MICB W12 Human Defence and Sharp Injuries
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Define Innate Defenses and Acquired defences. Give 1 example of each.
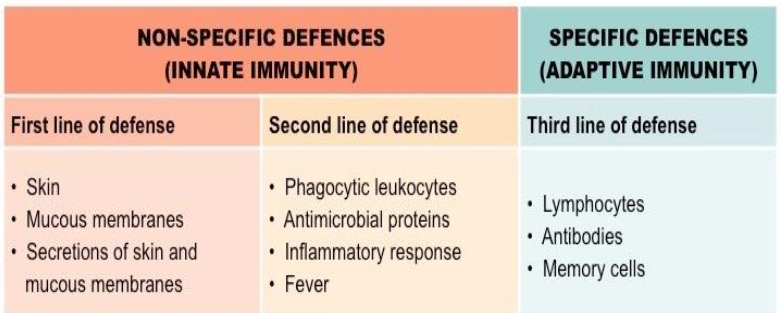
Innate = always active; first and second line of defense
Physical Barriers
Mechanical Barriers
Antimicrobial Chemicals
Cellular Barriers
Acquired = must be stimulated to be come active; third line of defense
Immune system learning to attack antigens
List examples of Physical/Mechanical barriers
skin, hair
Mucous membranes, eyes, nose, mouth, vagina
Defecation urination, vomiting
Washing action of secretions and excretions
Sticky nature of mucous
Coughing, sneezing,
List examples of Chemical barriers
Lysosome
Gastric juice
Saliva - dilutes MO’s and washes oral cavity
List examples of second line of defense - non-specific resistance
Phagocytosis
Inflammation
Fever
List examples of Third line of defense - specific resistance
Relites on antigens found in foreign microbes to initiate response
T-Lymphocytes
Cell-mediated response
helper T-cells and killer T-cells
B-Lymphocutes
Antibody mediated response
memory cells
plasma produces antibodies
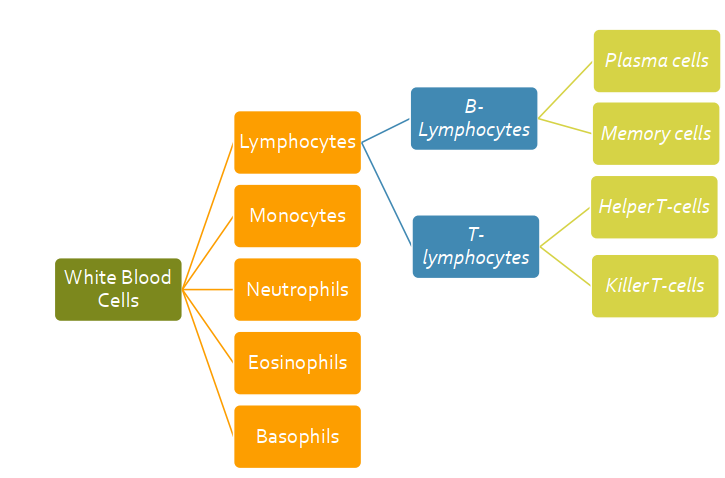
What are the 5 main types of Leukocutes (WBC)?
Lymphocyte
Monocytes
Neutrophils
Eosinophils
Basophils
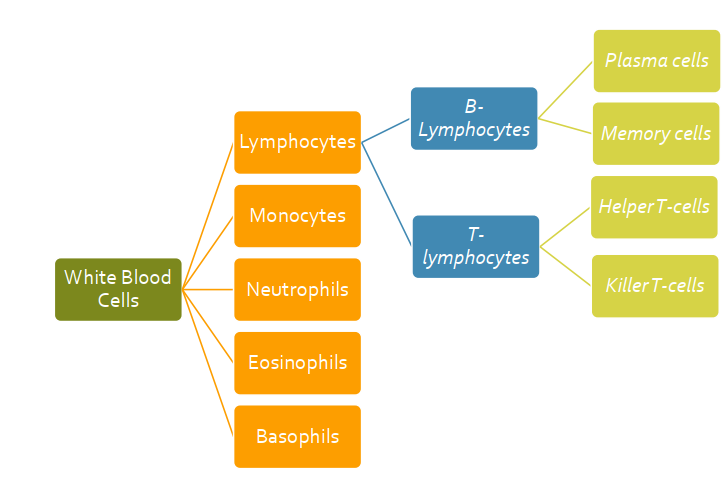
Describe Lymphocytes
more common in lymph than in blood
longest life span (memory cells)
include: be cells (plasma and memory) and T cells (helper and killer)
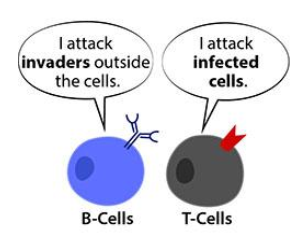
What kind of leukocyte is often referred to as “antibody mediated response”
B-lymphocytes (B-cells)
What is the function of Plasma B-cells?
Produces antibodies which bind to antigens of foreign particles so they can be eliminated
How Plasma B Cells Work
Antigen Encounter: When a B cell encounters a specific antigen (a foreign substance), it differentiates into a plasma cell.
Antibody Production: The plasma cell then produces antibodies that are highly specific to that antigen.
Antibody Release: These antibodies are released into the blood and lymphatic systems.
Target Neutralization/Destruction: Once in the bloodstream, the antibodies find and bind to their target antigen, leading to its neutralization or destruction by the immune system.
What is the function of Memory B-cells?
