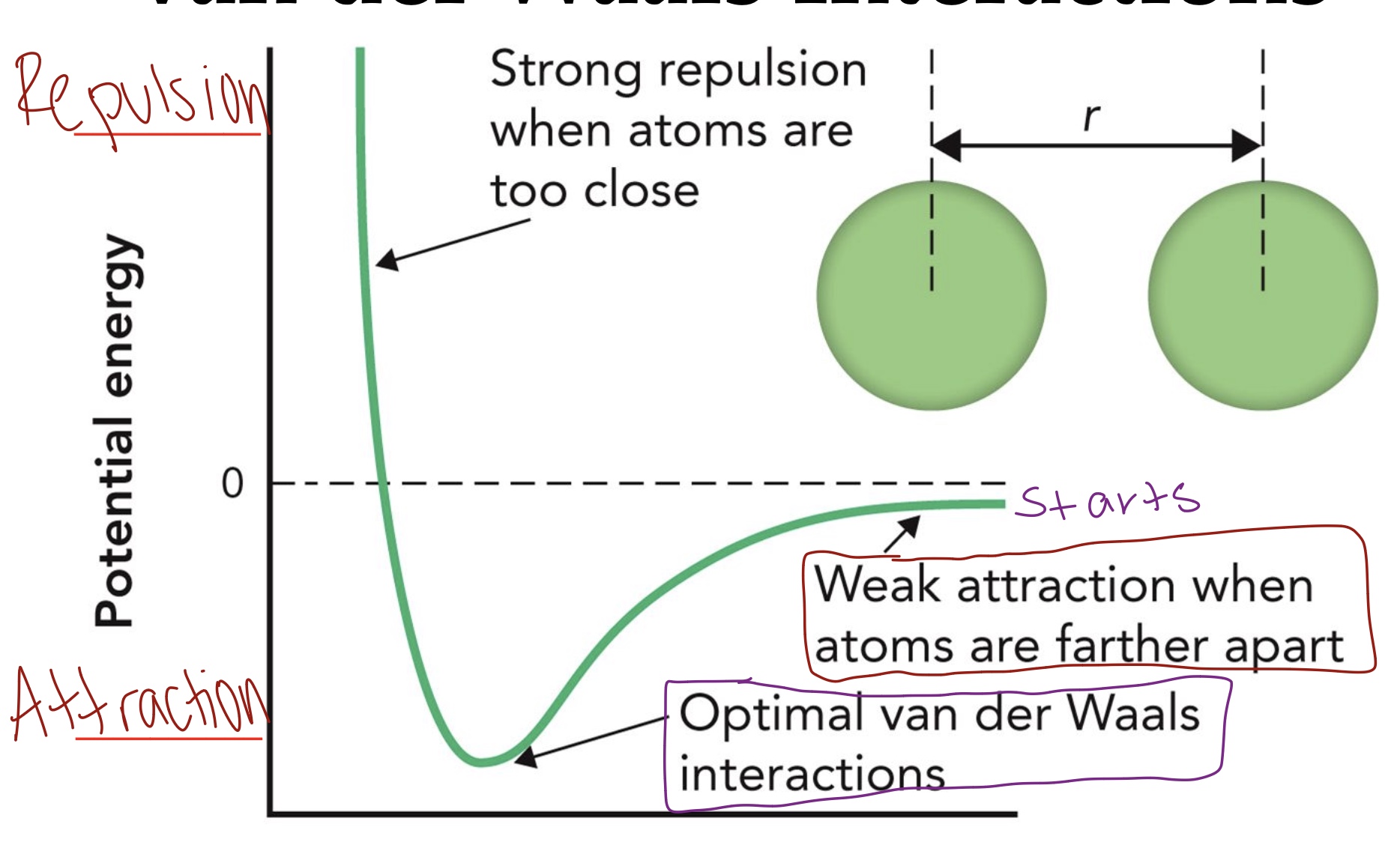
Van der Waals interactions
Occur between two neutral molecules/atoms by temporary dipole moments because of fluctuations in the electron clouds.
Ex: Gecko climbing the wall, base stacking
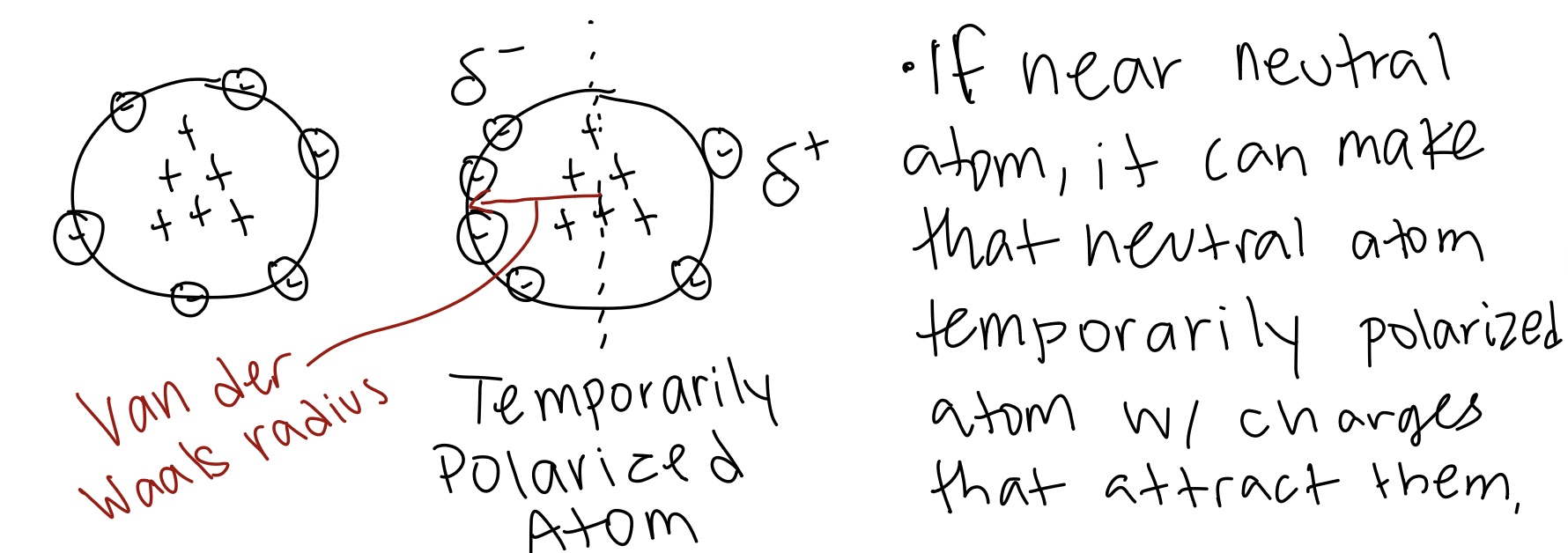
The maximum van der Waals attraction occurs
At a distance slightly greater than the sum of the van der Waals radii of the two atoms.
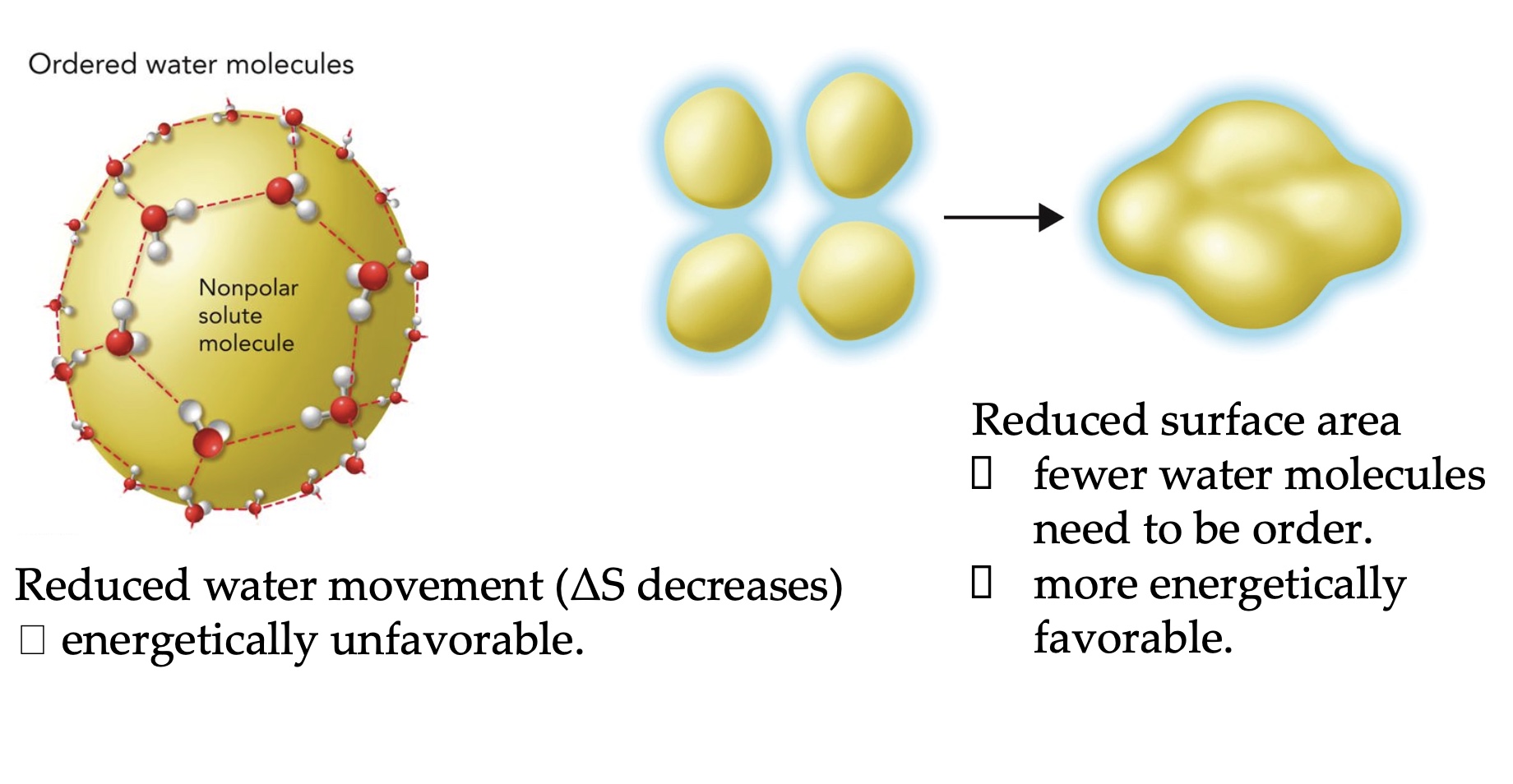
Hydrophobic effects
Due to the tendency for nonpolar molecules to pack close together away from water.
Ex: protein folding, protein-protein association, formation of lipid micelles, enzyme-substrate complex formation.
Order of strength for these interactions.
ionic (full charge) > hydrogen bonds (partial charge) > hydrophobic effects > van der waals
What are the four biomolecules
Fatty acids, nucleotides, amino acids, and simple sugars.
More than ___ percent of the mass of the cell is ___
70, water
In water there is an ____ electron distribution. Oxygen is more ____ than hydrogen. The bond angle is ____. H2O exhibits permanent ___ moments.
