AP Human Geography A Spatial Perspective
1/383
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
384 Terms
Absolute direction
the cardinal directions north, south, east, and west
absolute distance
distance that can be measured using a standard unit of length
Ex: 5 miles
absolute location
the exact location of an object, usually expressed in coordinates of longitude and latitude
Ex: the coordinates of New York City are 40.7128° N, 74.0060° W
acculturation
the process by which people within one culture adopt some of the traits of another while still retaining their own distinct culture
adherent
a person who is loyal to a belief, religion, or organization
administer
to manage the way borders are maintained and how goods and people cross them
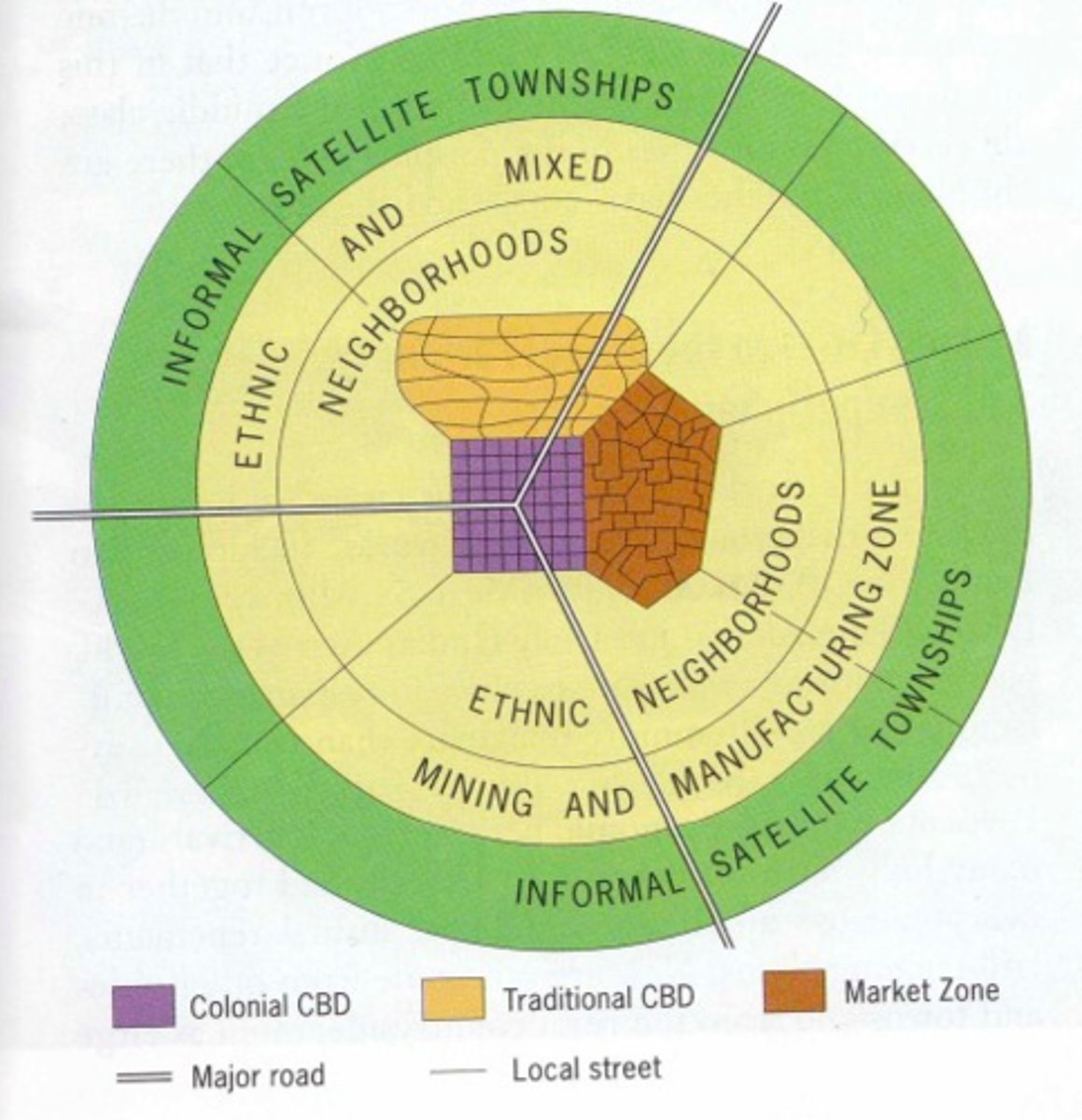
African city model
a model of urban development depicting a city with three central business districts, growing outward in a series of concentric rings
agglomeration
the tendency of enterprises in the same industry to cluster in the same area
Agribusiness
the large scale system that includes the production, processing, and distribution of agricultural products and equipment
agricultural biodiversity
the variety and variability of plants, animals, and microorganisms that are used directly or indirectly for food and agriculture
Agricultural Density
the total number of farmers per unit of arable land
agricultural hearth
an area where different groups began to domesticate plants and animals
Ex: the first agricultural hearths appeared in the Middle East, Mesoamerica, and East Asia
agricultural landscape
a landscape resulting from interactions between farming activities and a locations natural environment
agriculture
the purposeful cultivation of plants and raising of animals to produce goods for survival
agroecosystem
an ecosystem modified for agricultural use
antecedent boundary
a border established before an area becomes heavily settled
Ex: These are often based on landforms, such as mountains. The Andes Mountains are an antecedent boundary that form the eastern boundary of Chile, separating it from neighboring Argentina and Bolivia.
anti-natalist
describing attitudes or policies that discourage child-bearing
Ex: China's "One Child Policy"
aquifer
layers of sand, gravel and rocks that contain and can release a usable amount of water
arable land
land that can be used to grow crops
arithmetic density (crude density)
the total number of people per unit area of land
