CSN Nurs 101 Exam 3--Heart & Neck Vessels and Peripheral Vascular -Breast and Lungs, Abdomen
1/203
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
204 Terms
The jugular veins drain into the __________________ veins
subclavian
In the chest, the heart is located _____________________ and to the ________________
central, to the left
At what intercostal space is the base of the heart found?
2nd
At which sternal border is the base of the heart found?
Left
At which intercostal space is the apex of the heart found?
5th
After systemic circulation, blood goes back to the heart through which chamber?
Right atrium
What are the two AV valves?
tricuspid and mitral
What are the two semilunar valves?
pulmonic and aortic
Circulation of blood through the heart (learning help)
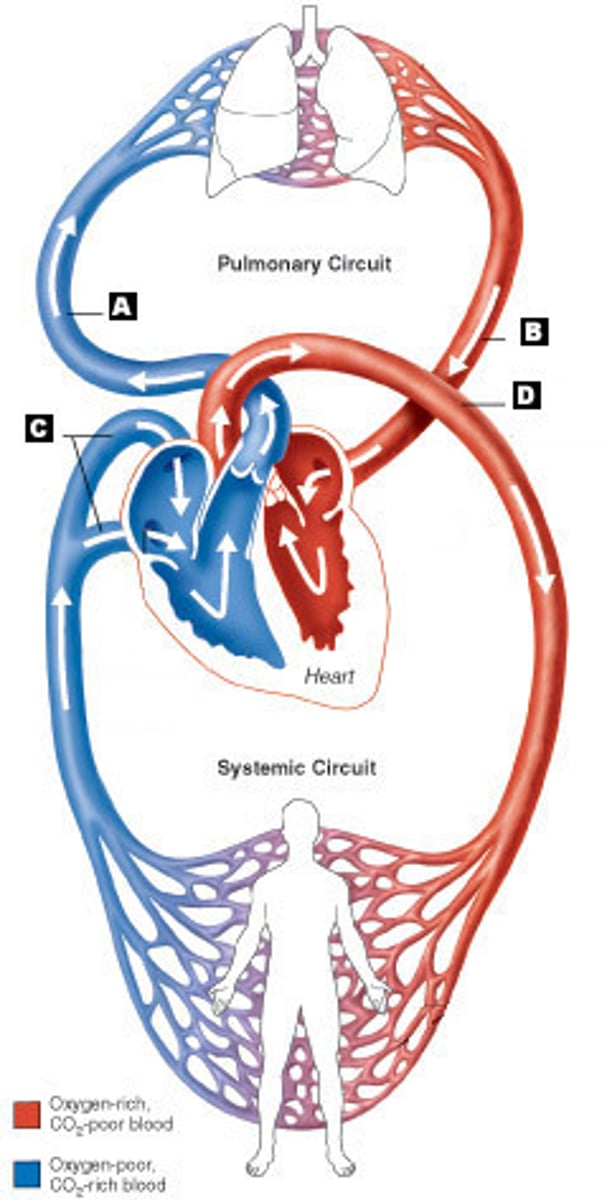
Starting with the vena cava, what is the correct blood flow through the heart to the body and back?
Pulmonic semilunar valve
Aorta
Left ventricle
Tricuspid valve
Pulmonic artery
Mitral valve
Right atrium
Left atrium
Aortic semilular valve
Right ventricle
Pulmonary veins
Right atrium
Tricuspid (AV)
Right ventricle
Pulmonic semilunar valve
Pulmonic artery (to the lungs)
Pulmonary veins (from the lungs back to ❤)
Left atrium
Mitral valve (AV)
Left ventricle
Aortic semilunar valve
Aorta (to the body)
When blood enters the vena cava, is it oxygenated or de-oxygenated?
De-oxygenated, because it has just been through systemic circulation and delivered its oxygen to the tissues. It is on its way to the lungs.
When the blood is on its way to the heart, what keeps it from slipping backwards back to systemic circulation?
valves
What stimulates contraction of the heart?
