Islam
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
What was the revelation and what is the significance to Islamic religion?
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What was the revelation and what is the significance to Islamic religion?
In a cave around Mecca in 610 CE had a vision of the archangel Gabriel while meditating,
told him to preach the word of Allah, the one God, to the world —> Muhammad formed religion
First he talked about it only to ones close to him and then started publicly speaking about the religion
This is where the Quran was revealed to Muhammad verbally by the archangel Gabriel
Muhammad
Born in Mecca about 570
He worked as a shepherd among Bedouins
Later he led caravans and became a successful merchant
At 40 he went to a desert cave and meditated
He was troubled by idol worship and moral ills of society
Here he heard the voice of the angel Gabriel calling him to be a messenger of God
Qur’an
Holy text of Islam → 114 chapters & composed in poetry form.
Written in Arabic.
Revelations of God → verbally revealed to Muhammad by the angel Gabriel from from 609-632 A.D.
Muhammad employed scribes to write down the messages as they were revealed to him.
How are Muslims expected to treat Christians and Jews?
Treat them equally as they are all “people of the book”
How is Muhammad the “Seal of the Prophets”
Koran names 25 prophets, including Noah, Abraham, Moses, Jesus, and Muhammad.
Muhammad is the “seal” (khatam) of the prophets – the last, the one that validates previous prophecy.
Came to “transmit the old message anew, and established through it a universal community […] the umma” (Denny, Intro to Islam, 69).
Similarities and differences between judasim, christianity, and islam
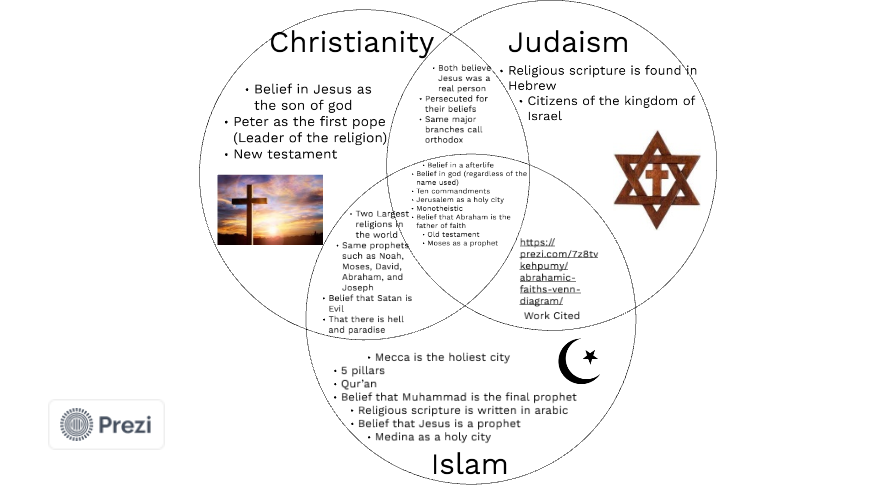
The Six Articles of Faith
Belief in One God
Belief in Angels
Belief in ALL the prophets
124,000 prophets, of whom 313 are also messengers
25 of these messengers are very important (mentioned in the Quran)
Belief in ALL the books revealed by God
(Torah, Bible, Qur’an)Belief in the Day of Judgment
- heaven and hell
- positive view of human nature
- Islam lacks concept of original sin
6. Predestination: Muslims believe in divine destiny
God wrote down all that has happened and will happen
Why do Muslims not portray images of Allah or Muhammed?
Many Muslims avoid depicting images of Allah (God) or Muhammad (the Prophet) because they believe such depictions could lead to idolatry, which is strictly forbidden in Islam.
(They believe he is too holy, thus the switching pronouns in the Koran and no pictures in fear they will start workshipping the image and not God, Allah,)
The hijrah
Mecca —> Medina
622 A.D. → Muhammad secretly leaves his home in response to assassination plots.
His followers go with him on this journey called “hijrah”.
Goes to Yathrib, which is later renamed Medina (city of the Prophet).
This is the first year of Muslim calendar.
What year is it now in the Islamic world and why?
What year is it now in the Islamic world?
1446 A.H. - WHY?
Anno Hegirae = lunar
The circling of the kabah, why, and impact
630 AD → Muhammad returned to Mecca, circled the Kabah 7 times & destroyed the idols within.
Broke the traditonal tribal religions and polytheism —> cleaned up the kabah to be back to monotheism, uniting the people under one god, Allah
The Five Pillars of Islam
Shahada (Declaration of Faith):
This pillar is the foundation of Islam, stating the belief in the oneness of God (Allah) and the prophethood of Muhammad.