artifact
a visible object or technology that a culture creates
Ex: buildings, roads, bridges, food, clothes
assimilation
a category of acculturation in which the interaction of two cultures results in one culture adopting almost all of the customs, traditions, language and other cultural traits of the other
asylum
the right to protection in a country
autonomous
having the authority to govern territories independently of the national government; for example, by having a separate currency
bid-rent theory
a theory that describes the relationships between land value, commercial location, and transportation(primarily in urban areas) using a bid-rent gradient, or slope; used to describe how land costs are determined
biodiversity
the variety of living organisms living in a location
Biotechnology
the science of altering living organisms, often through genetic manipulation, to create new products for specific purposes, such as crops that resist certain pests
Blockbusting
a practice be real estate agents who would stir up concern that black families would soon move into a neighborhood; the agents would convince white property owners to sell their houses below market prices
boomburg
a suburb that has grown rapidly into a large and sprawling city with more that a 100,000 residents
brain drain
the loss of trained or educated people to the lure of work in another-often richer country
break-of-bulk point
location where it is more economical to break raw materials into smaller units before shipping them further
Brownfields
abandoned and polluted industrial site in a central city or suburb
buddhism
the oldest universalizing religion, which arose from a hearth in northeastern India sometime between the mid sixth and mid fourth centuries B.C.E. and is based on the teaching of Siddhartha Gautama, called the Buddha
bulk-gaining industry
industry in which the finished goods cost more to transport than the raw materials
bulk-reducing industry
industry in which the raw materials cost more to transport than the finished goods
carrying capacity
the maximum population size an environment can sustain
cartographer
a person who creates maps
cash crop
a crop produced mainly too be sold and usually exported to larger markets
census
an official count of the number of people in a defined area, such as a state
Central Business District(CBD)
the central location where the majority of consumer services are located within a city or town because the accessibility of the location attracts these services