A. AV node
B. SA node
C. SV node
D. Purkinje fibers
B: SA node (sinoatrial node)
"the pacemaker of the heart"
The electrical conduction system of the heart starts with an impulse that travels from the ________ node, then to the __________ of ________, then to the left and right ___________ ___________, then to the _____________ ____________, which initiates the contraction of the heart muscle.
SA node
Bundle of His
Bundle branches
Purkinje fibers
Which are examples of subjective data to gather in a cardiac assessement? SATA.
A. Educational level
B. Emotional state
C. Cough
D. Edema
E. Chest pain
C, D, E
The patient says, "Whenever I lie down, I have a hard time breathing." What is this called?
Orthopnea
The patient also says, "I seem to have a small bladder these days. I get up ten times a night to go to the bathroom now." What is this called?
Nocturia
When inspecting the neck vessels, what are you looking for? SATA.
A. Pulsations
B. Symmetry
C. Lumps
D. Tattoos
A, B, C
When inspecting the jugular venous pulse, what indicates that there may be a small backflow of blood due to position?
A. Pulsation when the patient is lying flat
B. Pulsation when the patient is sitting up
C. Absence of pulsation
D. Pulsation when the patient is standing up
A
Rationale: There may be a small backflow of blood as it hits the tricuspid valve when a patient is lying down, because gravity is not working in the patient's favor. This is normal in many people. The next step would be to check the jugular venous pulse while the patient sits up.
The presence of a strong jugular venous pulse when a patient is upright may indicate that there is increased pressure in the heart and that blood is backing up. These symptoms may mean:
A. The patient is experiencing anxiety.
B. The patient has angina.
C. The patient has heart failure.
D. The patient has a weak tricuspid valve.
C
Since the jugular and carotid pulses are close to each other, how do you know which one you are feeling during palpation?
Palpate the neck AND the radial pulse at the same time. If the pulses match in strength, it is carotid (because they are both arteries and the pulse will be strong). If the neck is very light in comparison to the radial, it is the jugular pulse.
A nurse is auscultating the carotid artery. What should she tell her patient to do, so that she can hear most accurately?
A. She and her patient should breathe normally.
B. She and her patient should inhale, then hold their breaths.
C. She and her patient should exhale, then hold their breaths.
D. She and her patient should close their eyes.
C
A nurse is auscultating the carotid artery. She puts her stethoscope to the neck and hears a swishing sound. She looks at him and exclaims, "Sir, it sounds like you have a ____________!"
A. Bruit
B. Fruit
C. Huey
D. Phlooey
A
How many places will a nurse place her stethoscope when listening at the carotid artery?
3 on each side (under chin, mid-neck, upper clavicle)
Abnormal sounds are _______ pitched, and are best heard with the _________ side of the stethoscope
Low, bell
What causes a bruit?
Turbulent flow that creates a wave; usually from plaque build up or narrowing of the arteries
A nurse is inspecting a patient's precordium. She can see a pulsation close to the sternum. What is this called?
Heave/lift
The abnormal pulsation of a heave/lift is due the enlargement of what chamber of the heart? What is this called?
ventricles; ventricular hypertrophy
The nurse's patient had pulsations close to the sternum. Which side of the heart is experiencing ventricular hypertrophy?
Right
The nurse's next patient has left-sided ventricular hypertrophy. Where will the nurse see the pulsations?
Mid-clavicular line
When palpating the chest, the PMI is the place at which what pulse is felt?
apical
(PMI = point of maximal impulse)
The nurse puts her hand over her patient's heart to feel a thrill. What does this mean?
A. The nurse is thinks her patient is incredibly attractive.
B. The nurse gets excited when she feels heartbeats.
C. The nurse is trying to feel for the closing of semilunar valves.
D. The nurse is feeling for a vibration caused by turbulent blood flow through chambers of the heart.
D
When auscultating the chest, the "lub" sound is caused by the closing of the _______________ valves and the "dub" is caused by closing of the _______________ valves.
lub = AV valves (tricuspid, mitral)
dub = Semilunar valves (aortic, pulmonic)
This pattern of AV valves closing, then SL valves closing, marks the beginning and end of what heartbeat phase?
systole
S1 = lub = AV valves close = beginning of systole;
S2 = dub = SL valves close = end of systole
The nurse should auscultate the heart in a Z pattern. What is the acronym for the pattern of placements of the stethoscope, and what does the acronym stand for?