Unequal electron distribution
Oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen
The bond angle is 104.5
H2O exhibits permanent dipole moments
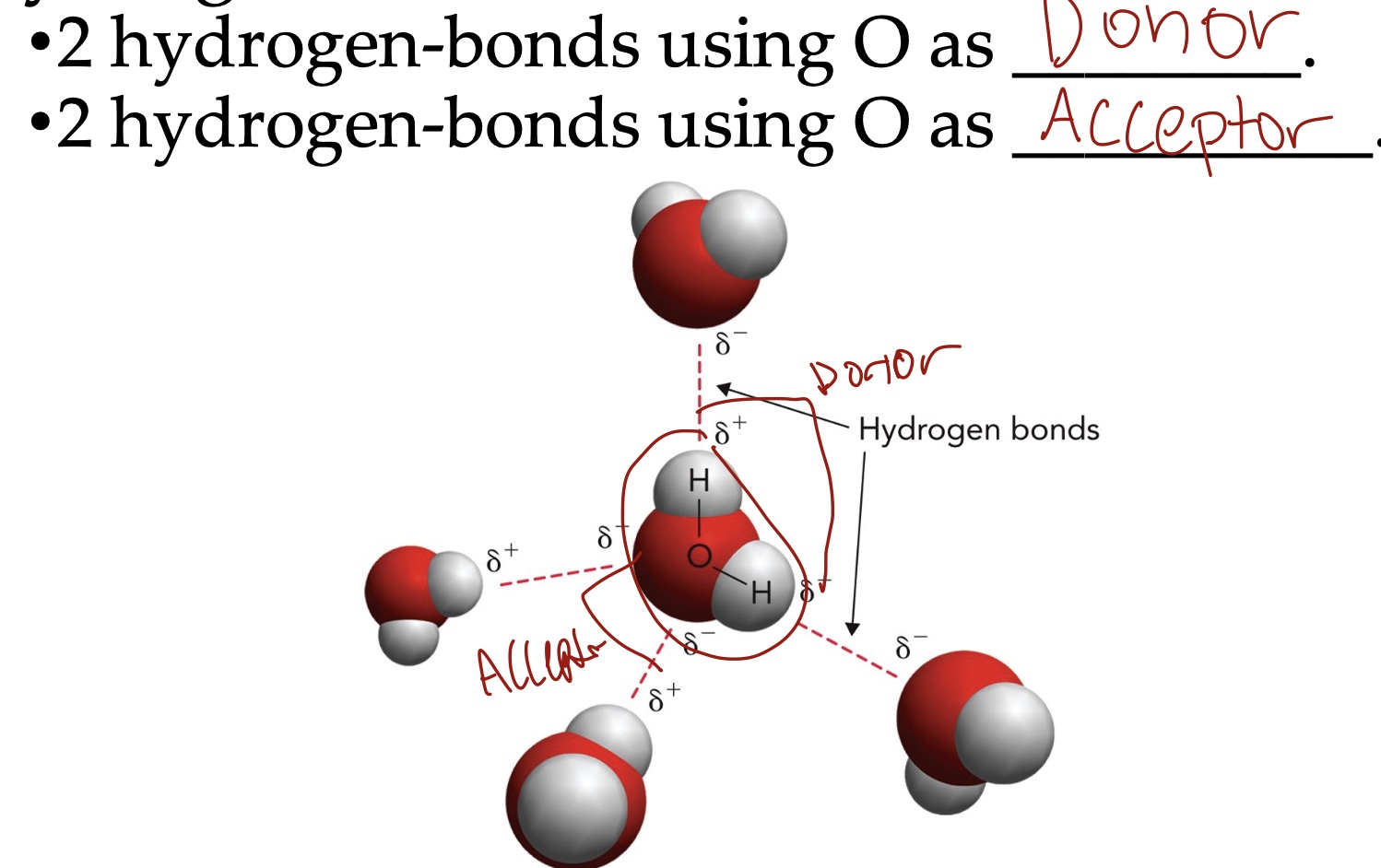
How many hydrogen bonds can water form?
Up to 4
Water is a good solvent for ____ and _____ substances.
ionic (charge) and polar (hydrophilic)
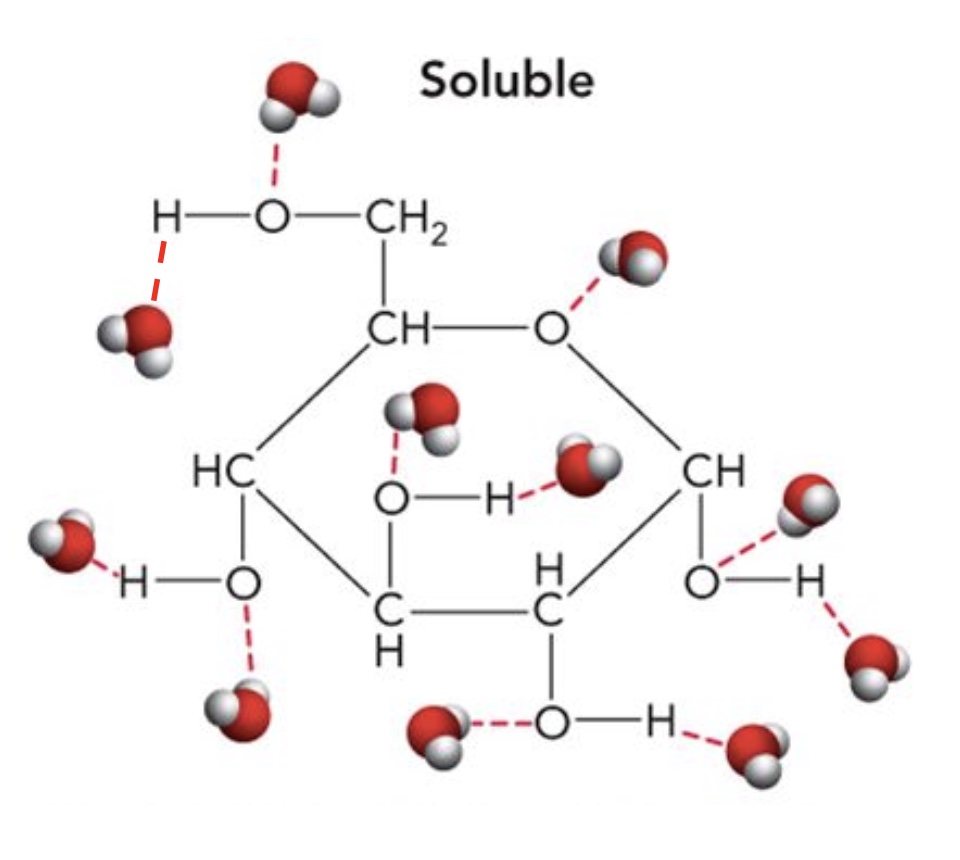
Water as solvent: Glucose has __ hydroxyl groups and a ring ____ to form H-bonds with water.
5 hydroxyl groups and an oxygen ring.
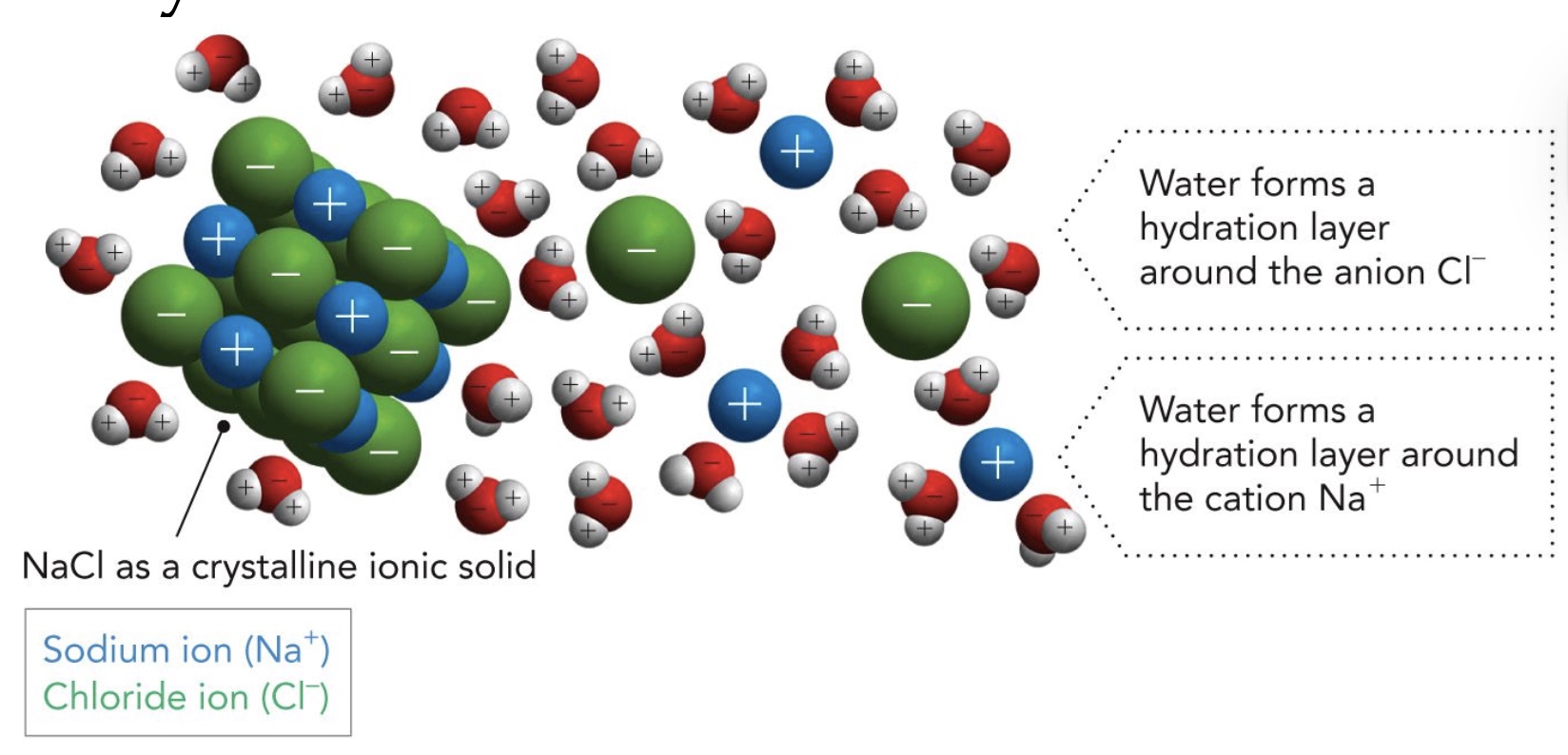
Water as solvent: Hydration of NaCl
H2O stabilizes ___ and ____ by weakening their electrostatic interaction thus disrupting crystallization.
Na+ and Cl-
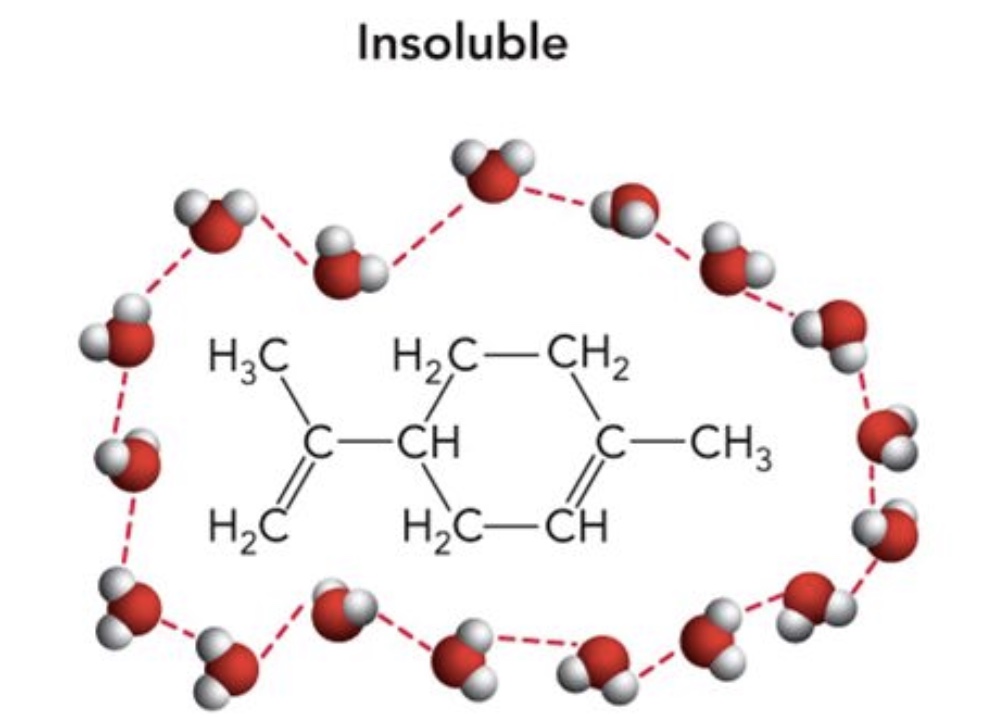
Water is a polar solvent for ____ substances (hydrophobic)
- Hydrocarbons -Aromatic rings -Amphipathic molecules
Nonpolar
Limonene _____ form H-bonds with water
CANNOT
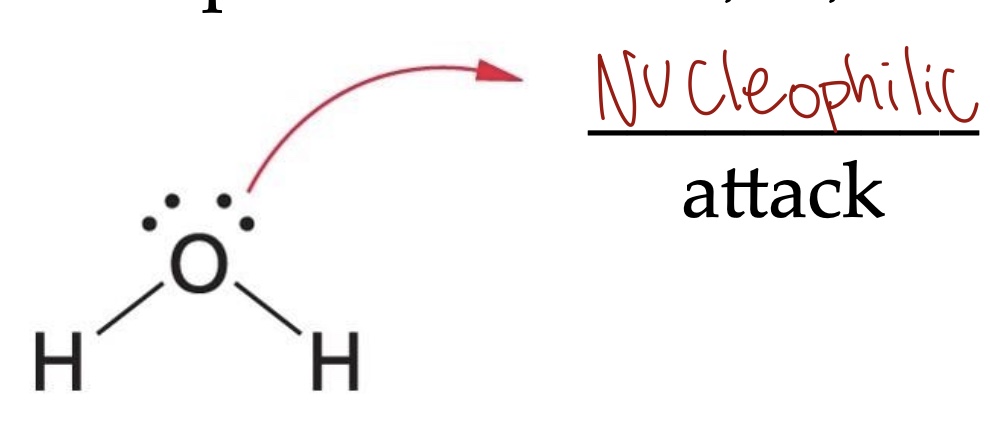
Nucleophiles are:
Common nucleophilic atoms: O, N, S, and C
Electrophiles:
Nucleophiles are electron-rich (either negatively charged or have unshared pairs of electrons)
Electrophiles are positively charged molecules
Water ionization constant: (25 C, 55.5M)
Kw=
[H+][OH-] = 1 × 10^-14 M^2
[H+] and [OH-] are reciprocally related
pH scale: The acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution depends on the concentration of _________ and can be described by a pH value (the negative logarithm of the H+ concentration).
