MLS 334 Exam 1
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
168 Terms
Microbiology
specialized area of biology that encompasses tiny life forms that are microscopic
Microscopic Organisms
includes microbes, bugs, germs, and microorganisms
Branches of Microbiology
bacteriology
mycology
parasitology
virology
phycology
physiology
taxonomy
Taxonomy
the orderly classification and grouping of organisms
Classification
arrangement of organisms into groups
Nomenclature
assigning names to various taxonomic rankings for each microbial species
Identification
discovering and recording the traits of organisms so they can be put into the taxonomic scheme
Categories of Classification
Genotype (genetic makeup) or Phenotype (media, gram stain, morphology, biochemical characteristics, antimicrobial resistance patterns)
Hierarchical Classification
Largest-Smallest
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Rules of Nomenclature
1. Use binary names (genus and species)
2. Capitalize the genus but not the species
3. Italicize the if types or underline if handwritted
4. Abbreviate initial capital letter and follow by species
5. Lowercase and non-italic for common name
Public Health
Focused on examining the health needs of entire populations with the goal of preventing health problems.
Infection
invasion and multiplication of microorganisms within a host
Carrier
person may harbor a pathogen that can be transmitted to others without eliciting disease themselves
Colonization
bacteria on our body surface that does not oleic an immune response or disease
Normal Flora
Organisms that exist in a symbiotic relationship with the host
Classification of Infectious Diseases
1. Microbiological (pathogen or causative agent)
2. Clinical (clinical manifestation - signs and symptoms)
3. Epidemiological (transmission and reservoir)
Chain of Infection
pathogen, reservoir, portal of exit, mode of transmission, portal of entry, susceptible host
Infectious Disease Periods
1. Incubation (no signs or symptoms)
2. Prodromal (vague, general symptoms)
2. Illness (most severe signs and symptoms)
3. Decline (declining signs and symptoms)
4. Convalescence (no signs or symptoms)
Individual Disease Prevention Measures
hand hygiene, food and water safety, condom use
Community Disease Prevention Measures
sanitation, water safety, blood-donor screening, isolation and quarantine
Lab Safety Organizations
OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration)
EPA (Environmental Protection Agency)
CDC (Center for Disease Control and Prevention)
JACHO (Joint Commission for Accred of Healthcare Orgs)
CLSI (Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute)
WHO (World Health Organization)
Exposure Control Plan
OSHA designed to protect employees against exposure to bloodborne pathogens - reviewed by employees annually
Standard Precautions
A strict form of infection control that is based on the assumption that all blood and other body fluids are infectious.
Droplet Precautions
close respiratory contact or exposure of mucus membranes/respiratory secretions
Airborne Precautions
Infectious Agents that can remain airborne for long periods of time and long distances
Contact Precautions
direct or indirect contact with patient or environment
Workplace Safety Precautions
practices done to reduce likelihood of an exposure to infectious agents (ex: no mouth pipetting, eating or drinking, disinfect surfaces, handwashing, disposal of sharps correctly)
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Protective equipment that blocks exposure to a pathogen or a hazardous material.
Biological Risk Assessment for Microbiologists
1. Processing patient specimens
2. handling actively growing cultures
Risk Group 1
No or low individual and community risk
Risk Group 2
Moderate individual risk, low community risk
Risk Group 3
High individual risk, low community risk
Risk Group 4
High individual and community risk
Biological Safety
-engineering control
-protects workers from aerosolized transmission of organism
-4 levels
BSL-1
-no potential for exposure to pathogenic material or biohazards
-lab work conducted on open bench
BSL-2
specific training, limited lab access, immunizations
BSL-3
negative air pressure due to exotic pathogens that are potentially aerosolized or inhales
BSL-4
class III BSC, positive protective suit, isolated lab
Chemical inventory
A list of every product used in the lab that contains chemicals - updated annually
Symbiosis
two different organisms living together, usually advantageous to both
Commensalism
A relationship between two organisms in which one organism benefits and the other is unaffected
Mutualism
both microorganism and host benefit
Parasitism
microorganism benefits but host is harmed
Normal Flora (indigenous)
microorganisms that are normally present in a specific site
Carrier State
person harbors organism but does not show any signs of the disease, may pass it on
Infection
pathogen penetrates host, enters tissue, multiplies
Infectious Disease
A disease that is caused by a pathogen, causes damage/disruption to the host, and that can be spread from one individual to another.
