Anatomical Terminology
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
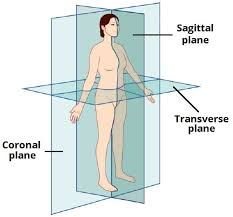
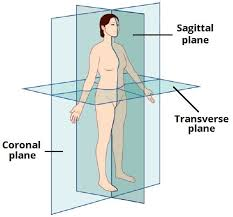
How does the sagittal plane split the body?
left and right
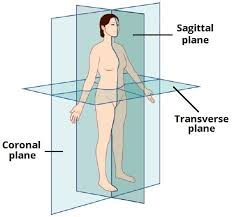

How does the coronal plane split the body?
front and back
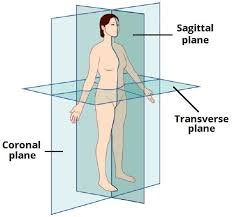
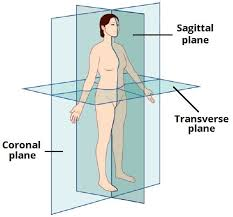
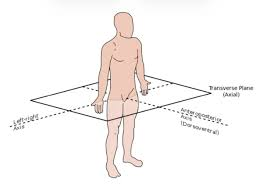
How does the transverse plane split the body?
in half (at a point)
What plane is this cut across?
sagittal plane
What plane is this cut across?
coronal plane
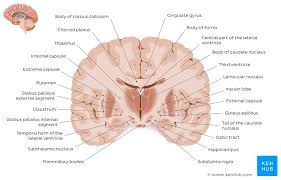
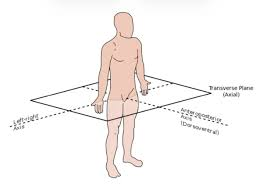
What plane is this cut across?
transverse plane
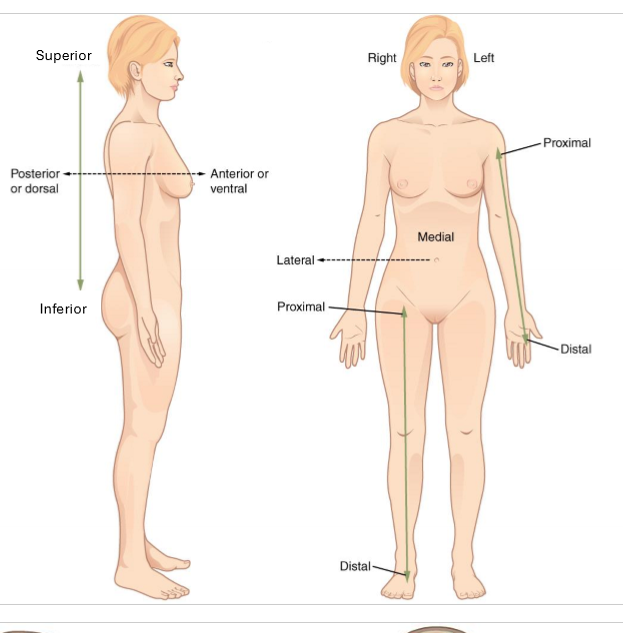
What is superior and inferior?
superior- closer to head (above)
inferior - closer to feet (below)
only for trunk
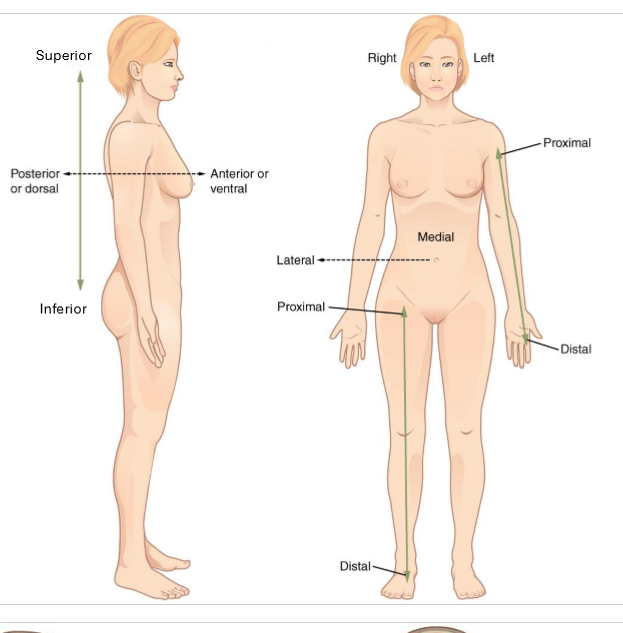
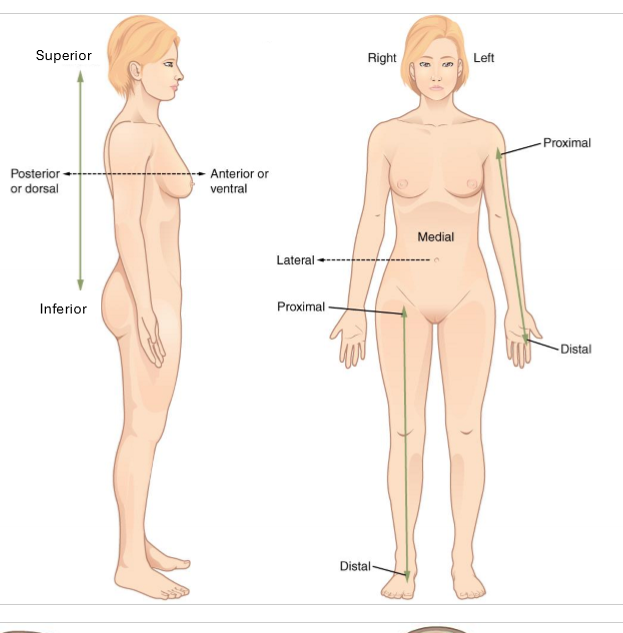
What is anterior and posterior?
anterior - in front of
posterior - behind
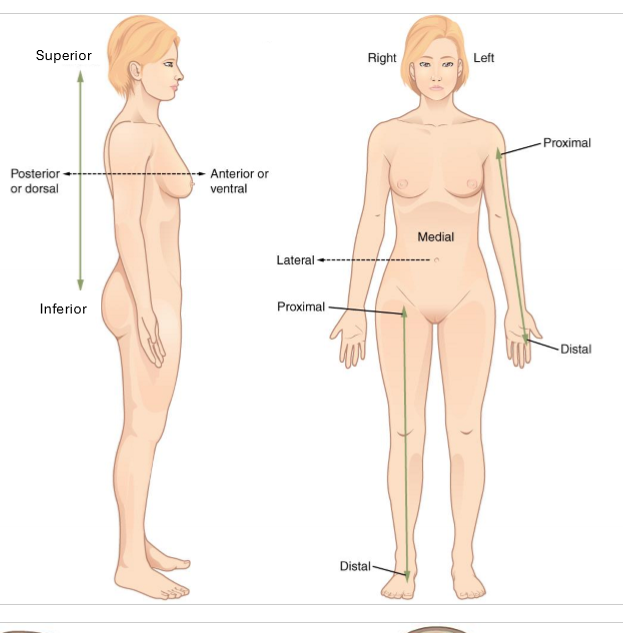
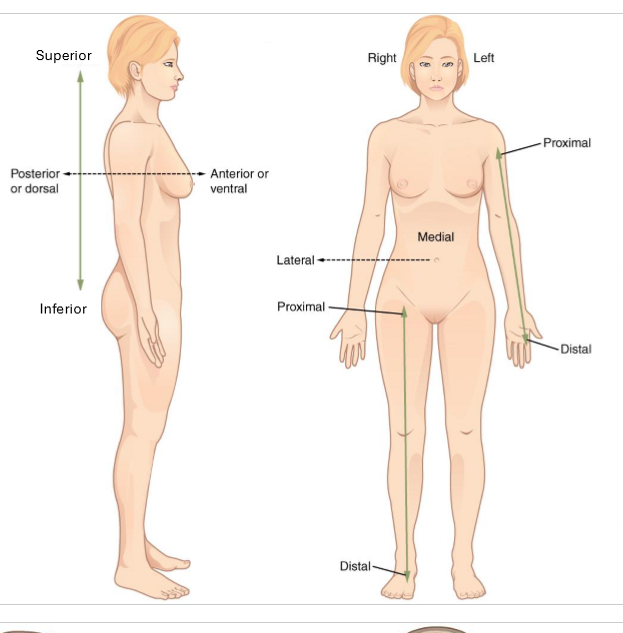
What is lateral and medial?
lateral - away from midline of body
medial - towards midline of body

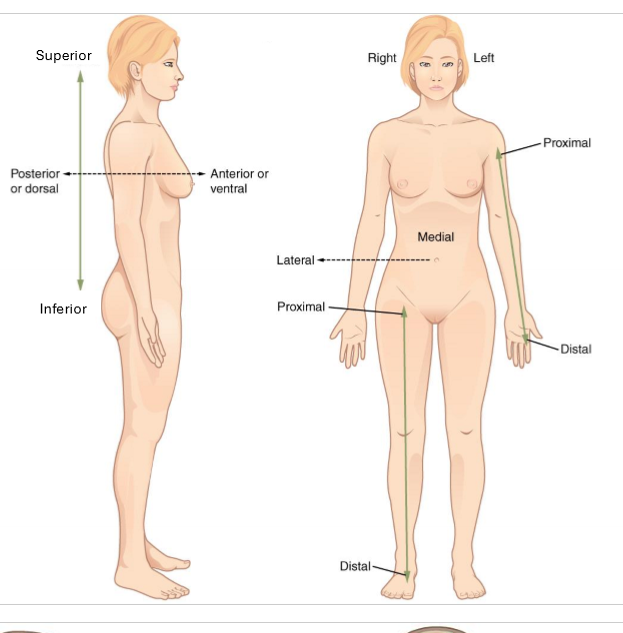
What is proximal and distal?
proximal - closer to trunk
distal - further from trunk
for arms and legs
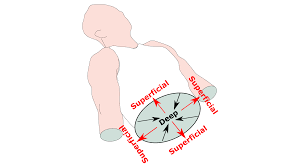
What is deep and superficial?
superficial - closer to body surface
deep - more internal
The wrist is ______________ compared to the fingers.
proximal
The chin is _________________ to the mouth.
inferior
The ribs are ______________ compared to the lungs.
superficial
The vertebrae are ________________ compared to the sternum.
posterior
The fibula is __________________ compared to the tibia.
lateral
The ankle is _________________ compared to the thigh.
distal
7. The patella is __________________ compared to the femur.
anterior
The heart is ______________ compared to the intestines.
superior
The nose is ________________ compared to the eyes.
medial
The brain is _________________ compared to the skull.
deep
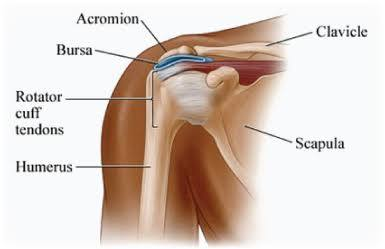
What is the acromial region?
bony, highest part of shoulder

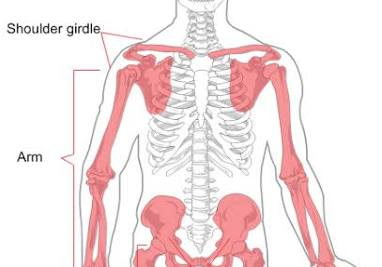
What is appendicular region?
extremeities and pelvis
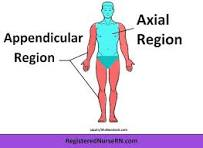
What is axial?
core of body, trunk and head
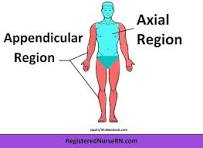
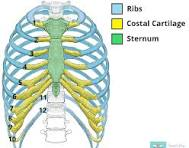
What is the costal region?
ribs and sternum


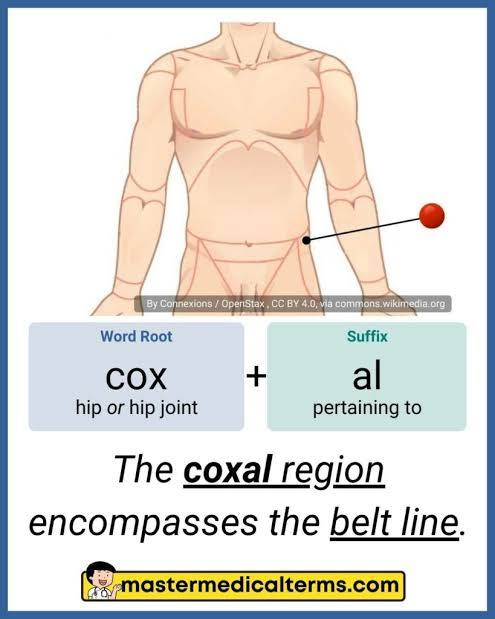
What is the coxal region?
hip region
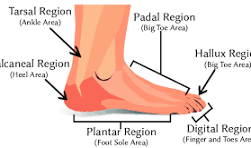
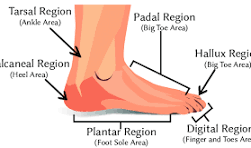
What is the hallux?
big toe
What is the pollex?
thumb
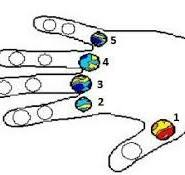
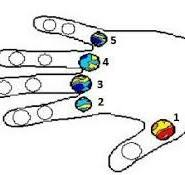
What is the umbilical region?