APETM "Ape to Man"
Aortic, Pulmonic, Erb's point, Tricuspid, Mitral
At the beginning of systole, what valves are open?
Semilular valves (the closing of AV valves marked the beginning of systole)
At which point is S2 heard the clearest?
Erb's point
At which point is S1 heard the loudest?
Mitral area
The aortic area is located at the __________ intercostal space, ___________ sternal border
2nd; right
The tricuspid area is located at the __________ intercostal space, ____________ sternal border
5th; left
Erb's point is located at the ____________ intercostal space, __________ sternal border
3rd; left
The mitral area is located at the ____________ intercostal border, ____-_________ line
5th; mid-clavicular line
The pulmonic area is located at the __________ intercostal space, __________ sternal border
2nd; left
A nursing student auscultates a classmate's precordium. He uses the diaphragm of his stethoscope. He doesn't hear any abnormalities and so he says, "Your heart sounds good. We're done with this part of the assessment." Is he correct?
A. Yes, because once you listen for abnormalities there is nothing else to follow up on.
B. Yes, because the mitral area is the site of most abnormalities.
C. No, because he is not supposed to give his opinion to the patient.
C. No, because once he listens with the diaphragm side for normal sounds, he needs to flip the stethoscope to the bell side to listen for abnormal sounds.
D
Rationale:
The diaphragm is for high-pitched, normal sounds. Abnormalities would likely not be detected with that side. The bell is for low-pitched, abnormal sounds. Both sides should be used in a precordium assessment.
What is regurgitation?
When valves do not close tight enough, allowing backflow of blood
Which is NOT a cause of regurgitation?
A. Lymphedema in extremities
B. Incomplete closing of valve
C. Prolapse of valve
D. Birth defect resulting in a hole in the heart
A
What is a heart murmur?
Structural defects in valves or unusual openings in chambers, that cause turbulent flow and a swishing sound when listened to with a stethoscope bell
The sound "lubsh dub" or "sh dub" indicates a ____________ murmur. The sound lub dubsh" indicates a ____________ murmur.
systolic; diastolic
Matching.
1. Systolic heart murmur
2. Diastolic heart murmur
A. Follows S1
B. Follows S2
1. A
2. B
The loudness and clarity of a heart murmur is on a scale from ____ to ___
1 to 6
What is true about heart murmurs? SATA.
A. They are early indicators of heart failure.
B. They are usually clearer in one area than another.
C. A grade IV murmur means a thrill that is palpable on the chest wall.
D. A murmur means fremitus of the precordium.
E. A systolic murmur follows S2.
B, C
Matching.
1. MI (Myocardial infarction)
2. Angina
A. Due to lack of oxygen to cardiac tissue
B. Can be due to coronary artery disease, exertion
C. Due to ischemia
D. Decreased cardiac output
E. Necrosis of myocardium
F. Chest pain due to lack of oxygen
1. C, D, E
2. A, B, F
When a patient has heart failure, the heart has failed as a ________.
Pump
HDL or LDL: which removes cholesterol within arteries and transports back to liver to be excreted?
HDL
What does LDL do?
transports cholesterol from the liver to the tissues
A nurse sees that a patient has a cholesterol level of 200, where HDL is 50 and LDL is 150. How should she educate her patient?
She should advise:
- HDL should be higher than LDL (H = happy, L = lousy)
- High LDL is associated with a higher risk of CAD
- Reduce intake of saturated fat and cholesterol
- Eat more soluble fiber
- Exercise
Matching.
1. Right sided heart failure
2. Left sided heart failure
A. The left ventricle does not function efficiently, thus allowing blood to back up into the lungs
B. The right side of the heart does not adequately pump forward, thus allowing blood to back up or pool systemically
1. B
2. A
Edema in the legs or arms is an example of ___________ sided heart failure.
