4.1 use basic scientific measurements and measurement tools
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
The SI base units for mass, length and time are
kilogram, meter, second
International System of Units ( SI Units)
a system of physical units based on the meter, kilogram, second, celcius, and kelvin together with a set of prefixes to indicate multiplication or division by a power of ten
* SI units are also used to measure volume.(liter)
7 base units
Kilogram, meter, second, mole, kelvin, candela, ampere
Meter (M)
instrument for measuring length
* Abbreviation M
kilogram (kg)
*SI unit for mass
*measures mass
Second
SI base unit for time
Ampere
*unit of electric current
* measures electrical current
Kelvin (K)
SI unit for temperature
Kelvin = Celsius + 273
mole (mol)
the SI base unit used to measure the amount of a substance
* measures amount of a substance.
Candela ( cd)
the standard unit of luminous intensity
* measures luminous intensity
Length
Distance between two points, measured in meters.
metric ruler/meter stick
instrument used to measure length .
( si uses the meter end of the ruler)
The SI base unit for volume
liter (L)
Surveyor's wheel( measuring wheel)
Used to determine longer or along nonlinear path.
Measuring tape
Measures length in inches or centimeters.
* inches are divided into 1/16th of an inch and centimeters are divided into millimeters.
. measures linear distances
linear distance
how far across the earth a person, an idea, or a product travels
Nonlinear distances
Mass
*A measure of the amount of matter in an object
Volume
The amount of space an object takes up or occupies.
* Volumes are measured by using glassware or plasticware.( in liters)
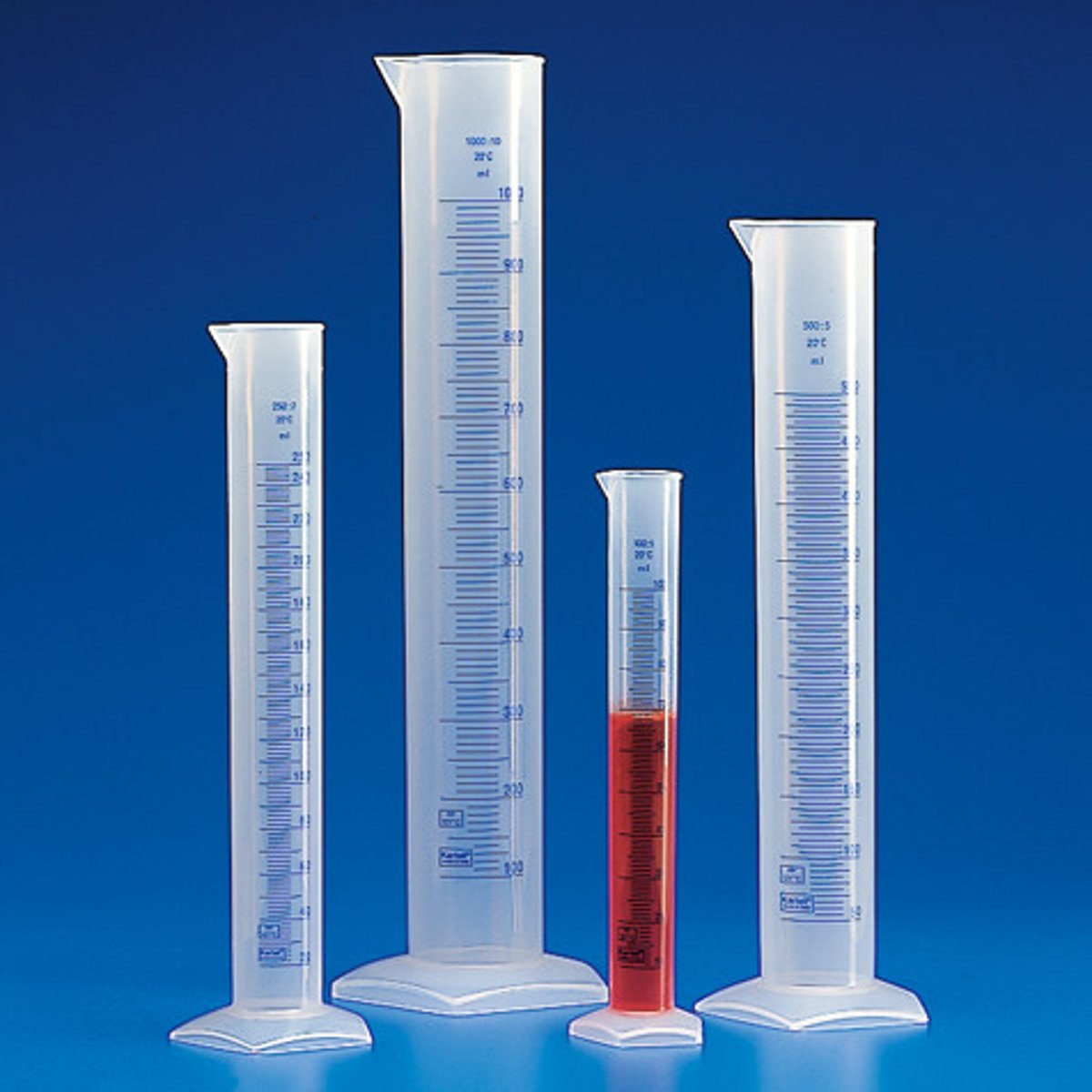
graduated cylinder
*used to measure the volume of a liquid.