central area of abdomen
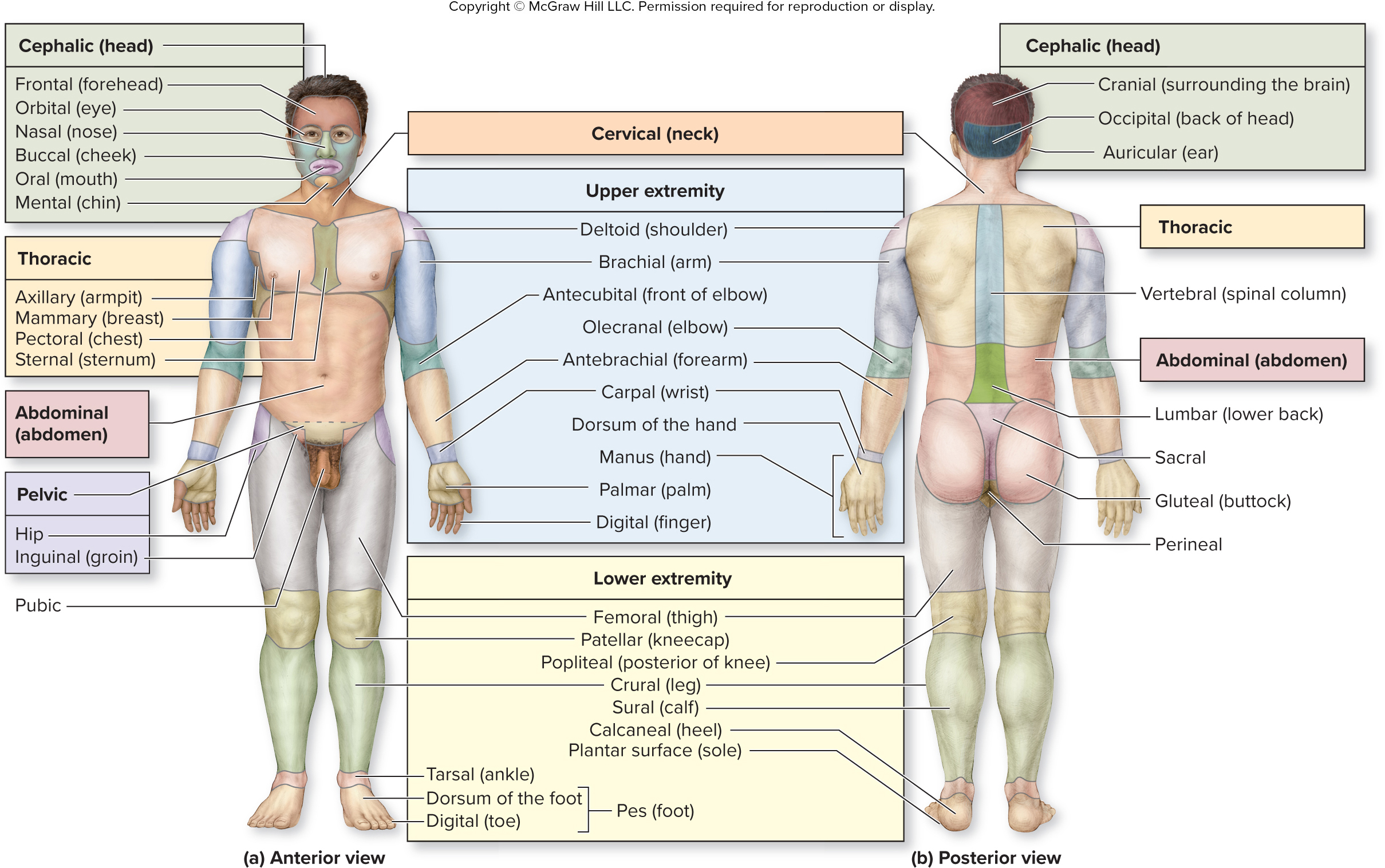
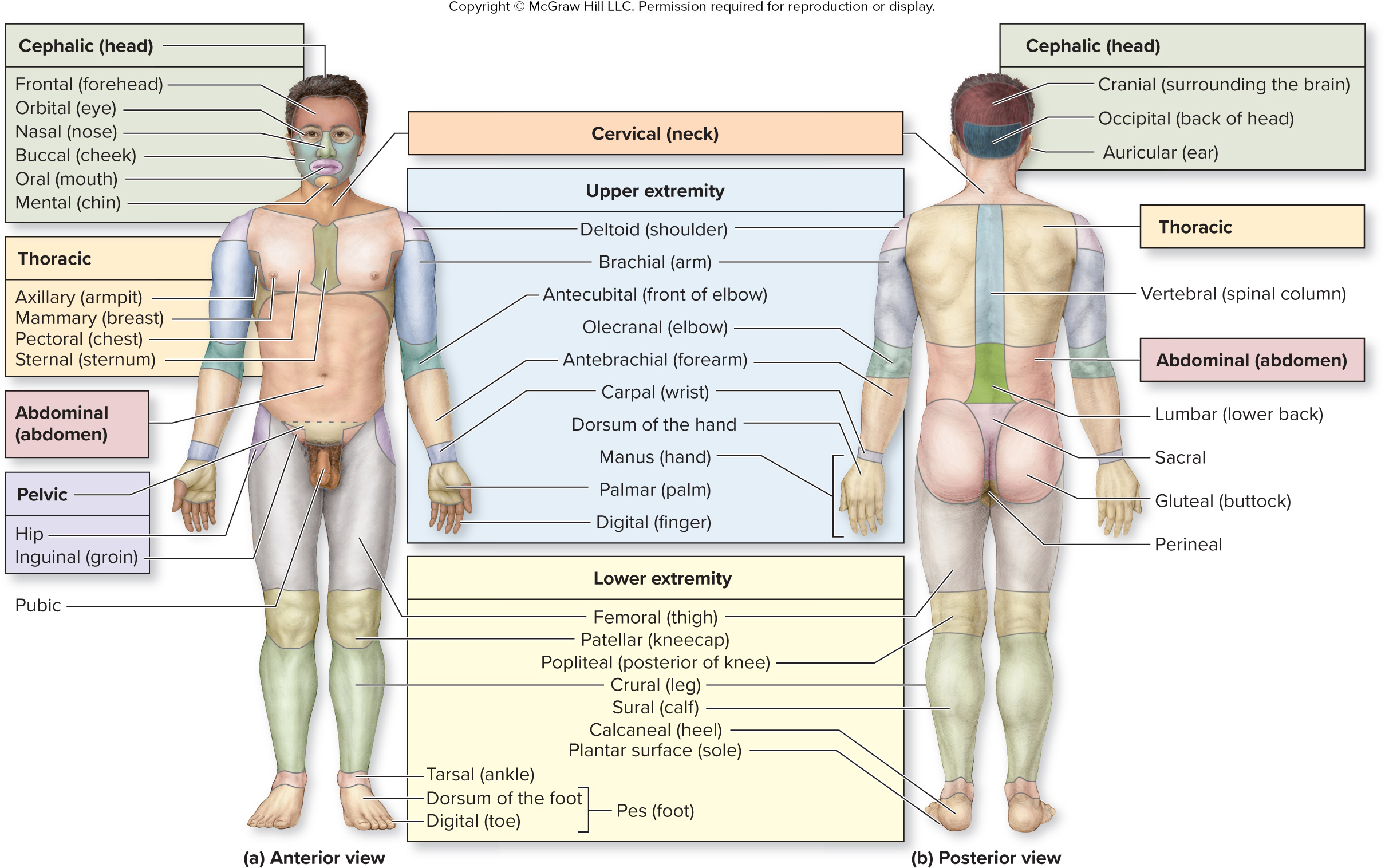
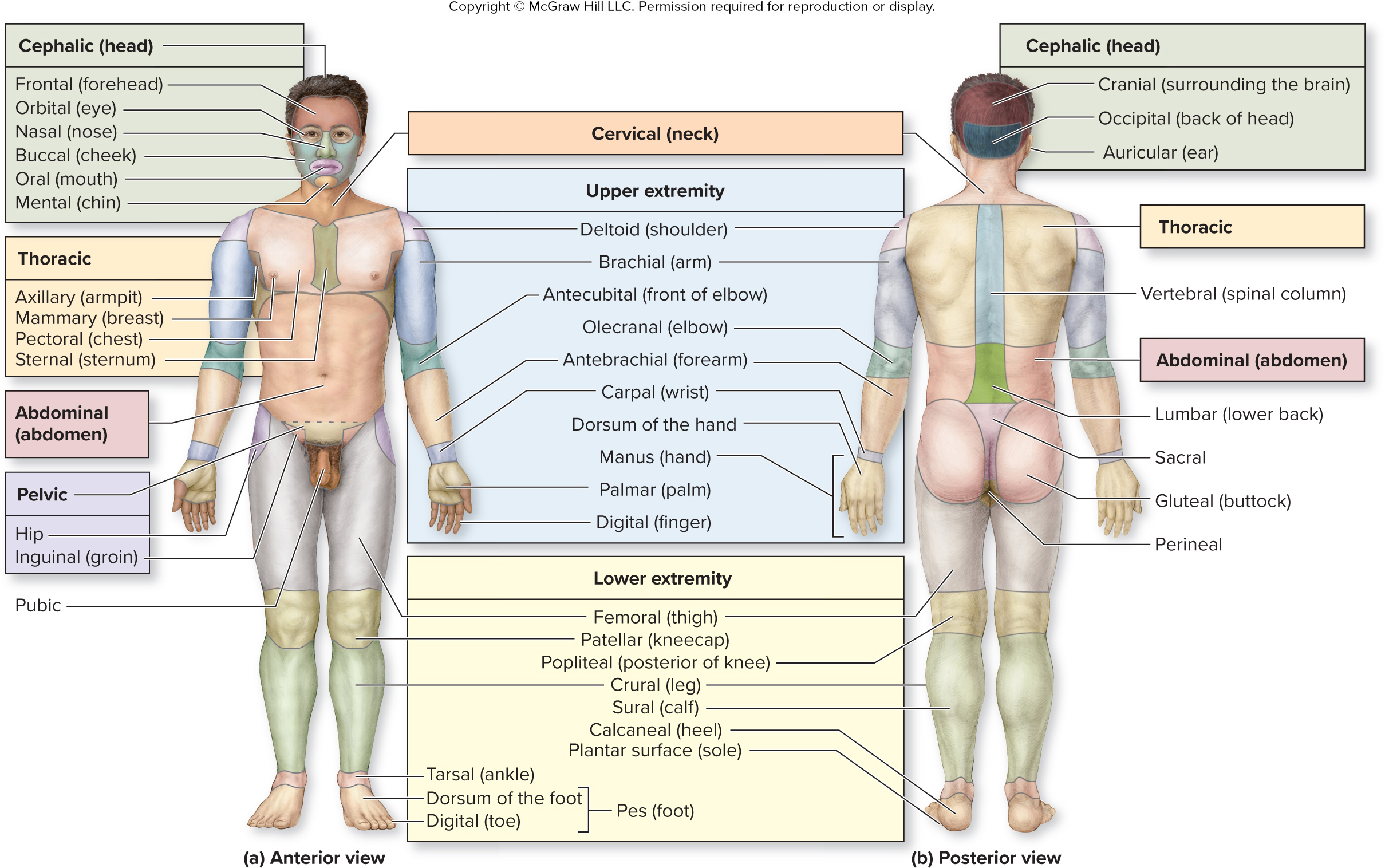
What are the words for the parts of the cephalic (head) region?
forehead
eyes
nose
cheek
mouth
chin
frontal
orbital
nasal
buccal
oral
mental
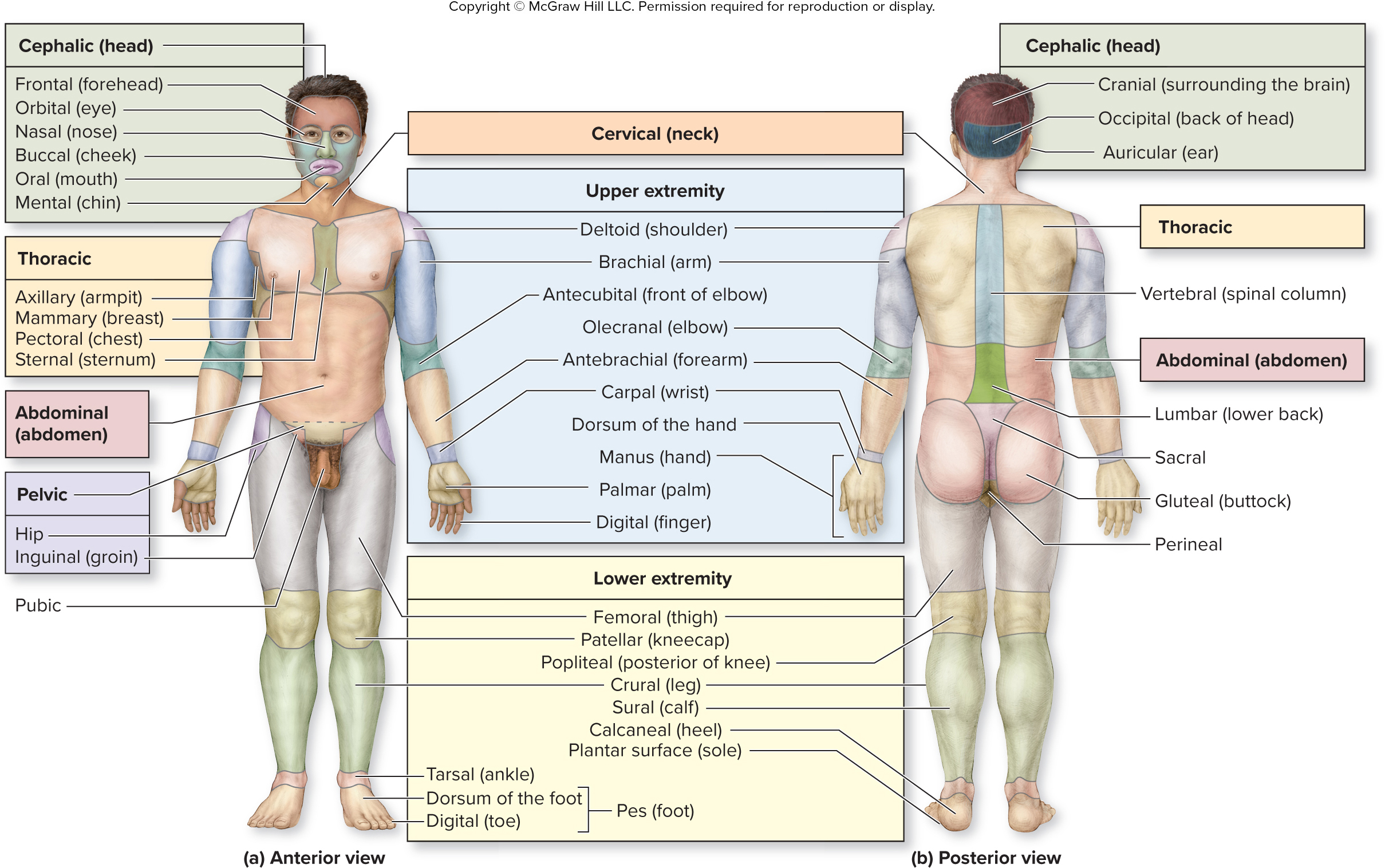
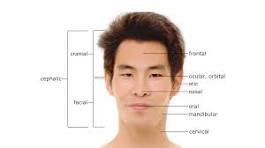
What is the cephalic region?
head

What are the words for the parts of the thoracic region?