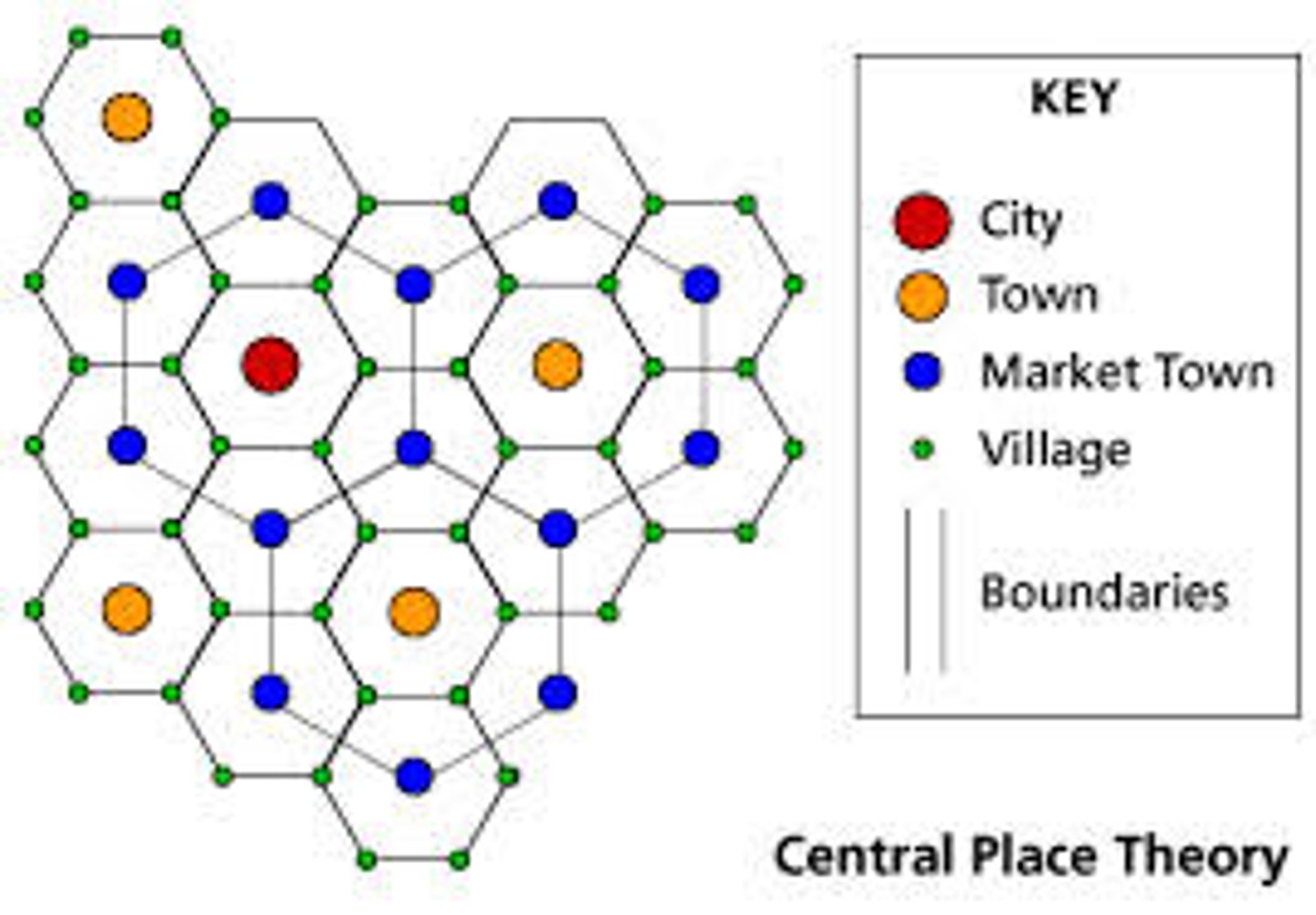
central place theory
a theory used to describe the spatial relationship between cities and their surrounding communities
centrifugal force
a force that divides a group of people
centripetal force
a force that unites a group of people
chain migration
a type of migration in which people move to a location because others from their community have previously migrated there
choke point
a narrow strategic passageway to another place through which it is difficult to pass
Ex: The Suez Canal
Christianity
a universalizing religion based on the teachings of Jesus Christ that began in what is now West Bank and Israel around the beginning of the common era and has spread to all continents
circular migration
migration pattern in which migrant workers move back and forth between their country of origin and the destination country where they work temporary jobs
circulation
temporary, repetitive movements that recur on a regular basis
climate
the long term patterns of weather in a particular area
climate region
an area that has similar climate patterns generally based on its latitude and its location on a coast or continental interior
Clustered Settlements/nucleated settlements
a rural settlement pattern in which residents live in close proximity to one another, with farmland and pasture land surrounding the settlement
collectivist cultures
a culture in which people are expected to conform to collective responsibility within the family, and to be obedient to and respectful of elder family members
colonialism
the practice of claiming and dominating overseas territories
Colombian Exchange
the exchange of goods and ideas between the Americas, Europe, and Africa that began after Christopher Columbus landed in the Americas in 1492
commercial agriculture
an agricultural practice that focuses on producing crops and raising animals for the market for others to purchase
commodity chain
a network of people, information, processes, and resources that work together to produce, handle, and distribute a commodity or product
commodity dependence
an aspect of dependency theory that occurs when more than 60% of a country's exports and economic health are tied to one or two resources
comparative advantage
the relative cost advantage a country or organization has to produce certain goods or services for trade
complementary
the mutual trade relationship that exists between two places based on the supply of raw materials and the demand for finished products or services