Transiet Microbes
microbes that occupy the body for a SHORT amount of time
Resident Microbes
microbes that have established residence (long-term)
Microbial Flora Composition
-nutritional factors
-antibacterial substances (fatty acids, lysozyme, bile)
-environment (gaseous atmosphere, low pH, moist or dry)
Sites that contain normal flora
-skin and mucous membranes
-upper respiratory tract
-GI tract
-outer opening of urethra
-external genitalia
-vagina
-external ear and canal
-external eye
Sterile Sites
internal organs and tissue (heart, liver, kidneys, brain, etc.)
blood, urine (in bladder, ureters, and kidneys), and CSF
Skin Flora
-on the skin surface, hair follicles, and apocrine sweat glands
-colonize the skin surface to prevent pathogens from colonizing
Types of Microorganisms Found on the Skin
Candida spp.
Micrococcus spp.
Staphylococcus spp.
Clostridium spp.
Propionibacterium spp.
Diphtheroids
Mouth Flora
-supports anaerobic growth (low redox potential)
-on the buccal mucosa and tooth surface
Microorganism Found in the Mouth
Streptococcus mitis
Streptococcus sanguis
Streptococcus salivrius
Streptococcus mutans
Respiratory Tract Flora
only in the upper respiratory tract (lower is considered sterile)
Microorganism in the Nose and Nasopharynx
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Diphtheroids
Haemophilus parainfluenzae
Streptococcus spp.
Microorganisms in the Oropharynx
Diphtheroids
Streptococcus mitis
Streptococcus sanguis
Streptococcus salivrius
Streptococcus mutans
Streptococcus milleri
Staphlyococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
GI Flora
-located in the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and colon
-environment favors anaerobes
-beneficial relationship (ferment waste to generate vitamins and contain digestive enzymes)
-stomach îs normally sterile (acidic pH)
Microorganisms Found in the GI Tract
Bacteroides spp.
Clostridium spp.
Enterobacteriaceae
Eubacterium spp.
Fusobacterium spp.
Peptostertococcus spp.
Peptococcus spp.
Staphylococcus aureus
Enterococcus spp.
Microogranisms Found in the Genitourinary Tract
Lactobacillus spp.
Bacteroides spp.
Clostridium spp.
Peptostreptococcus spp.
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Enterococcus spp.
Diphtheroids
Microbial Flora Role in Infectious Disease
-opportunistic infections (host environment change or weakened immune system)
-trauma
-immunosuppressed host
Microbial Flora Infectious Disease Protection
prime immune system and block colonization of pathogens
Pathogenesis
development of disease
Pathogenicity
ability of a microorganism to cause disease
Opportunistic Pathogen
causes disease only in the absence of normal host resistance
True Pathogen
capable of causing disease in healthy persons with normal immune defenses
Iatrogenic Infection
infections from medical treatments or procedures
Virulence
ability for a microorganism to cause disease
Virulence Factors
enhance ability to cause disease and includes capsules, toxins, adhesive fimbriae, ability to survive intracellularly
Host Resistance
physical barriers (intact skin)
cleansing mechanisms (tears, urine cilia)
low pH (acidic in stomach and vagina)
antimicrobial substances (fatty acids on skin, HCl in stomach, lysosomes, immune proteins)
indigenous microbial flora
phagocytosis
inflammation (accumulation of phagocytic cells and release of mediators)
digestion of foreign particles by enzymes
Phagocytosis
-primary mechanism against extracellular bacteria (polymorphonuclear cells and macrophages)
not effective for intracellular pathogens
Diapedesis
movement of WBCs from blood vessels into tissues
Chemotaxis
chemically stimulated movement of phagocytes to a site of damage
Steps of Phagocytosis
1. Attachment (organism to phagocyte)
2. ingestion (enclose in phagosome, fuse with lysosomes, degranulation)
3. Killing (increased metabolic activity and glycolysis, release enzymes)
Mechanisms to Resist Phagocytosis
capsules
Immune System
how the body protects itself from disease
Innate Immunity
natural, nonspecific (physical and chemical barriers, phagocytosis)
Adaptive Immunity
specific (b and t lymphocytes)
passive acquired immunity
mom passes antibodies to baby
active acquired immunity
response to antigen (disease or vaccination)
Humoral Immunity
initiated by antibodies/immunoglobulins
Classes of Antibodies
IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, IgE (decreased %)
Primary Antibody Response
IgM appears first, followed by IgG
Secondary Antibody Response
rapid increase in IgG
Cell-Mediated Immunity
protects against intracellular pathogens (t-helper CD4+ and cytotoxic t-cells CD8+)
Sign
objective evidence of disease from an observed (ex: fever)
Symptom
subjective evidence of a disease sensed by patient such as pain or a headache
Laboratory Signs of Infection
elevated WBC (bacterial = neutrophils and viral = lymphocytes)
elevated ESR and C-reactive protein
-high lactic acid may indicate sepsis
Prokaryotic Cell
-no membrane bound nucleus or organelles
-ribosomes (RNA and protein) found free in cytoplasm and attached to cytoplasmic membrane
-70S ribosome complex (dissociate into 50S and 30S with centrifugation)
-Endospores to increase survival
Bacteria cell envelope includes...