armpit
breast
chest
sternum
axillary
mammary
pectoral
sternal
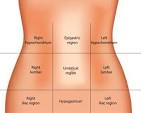
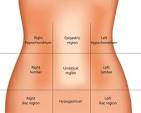
What is the abdominal region?
abdomen
What is the pelvic region?
hip and groin
What is the inguinal region?
groin
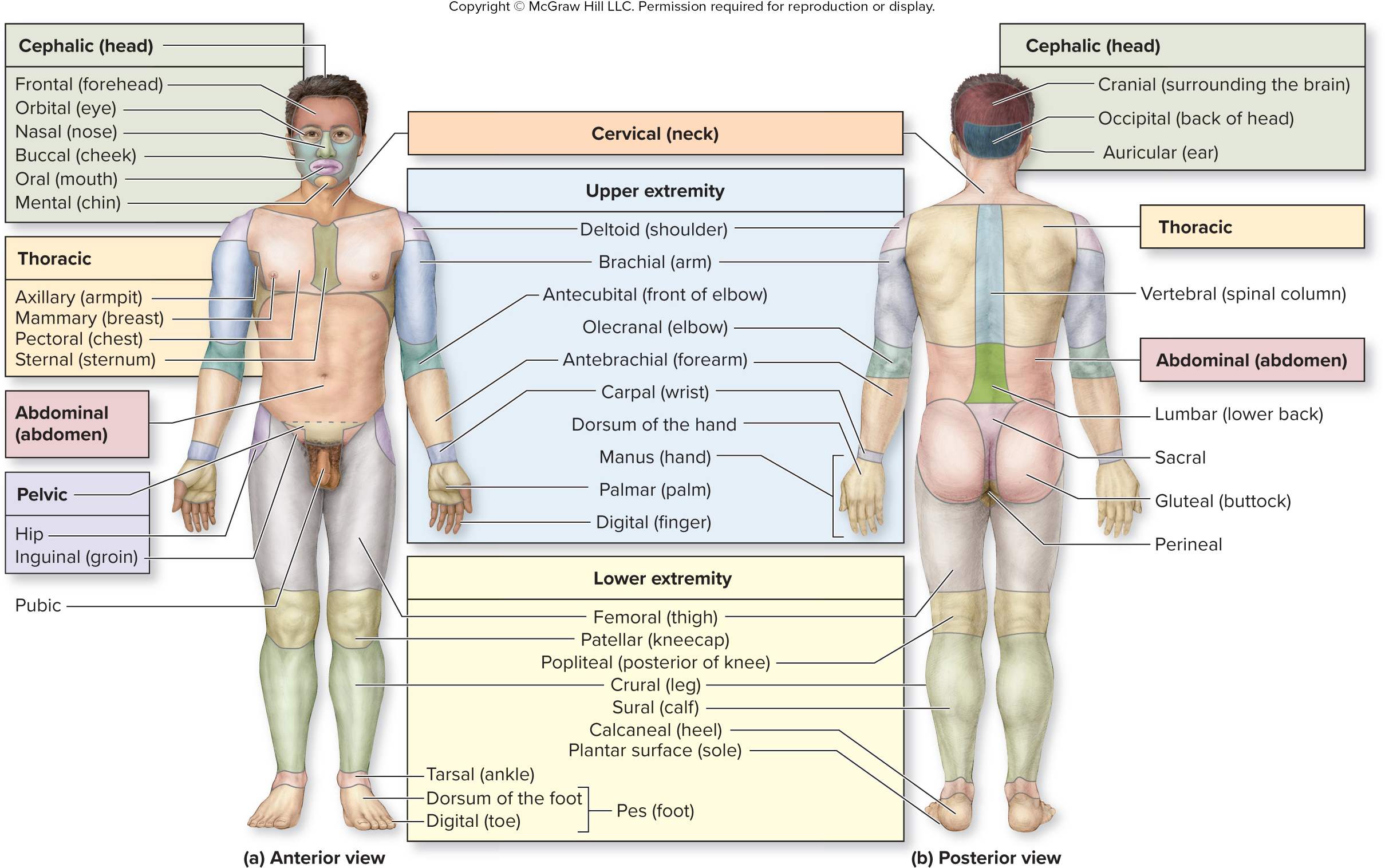
What is the cervical region?
neck
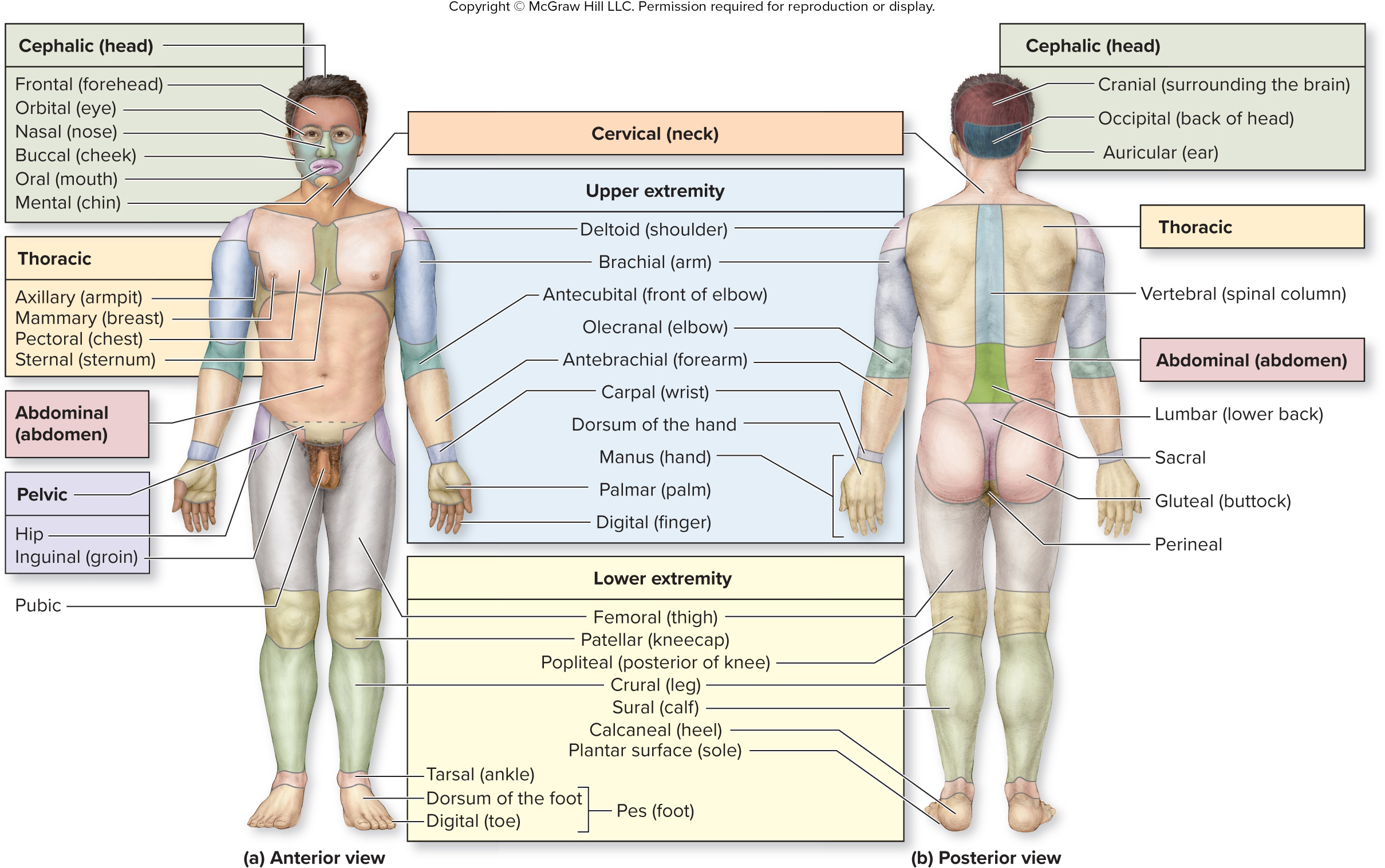
What are the words for the parts of the upper extremities (arms) region?
shoulder
arm
front of elbox
elbow
forearm
wrist
back of hand
hand
palm
finger
shoulder - deltoid
arm - brachial
front of elbow - antecubital
elbow - olecranal
forearm - antebrachial
wrist - carpal
back of hand - dorsum of hand
hand - manus
palm - palmar
finger - digital
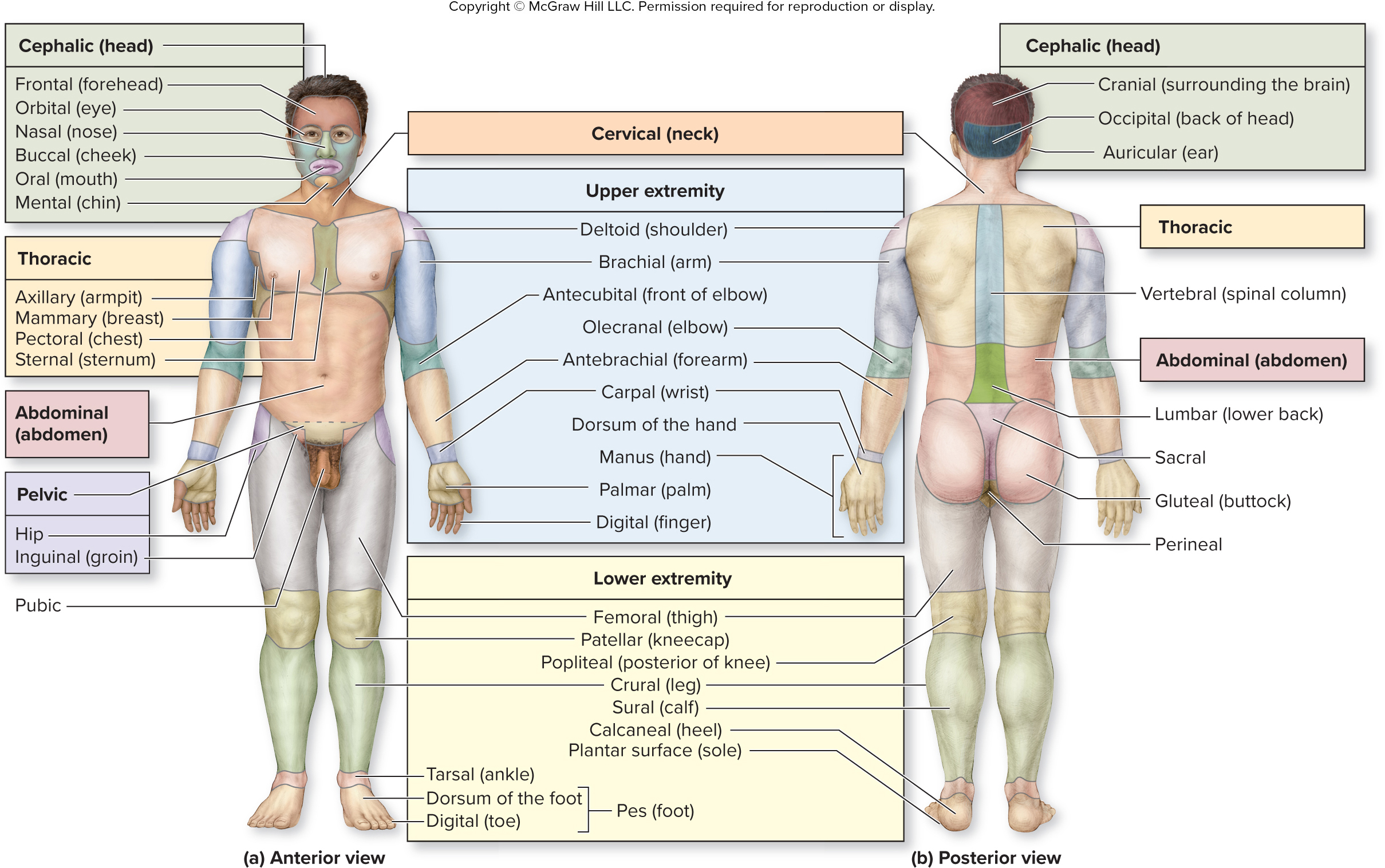
What are the words for the parts of the cephalic (head) region?