* used when measurements does not need to be precise.
measures volumes ranging from 10ml to 1000 ml or 1 liter.

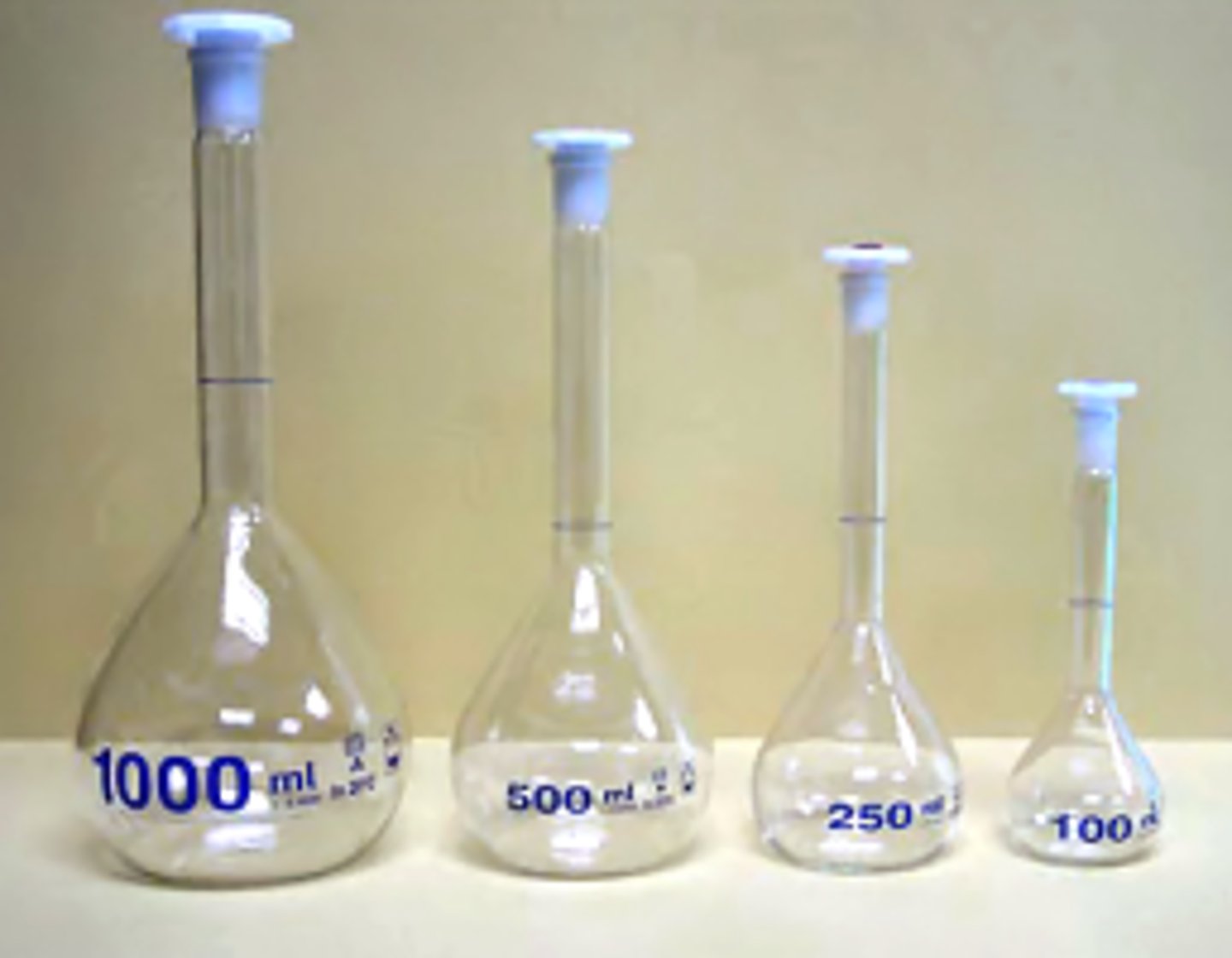
volumetric flask
*used for making liquid solutions of precise volumes.