Is activated in response to a second encounter with a pathogen.
memory cells can live for years unlike most WBC which may only live a few days
Compare and contrast Helper T-cells and Killer/cytotoxic T-Cells.
Helper T-cells (CD4⁺):
Function: “Managers” of the immune response.
Release cytokines to activate B-cells, macrophages, and cytotoxic T-cells.
Do not directly kill infected cells.
Cytotoxic/Killer T-cells (CD8⁺):
Function: Direct “attackers.”
Bind to and destroy virus-infected, tumor, or transplanted cells by releasing perforins and granzymes.
Work after activation, often signaled by Helper T-cells.
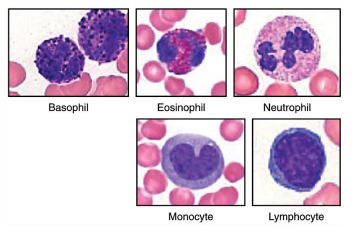
Describe Monocytes and its function.
Monocytes are large, circulating white blood cells with a kidney-shaped nucleus.
Largest WBC
Phagocytic
Turn into macrophages when they leave the blood stream
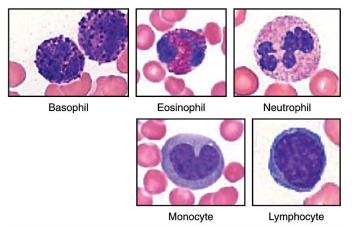
Describe Neutrophils and its function.
Neutrophils are the most abundant granulocytes; first responders to infection
makes pus
phagocytic
often referred to as PMNs=Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes
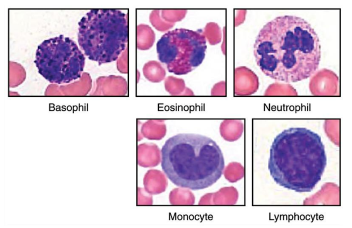
Describe Eosinophils
Found mostly in mucous membranes
deals with parasitic infections and allergic reactions
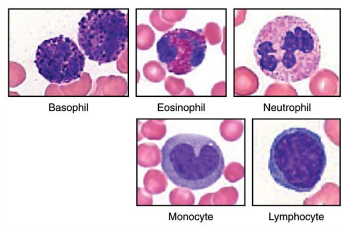
Describe Basophils
rarest of the WBC
responsible for allergic and antigen response by releasing histamines
Inflammation is ___ line of defense. Describe the process.
Second line of defense - innate immunity
Blood supply to site increased
Capillary permeability increased to allow immune cells to reach the site
Neutrophils and macrophages are already present at the site
WBC migrate from capillaries into affected tissue
What is the sequence of WBC arrival the site of affected tissue?
*Neutrophils are the earliest cell to arrived, then monocytes/macrophages, then lymphocytes
Neutrophils → monocyte/macrophage → lymphocytes
Phagocytic cells are part of the __ line of defense. How do they work?
2nd line of defense of innate immunity
Phagocytic cells are constantly patrolling to destroy any foreign particles/pathogens
Cell membrane of a phagocyte will surround bacterial/pathogen to create a pocket that will enclose the bacteria. = phagosome
Lysosome merge with phagosome = phagolysosome
Lysosomal enzymes released into the phagosome to kill the bacteria
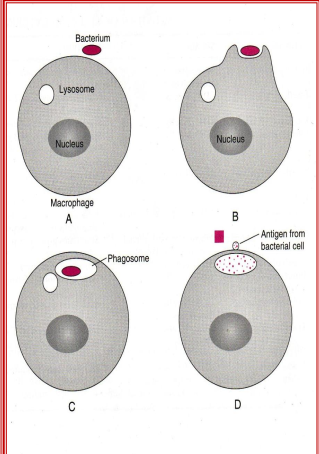
Most of the time ___ and ____ function as low-level garbage collectors.
Macrophages and Neutrophils
Which conditions is not protected against by our Long-term immunity?
Dental caries, periodontal disease, gonorrhoea, common cold
What is Artificial Immunity?
The immunity we get by being immunized or vaccinated against a specific disease
What are examples of damages by our own immune system to our body?
antibody-mediated allergic reaction in nose/eyes = hay fever or respiratory = asthma
anaphylactic shock → allergy to a substance causing widespread reaction affecting blood stream, lungs and heart
contact dermatitis → cell-mediated allergic reaction to something
Percutaneous injury
through the skin injury
What are the main diseases that are primarily associated with sharp injuries ?
Hep B, HepC and HIV.
What is the CDHO IPAC definition of Handling Sharps and Exposure prevention?
Sharps are devices that are capable of causing a cut or puncture wound. Sharps should be kept out of the reach of clients and safely collected in a clearly labelled puncture-resistant container at point of use and/or must be transported to the reprocessing area in a leak-proof covered container
(i.e. plastic tray with a secured hard plastic cover) or cassette.
Blood-borne pathoigens exposure can occur via…
percutaneous injuries
non-intact skin
through the eyes, mouth, nose
What must be included in the exposure management protocol in the IPAC manual?
First aid procedures
Treatment procedure
What must be documented in the Exposure Management Report?
Documentation of the incident
Name and vaccine status of persons exposed
Record date and time of the incident and what was the Occupational Health Care Worker doing, including DH procedure being performed
Identify what preventative measures were being implemented at the time (ex. utility gloves while handling sharps)
Document name and health status of source person if known; include any blood-borne diseases (ex. Hep B, HepC, HIV)