surrounding brain
back of head
ear
cranial
occipital
auricular
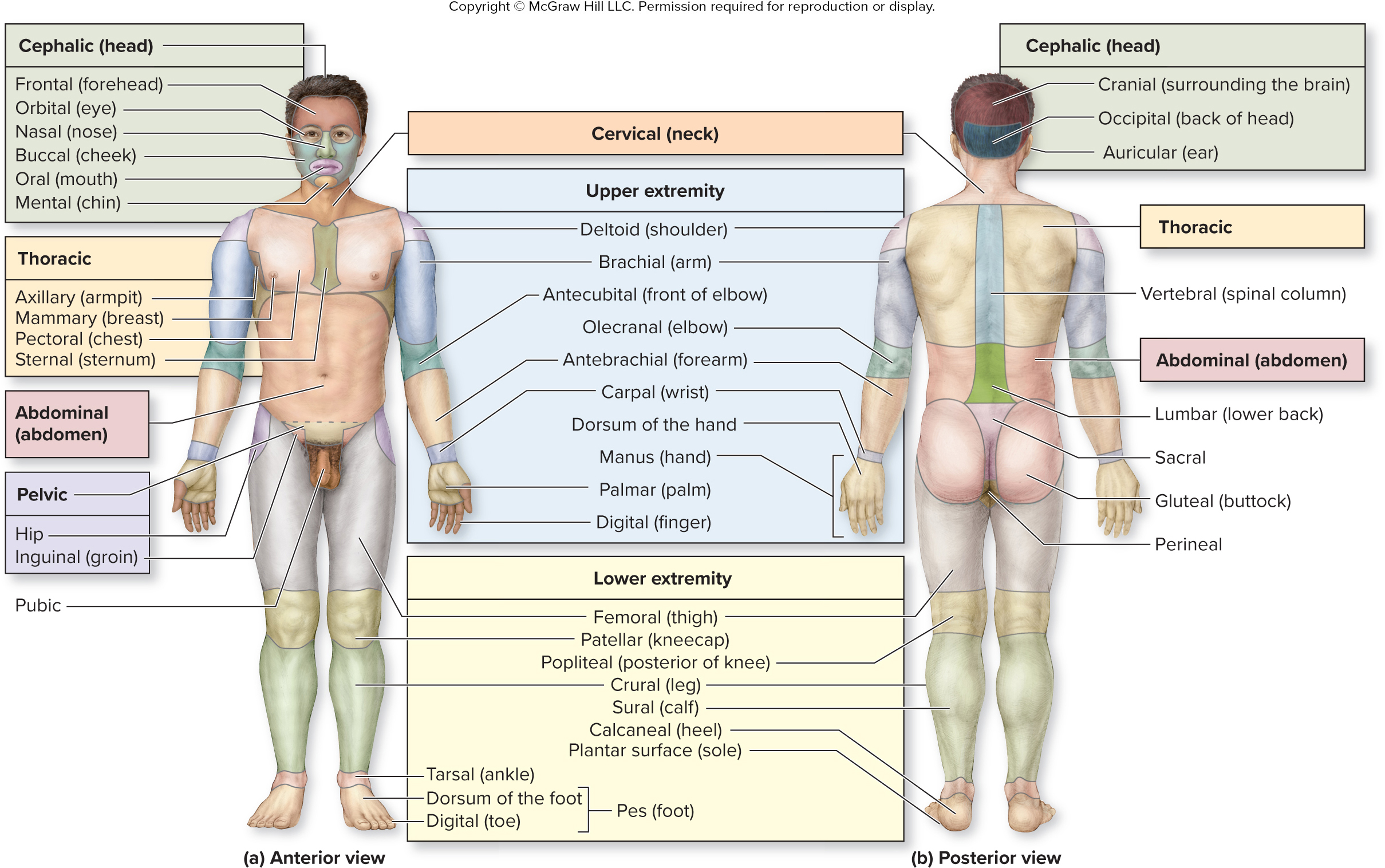
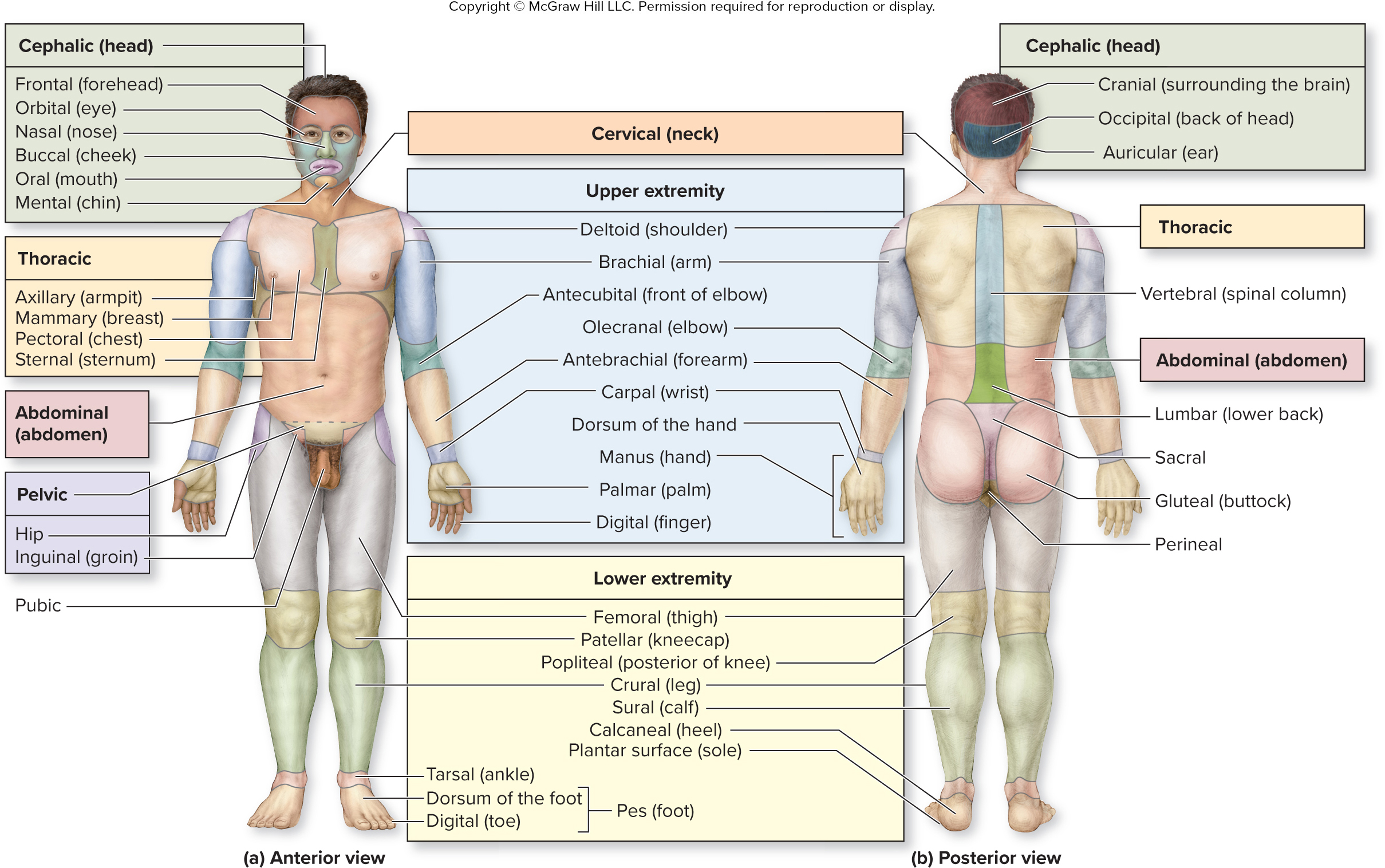
what is the vertebral region?
spinal column
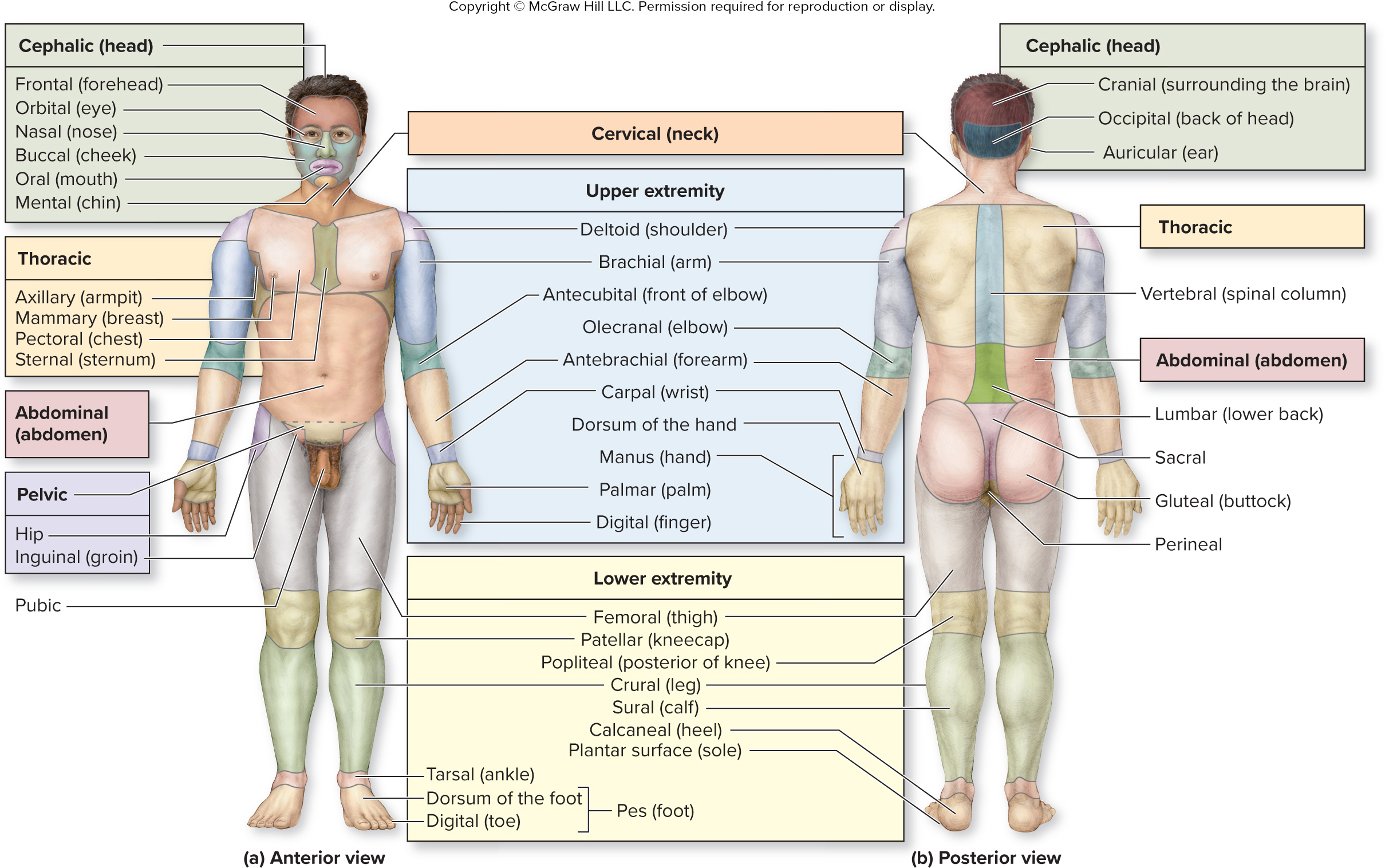
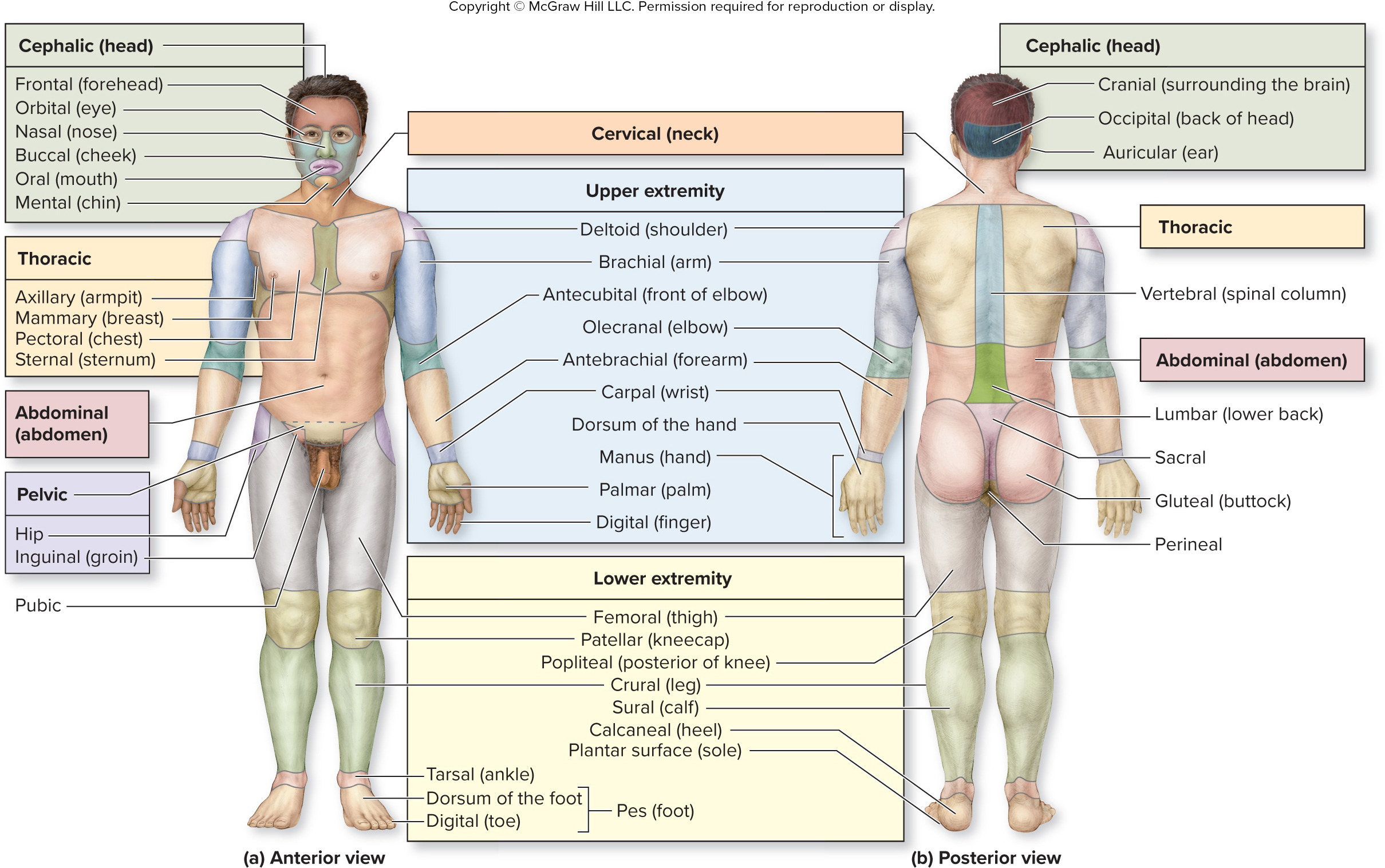
What is the abdominal region?
