Neuro midterm
1/51
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pt 1, covers lectures 1-4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What are the 2 MAIN divisions of the nervous system?
Central and peripheral
The brain and spinal cord make up the _____ nervous system?
Central
What are the 2 divisions of the peripheral nervous system?
Somatic and autonomic
The somatic NS is made up of the somatic _______ and the somatic ____ systems.
Sensory, motor
what is the somatic NS responsible for?
Transmits sensory input and controls muscle movement.
what are the 2 subdivisions of the autonomic NS?
Sympathetic and parasympathetic
What is the function of the sympathetic NS?
Manages stress, danger, or intense physical activity. “Fight or flight.“
What is the function of the parasympathetic NS?
Energy conservation, digestion, waste elimination. “Rest and digest.“
What is the function of microglia?
Immune surveillance and phagocytosis
What is the function of ependymal cells?
Creates and circulates cerebrospinal fluid
These cells maintain the extracellular environment, remove excess neurotransmitters, direct neural growth, and induce the blood-brain barrier in the CNS.
Astrocytes
The equivalent of astrocytes in the PNS
Satellite cells
These cells create myelin in the PNS
Schwann cells
These cells create myelin in the CNS
Oligodendrocytes
What are the 4 functional zones of a neuron?
Input, integration, conduction, output
What structure(s) are in the zone of input?
Soma and dendrites
What structure(s) are in the zone of integration?
Axon hillock
What structure(s) are in the zone of conduction?
Axon
What structure(s) are in the zone of output?
Axon terminal
Which functional zone communicates with other cells through neurotransmitter release?
Zone of output
What does the zone of integration do?
Sums up incoming IPSPs and EPSPs to decide whether to fire an action potential
What does the zone of conduction do?
Transmits the action potential
In which functional zone does postsynaptic potentials occur?
Zone of input
What is a unipolar neuron?
Only has one process that extends from the soma
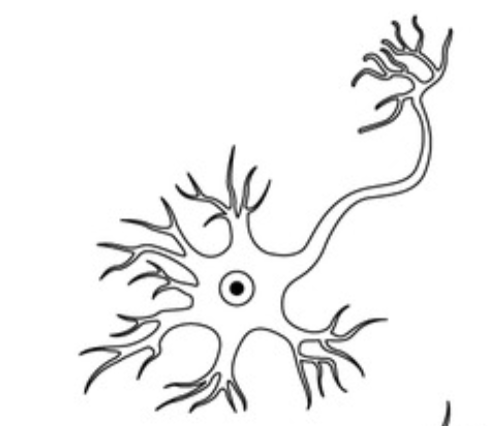
Is this a unipolar, bipolar, or multipolar neuron?
Multipolar
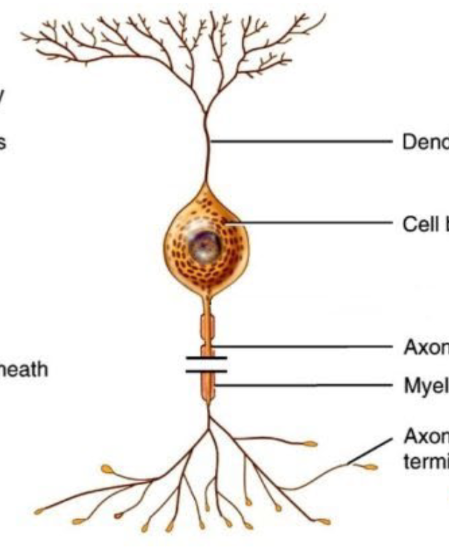
Is this a unipolar, bipolar, or multipolar neuron?
