Skeletal System
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
144 Terms
Upper Extremity
Humerus, radius, ulna, scapula, clavicle, carpals, metacarpals, phalanges
Lower Extremity
2 coxal bones, femur, tibia, fibula, patella, tarsals, metatarsals, phalanges
Process
Any bony prominence/projection
Fissure
Narrow passageway
Facet
Smooth, nearly flat articular surface
Fovea
A pit
Foramen
A hole in the bone
Fossa
Shallow depression
Condyle
Rounded process that usually articulates with another bone
Tubercle
Small rounded projection
Epicondyle
Small projection on or above a condyle
Trochanter
A large, somewhat blunt process
Tuberosity
A medium process
Head
The larger end of a long bone
Meatus
Canal-like passageway
Spine
Ridge on top of a bone
Sinus
A hollow space within a bone
Suture
Interlocking line of union between bones
Synarthroses Joints
Immovable joints; no significant movement
Synarthroses Example
Sutures of the skull
Amphiarthroses Joints
Slightly movable joints; slight movement
Amphiarthroses example
Intervertebral discs (b/w discs of vertebrae)
Diarthroses Joints
Freely movable joints; free movement
Ball and Socket Joint
Ball-shaped surface of one rounded bone fits into cup-like depression of another. Allows true free movement; backwards, forwards, sideways, and rotation
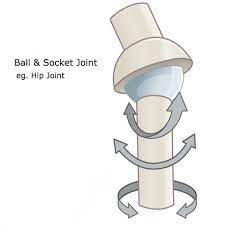
Ball and Socket Joint EX
Hip and shoulder
Hinge Joint