abdomen
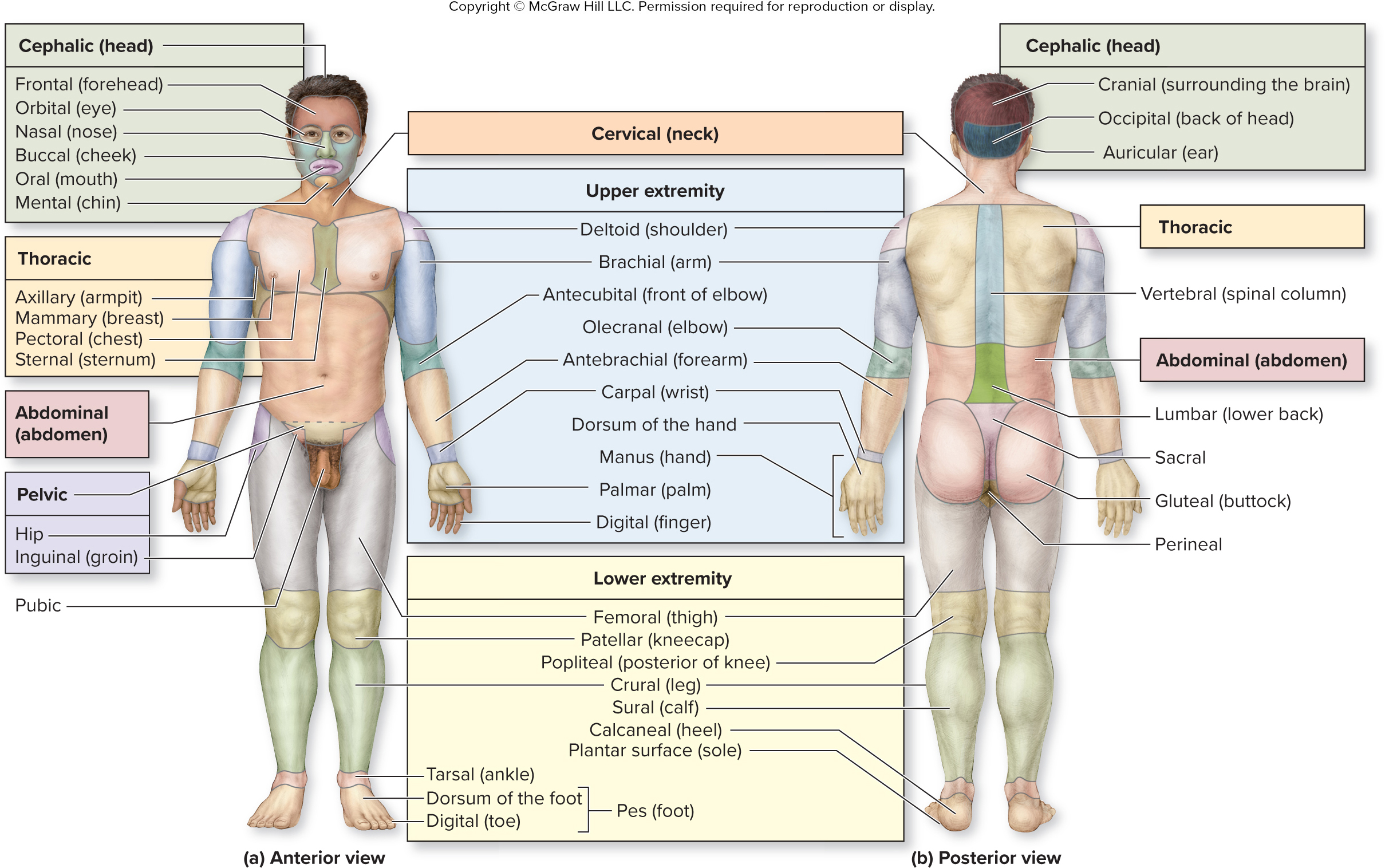
What is the sacral region?
between butt cheeks

What is the gluteal region?
buttock
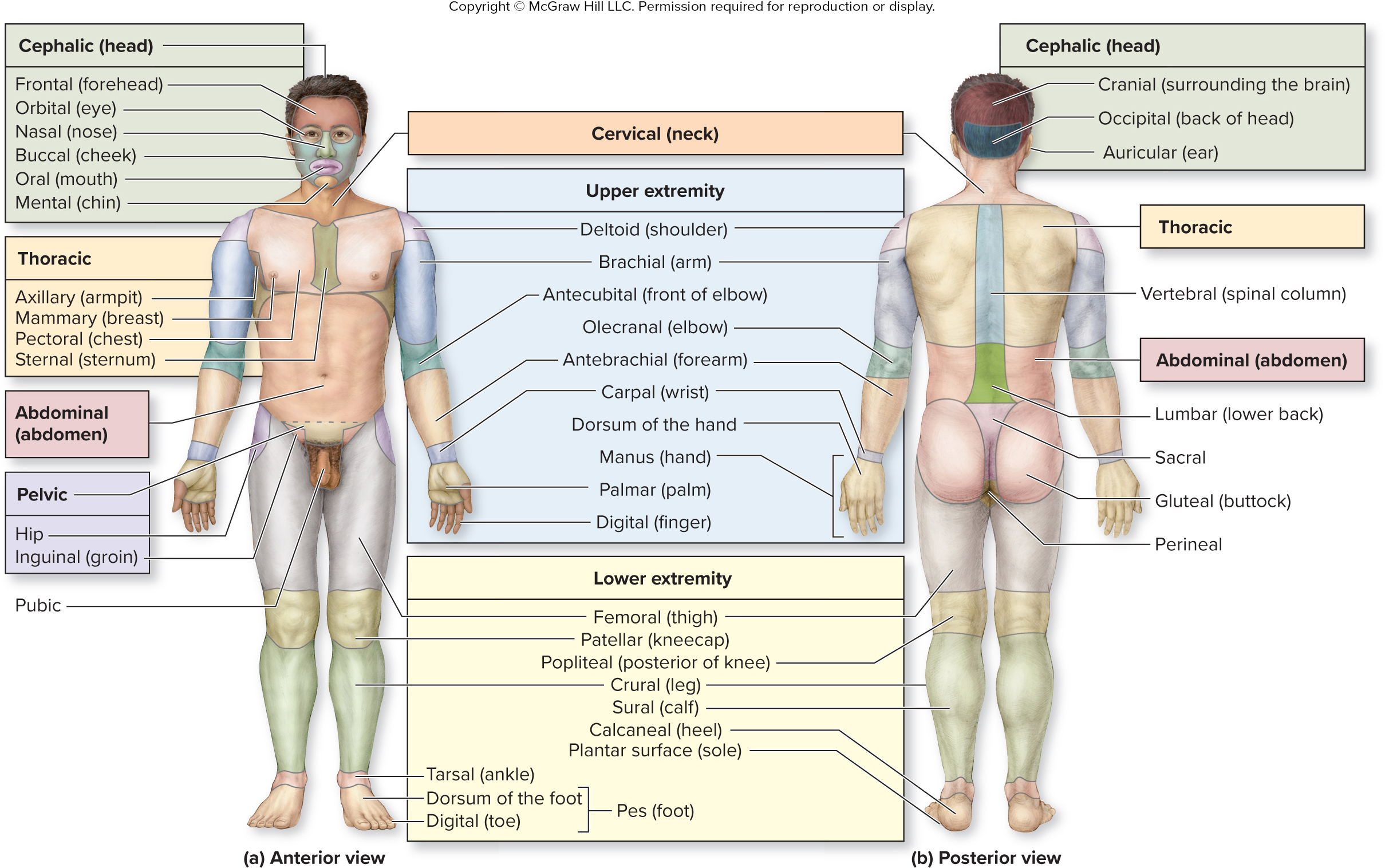
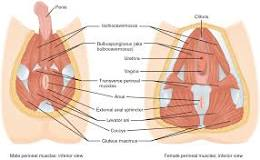
What is the perineal region?
anus basically
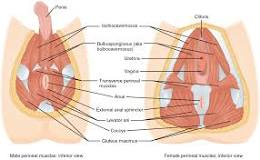
What are the words for the parts of the lower extremities (legs) region?
thigh
kneecap
posterior of knee
leg
calf
heel
sole of foot
thigh - femoral
kneecap - patellar
posterior of knee - popliteal
leg - crural
calf - sural
heel - calcaneal
sole of foot - plantar surface
What are the words for the parts of the pes (foot) region?
ankle
front of foot
toe
tarsal
dorsum of foot
digital

What is the thoracic region?
axillary (armpit), mammary, pectoral, and sternal region
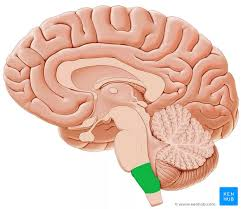
What cavity is this?
cranial cavity (head)
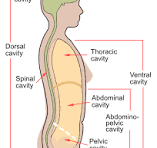
What is the dorsal body cavity?
cranial and vertebral cavity, encloses brain and spinal cord
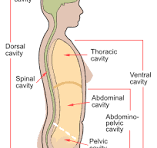
What is the vertebral cavity?
encloses spinal cord
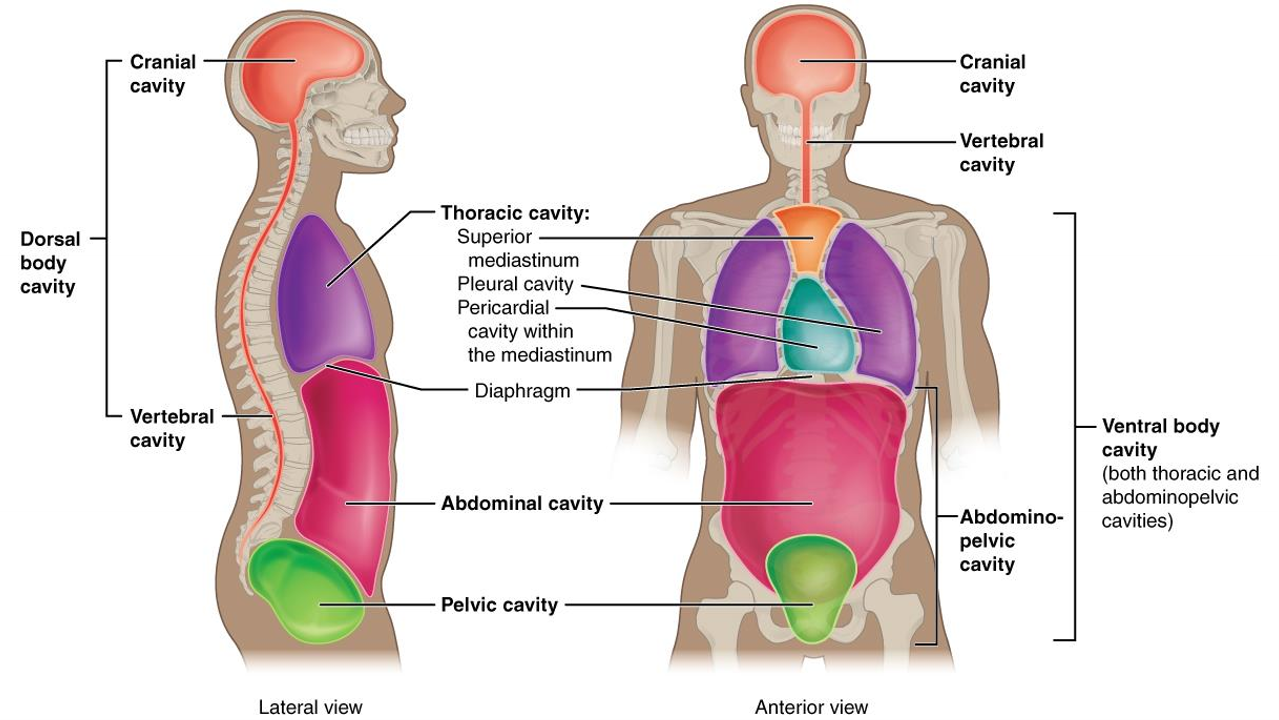
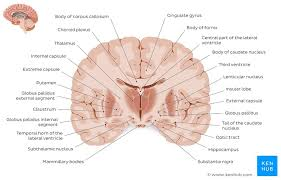
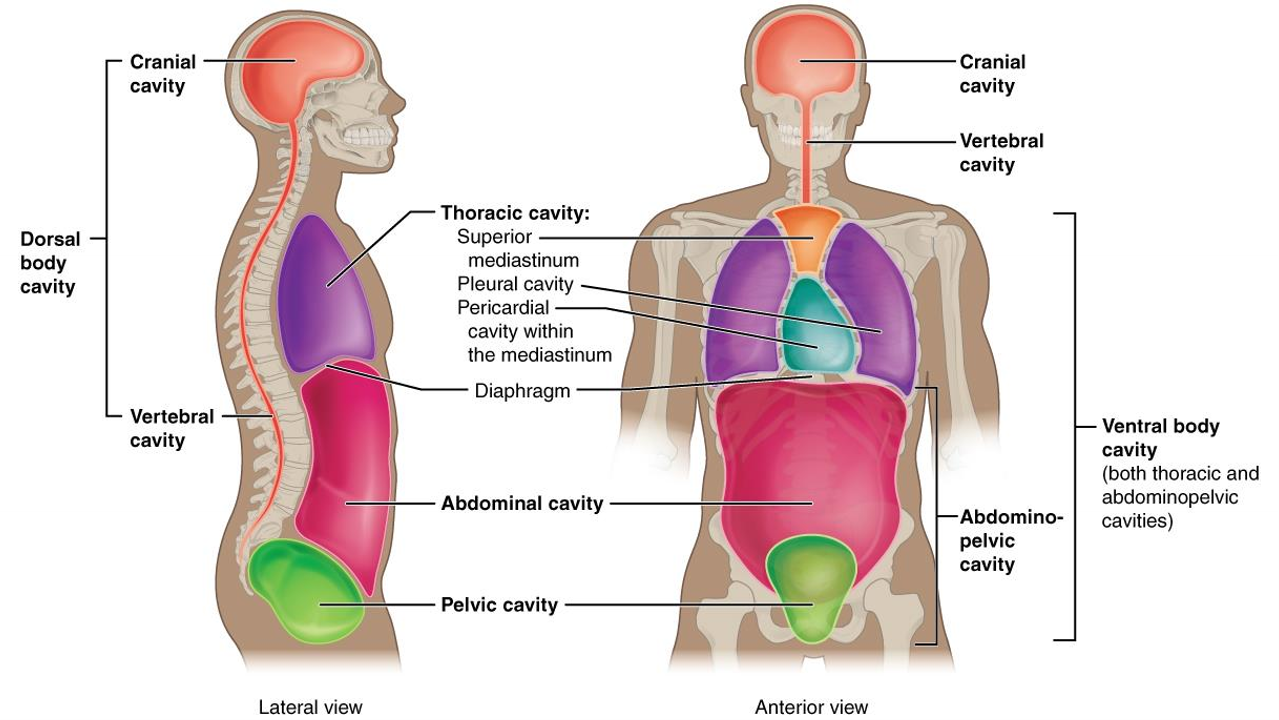
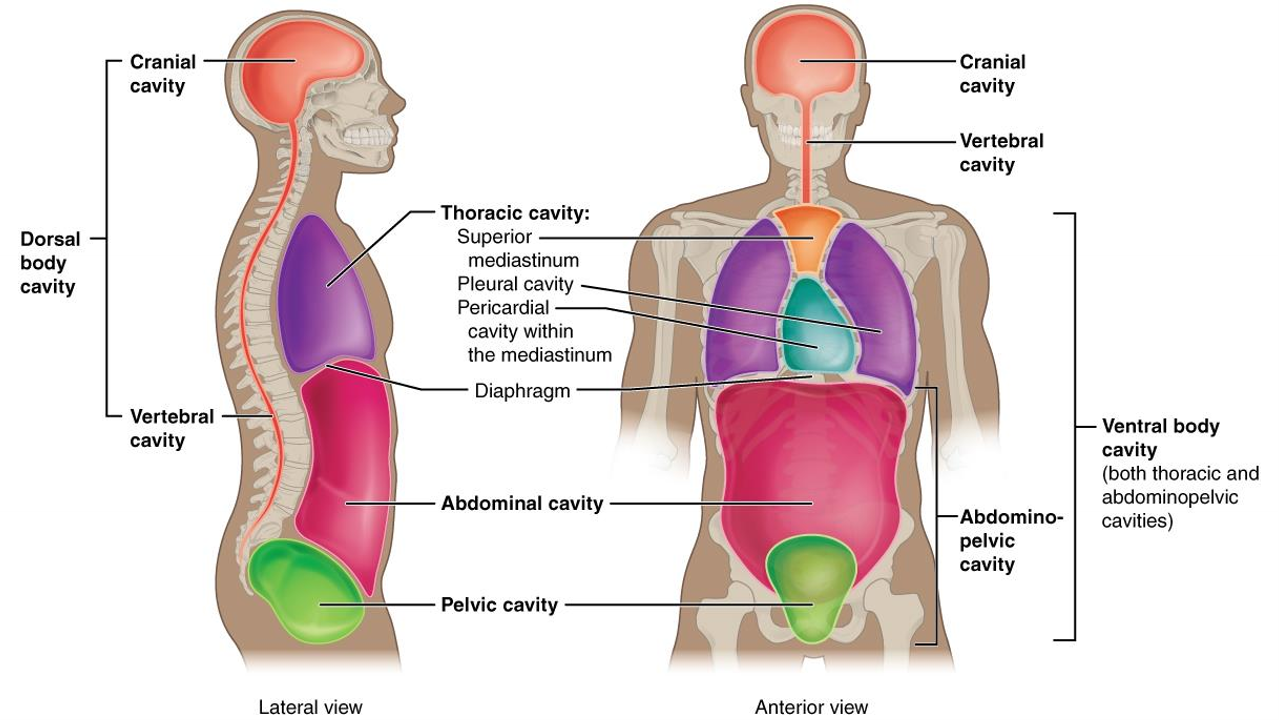
What cavity is in purple?