Right
Rationale:
Blood backs up in the extremities because those are the farthest points the blood has to travel.
Low blood pressure is an example of ____________ sided heart failure.
Left
Rationale:
Because less blood is returning to the heart to be oxygenated, there is less blood to pump out, resulting in a low blood pressure.
Decreased cardiac output is an example of _________ sided heart failure.
Left
Rationale:
Because less O2-rich blood is actually flowing through the body for systemic circulation, the brain thinks the body has lost fluid; therefore, it sends a message to the kidneys to retain as much as fluid as possible. The heart has failed as a pump.
Crackles in the lungs is an example of ___________ sided heart failure.
Left
Rationale:
Pulmonary congestion indicates fluid build up in the lungs, due to inadequate contraction of the left ventricle to move all of the oxygenated blood out
Jugular Venous Distention (JVD) is an example of ___________ sided heart failure.
Right
Rationale:
Backup occurs when venous return is greater than the heart's ability to pump the blood back out; this is usually due to a weakened right side (often worn out from overworking to compensate for a weak or inefficient left side)
Dyspnea and orthopnea are examples of _________ sided heart failure.
Left
Rationale:
Since the left ventricle doesn't pump efficiently, the body does not get enough oxygen-rich blood. The blood backs up into the lungs instead, which causes shortness of breath and and other respiratory difficulties.
How are the kidneys affected by left-sided heart failure?
When there is not enough O2-rich blood in systemic circulation, the brain thinks that the body has lost fluid. It sends a message to the kidneys to stop elimination and to retain salt and fluids instead. The fluid enters regular systemic flow to make up for a perceived deficit; however, there is no actual volume deficit. This becomes fluid overload and results in edema.
The peripheral vascular system contains vessels for transporting what three fluids?
blood, fluid, lymph
Why does blood not flow backward in the arteries?
Because the heart is constantly propelling blood forward in a high pressure wave
The peripheral vascular system is made up of what three kinds of vessels or system of vessels?
arteries, veins, lymph system
What are characteristics of veins? SATA.
A. They have a low pressure system.
B. They take blood into systemic circulation.
C. They have a system of valves.
D. Skeletal muscle contraction propels blood forward.
E. Veins have multi-directional flow.
F. Veins are deeper than arteries.
A, C, D
Rationales:
A: There is no pressure wave.
B: Veins RETURN blood FROM systemic circulation.
C: Intraluminal valves keep blood from flowing backwards or collecting.
D: Muscle contraction squeezes veins, propelling blood forward. When muscle contraction stops, valves keep blood moving in one direction.
E: Veins have a UNI-directional flow because of valves.
F: Veins are more SUPERFICIAL than arteries.
What is thrombophlebitis?
Inflammation of a vein with clot formation
What veins are accessible to examination?
Upper--jugular, subclavian
Arm--cephalic, basilic, median cubital
Leg--great saphenous, small saphenous
Do blood clots occur in superficial or deep veins?
Both
If a patient is bedridden, what precautions are taken to ensure that clots do not develop?
TED hose, SCDs (sequential compression device)
What kind of compression does TED hose provide?
A. None
B. Intermittent
C. Constant
D. Thermal
C
What kind of compression does SCD provide?
Intermittent
On a very long flight, how might a person avoid getting a DVT or thrombophlebitis?
Get up and walk, dorsiflex/plantarflex while seated. Move as much as possible to get the blood moving.
"When blood pools in veins, it ______________"
clots
(quote from Ron)
When a person breathes in, a pressure gradient is created. With each inspiration, abdominal pressure goes ______ and thoracic pressure goes _________.
abdominal = up
thoracic = down
In what way is the lymphatic system the "sewer system" of the body?
When arteries transfer fluid to veins, a small amount leaks out. The lymphatic vessels retrieve the excess fluid from tissue spaces so that it doesn't collect and cause edema.