Bipolar
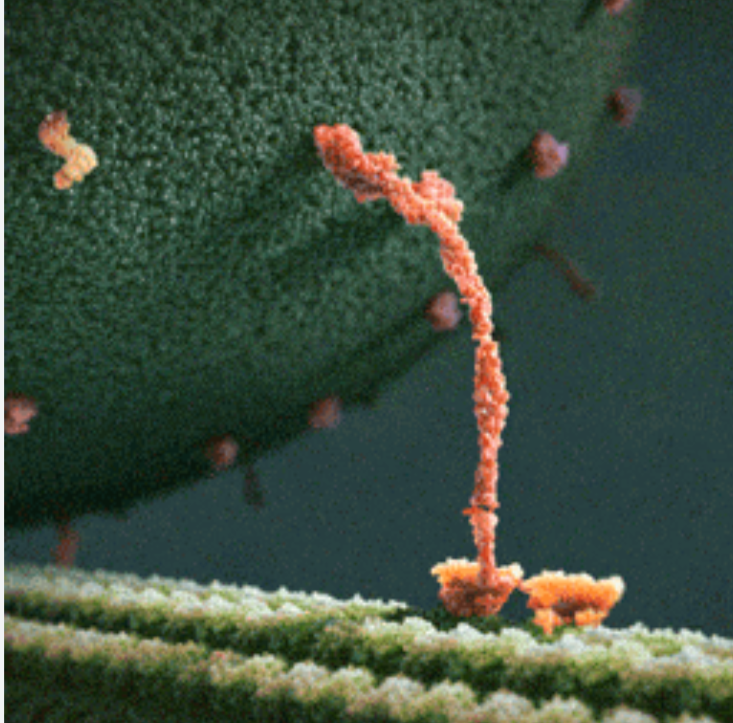
Who is this cunty diva and what does she do
Motor protein; travels on microtubules transporting vesicles and organelles
What direction do kinesins travel in?
Anterograde(away)
What direction do dyneins travel in?
Retrograde(return)
These motor proteins travel on actin in the periphery of the neurons
Myosin
Organize the levels of compartmentalization from most to least broad: nuclei, wiring diagrams, tripartite brain, and cell type.
Tripartite brain(most broad), nuclei, wiring diagrams, cell type(finest).
Is the inside of the cell more positive or negative for a resting membrane potential of -70mV?
More negative
At rest, does a neuron cell have a higher intracellular or extracellular K+ concentration?
Intracellular
At rest, does a neuron cell have a higher intracellular or extracellular Na+ concentration?
Extracellular
Does K+ move inside or outside the cell through leak channels?
Outside
What is the primary driving force of K+ movement across the membrane? Electric, chemical, or both?
Chemical due to the small concentration of K+ outside. However, there is a small electric force pushing K+ inside, which is overpowered by the chemical force.
Does Na+ move inside or outside the cell through leak channels?
Inside
What is the primary driving force of Na+ movement across the membrane? Electric, chemical, or both?
Both forces push Na+ inside the cell.
What is equilibrium potential?
The voltage at which there is no net movement of ions across a membrane
What is the chloride potassium symporter?
Drives Cl- out the cell using the diffusion force from K+.
This equation calculates RMP while considering the permeability and concentration gradients of ions.
Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation
This equation gives the equilibrium potential for an ion at any given concentration gradient
Nernst equation
Once the threshold has been reached, what event is responsible for the rising phase of an action potential?
Voltage gated Na+ channels open; Na+ rushes into the cell
True or false: the rising phase is hyperpolarization
False
What event(s) are responsible for the falling phase of an AP?
Na+ channels inactivate while K+ continues to leave the cell, making the inside of the cell more negative.
How do cells return to RMP after the undershoot?
K+ channels close while Na+ channels deinactivate, allowing some Na+ to enter the cell.
What does tetrodotoxin do?
Blocks voltage gated Na+ channels, inhibiting action potential firing
What will increasing axon diameter do to action potential velocity?
Decreases internal resistance, allowing ions to diffuse farther
How does increasing myelin increase action potential velocity?
Increases membrane resistance. Restricts membrane proteins to nodes, increasing conductivity
Nodes of ranvier contain high concentrations of _____ which regenerate ____.
VG ion channels; action potentials
What is saltatory conduction?
APs travel rapidly down insulating myelin and “jump“ between nodes of ranvier, allowing for increased speed and efficiency.
Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks ____.
myelin sheath