pH=
Hydrogen ion (H+)
pH= -log[H+] = long 1/[H+]
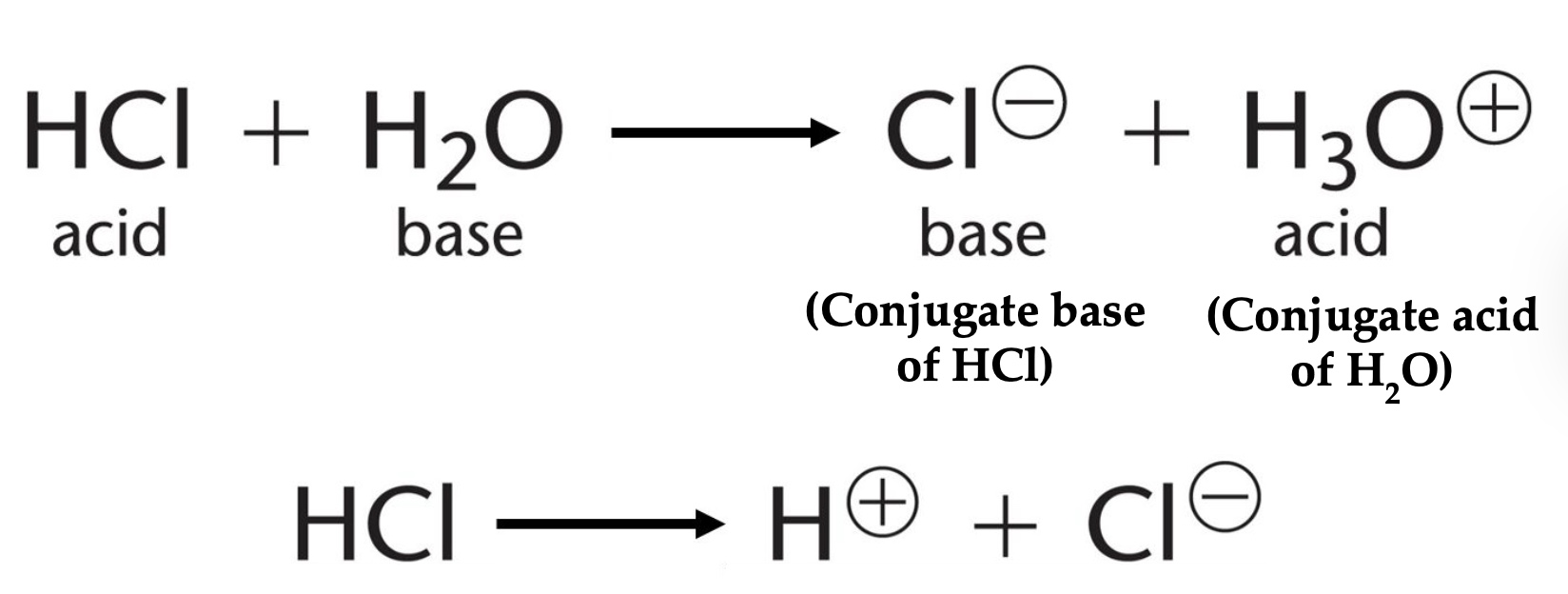
Acids are proton _____, whereas bases are proton ____
Acids= proton donors
Base= proton acceptors
Strong acids _______ in water.
Completely dissociate
Weak acids ______ in water.
The extent of dissociation is determined by the ___ of the solution.
Partially dissociate
pH
Why is Weak Acid an Important Concept?
Many biological molecules or their components are weak acids
Amino acids, DNA, and RNA
Why is Weak Acid an Important Concept?
The ionization state of these weak acids regulates not only their ________ but also their ____ other biological molecules.
Function, interaction
Why is Weak Acid an Important Concept?
The structure and function of these molecules is often regulated by the ___ of the solution
pH
What is the Ka and what does it mean if it is big?
What about a small pKa?
Acid dissociation constant. Bigger Ka, stronger acid
Small pKa, stronger the weak acid
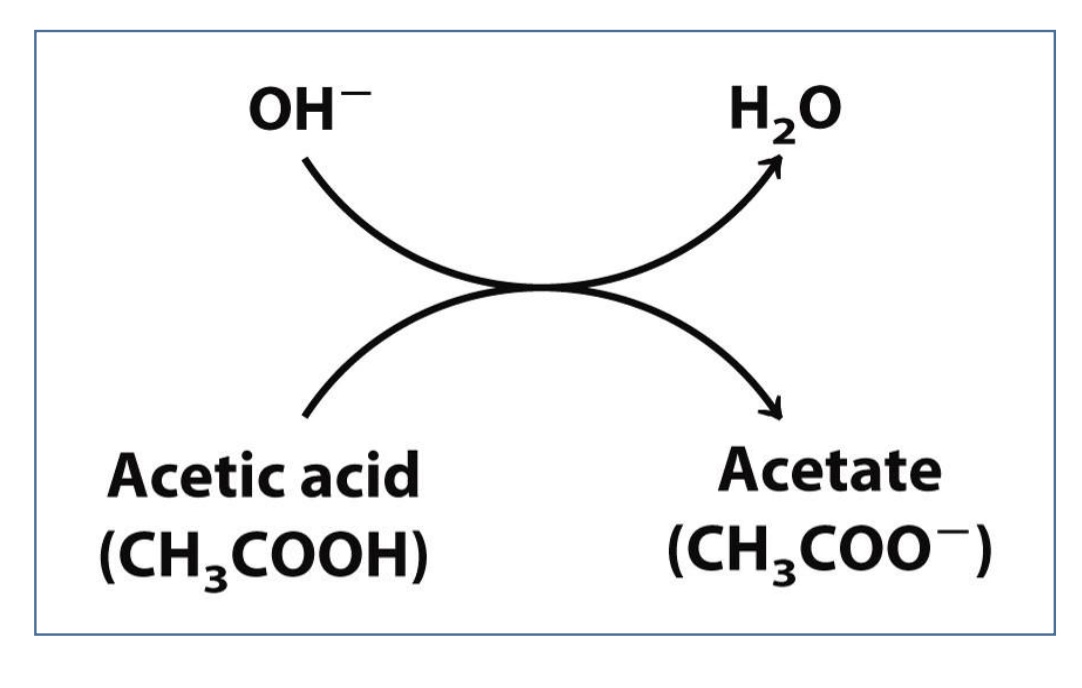
The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation shows the direct relationship between the ___ of a solution and the ratio of the ____ for [A-] to the _____ form [HA] of some ionizable group.
pH, deprotonated, protonated
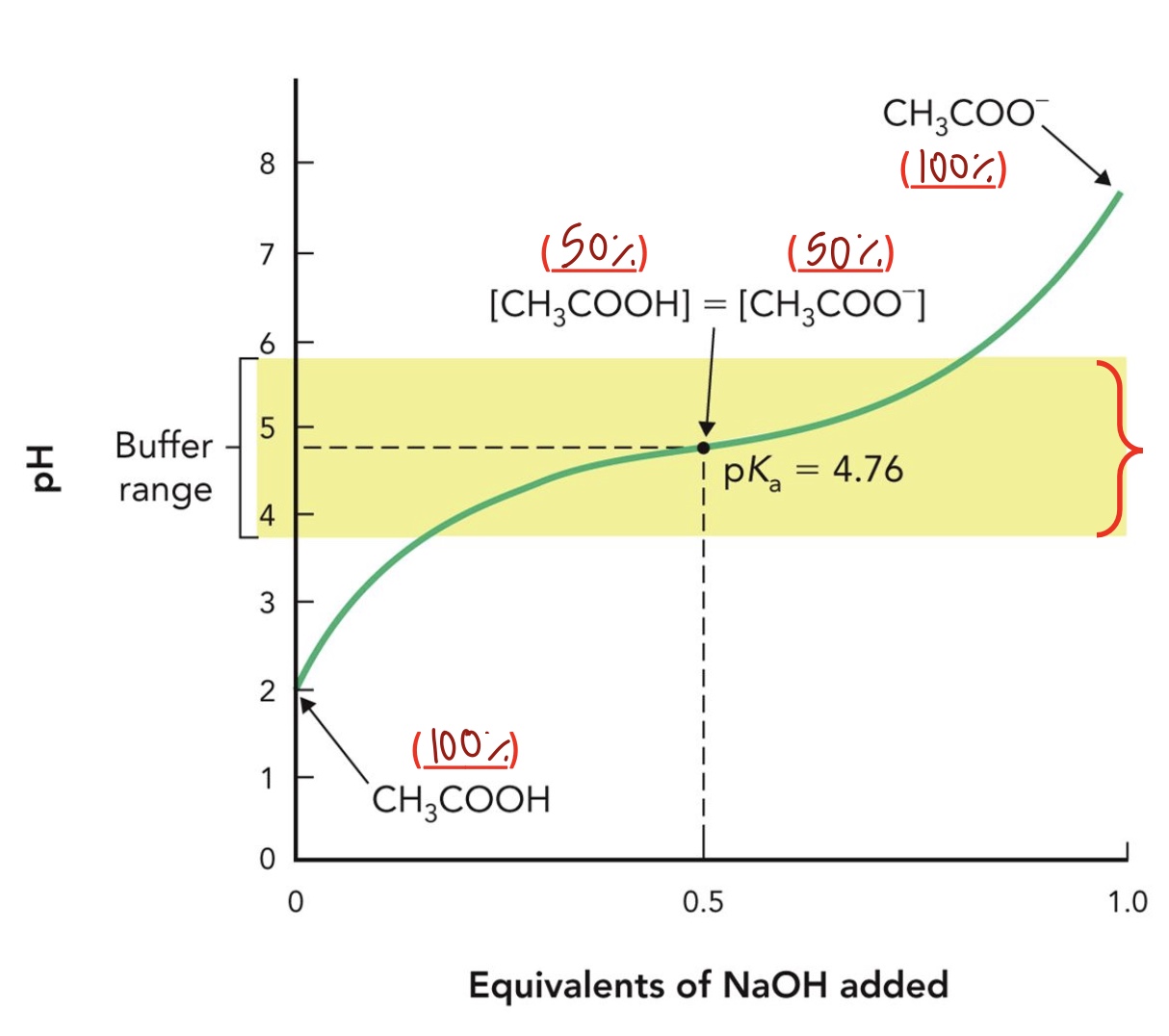
Titration Curve: The titration curve of weak acids is used to determine the amount of weak acid that is being ____ at different __ conditions
Deprotonated, pH
Buffer range
within 1 pH unit above or below the pKa
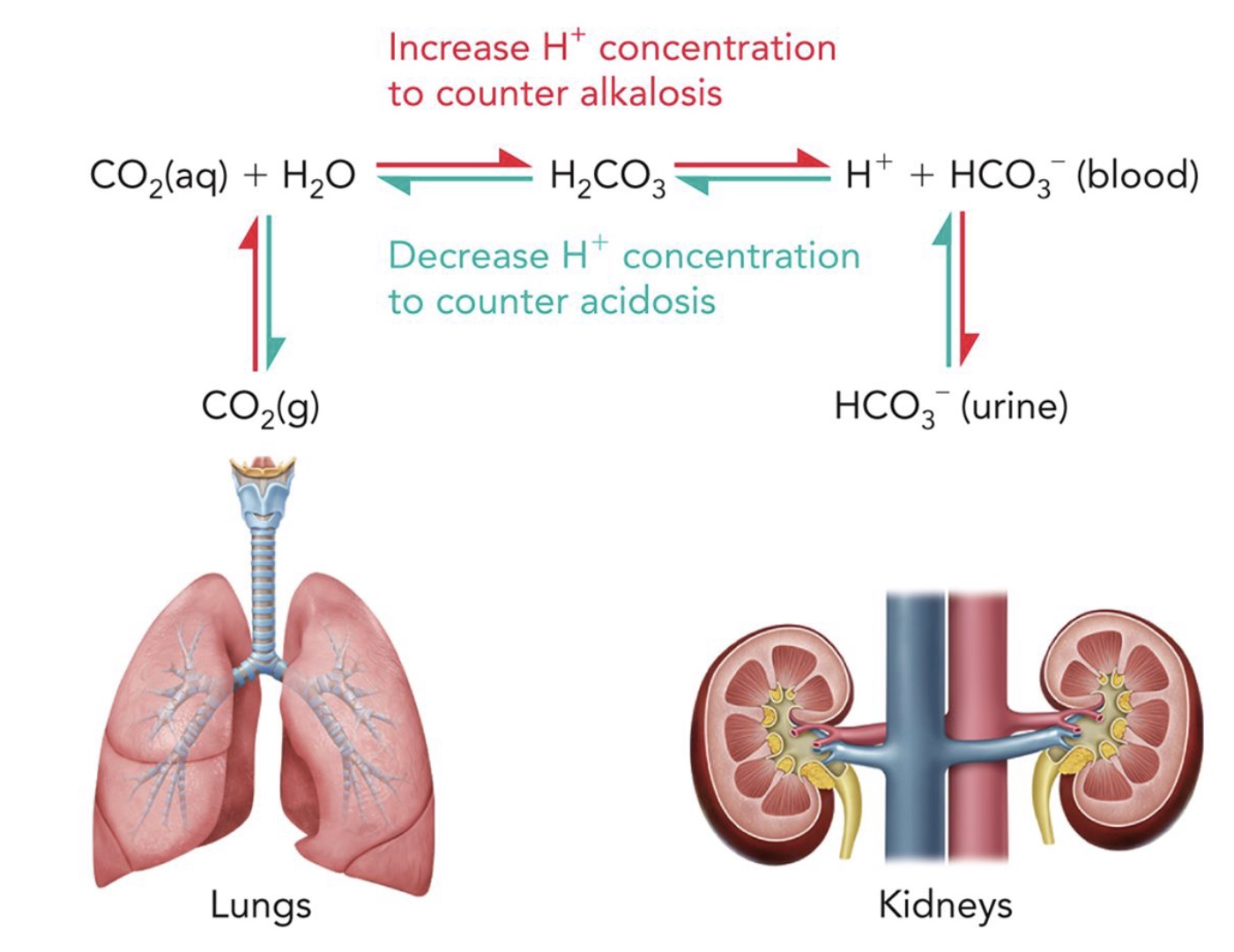
Biological buffering systems: Carbonic acid (H2CO3) and bicarbonate (HCO -) buffering system is used to _____ physiological pH. What is acidosis and alkalosis?