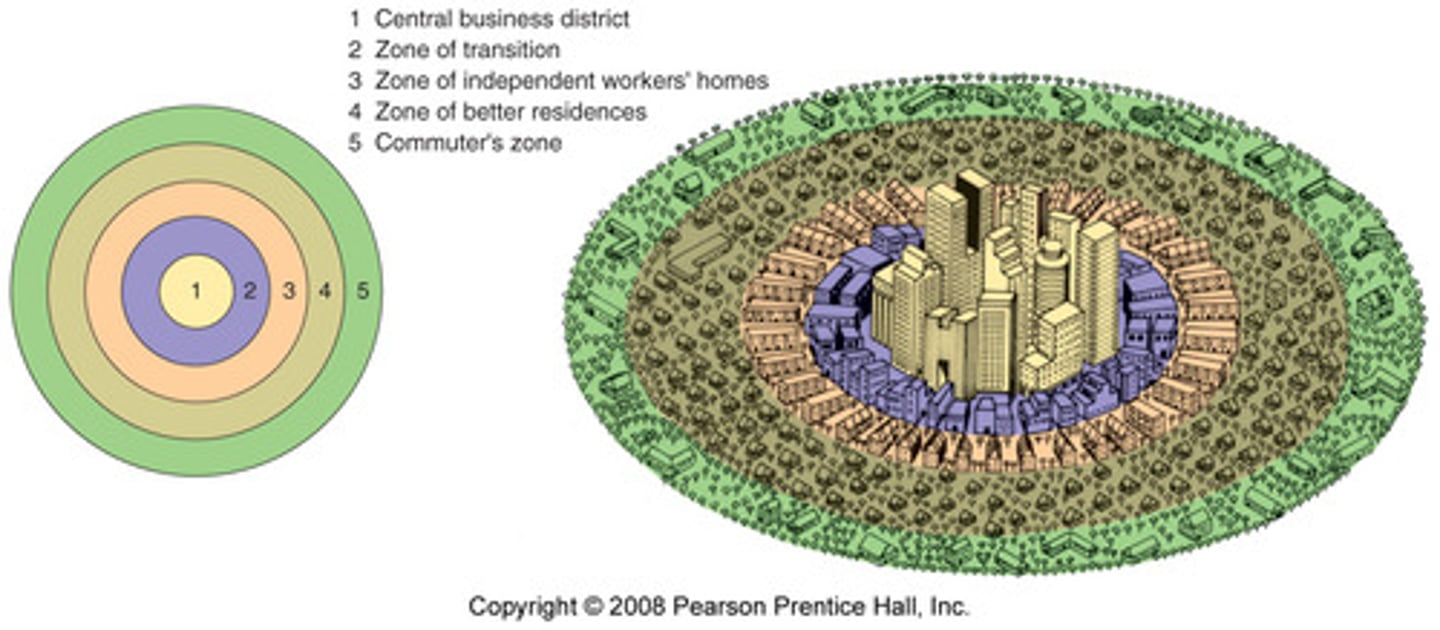
Concentric Zone Model
a model of urban development depicting a city growing outward from a central business district in a series of concentric rings
concurrent
sharing authority
consequent boundary
a type of subsequent boundary that takes into account the differences that exist within a cultural landscape, separating groups that have different languages, religions, ethnicities, or other traits
Contagious Diffusion
the process by which an idea or cultural traits spreads rapidly among people of all social classes and levels of power
core
classification of a country or region that has wealth, higher education levels, more advanced technologies, many resources, strong militaries, and powerful allies
cottage industry
pre-industrial form of manufacture in which member of families spread out through rural areas worked in their homes to make goods
creolization
the blending of two or more languages that may not include the features of either original language
crop rotation
the varying of crops from year to year to allow or the restoration of valuable nutrients and the continuing productivity of the soil
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
the number of births in a given year per 1,000 people in a given population
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
the number of deaths in a given year per 1,000 people in a given population
cultural appropriation
the act of adopting elements of another culture
cultural convergence
the process by which cultured become more similar through interaction
cultural divergence
the process by which cultures become less similar due to conflicting beliefs or other barriers
cultural hearth
an area where cultural traits develop and from which cultural traits diffuse
cultural landscape
a natural landscape that has been modified by humans, reflecting their cultural beliefs and values
cultural norm
a shared standard or pattern that guides the behavior of a group of people
cultural relativism
the evaluation or cultural practice
cultural trait
a shared object or cultural practice
culture
the beliefs, values, practices, behaviors, and technologies shared by a society and passes down from generation to generation
Dept-for-nature swap
agreement between a bank and a peripheral country in which the bank forgives a portion of the country's debt in exchange for local investment in conservation measures