thoracic
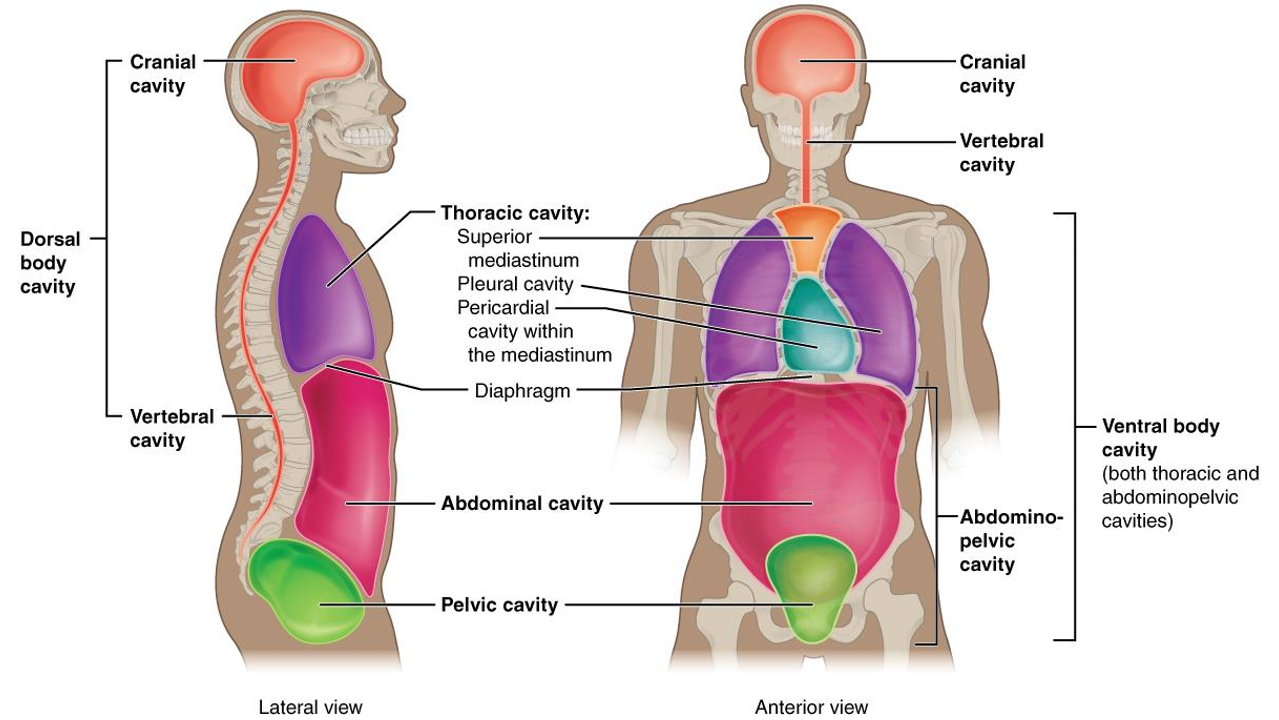
What is the thoracic cavity?
above diapghram, contains heart and lungs,
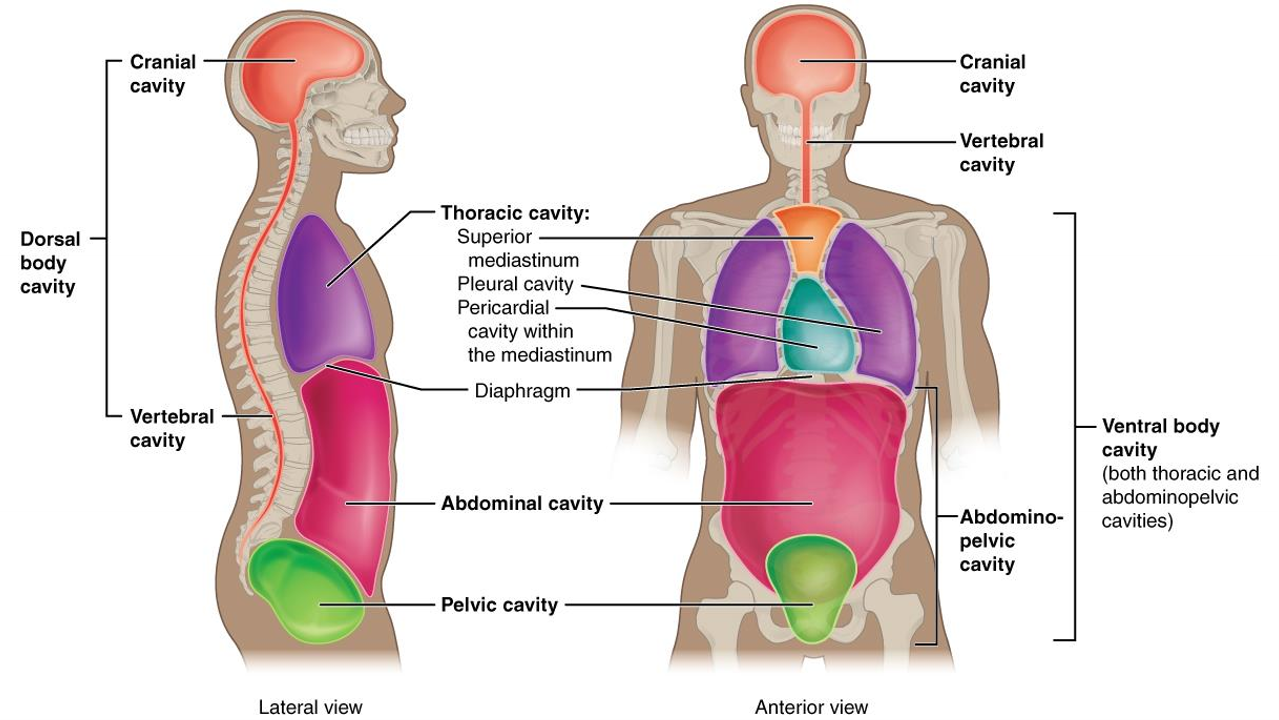
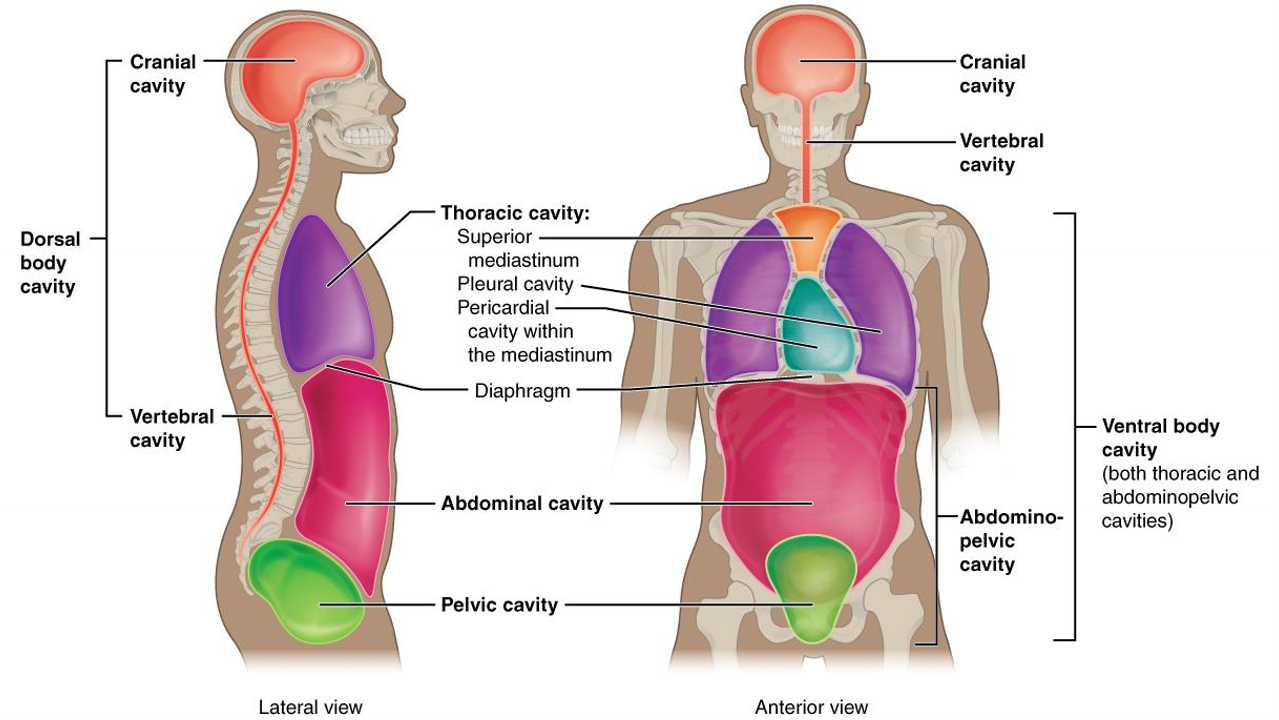
What is the abdominal cavity?
stomach, liver, intestines, kidney, etc.
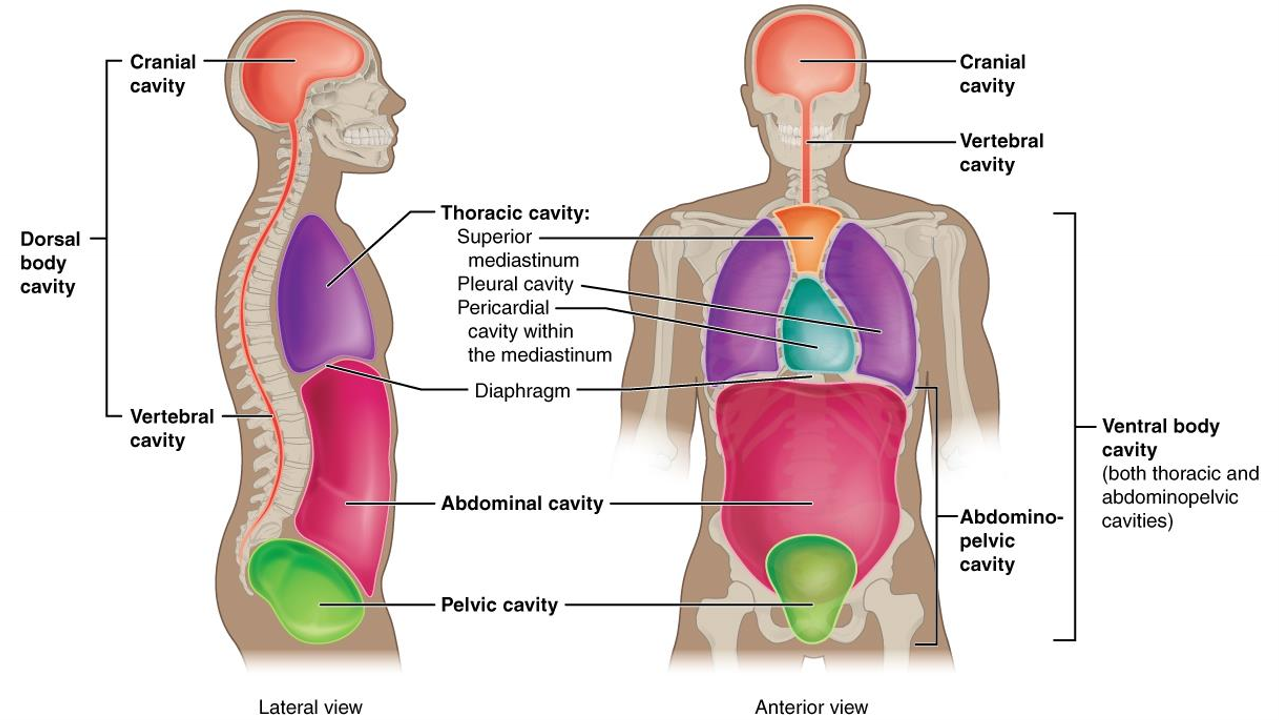
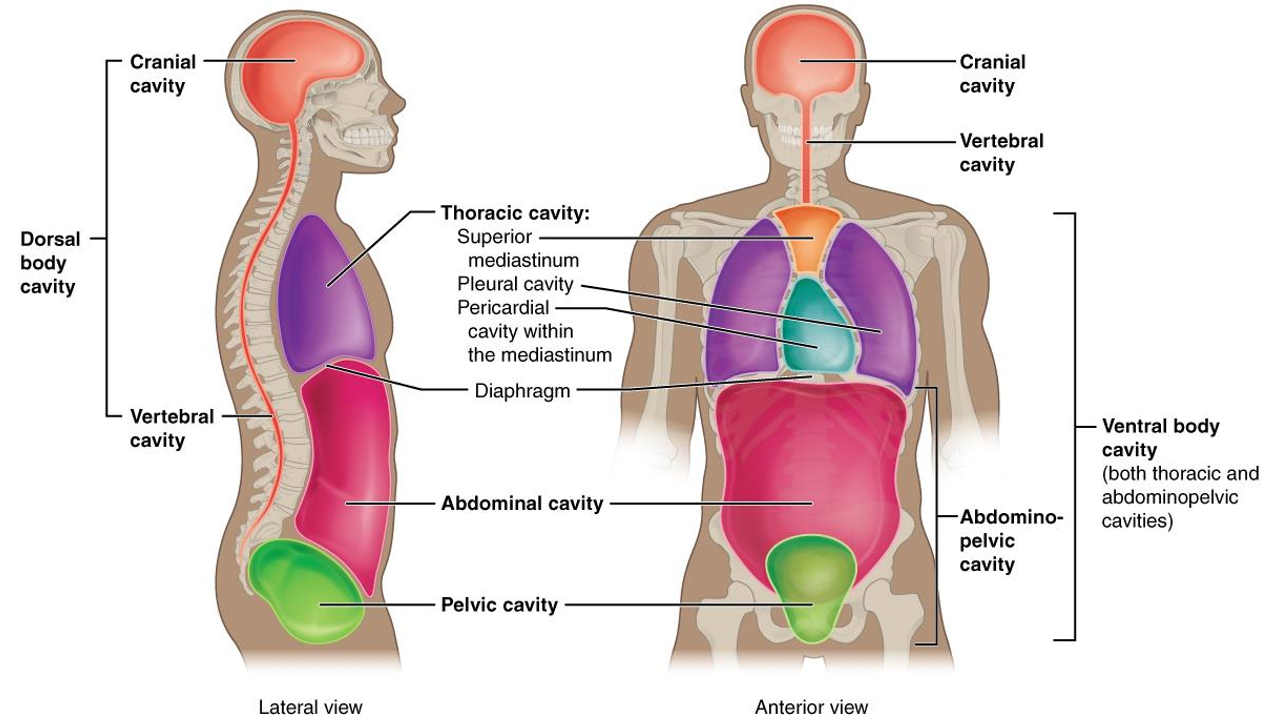
What is the pericardial cavity?