Maintain
Acidosis → When blood pH falls below 7.4
Alkalosis → When blood pH rises above 7.4
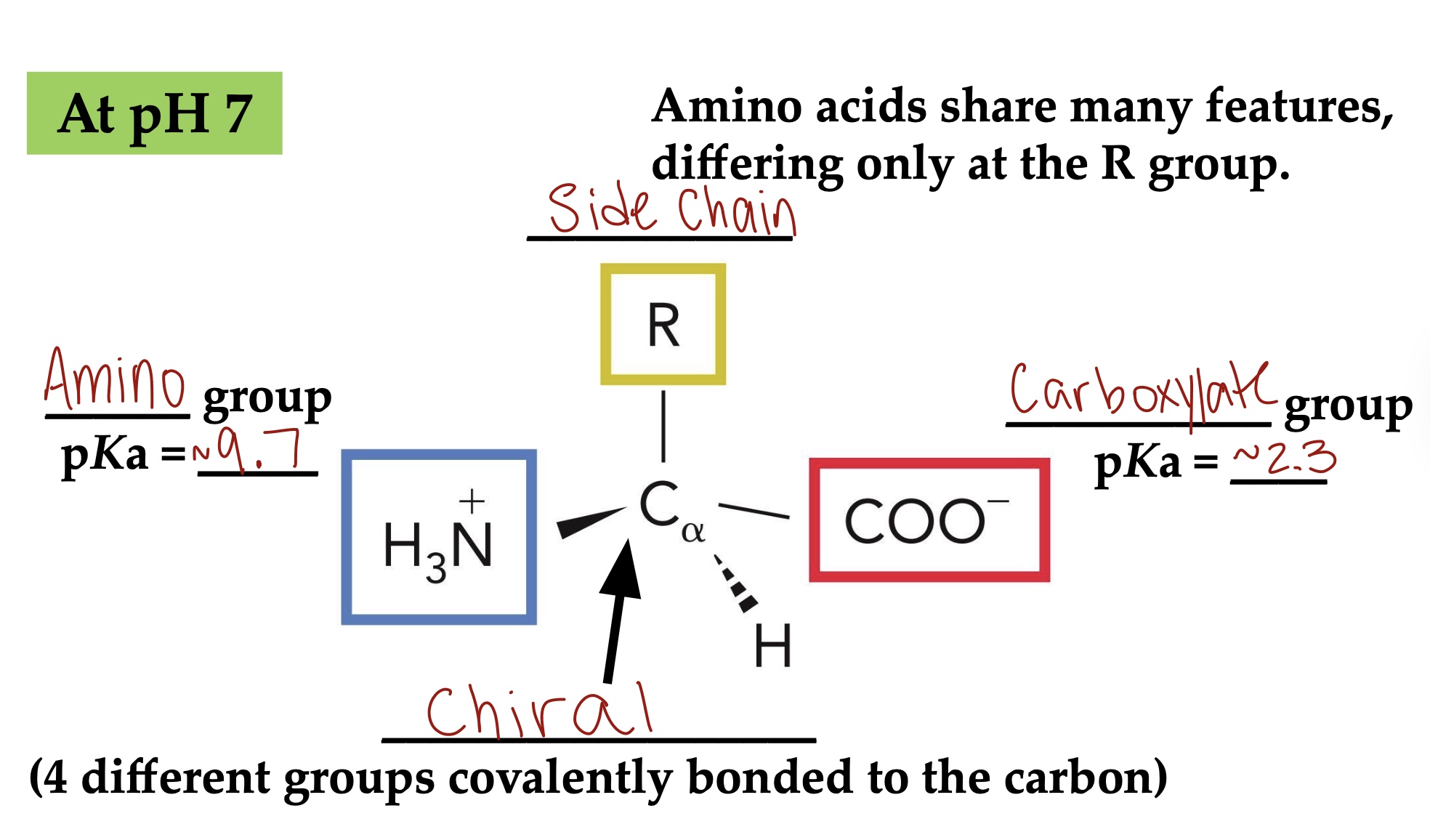
Proteins are linear heteropolymers of ___ -amino acids
Alpha
Amino acid structure
L and D forms
→ Horizontal bonds project TOWARD viewer
→ Vertical bonds project AWAY from the viewer
→ NH3 on top
→ COO on bottom
IF R is on LEFT → L FORM
IF R on RIGHT → D FORM
MOST ARE L FORM
Naturally occurring proteins contain nearly all ___ amino acids, except _____which contain an asymmetric α-carbon.
L, glycine
________ molecules with the same chemical formula but differ in their arrangement or configuration of atoms in space.
Stereoisomers
______ non-superimposable mirror image. (L and D forms are enantiomers)
Enantiomers
Polar/hydrophilic amino acids, On the protein _______. Forming ___ bonds with water.
Surface, H bonds
Nonpolar/hydrophobic amino acids: Cluster in the _____. Minimizing interaction with ____.
Interior, water
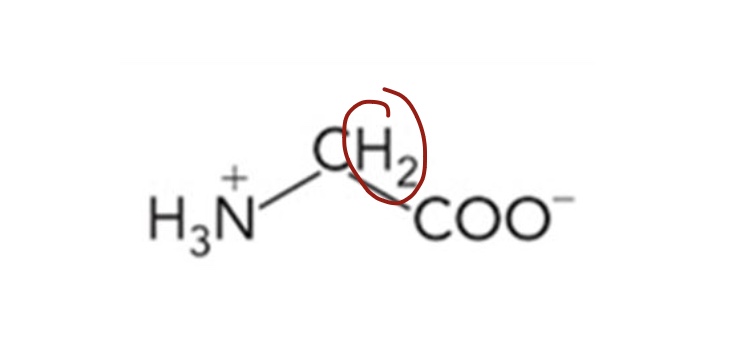
What amino acid is this? 3-letter code? Characteristics?
Glycine (Gly)
Nonpolar hydrocarbon R groups
α-carbon is not chiral
Chemically inactive
Flexible and able to form sharp turns in proteins
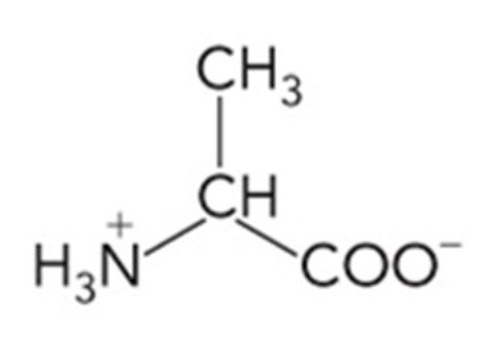
What amino acid is this? 3-letter code? Characteristics?
Alanine (Ala)
Nonpolar, hydrocarbon R group
Methyl group side chain
Relatively small
Chemically inactive
Flexible
Glycine and Alanine = ____ in proteins
15%
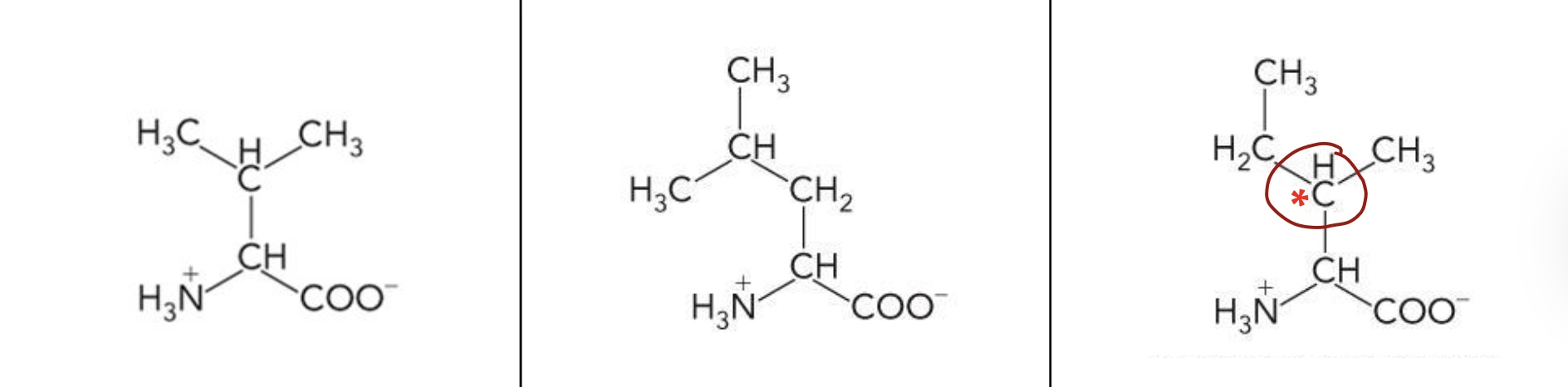
What amino acid is this? 3-letter code? Characteristics? (Left to right name)
Valine (Val), Leucine (Leu), Isoleucine (Ile)
Nonpolar hydrocarbon R groups
Branched hydrocarbon side chain
Highly hydrophobic
ile has an additional stereocenter
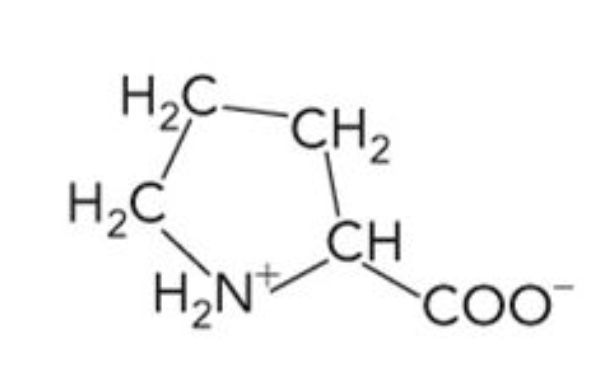
What amino acid is this? 3-letter code? Characteristics?
Proline (Pro)
Nonpolar, hydrocarbon R group
Forms cyclic structure with restricted conformation
Cannot form H bonds in a polypeptide
Usually found at the turns of polypeptide chain
What amino acid is this? 3-letter code? Characteristics?
Methionine (Met)
Nonpolar, hydrocarbon R group
Thioester sidechain makes hydrophobic
Sulfur is unreactive
1st amino acid in a polypeptide
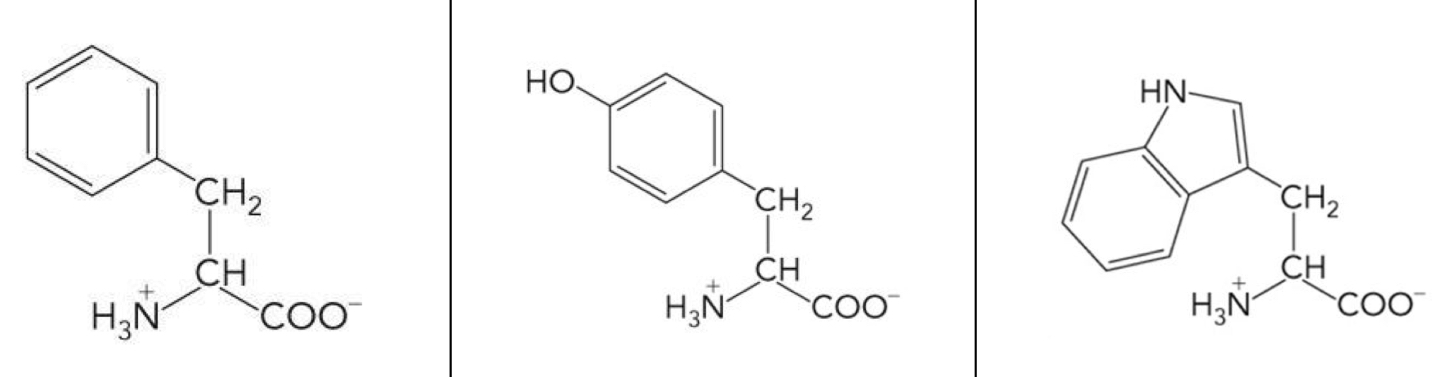
What amino acid is this? 3-letter code? Characteristics? (Left to right)
Phenylalanine (Phe), Tyrosine (Tyr), Tryptophan (Trp)
Nonpolar, aromatic R groups
Bulky aromatic side chain
Very hydrophobic, but Phenylalanine is more hydrophobic
Tyr and Trp are amphipathic and are often found at the amphipathic transition of the exterior and interior of a protein.