Salat (Prayer):
Muslims are obligated to pray five times a day, facing the direction of the Kaaba in Mecca, as a way to connect with God and express gratitude.
Zakat (Charity):
This pillar involves giving a portion of one's wealth to the poor and needy as a form of purification and social responsibility.
Sawm (Fasting):
During the month of Ramadan, Muslims abstain from eating and drinking from dawn until sunset as a form of spiritual discipline and reflection.
Hajj (Pilgrimage):
If physically and financially able, Muslims are expected to make a pilgrimage to Mecca at least once in their lifetime, a journey that symbolizes unity and submission to God.
Judasim, Islam, and Christianity share a belief in…
Monotheism and ethical conduct
The Hidjra, Muhammad’s journey from Mecca to Medina in _____, is important to Muslims because the journey..
622 AD, Signified the establishment of the Islamic faith
How do Christian concepts of governmental law differ from Islamic concepts of governmental law?
Christian = give ceaser what is his and give god what is gods (divison of religion and state)
Islamic = everything is gods (allahs)
Sharia Law
Islamic law code developed by Muslim scholars by interpreting the Qur’an.
It regulates moral conduct, family life, business practices, government, and other aspects of the Muslim community.
It helped unify the expanding Muslim community.
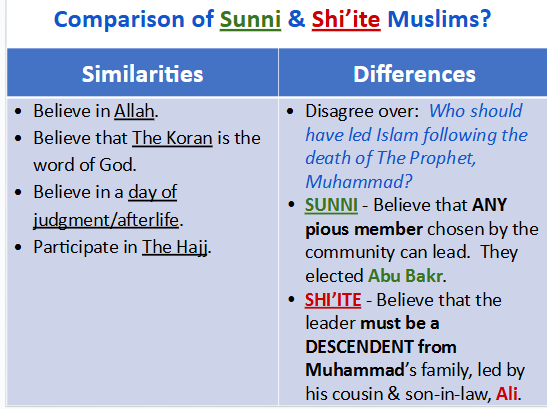
Muslims were split into two groups after Muhammad died, the Sunni and the Shi’ia.
The Sunnis believed and elected person (like Abu Bakr) should take over after Muhammad
The Shi’ia believed someone who is DIRECTLY RELATED to Muhammad was already appointed his sucsessor (Ali)
Sunni = Saudi Arabia (around 80%)
Shi’ia = Iran (around 20%)
THESE ARE SECTS OF ISLAM
What countries may experience turmoil based on sectarian rifts deomestically?
Yemen and Iraq
Comparison of Sunni and Shi’ite Muslims
Shi’ia disregard the first 3 caliphs in history because they (Abu Bakr, etc.) were not descendants of The Prophet.
Shi’ia believe that Ali, Muhammad’s son-in-law, should have been named caliph.
It is not until Ali rules that they acknowledge the caliphs.
But when Ali was killed (by the Umayyad) the split intensified.
Most Shi’ia today live in Iraq and Iran.
10% of Muslims today = Shi’ia
Just like other major religions with sects, the split involves different interpretations of beliefs and texts.
More branches have splintered off from the original two...
Rashidun dynasty: 632-661
After the Prophet Muhammad died (632 AD), his first successor was Abu Bakr.
He was named the first caliph, or successor.
For the most part, Abu Bakr was able to unite Muslims under his rule.
Abu Bakr and his next 3 successors will help to gain more land.
Umayyad dynasty: 661-750
First power established after the death of the last caliph, Ali.
Shia Muslim → greatly expanded territory.
Abbasid dynasty: 750-861
Shia Muslims → Overthrew Umayyad.
Moved the capital from Damascus to Baghdad.
Golden age associated with the Abbasid.
The Golden Age of Islam
Abbasid Political Policy = NO EXPANSION
focus on organized & efficient administration→ bureaucracy
Non-Arab Muslims were allowed to hold positions of power now
Heavily encourage conversion → more than Umayyad Caliphate
CAPITAL MOVE to BAGHDAD
During the Golden Age of Islam why and where did they move the new capital?
MOVED TO BAGHDAD
By moving closer to Persian territory the caliphate was heavily influenced by Persian customs (hence bureaucracy & participation of non-Arabs).
Persian officials held important government offices.
Vizier → head of the bureaucracy; was a position in Persian bureaucracy.
What was the golden age?
Abbasid Caliphate under Caliph Haroun Al Rashid Reign: 786-809
What is a Caliphate?
Eras ruled by a Caliph (sucsessor of Muhammad)
How did geography play a role in the Golden Age of Islam?
Tons of trade routes!
Prophets ENCOURAGED trade —> impact on the Day of Judment