surrounds and protects heart
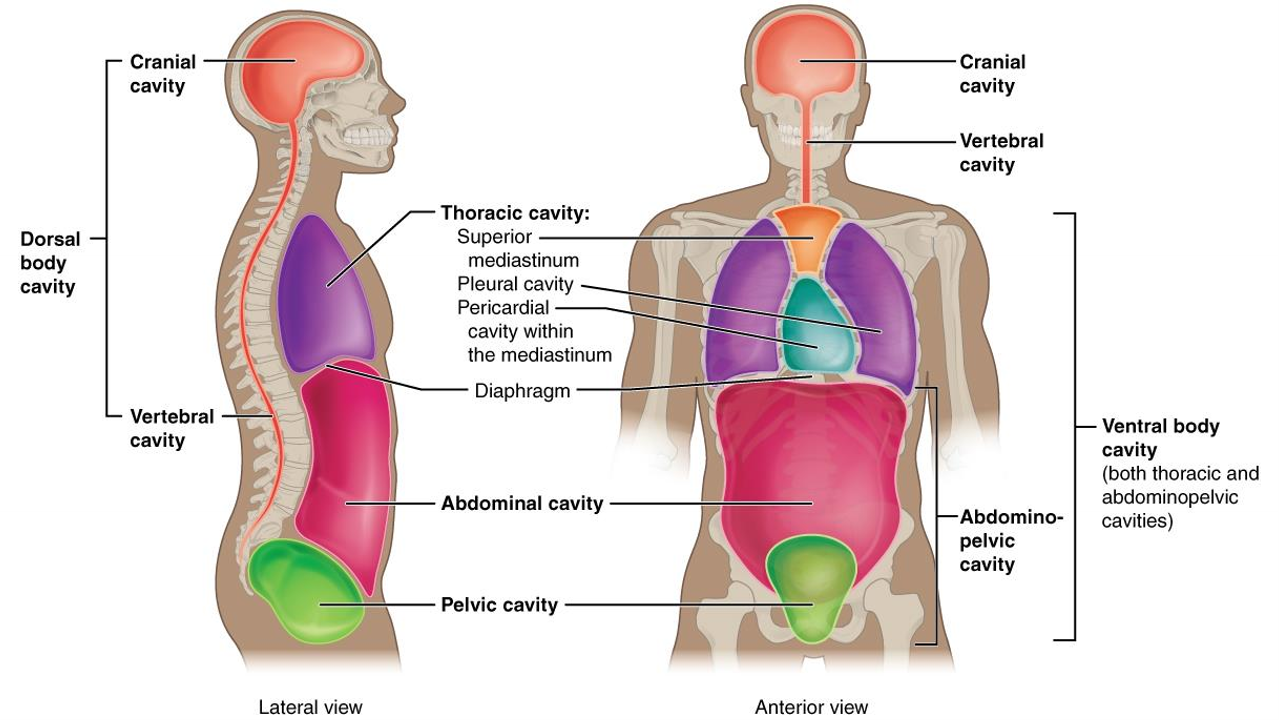
What is the pelvic cavity?
in pelvis, has bladder, reproductive organs, rectum
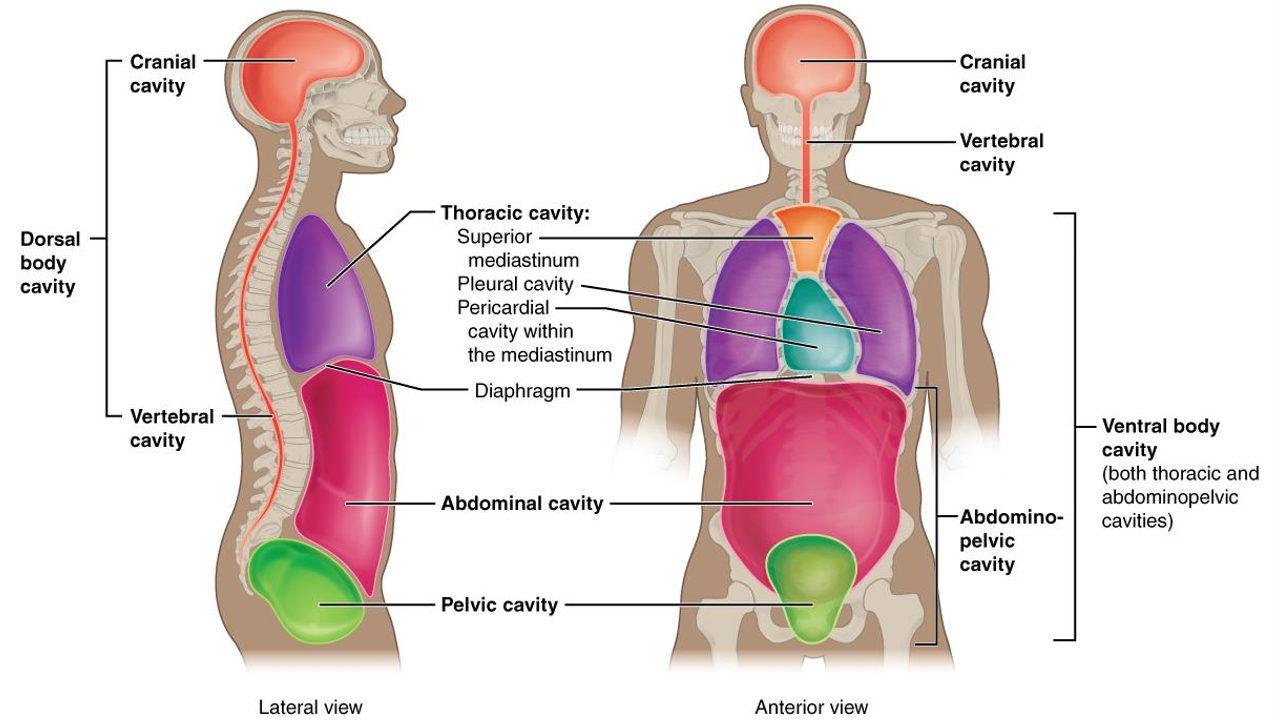

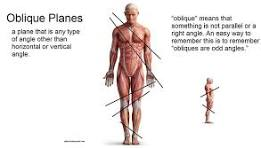
What is the oblique plane?
angled plane
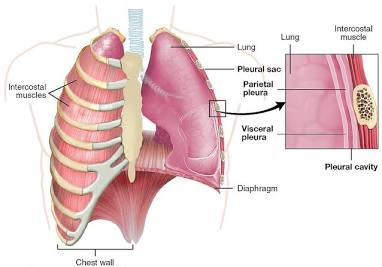
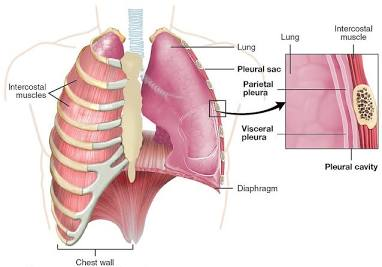
what is the pleural cavity?
each lung
What are the four basic types of tissue and their general functions?
epithelial - line and protect, form gland, protection, absorption
muscle - movement
nervous - internal communication
connective - connects structures, provides suppot
How is epithelial tissue categorized?
simple - 1 layer
stratified - 2+
squamos - flat
cubodial
columnar
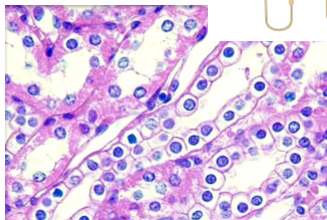
What is this?
simple cubodial

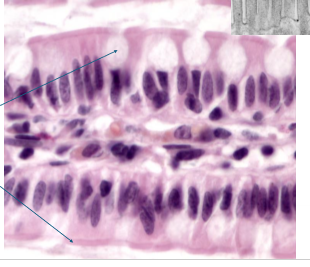
What is this?
simple columnar epithelial
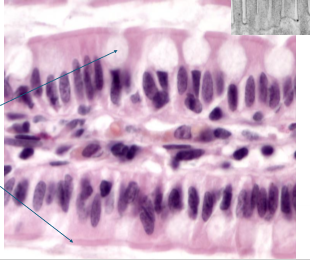
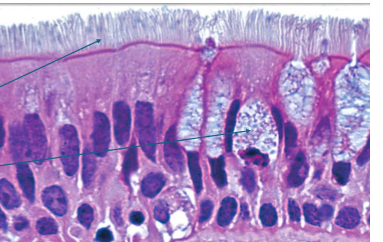
what is this?
PCCE
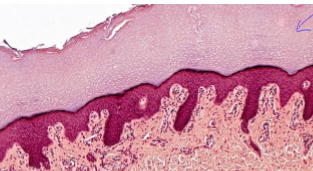
what is this?
stratified squamos epthitelial, keratinized
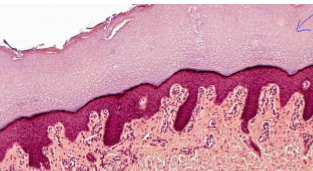
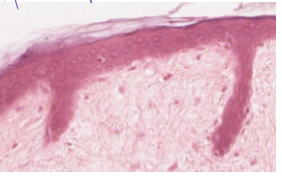
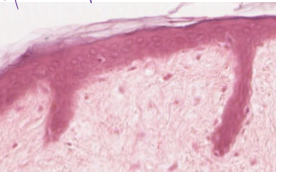
what is this?
stratified squamos epthitelial, keratinized
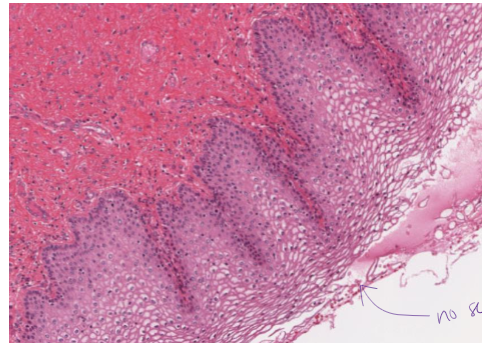
what is this?
stratified squamous epithelial, non-keratinized
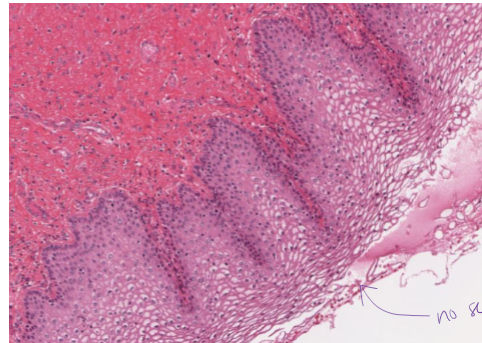
What is this?