Tyr and Trp absorb UV light at 280 nm, can be used to measure protein concentration.
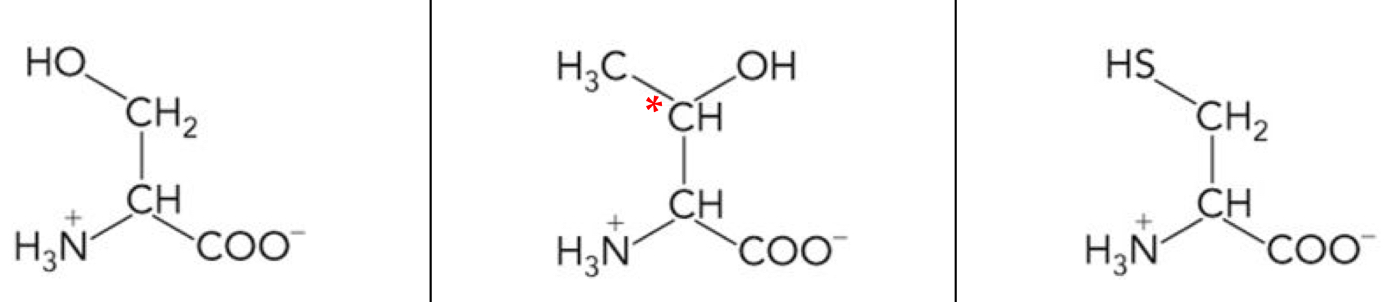
What amino acid is this? 3-letter code? Characteristics? (Left to right)
Serine (Ser), Threonine (Thr), Cysteine (Cys)
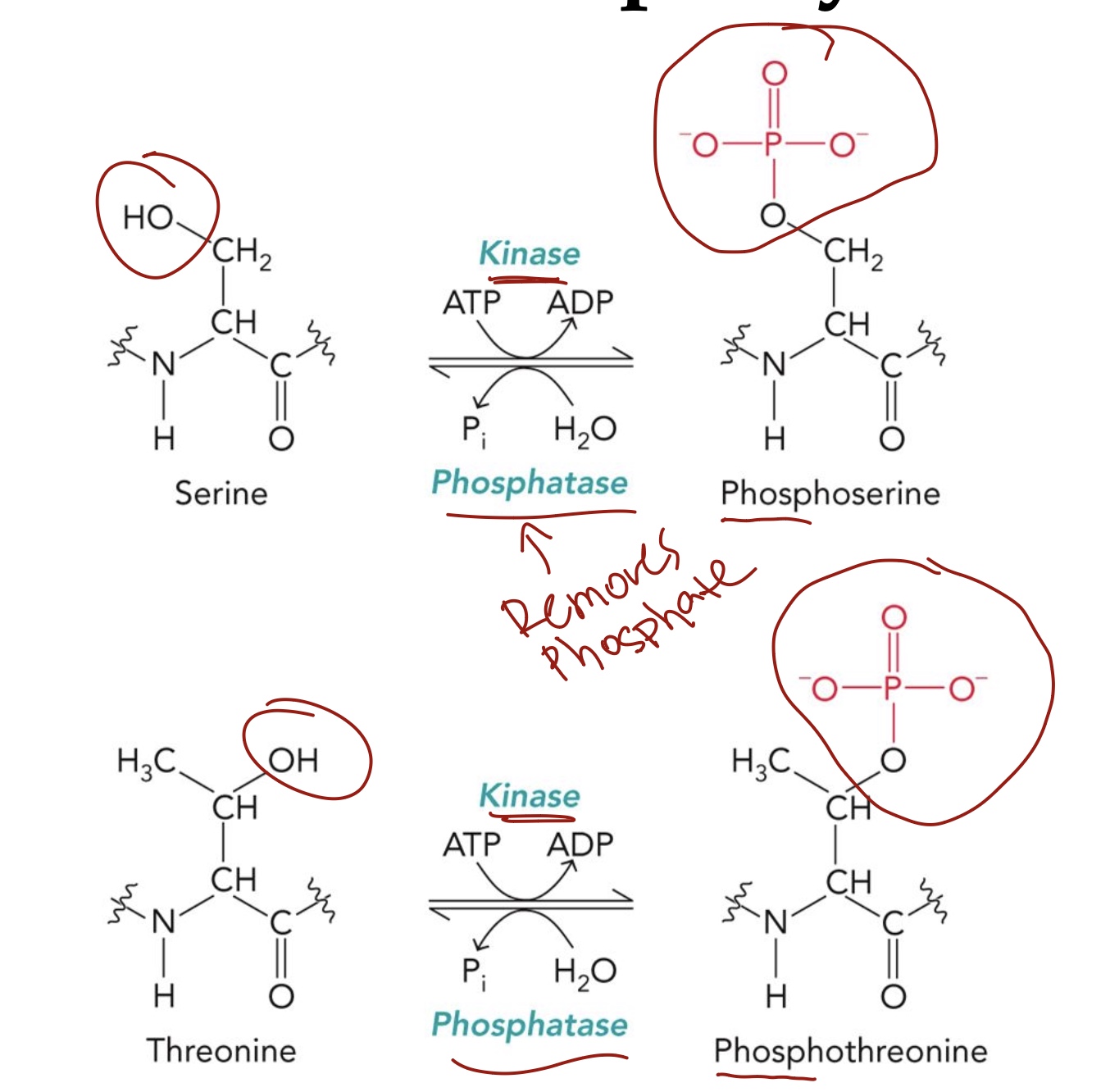
Ser & Thr have a Hydroxyl group, can be phosphorylated to regulate enzyme function.
Polar, uncharged R groups
Thr has a second stereocenter
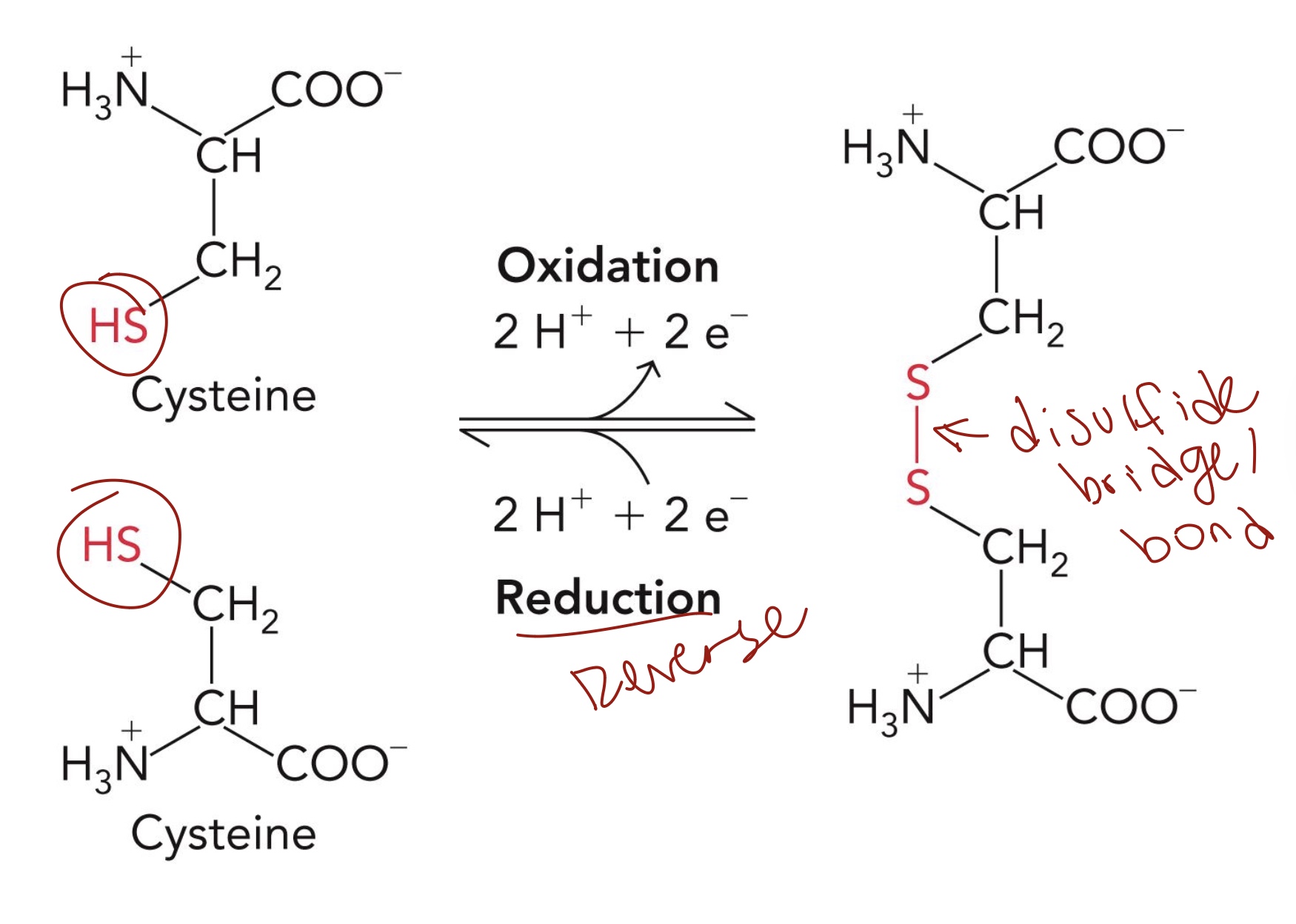
Cys has a sulfhydryl group, can form disulfide bridge in folded protein.
They are hydrophilic and good nucleophiles playing key roles in enzyme activity.
Ser & Thr Phosphorylation
Disulfide Bond Formation: Cysteine
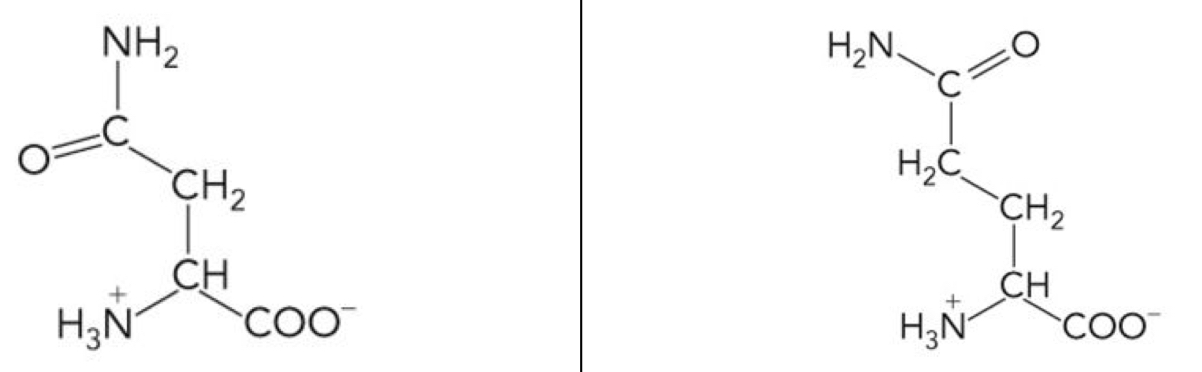
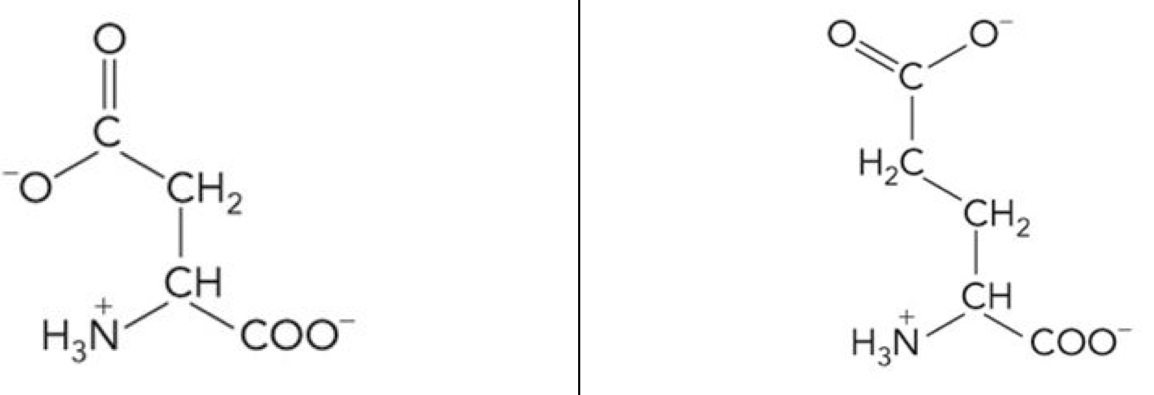
What amino acid is this? 3-letter code? Characteristics? (Left to right)
Asparagine (Asn), Glutamine (Glu)
Polar uncharged R groups
Highly hydrophilic because the side chains can form Hydrogen Bonds
Their side chains can act as both H-bond Donor or Acceptor

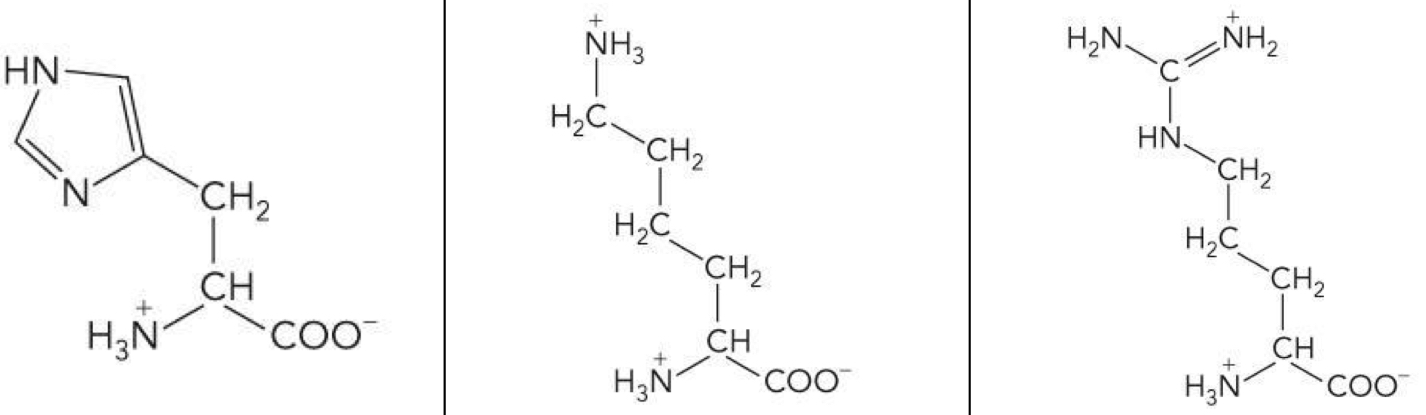
What amino acid is this? 3-letter code? Characteristics? (Left to right)
Histidine (His), Lysine (Lys), Arginine (Arg)
Polar, positively charged R groups
Side chains are positively charged → Highly hydrophilic
His carries a positive charge at pH 6, function as both a hydrogen donor and acceptor at neutral pH.