A modified version of a saddle joint; cylindrical part of a joint articulates with cylindrical depression. Permits motion in only one plane
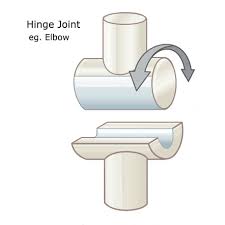
Hinge Joint EX
Elbow and knee
Pivot Joint
Cylindrical surface of one bone rotates within a ring. Allows for rotation around the length of a bone, and only allows for rotation.
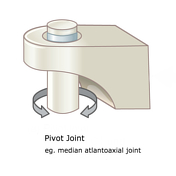
Pivot Joint EX
Atlas and axis; radius and ulna
Saddle Joint
Joint between concave and convex surfaces. Allows grasping and rotation
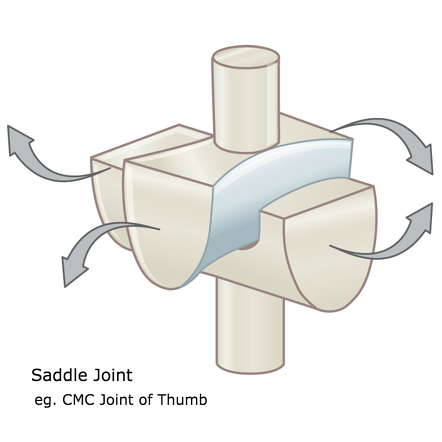
Saddle Joint EX
Type of joint found at the base of each thumb; carpometacarpal joint of the thumb
Gliding Joint
Opposed surfaces of bones are flat/almost flat. Allows one bone to slide over another. Up and down, left and right, and diagonal
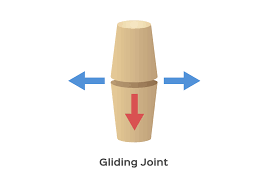
Gliding Joint EX
Carpals/tarsals/clavicle; found in wrist and ankles
Condyloid Joint
Oval-shaped condyle bone fits into elliptical cavity of another; synovial joint that does everything except rotating
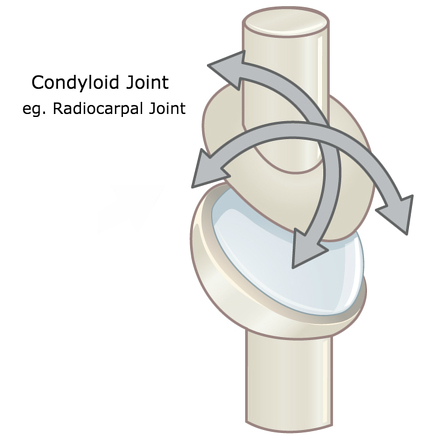
Condyloid Joint EX
Wrist, occipital condyle of skull with 1st vertebrae
Joints between cranial bones
Synarthroses
Joints between bodies of vertebrae
Amphiarthroses
Joint found between ribs and articulating vertebrae
Gliding
Joint at the elbow between the ulna and the humerus
Hinge
The joint between the occipital bone and the atlas