Aerolar CT

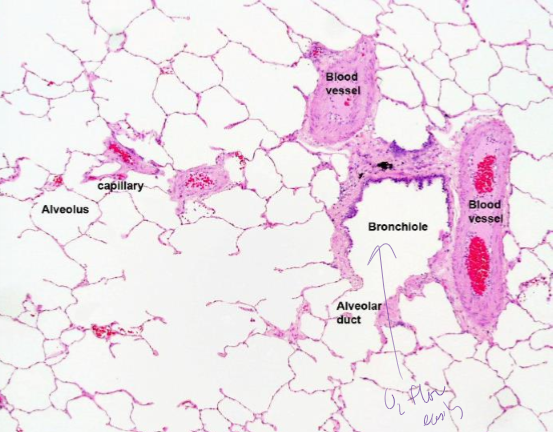
what is this?
simple squamos epithelial
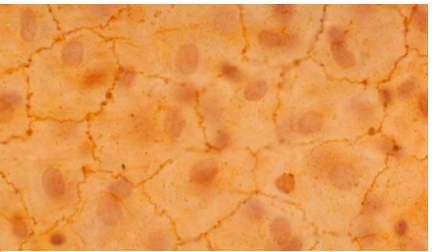
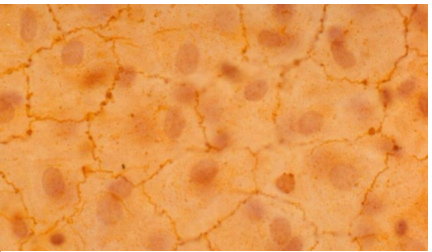
What is simple squamous epithelial
1 layer sheet
1 nuclei in each
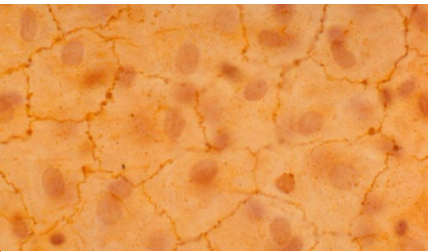
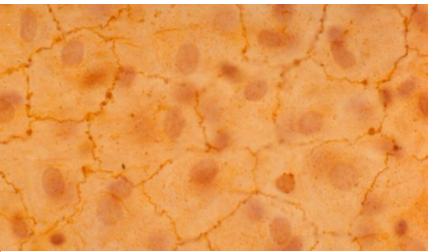
what is simple cubodial epithelial?
single layer of cells, as tall as wide
nucle in middle
absorption and secretion
kidney tubules, endocrdine glands
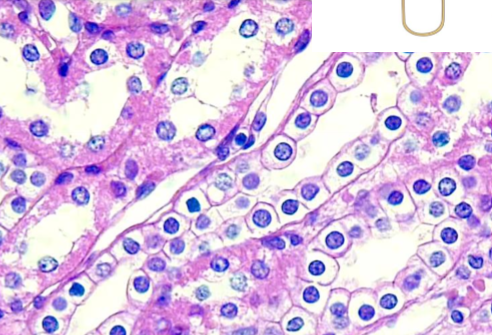
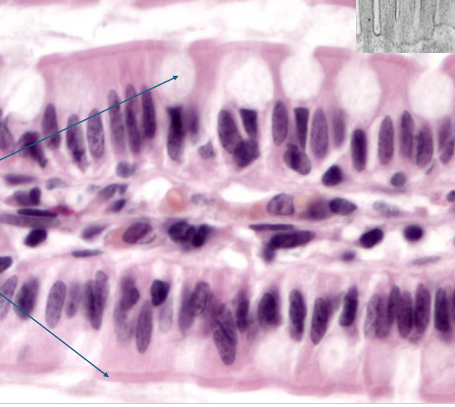
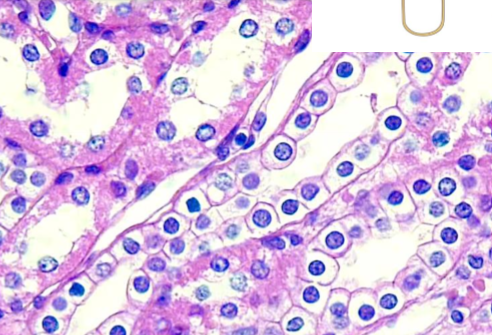
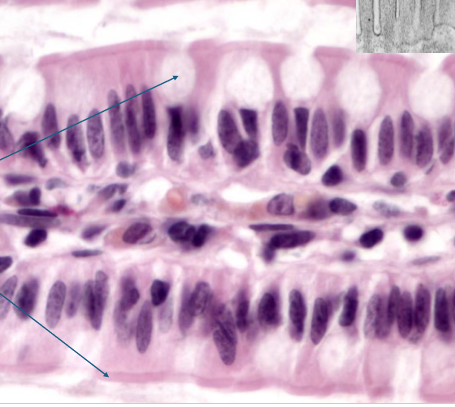
what is simple columnar ET?
taller than wide
regulated absorption and secretion
lining of digestive tract
nuclei more basal
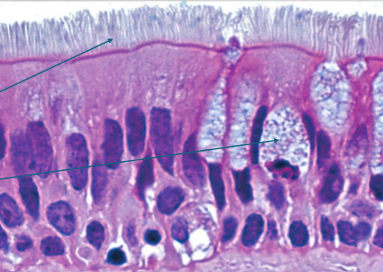
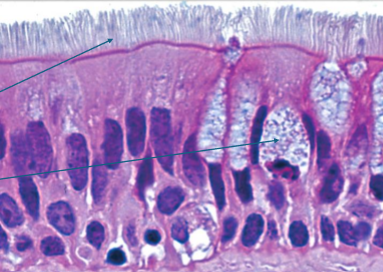
What is PCCE?
found in upper airway,s helps protect and move mucus
all cells attached to basement membrane, don’t all reach apical surface
lots of goblet cells
cilli on apical surface
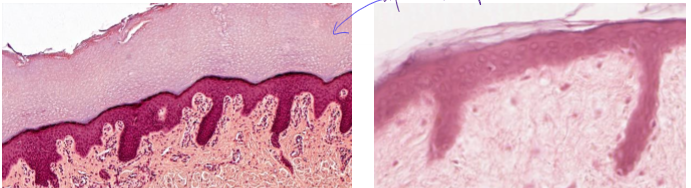
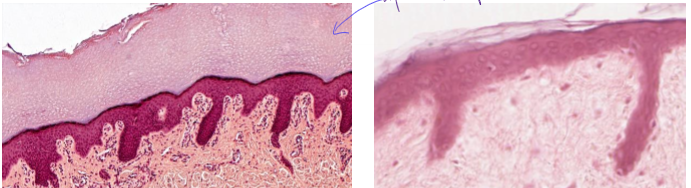
What is stratified squamous ET, keratinized?
2+ later squamous cells with keratin on apical side (no nuclei in keratin)
found on skin
surface cells are squamos
protective
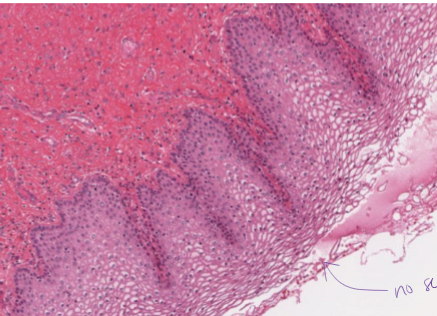
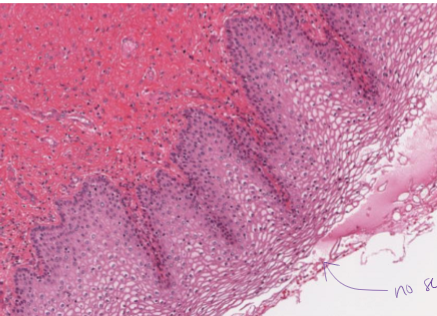
What is stratified squamous ET, non-keratinized?
2+ later flat epithelial cells with no ketain
protective
not on skin, found in mouth, esophagus, vagina
nuclei extend to edge
What are the three major components of connective tissue?
cells
protein fibers (collagen, reticular, elastic)
ground substance
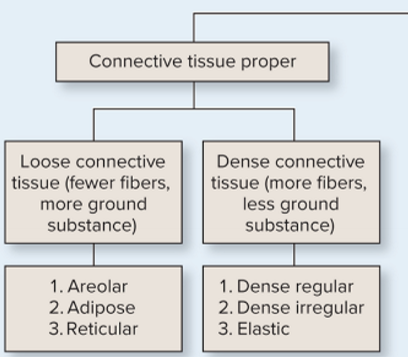
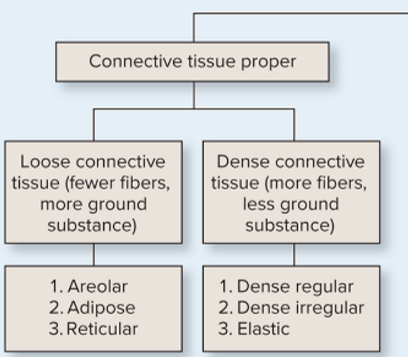
What is CT proper and what are the types of CT proper?
loose (fewer fibers, more ground substance)
dense (more fibers, less ground substance)
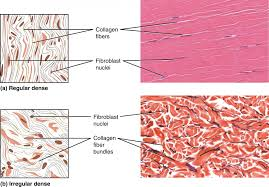
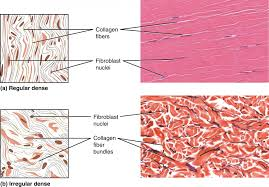
What are the types of CT proper and how do you identify them?
aerolar (loose) - mostly fluid, smaller collagen fibers and bundles. lots of fibroblasts.
aidpose (loose) - far, nuclei pushed to sides, looks like blobs
reticular (loose) - lymph nodes and spleen
dense regular CT - little ground matrix, collagen fibers in parallel; ligaments and tendons
dense irregular CT - large bundles of collagen in multiple diretions; deep dermis
elastin CT - trachea, vocal chords; dense CT
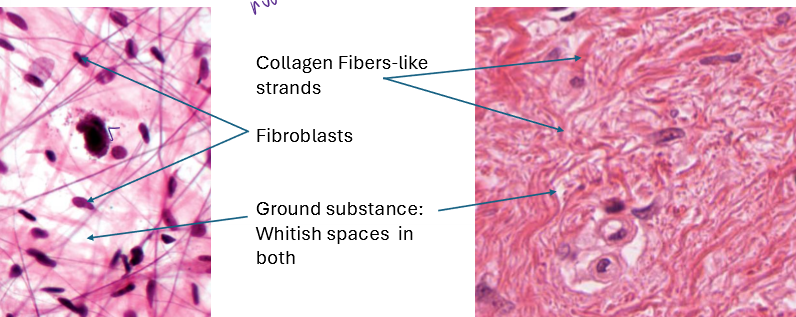
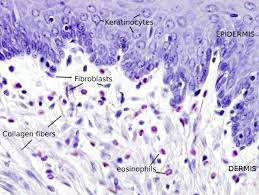
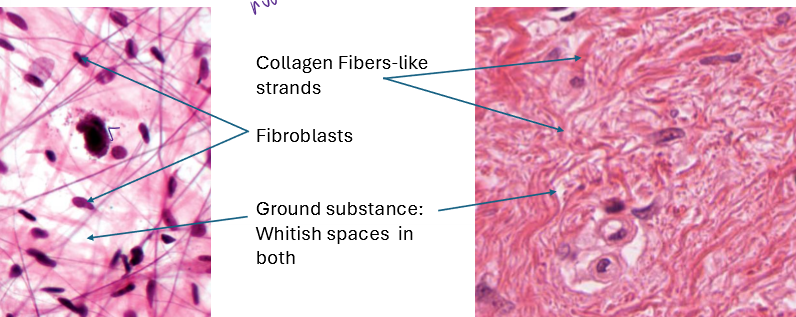
What is aerolar CT and how do you identify it?
binds tissues together
mostly fluid, smaller collagen fibers and bundles. lots of fibroblasts
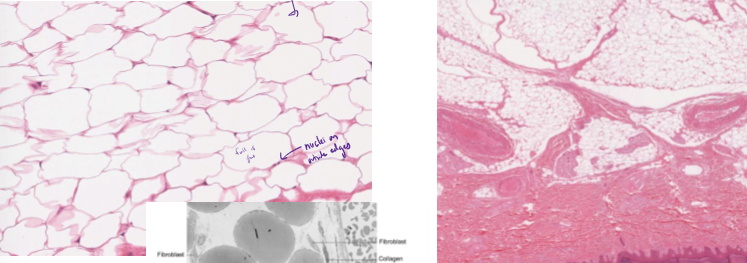
What is adipose CT and how do you identify it?
fat
nuclei pushed to sides
white blobs
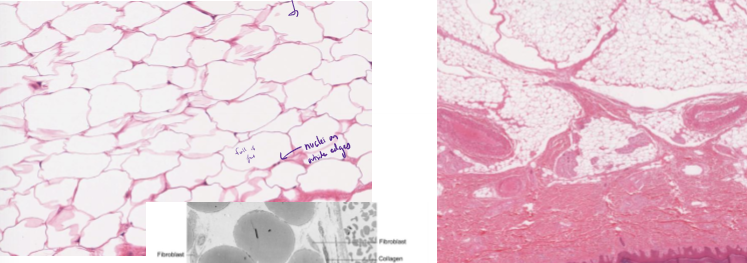
Where is reticular loose CT?
lymph nodes and spleen
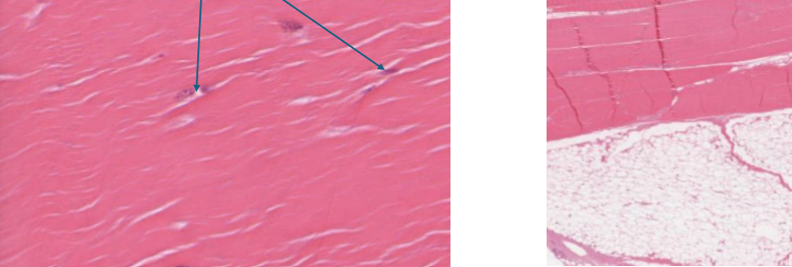
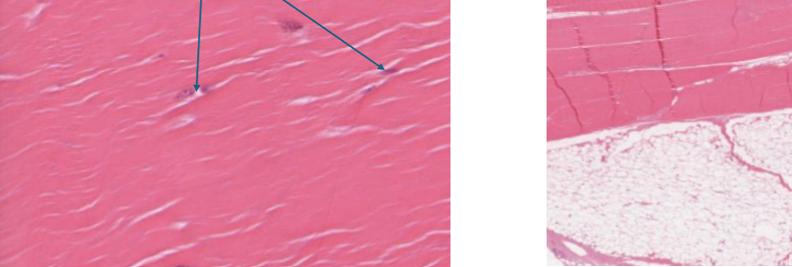
What is dense regular CT and how do you identify it?
ligaments and tendons
collagen fibers in one direction
little ground matrix, occasional fibrolasts
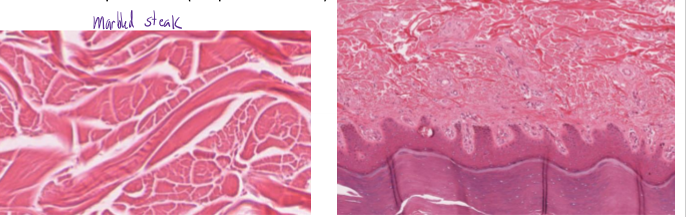
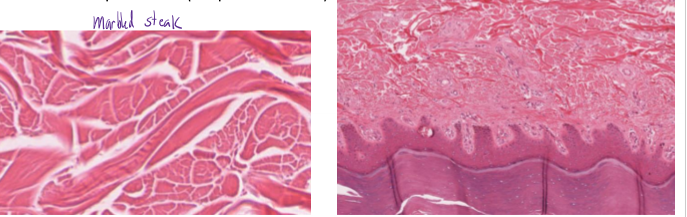
What is dense irregular CT and how do you identify it?
dense CT
collagen fibers in many directions, little ground matrix
found in deeper dermis
looks like marbled steak
What and where is Elastin CT?
dense proper CT
found in trachea and vocal chord blood vessels
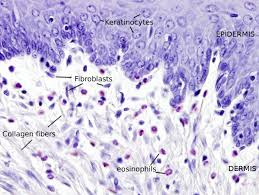
What are fibroblasts?
cells in CT that produce fibers