These charges are important for protein separation
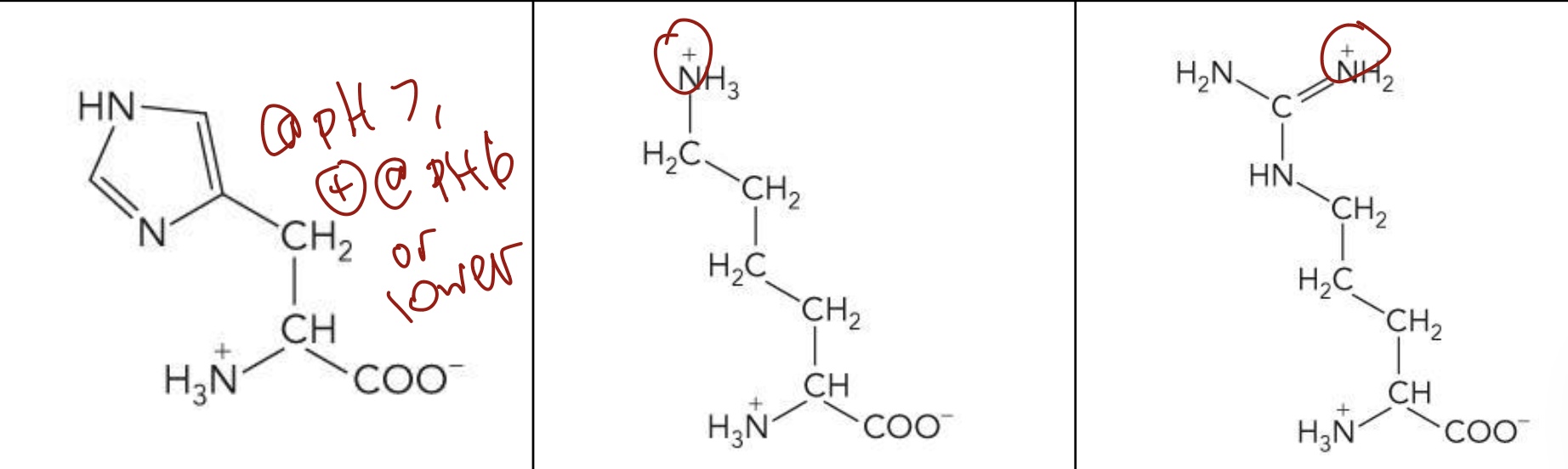
What amino acid is this? 3-letter code? Characteristics? (Left to right)
Aspartate (Asp), Glutamate (Glu)
Polar, negatively charged R groups
Side chains are negatively charged → Highly hydrophilic
Asp and Glu are dicarboxylic amino acid
These charges are important for protein separation
Why knowing the ionic state of amino acid side chain is important?
The ionic state influences the protein folding, therefore the 3D structure of proteins.
The ionic state influences the activity of the proteins.
Ionizable groups in amino acids
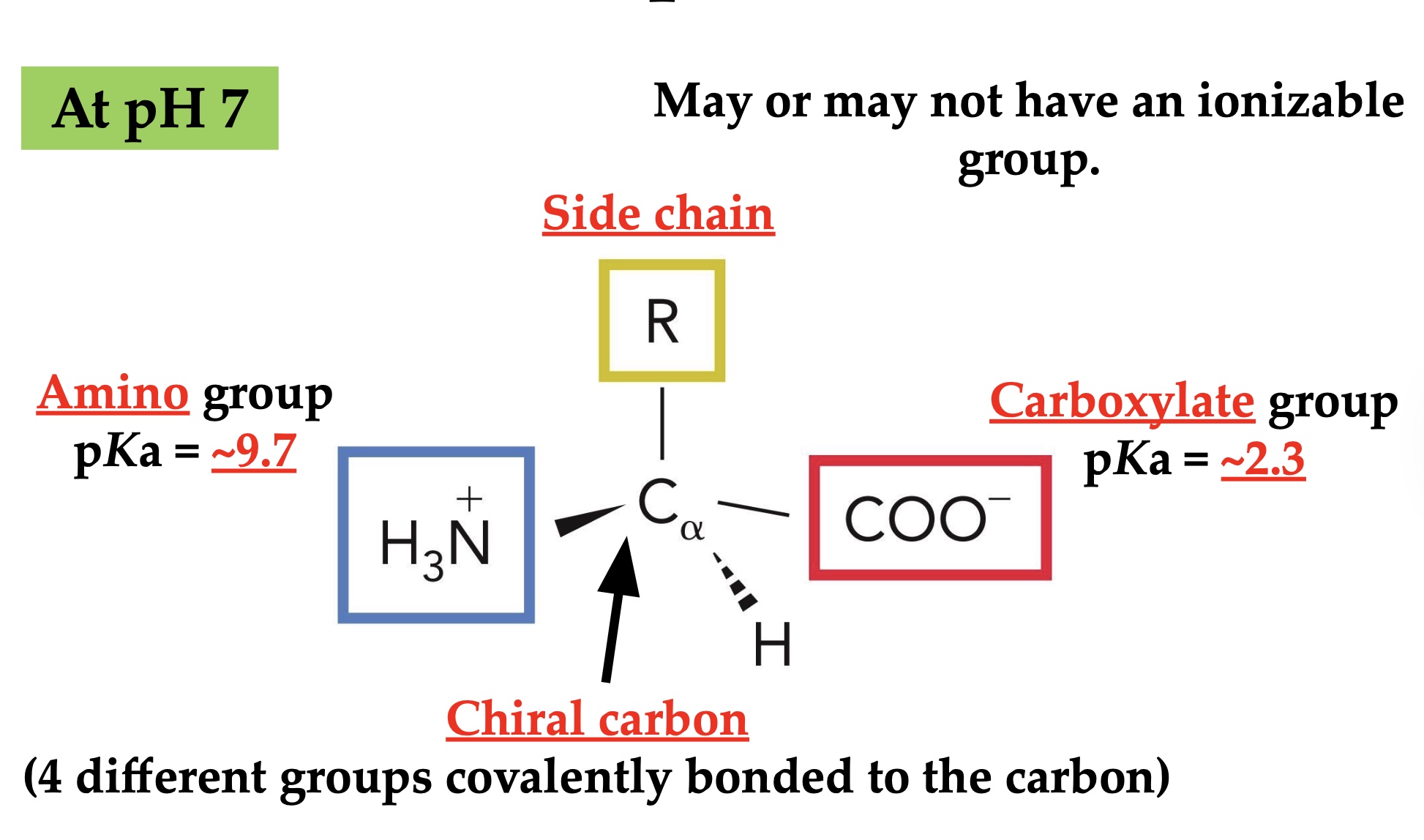
Zwitterion
A molecule carrying both positive and negative charges with zero net charge.
Isoelectric point (pI)
A point on the pH range where the average charge on the molecule sums to Exactly zero
The average of the two pKas between the zwitterion.
What amino acids are hydrophobic? Which are aromatic of these?
Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Proline, Methionine, Phenylalanine (aromatic), Tyrosine (aromatic), Tryptophan (aromatic)
What amino acids are hydrophilic (polar)? Which are uncharged, positively charged, and negatively charged?
Uncharged: Serine, Threonine, Cysteine, Asparagine, Glutamine
Positively charged: Histidine, Lysine, Arginine
Negatively Charged: Aspartate, Glutamate
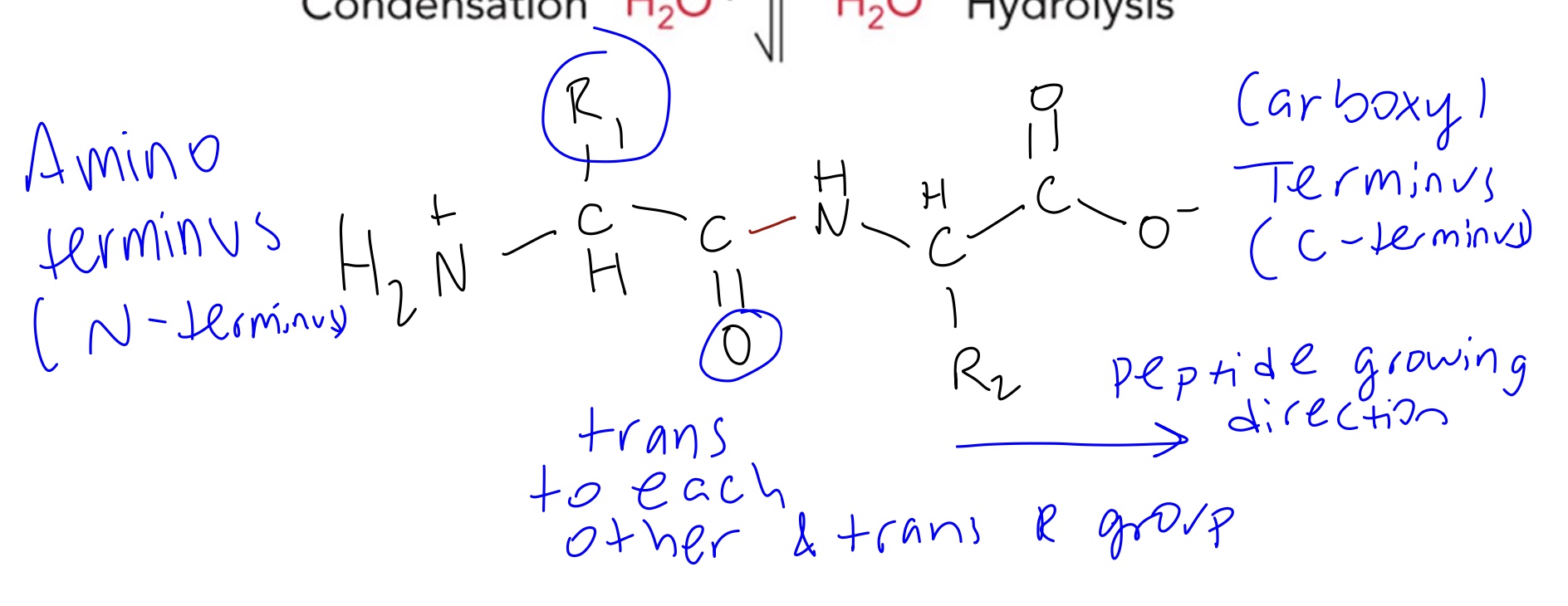
Primary (1 ̊) structure refers to the _____ that makes up the protein.
Amino acid sequence
Proteins with less than ____ amino acids are called _____ or ______.
40, peptides or oligopeptides
Proteins are usually modified with ____metal ions or co-enzymes) or
____________ or ____.
co-factors, carbohydrates, lipids
Where are peptides important in biological compounds?