Condyloid
Joint between femur and os coxa
Ball and Socket
Joint between atlas and axis
Pivot
Joint between the radius and carpals
Condyloid
Joint between thumb and metacarpal
Saddle
Joint between carpals
Gliding
Joint between the proximal ulna and radius
Pivot
Joint between the sacrum and the ilium
Gliding
Joint between knee and tibia
Hinge
Joint at the shoulder between the humerus and the scapula
Ball and Socket
Compound Fracture (Open)
Bone is broken and a fragment of bone protrudes through an open wound in the skin
Simple Fracture (Closed)
Bone is broken cleanly; the ends do not penetrate the skin
Complete Fracture
Bone is broken all the way through
Incomplete Fracture (Greenstick)
Bone is bent but broken only on outer curve of bend; bone fragments still partially joined
Communited Fracture
Bone is splintered or crushed into several pieces
Impacted Fracture
Bone breaks, two bones pushed together; fragments driven into each other
Spiral Fracture
Fracture line spirals around shaft of bone; often slower to heal
Oblique Fracture
Fracture at an angle to the bone; diagonal to a bone's axis
Compression Fracture
Occurs when the bone is pressed together (compressed) on itself; i.e. vertebral column
Depression Fracture
Broken bone portion is pressed inward (indented); typically a skull fracture
Longitudinal Fracture
Vertical break; a fracture that runs parallel to the long axis of the bone
