Test #1 ANPS 1190 Cell Chemistry, Test #1 ANPS 1190 Cell Structures, Test #1 ANPS 1190 Connective Tissue, Test #1 ANPS 1190 Cell Cycle, Test #1 Intro to Tissues and Epithelial Tissue
1/205
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
206 Terms
ion
A charged atom
cation
positive ion
anion
negative ion
ionic bond
intramolecular bond between oppositely charged ions
nonpolar covalent bond
intramolecular bond with equal sharing of electrons between covalently bonded atoms
polar covalent bond
intramolecular bond with unequal sharing of electrons
hydrogen bond
the intermolecular force occurring when a hydrogen atom in a molecule is attracted to N,O,F
hydrophilic
attracted to water (polar)
hydrophobic
repulsion from water (nonpolar)
dehydration synthesis
process of combining molecules, resulting in H2O molecule produced
hydrolysis
process of breaking molecules by splitting H2O into OH and H and then adding back to molecule
ph
the measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution
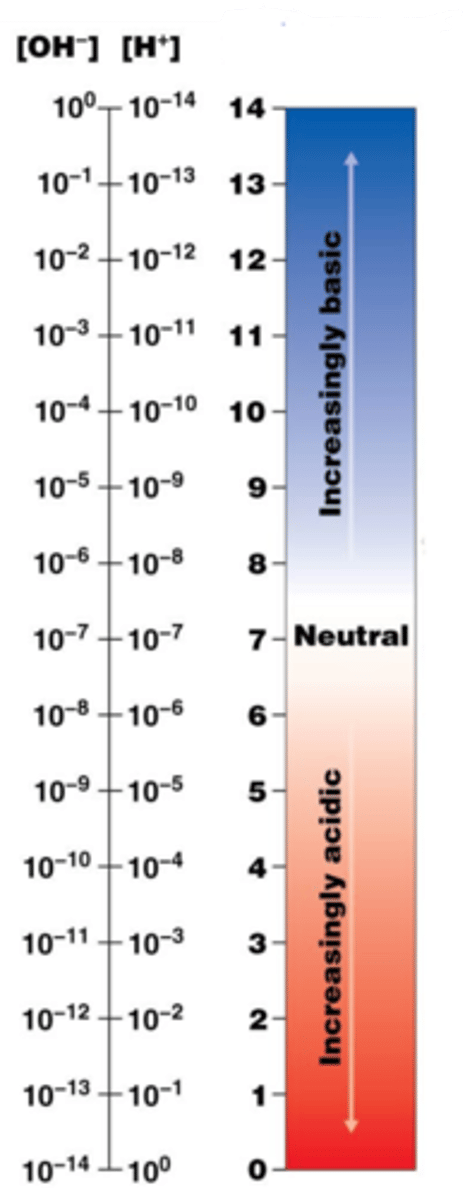
ph scale
measurement of H+ ions in solution (value of pH is negative exponent of base 10 number of H+ in solution)
lower number means higher concentration of H+
higher number means lower concentration of H+
acid
pH less than 7, higher concentration of H+ ion
base
pH higher than 7, lower concentration of H+ ion
enzyme
proteins that regulate the rate of chemical reactions in the body
Lower activation energy required
activation energy
energy required to add to system for reaction to start
denature
change in protein shape, resulting in loss of protein function
organic molecule
building blocks of human cell
carbon
can share 4 e- and may form, single, double, or triple bonds
Bond patterns can be Straight Chain, Branched Chain, or Ring
lipid
hydrophobic molecule with 5 classes:
Phospholipids/glycolipids
Fatty Acids
Glycerides
Steroids
Eicosanoids
fatty acid
energy storage in form of building blocks of lipids
Nonpolar
glyceride
lipid with glycerol backbone
triglyceride
lipid with glycerol backbone and 3 fatty acid tails
phospholipid
lipid with glycerol backbone, 2 fatty acid tails (nonpolar) and phosphorous containing head (polar) and are amphipathic
amphipathic
partially hydrophobic and partially hydrophilic
cholesterol
lipid (steroid) important in cell membrane
steroid
lipid including cholesterol and sex hormones
carbohydrate
hydrophilic compound. sugar groups are important energy sources
monosaccharide
single sugar molecule
disaccharide
2 sugar molecules
polysaccharide
many sugar molecules
glucose
most common monosaccharide in human body
glycogen
polysaccharide storage of glucose
ribose
sugar in RNA
deoxyribose
sugar found in DNA (lacking an oxygen in ring)
protein
molecule important for many structures and functions in cells
fibrous protein
allow structural support and movement of cell
globular protein
allow many metabolic processes, transports, catalysis, pH regulation, body defense, protein management
protein structure
primary: amino acid list
secondary: shapes of alpha-helix or beta-sheets
tertiary: final shape after folding from inter/intra molecular attractions, final functional shape
quaternary: if needs multiple proteins, the shape from combined proteins
amino acid
20 subunits of proteins with different radicals changing attractions and thus shape
peptide bond
bonds which connect amino acids
nucleic acid
molecule made to store and transfer info
nucleotide
base unit of nucleic acids
nucleotide bases
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine, Uracil
rna
single stranded form of nucleic acid and nucleotide base and phosphate- ribose sugar backbone
dna
2 antiparallel strands of bases with nucleotide base and phosphate- deoxyribose sugar backbone
atp
phosphorylation
intracellular