Are lymphatic vessels high or low pressure?
low
How do lymphatic vessels resemble veins?
- They are thin-walled and have valves.
- They are a low pressure system.
- Fluid is propelled by skeletal muscle contraction.
What are the two main trunks of the lymphatic system?
Right lymphatic duct (everything from right upper quadrant)
Thoracic duct (everything from the rest of the body)
The fluid collected by the right lymphatic duct and thoracic duct goes back into circulation through what vessels?
Left and Right subclavian veins
As fluid passes through the lymphatic system what are "gate keepers" along the way that clear out foreign invaders?
Lymph nodes
After lymph nodes trap pathogens, what do they send in to destroy them?
lymphocytes
Then the filtered fluid returns to the heart
When lymphocytes are sent to an area to fight a pathogen, what is the effect to that area of the body?
The lymph node will swell up because of the number of lymphocytes; it is localized to where the infection is
How many lymph nodes are in the body?
Around 700, usually very deep; you can feel them when they are swollen due to a localized infection
The following are purposes of the lymphatic system EXCEPT:
A. Absorb lipids from the intestinal tract
B. Filter blood, removing waste and water to make urine
C. Conserve fluid and plasma proteins
D. Major part of the immune system
B: This is the function of the KIDNEYS
When assessing peripheral vascular system, the nurse asks the patient, "Have you been experiencing leg cramps?" The patient says, "Why yes, when I walk my legs really hurt but when I stop, I'm fine again." The nurse knows that her patient has what condition?
intermittent claudication
With intermittent claudication, why is there pain when the patient is in motion, but relief when he stops?
When walking, the demand for oxygen goes up; when stopped, the demand for oxygen goes down. A blockage means that tissues can't get oxygenated blood. Without oxygen, the tissues begins to die (Ischemia), leading to pain.
A male patient has one baby-smooth leg and one hairy-like-a-gorilla leg. What could this tell the nurse about his circulation?
Oxygen is needed for hair supply, and so the fact that one leg has no hair may indicate that there is poor circulation in that extremity.
A 45-year-old patient's left leg is swollen to double the size of her right leg. She tells you she recently battled cancer and is in remission. What could be the cause of the swelling?
Lymphedema; When the lymphatic system becomes overwhelmed, damaged, or blocked for an extended period of time, lasting swelling occurs.
A classmate whispers, "It's time to do my peripheral vascular assessment and I can't remember how to check for edema!" You come to her rescue and tell her to:
"Firmly press the skin for 5 seconds and release."
The grading scale for pitting edema goes from ____ to ____ and is based on the depth of the impression and the time it takes to return back to normal
1+ to 4+
What grade would lymphedema be on the pitting edema scale?
It would not be graded on this scale. It is not a pitting edema.
What condition is commonly the cause of pitting edema?
CHF
After you palpate the brachial and radial pulses, what should you assess next
capillary refill (note whether color comes back "brisk" or "sluggish")
When palpating the lower extremities, what is "the true test of lower extremity?"
Dorsalis pedis
(but also check for posterial tibial and popliteal)
Risk factors for venous disease include all EXCEPT:
A. Prolonged standing, sitting, or bedrest
B. Hypercoaguable states
C. Vein wall trauma
D. Artery insufficiency
E. Obesity/Pregnancy
F. History of heart failure
D: The state of the arteries is not a risk factor for venous disease
Risk factors for Arterial disease include all EXCEPT:
A. Diabetes
B. Vascular disease
C. Increased lipid levels
D. Smoking
E. Inherited predisposition
F. Being an older adult
G. Orthostatic hypotension
G: HYPERTENSION is a risk factor because of the increased pressure to the arteries
Matching.
1. Peripheral Vascular Disease: Arterial
2. Peripheral Vascular Disease: Venous
A. Stasis ulcer (drainage)
B. Cyanosis
C. Claudication
D. Pain with prolonged standing/sitting; relief with walking d/t milking action
E. Relief with rest
F. Ischemic ulcer
G. Brown discoloration, red, warm, swollen
1. B, C, E, F
2. A, D, G