de facto segregation
segregation that results from residential settlement patters rather than from prejudicial laws
define
the explicitly state in legally binding documentation such as a treaty where boundaries are located, using reference points such as natural features or line of latitiude and longitude
deforestation
loss of forested land
Deindustrialization
process by which a country or area reduces industrial activity particularly in heavy industry manufacturing
delimit
to draw boundaries on a map in accordance with a legal agreement
demarcate
to place physical objects such as stones, pillars, walls, or fences to indicate where a boundary exists
demographics
data about the structures and characteristics of human populations
Demographic Transition Model
a model that represents shifts in the growth of the worlds populations, based on population trends related to birth rate and death rate
Denomination
a separate church organization that unites a number of local congregations
density
the number of things-people, animals, or objects- in a specific area
dependency ratio
the number of people in a dependent age group(under age 15 or age 65 and older) divided by the number of people in the working-age group(age 15 to 64) multiplied by 100
dependency theory
the theory that describes the development challenges and limitations faced by poorer countries and the political and economic relationships poorer countries have with richer countries
desertification
a form of land degradation that occurs when soil deteriorates to a desert-like condition
devolution
the process that occurs when the central power in a state is broken up among regional authorities within its borders
dialect
a variation of a standard language specific to a general area, with differences in pronunciation, degree of rapidity in speech, work choice, and spelling
diffusion
the process by which a cultural trait spreads from one place to another over time
Disamenity Zones
a high-poverty urban area in a disadvantaged location containing steep slopes, flood-prone ground, rail lines, landfills or industry
dispersed
spread out
dispersed settlement
a rural settlement patter in which houses and building are isolated from one another, and all the homes in a settlement are distributed over a relatively large area
Distance Decay
a principle stating that the farther away one thing is from another, the less interaction the two things will have
distribute
to arrange within a given space