Steps for bone repair
1.) Bone bleeds
2.) Inflammation around infected area
3.) Forms bony framework called callus
4.) Callus tissue stabilizes bone fragments
5.) Healing, remodeling
Male and Female Skeletal Differences
Male bones are larger, distinct bumps. Narrow, tunnel-like pelvis. Female bones are smoother, smaller. Wider pelvis, more circular
Skeletal Age Differences
Between childhood and adolescence, bones begin to enlargen and ossify. Reach maturity at 25. Bone density begins to decline at 50.
Environmental Skeletal Factors
Nutrition - affects bone growth
Load Bearing/Mechanical Stress - affect how bone tissue is remodeled
Exercise - Helps reverse bone loss
hypo
under, below
hyper
above, over
itis
inflammation
osteo
bone
oma
tumor
a, an
without
ab
away from
ad
toward
algia
pain
arthro
joint
ectomy
cut out; removal
pathy
disease
Achondroplasia
The most common type of short-limbed dwarfism.
Arthrocentesis
Surgical puncture to remove fluid from the joint space
Bursitis
Inflammation of fluid-filled sac (bursa) in a joint
Dislocation
Displacement of a bone from a joint; a separation of two bones where they at a bone joint
Fallen Arches
Weakening of the tendons and ligaments supporting the arches of the foot
Gout
Swollen, red, acutely painful great toe joint; uric acid/purine in joints
Hemarthrosis
Blood within a joint space
Lumbargo
Mild to severe lower back pain
Lyme Disease
