Circulation
1/17
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What are the cellular elements of blood>
White blood cells, red blood cells, platelets
White blood cells
fight infection
red blood cells
transport oxygen and reomve carbon dioxide
Platelets
are cell fragments and resposible for clotting
What percentage of blood is cellular?
45%
what percentage of blood is plasma?
55%
What is plasma?
Plasma is responsible for maintaining osmotic pressure, acts as a buffer during pH changes, lipid transport, clotting, and defense. They transport nutrients, waste products, respiratory gases, and hormones
Explain the life cycle of a red blood cell
Stem cell → 1 daughter cell remains a stem cell and the other daughter cell commits to becoming a specialized cell → rybosm synthesizes → hemoglobin accumulates → nucleus ejected
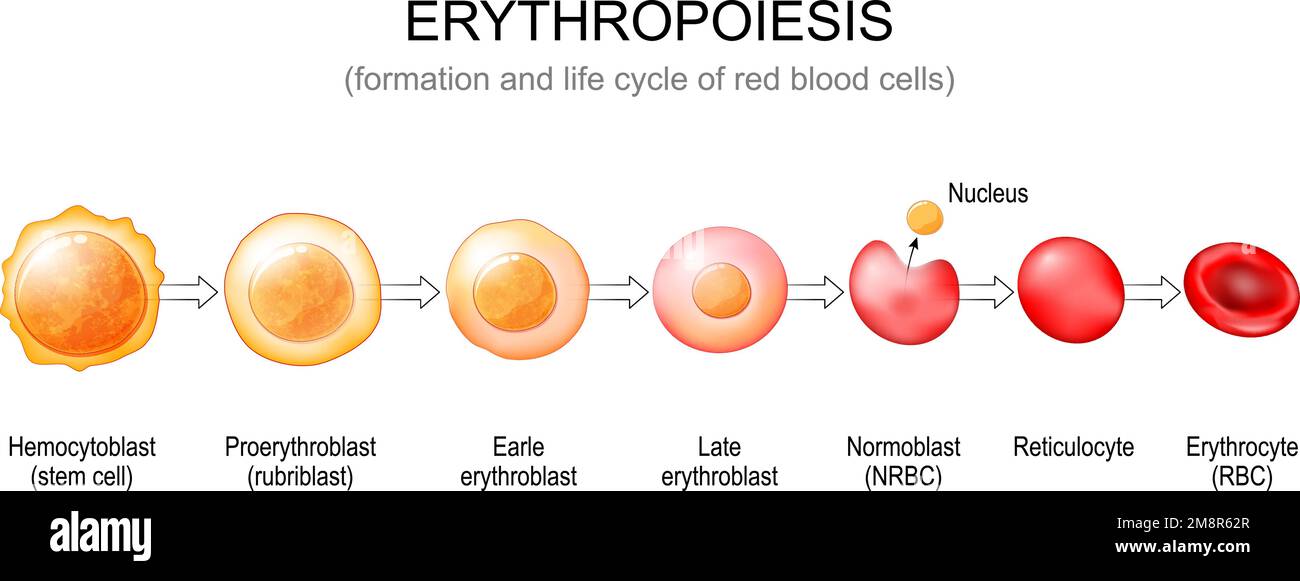
How does the body know when to produce more rbc?
kidney stiulates eruthroprotein → stimulates bone marrow to make more rbc → low oxygen in kidney → hypoxia inducible factor high → epo keeps being made
Explain the pulmanary circuit
right atrium → tricuspid valve → right ventricle→ pulmanary semilunar valve → pulmanary trunk → pulmanry arteries →pulmanary capillaries in lungs → pulmanary veins → left atrium → mitral valve → left ventricle → aortic semilunar valve → aortic arch
Explain the systemic circuit
aorta→ systemic arteries of the upper body → systemic capillaries of head and forelimbs → superir vena cava → into the right atrium
aorta → thoracic aorta →abdominal aorta → capillaries of lower body and limbs → inferior vena cava → right atrium
Arteries
take blood away from the heart
veins
return deoxygenated blood and waste back to the heart
Capillaries
facilitate diffusion of oxygen ato cells and place where CO2 is picked up. Capillareis are very thing and poures
What is blood pressure?
it is the contraction of heart ventricles makes which exerts a force in all directions on the blood vessel
How can blood pressure change?
Extra fluid, fluid properties, or narrowing of the vessel diameter can increase blood pressure.
If there were a tear in the epithelial lining, white blood cells respond, leading to fat cells and cholesterol to accumulate,e creating plaque which narrows the blood vessel walls
what is atherosclerosis?
It is the hardening of arteries by accumulation of fatty deposits. If it is a complete blockage it can lead to a heart attack or stoke
What are some treatments for atherosclerosis?
Angioplasty: inserts a balloon that blows it, pushing the plaque, and adding a stent, allowing blood to flow again
after bypass surgery, taking a blood vessel and attaching it before the blockage, and after the blockage. Essentially reroutes blood