plasma membrane and cell wall
Plasma Membrane (Cell Membrane)
-phospholipid bilayer (with embedded proteins)
-functions as an osmotic barrier
Cell Wall Categories
-gram positive
-gram negative
-acid-fast
-absence/none
Gram Positive Cell Wall Structure
-one major layer
-composed to peptidoglycan, teichoic acid, lipoteichoic acid, mycelia acids, and polysaccharides
-no outer membrane
-narrow periplasmic space
-penetrable to molecules
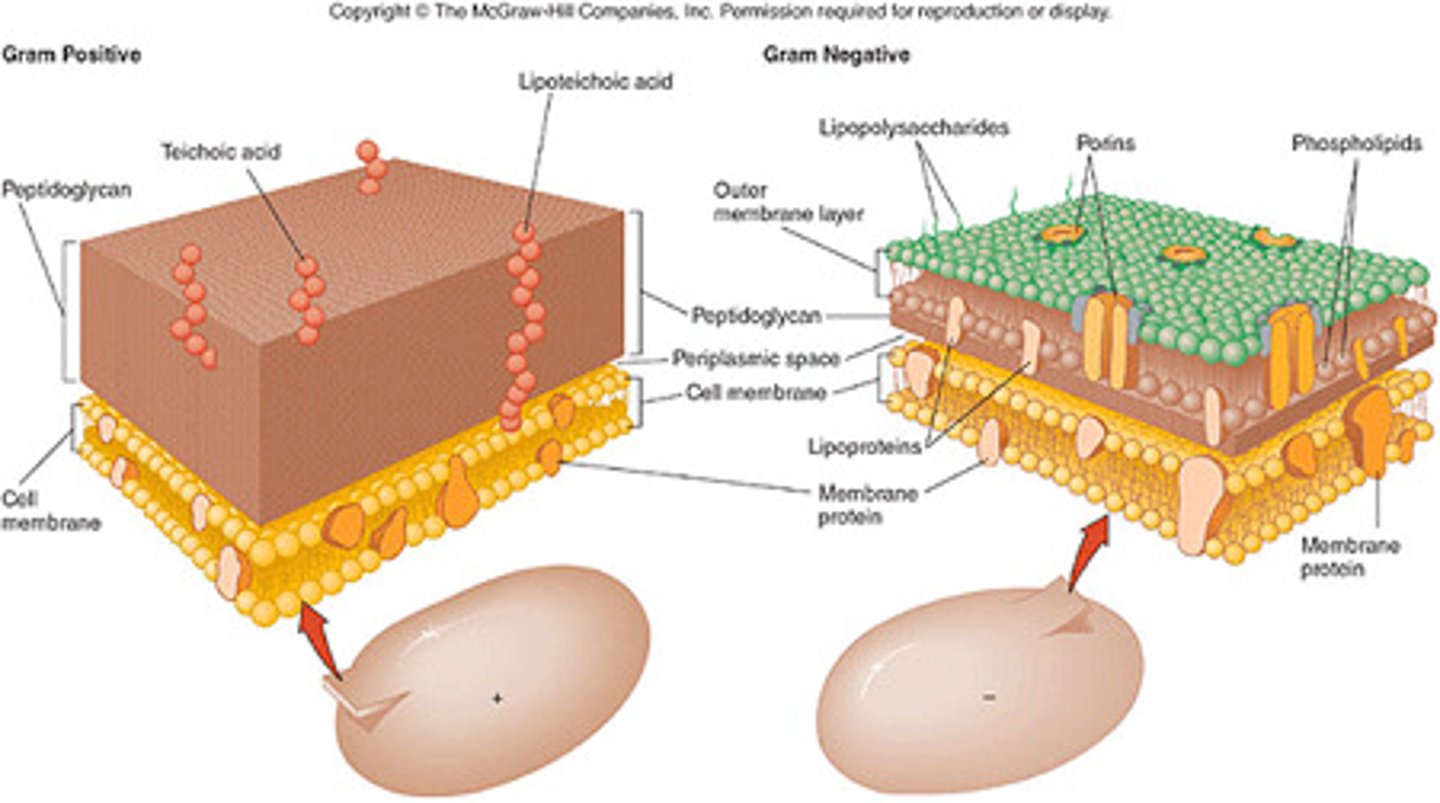
Peptidoglycan (Murein)
the polymer of alternating N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM) and N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and pentapeptide (5 amino acids) subunits linked together by peptide chains; a major constituent of bacterial cell walls
Peptidoglycan Function
prevents osmotic lysis
Teichoic Acid Function
cell wall strength
Surface Protein Function
enzymes and adhesions
Periplasm Function
nutrient breakdown