in the cell
extracellular
outside the cell
interstitial fluid
fluid between cells
plasma membranes
outside membrane of cell
phospholipid bilayer
double layer of phospolipids with hydrophobic tails facing inside and the hydrophilic heads facing out
integral membrane protein
embedded through membrane
peripheral membrane protein
embedded on either inside or outside of membrane
transport protein
allow substances through the hydrophobic membrane
ion channel protein
a pore in a cell membrane through which ions can pass
receptor protein
receptor binds on one side and opens protein on other side to signal
anchoring protein
connects membrane to cytoskeleton and to extracellular molecules
membrane enzyme
catalyze surface reactions (allow metabolic pathways)
cell-cell junction protein
allow cells to bind to neighboring cells
recognition/identity protein
allow identification (antigens read by antibody recognition proteins)
glyocalyx
carbohydrate chains branching from external cell surface
proteoglycans (protein attached to carb), glycolipids (carb attached to lipid), glycoproteins (carb attached to protein)
fluid mosaic membrane
phospholipid bilayer is freely able to move similar to a fluid
permeability
ability for particles to pass membrane
impermeable: nothing can pass
freely permeable: anything can pass
selectively permeable: things can pass but not everything without aid
passive transport
movement of substance across membrane without ATP (diffusion)
active transport
movement of substance across membrane with ATP (primary/secondary or bulk)
osmosis
diffusion of water
Tonicity in cells
isotonic- normal balance
hypotonic- low NaCl (leads to shrinking)
hypertonic- high NaCl (leads to lysis)
Cytoplasm
interior of cell, outside nucleus
membranous
organelle that have interior compartments
organelles
small structures in cell to do certain functions
double membrane
one membrane enclosed by another (nuclear membrane, mitochondria)
nucleus
most prominent, control center of cell
nucleoplasm
material within nucleus
nucleolus
areas within nucleus evident of active protein synthesis
chromatin
non condensed chromosomes
chromosome
Genetic information bundled into packages of DNA
histone protein
protein for DNA organization
gene
segment of DNA on chromosome coding for certain functions
transcription
DNA to mRNA (includes mRNA processing- splice out introns and keep exons)
translation
mRNA turned into protein/amino acid sequence with ribosome and tRNA
nuclear pore
channel in nuclear membrane for mRNA exit
complementary base pairing
DNA: A-T, G-C
RNA: A-U, G-C
mRNA
messenger RNA, allows genetic info to leave nucleus for instructions
rRNA/ribosome
site for translation
tRNA
bind to amino acids and bring to ribosome to allow polypeptide to be put together
free vs fixed ribosome
in cytoplasm vs on rough ER
loose in cytoplasm: protein is for intracellular function
rough ER: proteins to be packaged and exit cell
endoplasmic reticulum and cisternae
internal compartments of ER
membranous organelle for storage, transport, and synthesis of molecules
rough vs smooth ER
rough- produce proteins with ribosome
smooth - lipid synthesis
golgi apparatus
modify (fold) and package proteins for transport out of cell
secretory vesicle
section fuses with membrane to allow contents to be pushed out of cell
lysosome
contains digestive enzymes to break down molecules
mitochondria and christae
creates ATP in the internal folds (christae)
cytoskeleton
structural framework of the cell
microfilaments
smallest- allow movement and support
intermediate filaments
strong, resist stress, stabilize positions of organelles
microtubules
largest, long and hollow, create movement and connect to centrosome for cell division
centrioles at centrosome
form spindles to pull apart chromsomes