Hormones, neuropeptides, antibiotics, toxins
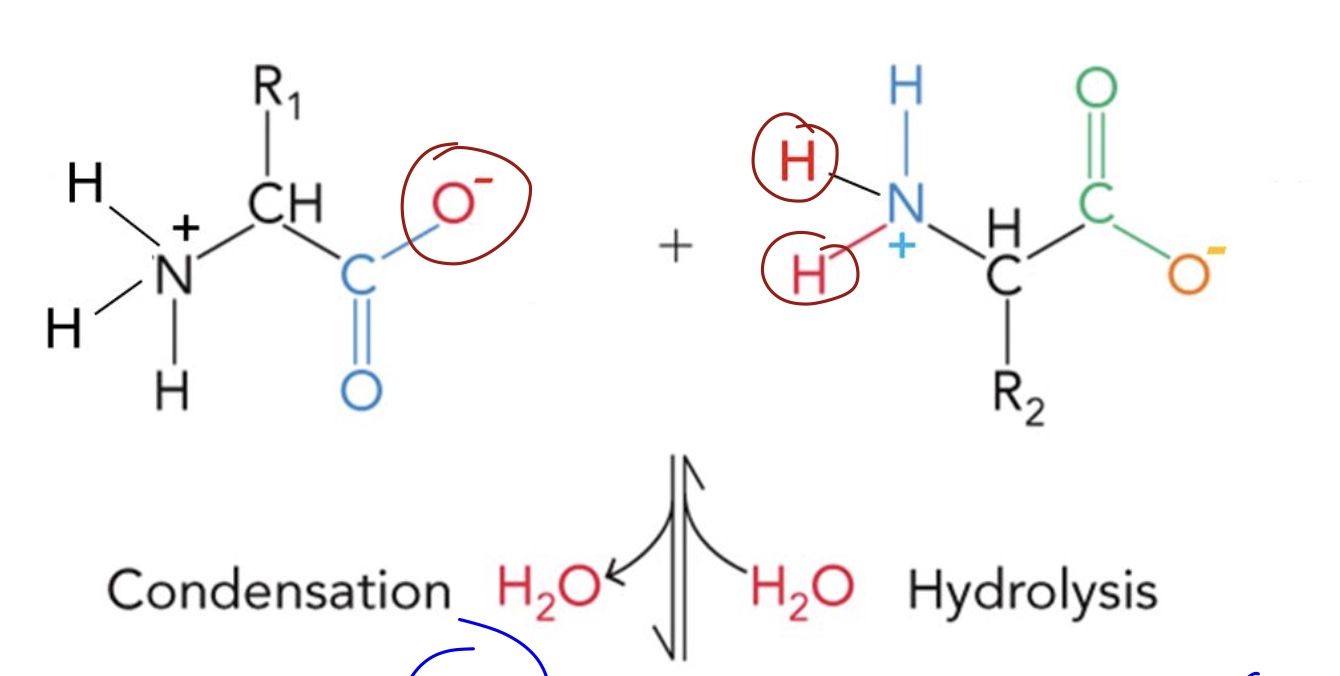
Draw the resulting peptide bond
Electrons are delocalized over ____, the _____________ and the ____.
Carbonyl oxygen, carbonyl carbon, and amide nitrogen.
The Ramachandran plot shows the allowable combination of φ and ψ angles for any two amino acid residues on the basis of ______.
Steric hindrance
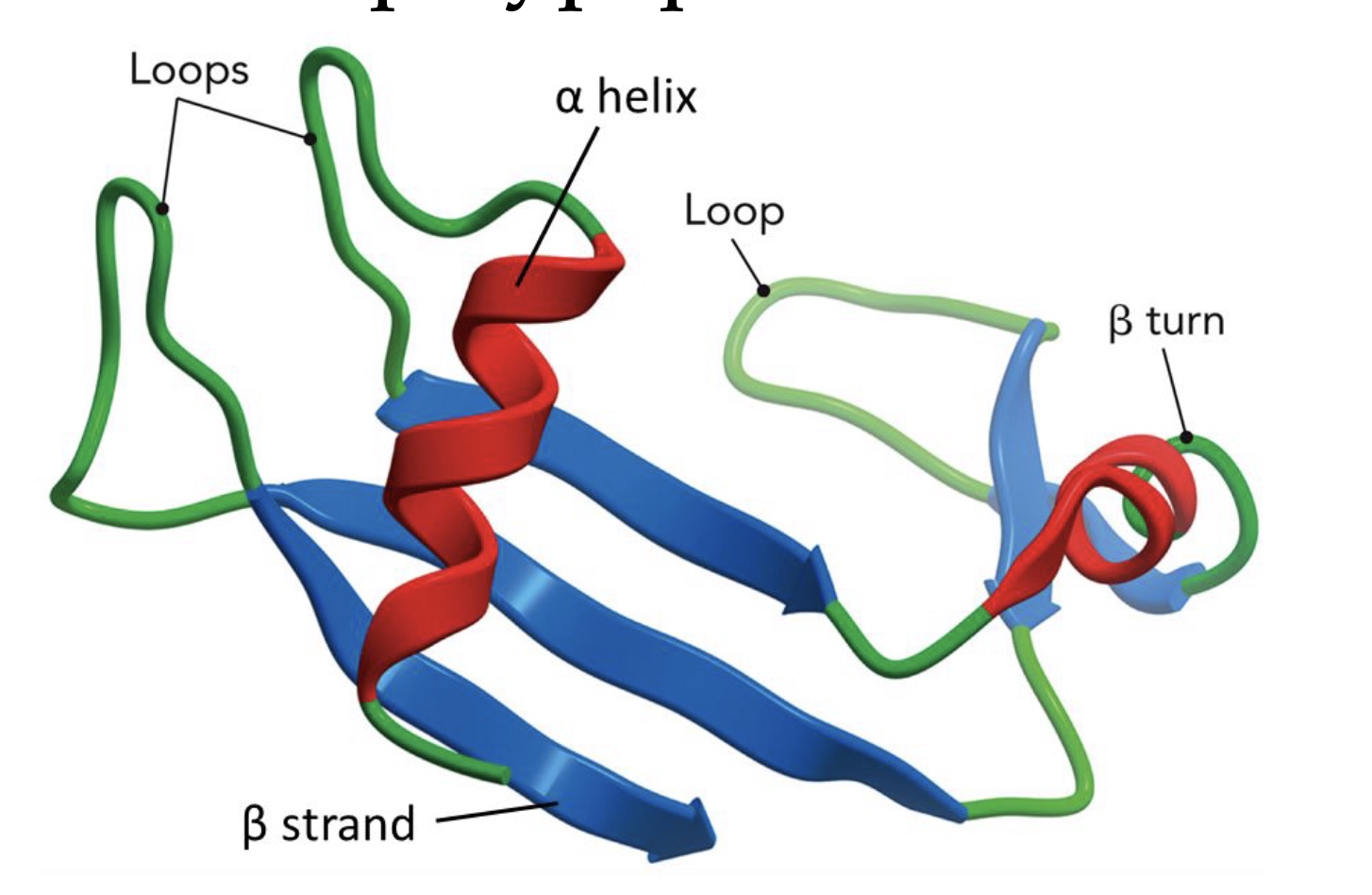
Specific regions in this plot reflect specific _____ found in proteins.
Secondary structures
The map can be used to predict whether a sequence of amino acids can form which types of _____ structure.
secondary
Secondary (2 ̊) structure refers to the regular _____ arrangement of local regions of the polypeptide backbone.
repetitive
Alpha helix: Almost all are ___ helix
Right-handed
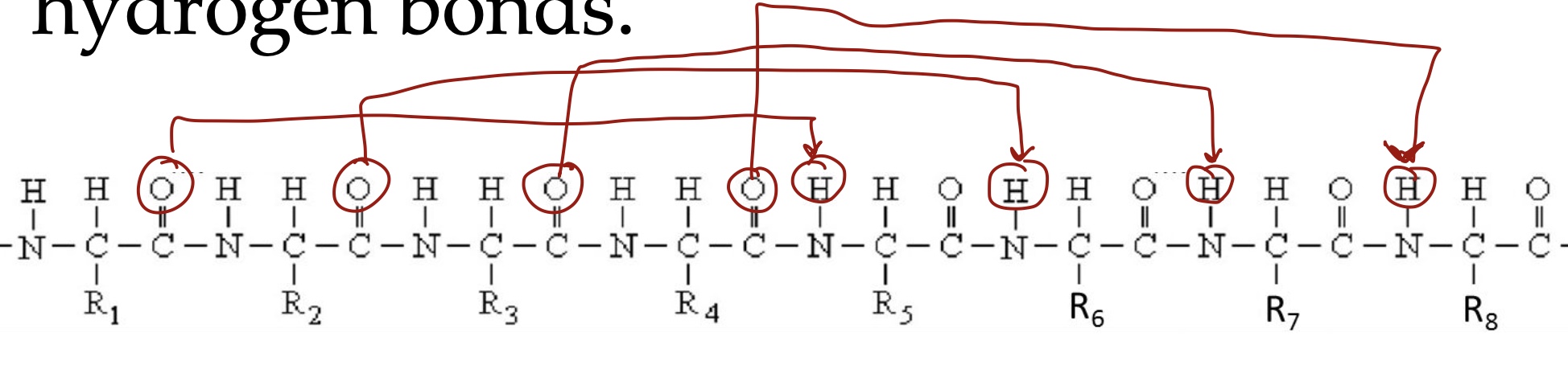
Alpha helix: H-bonds between ____ and the ____ residue of the _____ toward the C-terminus. Do the R groups participate in H bonds?
Carbonyl oxygen (n), (n+4), amide hydrogen. No they do not.
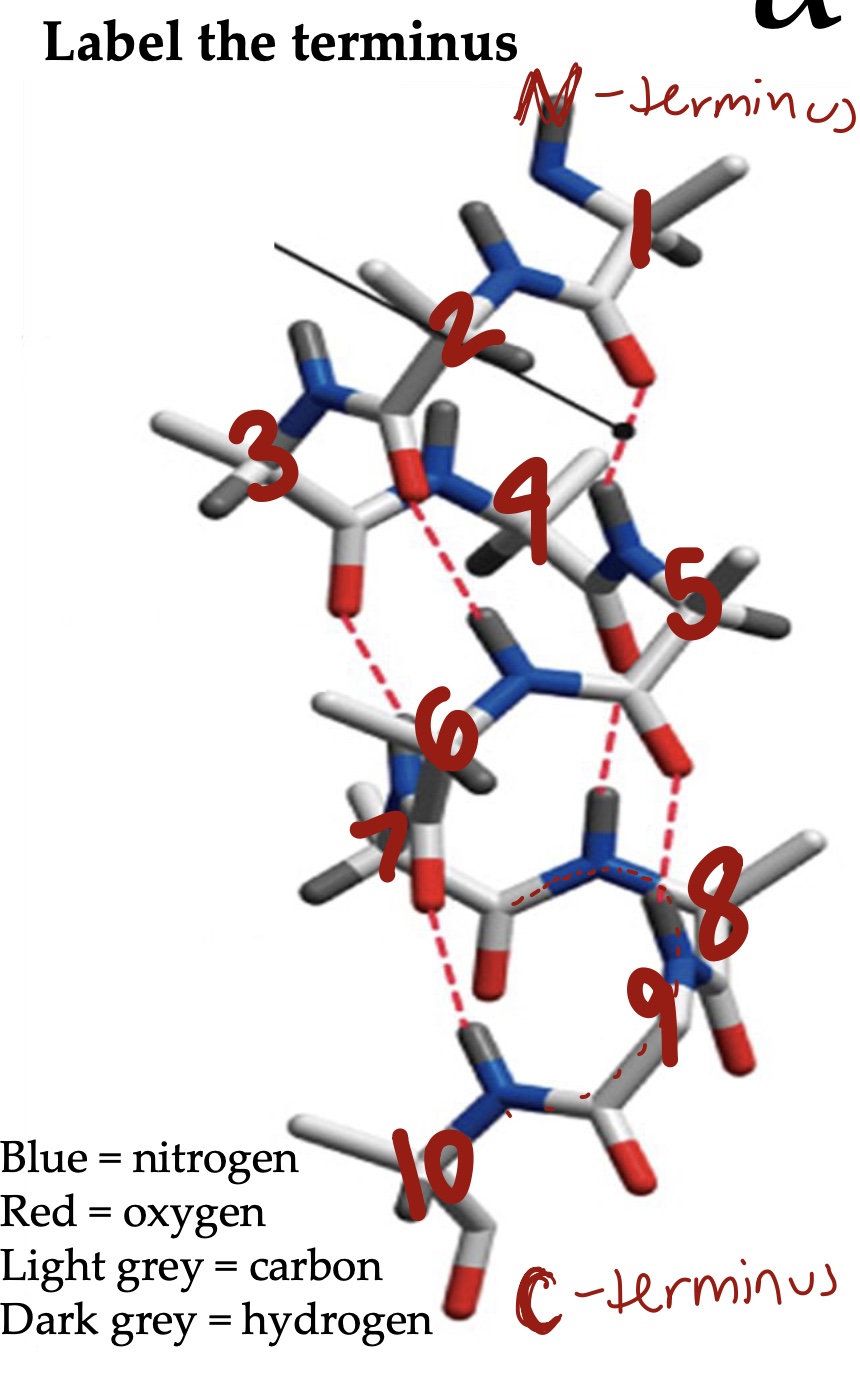
Alpha helix: The length of hydrogen bond ____. ___ amino acids per turn.