Bacterial infection caused by a tick bite, left untreated it can attach the synovial membrane of joints
Ostectomy
Surgical removal of all or part of a bone
Osteoitis
Inflammation of the bone
Osteoma
Bone tumor
Osteonecrosis
Death of bone tissue due to insufficient blood supply
Osteoporosis
A condition in which the body's bones become weak and break easily (due to lack of calcium)
Rickets
Abnormalities in shape and structure of bone caused by Vitamin D deficiency
Rheumatism
Any disease marked by inflammation and pain in the joints, muscles, or fibrous tissue
Scoliosis
Sideways curvature of the spine
Spinal Bifida
Birth defect; lack of union between lumbar vertebrae
Sprain
Injury to a ligament/pulled ligament
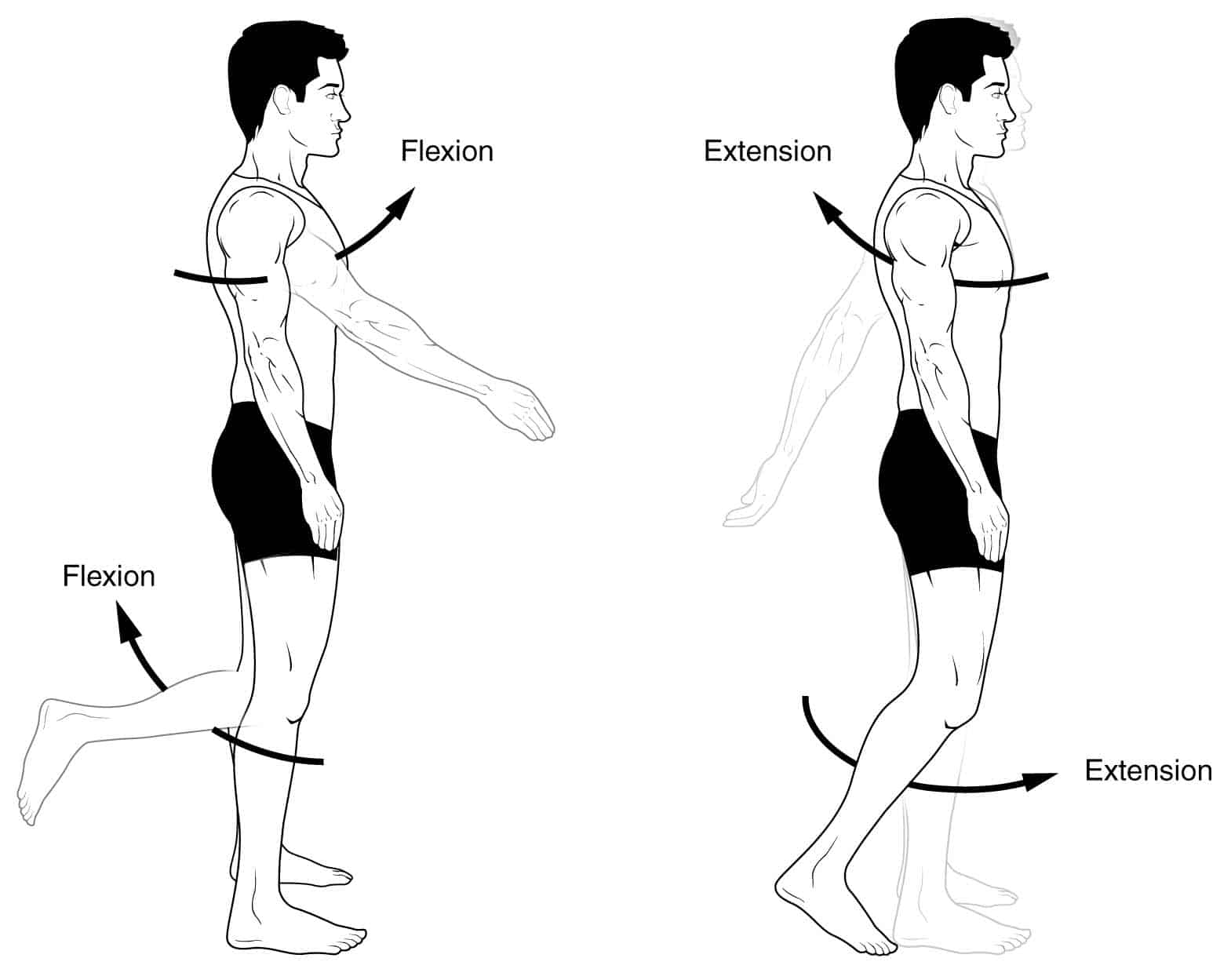
Flexion
Two end portions of an extremity are brought closer together
Dorsiflexion
A type of flexion movement where the toes point towards the shin
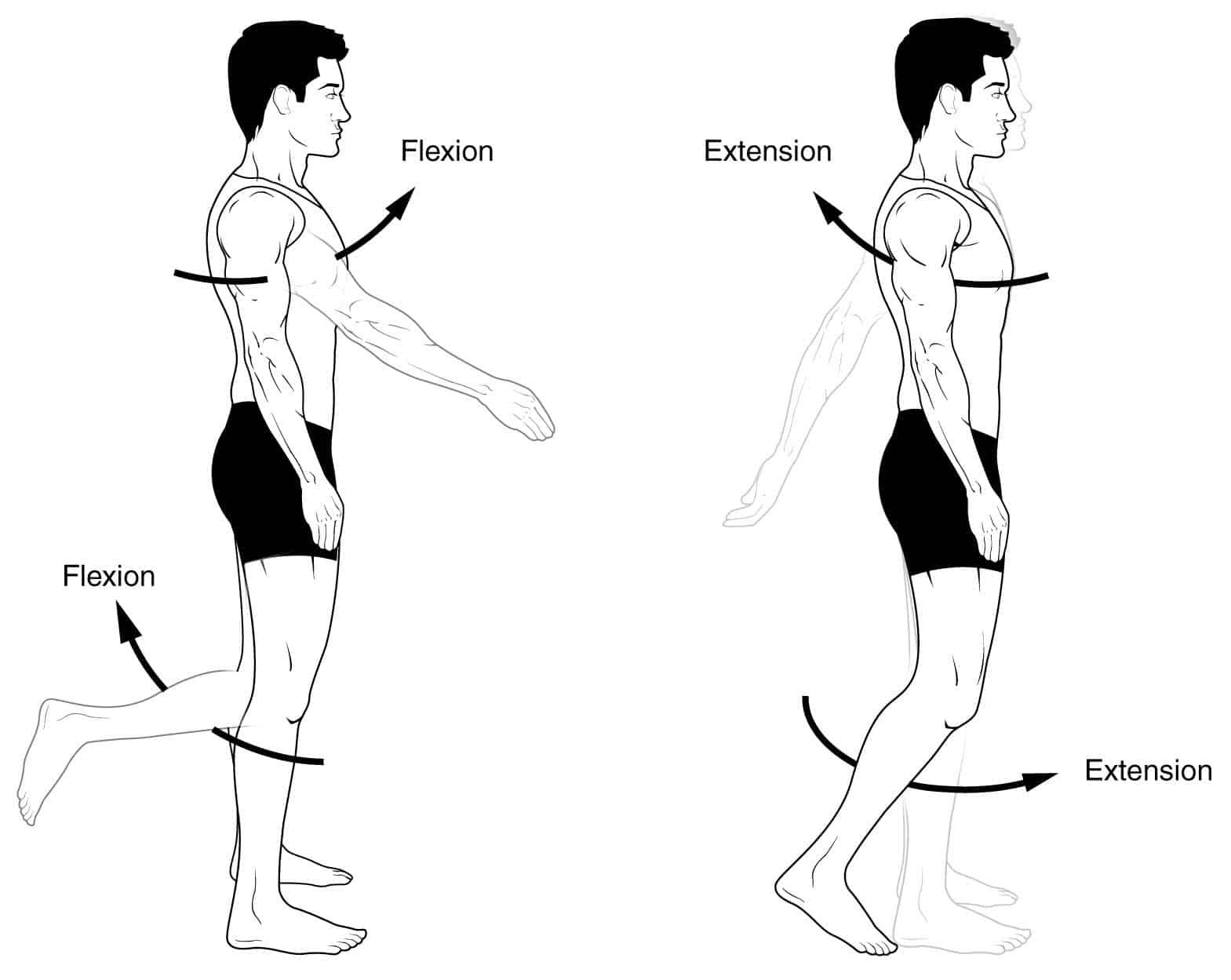
Extension
Two end portions of an extremity move further apart
Plantar Flexion
A type of extension movement where the toes point downward
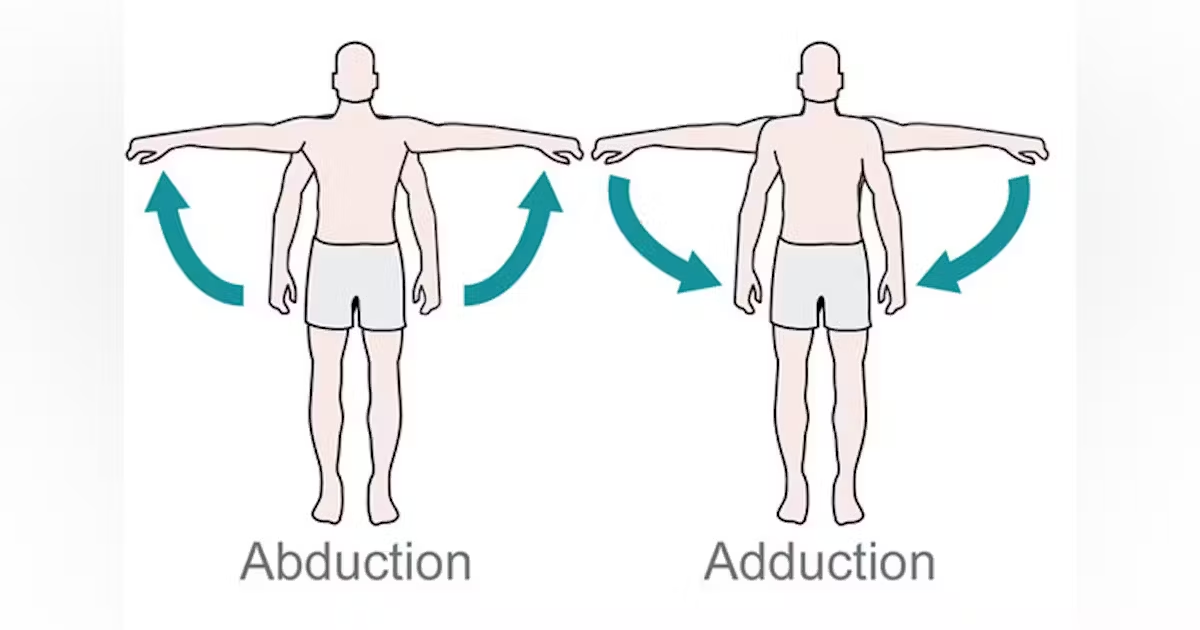
Abduction
Movement of an extremity laterally, away from the median plane of the body
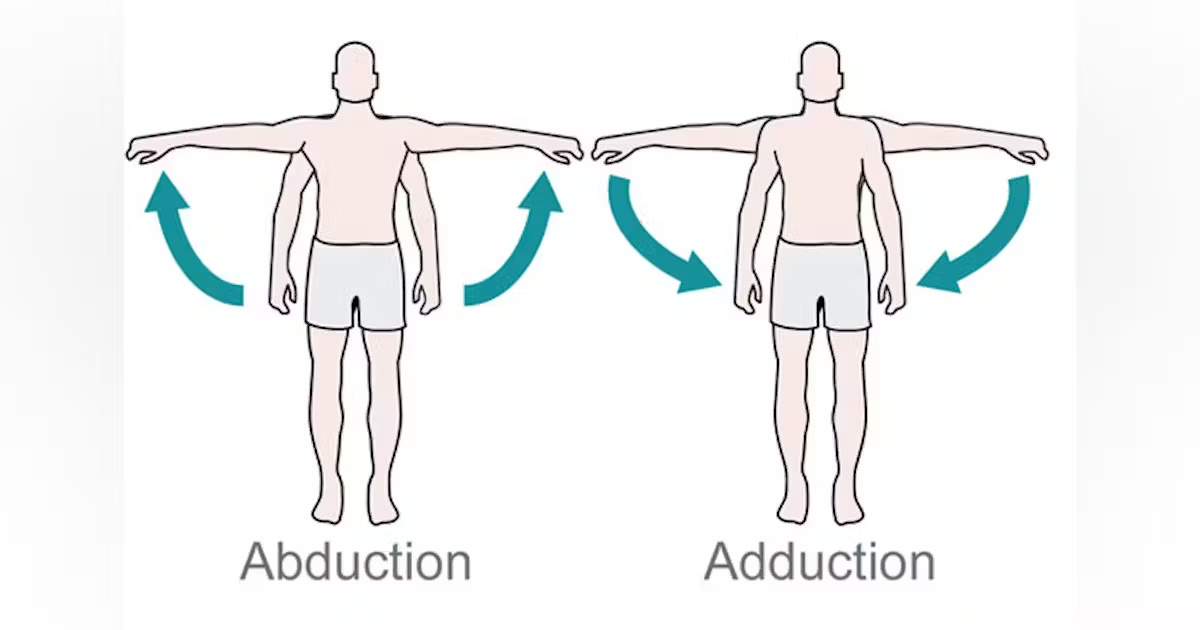
Adduction
Movement of an extremity along the median plane of the body
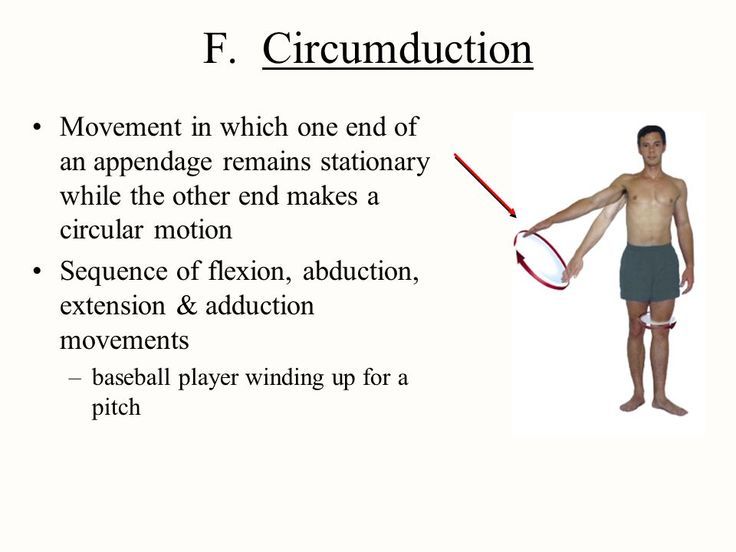
Circumduction
Movement of an extremity in a cone-shaped path