2.8 nm, 3.6
Most amino acids can be accommodated within the structure of an α helix, but not proline. Why?
There is not an amide hydrogen and the rigid ring restricts conformation.
To stabilize the helix ___ charged amino acids are often found on the -terminus, whereas ____ charged amino acids are often located on the __-terminus.
Negatively, N, positively, C
The N- and C-termini tend to be located on protein _____, where the charge can be neutralized by interacting with _____ or _____
Surface, H2O, charged ions (PO4 2- or Mg2+)
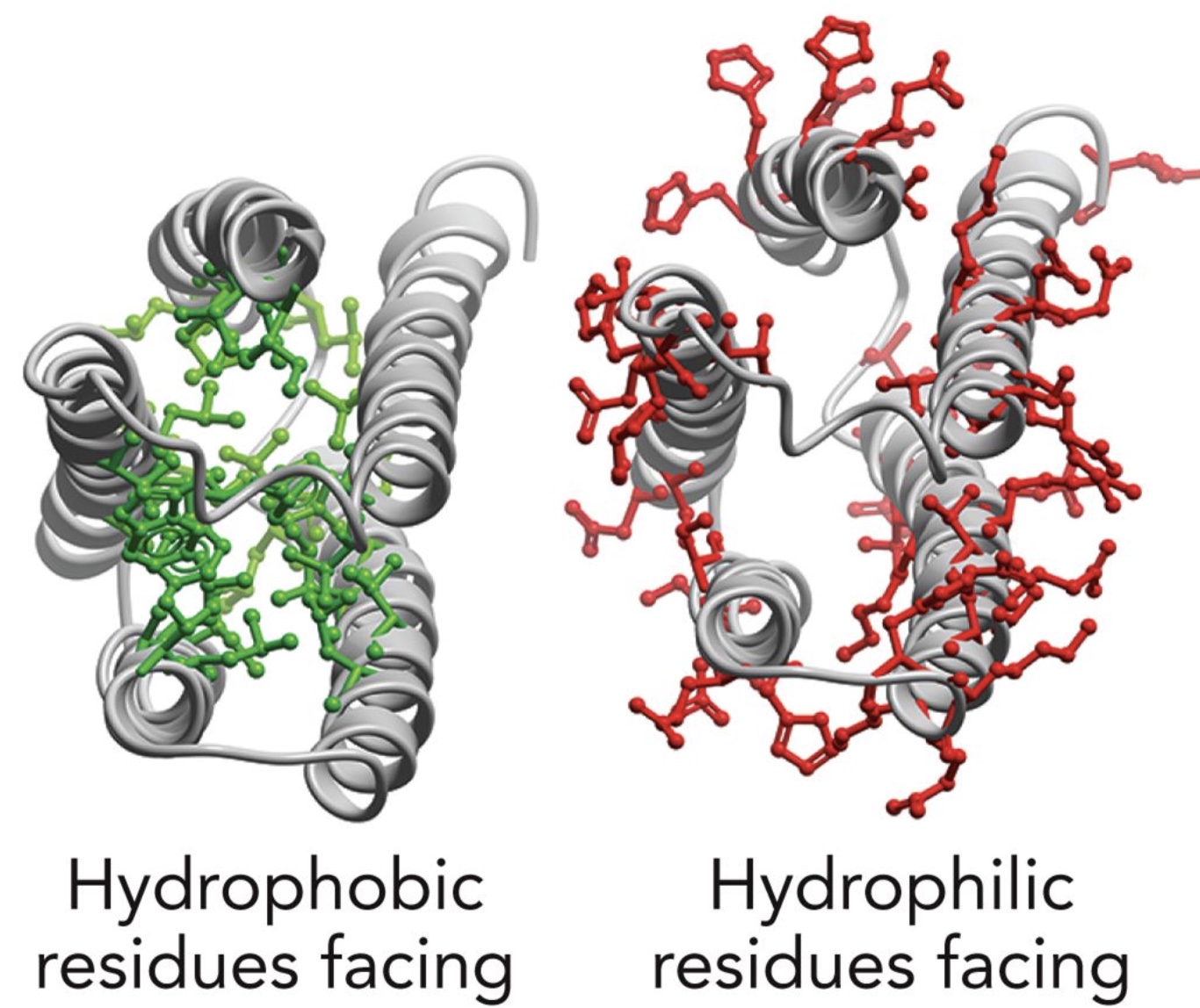
Lefr: inward, Right: outward
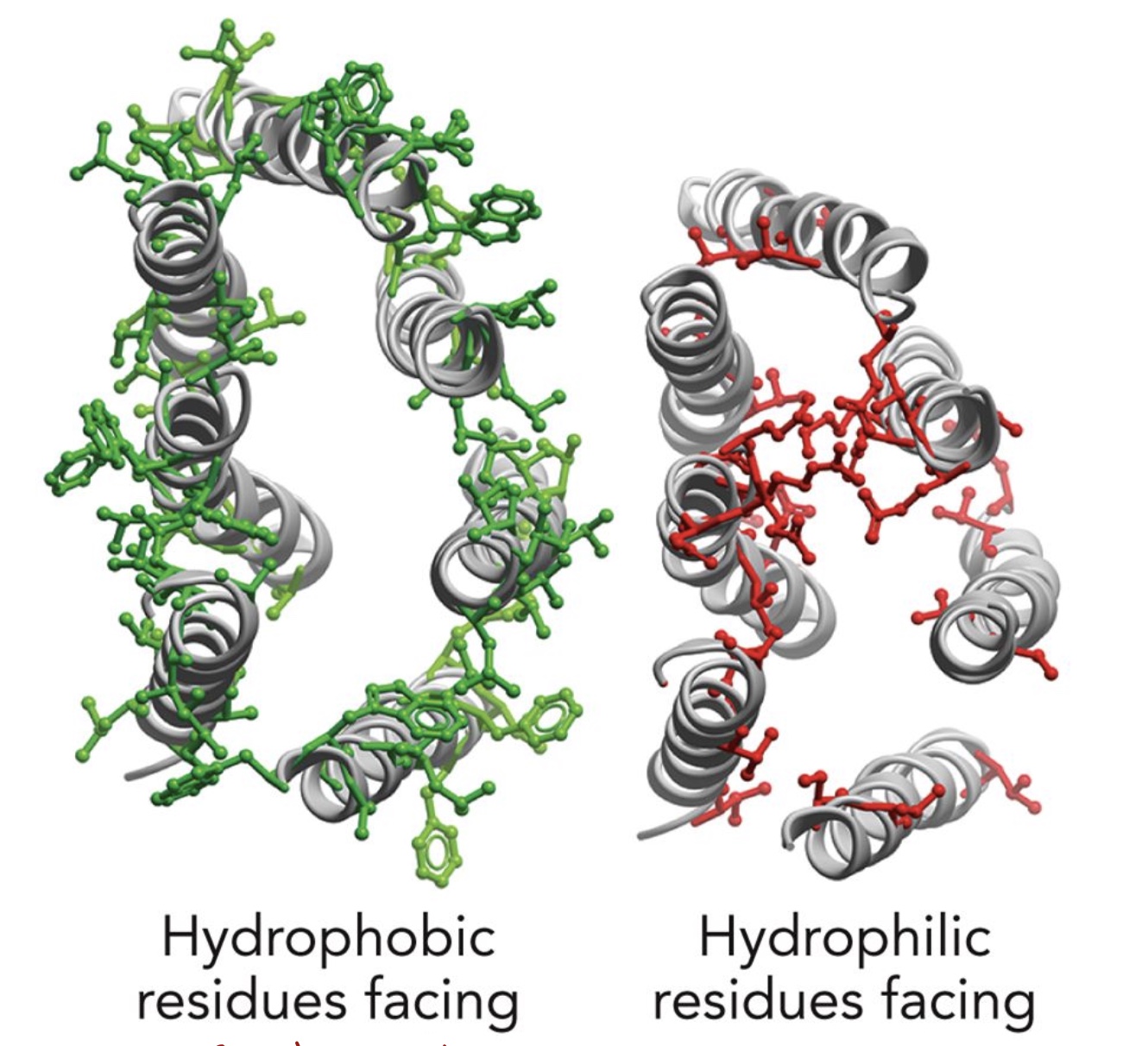
Left: Outward, Right: Inward
In the ribbon model, β strand is depicted as an _____. The arrow head is pointing toward the C-terminus.
Arrow
Side chains are positioned ___ and ____the polypeptide backbone
Above and below
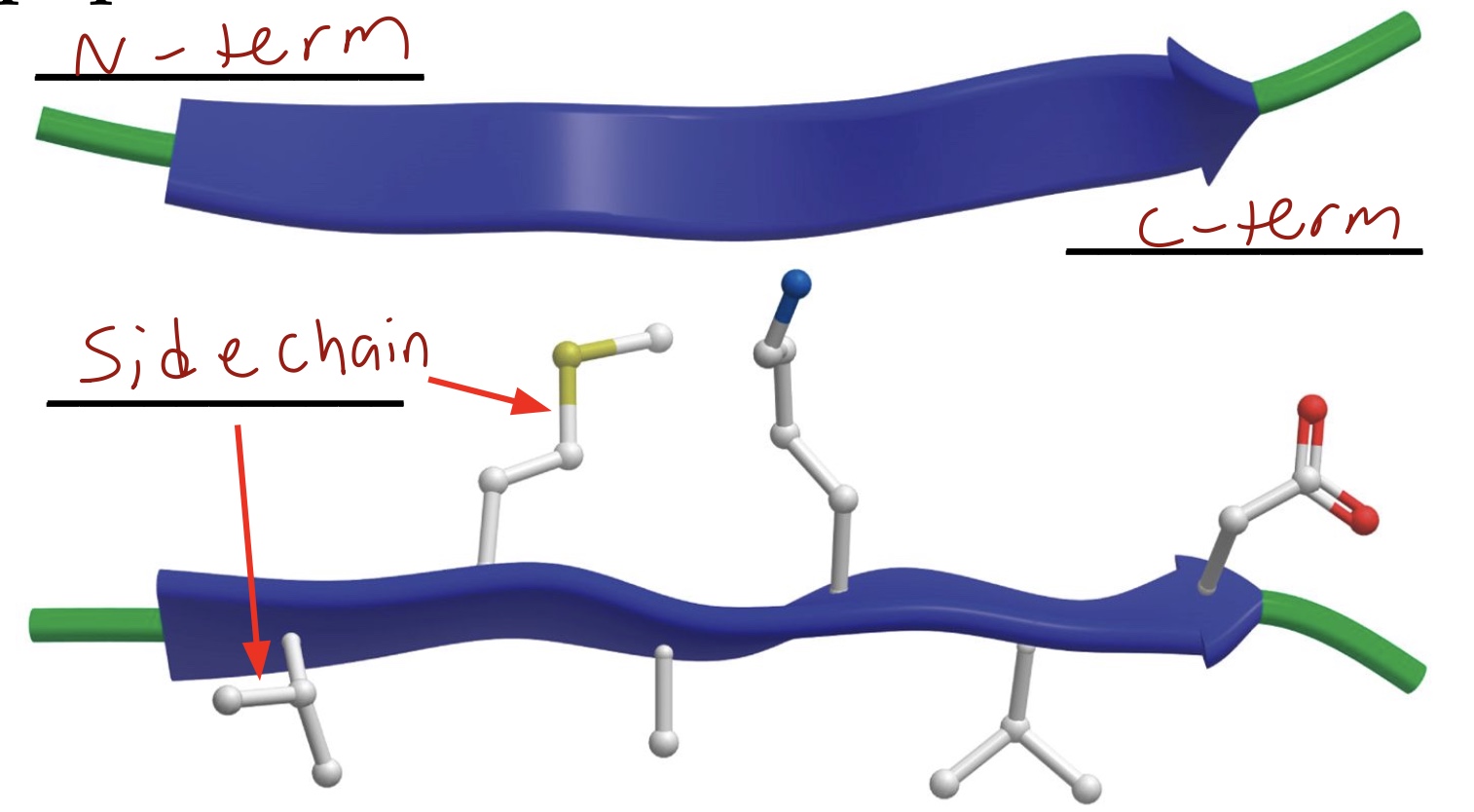
β Strand & β Sheet: A peptide chain is almost _____ in a β Strand.
Extended
β-strands arranged side by side to become β-sheets, which are held together by ____ between backbone ___ and ___ groups on _____strands.
H-bonds, CO, NH, separate.
Parallel vs antiparallel in β-strands and sheet
Parallel: H-bond is not perpendicular (WEAKER)
Antiparallel: H-bond is perpendicular (STRONGER)
β-strands and sheet: The R groups are in ____, pointing ____ and ____ to H-bonding surface.
Hydrophilic R groups facing ___ solvent
Hydrophobic R groups facing ____ of the protein.
Trans, outward, perpendicular.
Aqueous
Inside