* each volumetric flask is calibrated for a single volume
*The most accurate way to measure large volumes of liquid.

Pipettes
measures small amounts of liquids accurately
Graduated pipettes
* delivers measurements ranging from 0.1 to 25 ml and can easily dispense liquids in small increments
*Different Volumes
Two Types = Mohr and Serological
*Consist of a long tube with a series of graduations or marks to indicate different calibrated volumes.
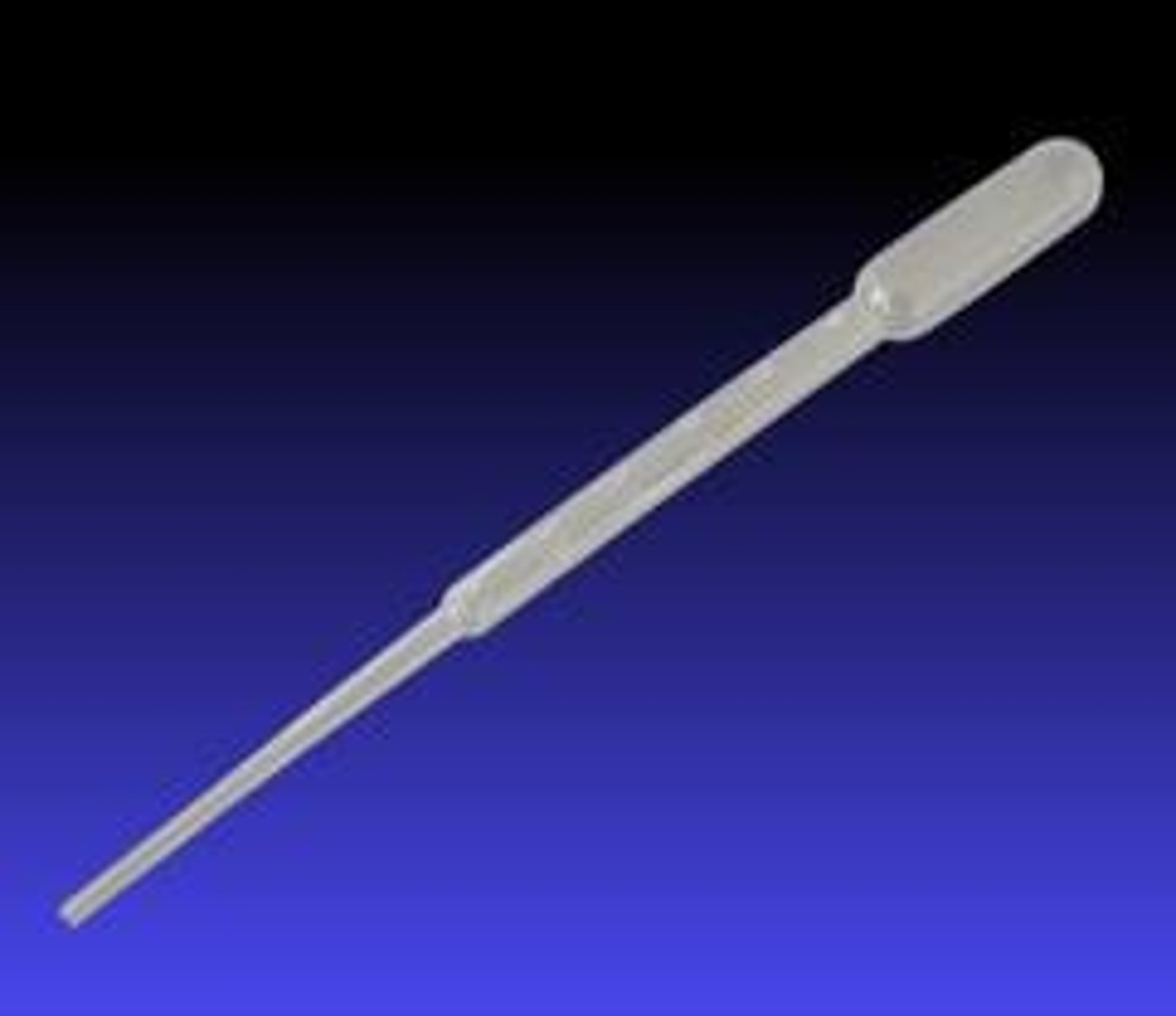
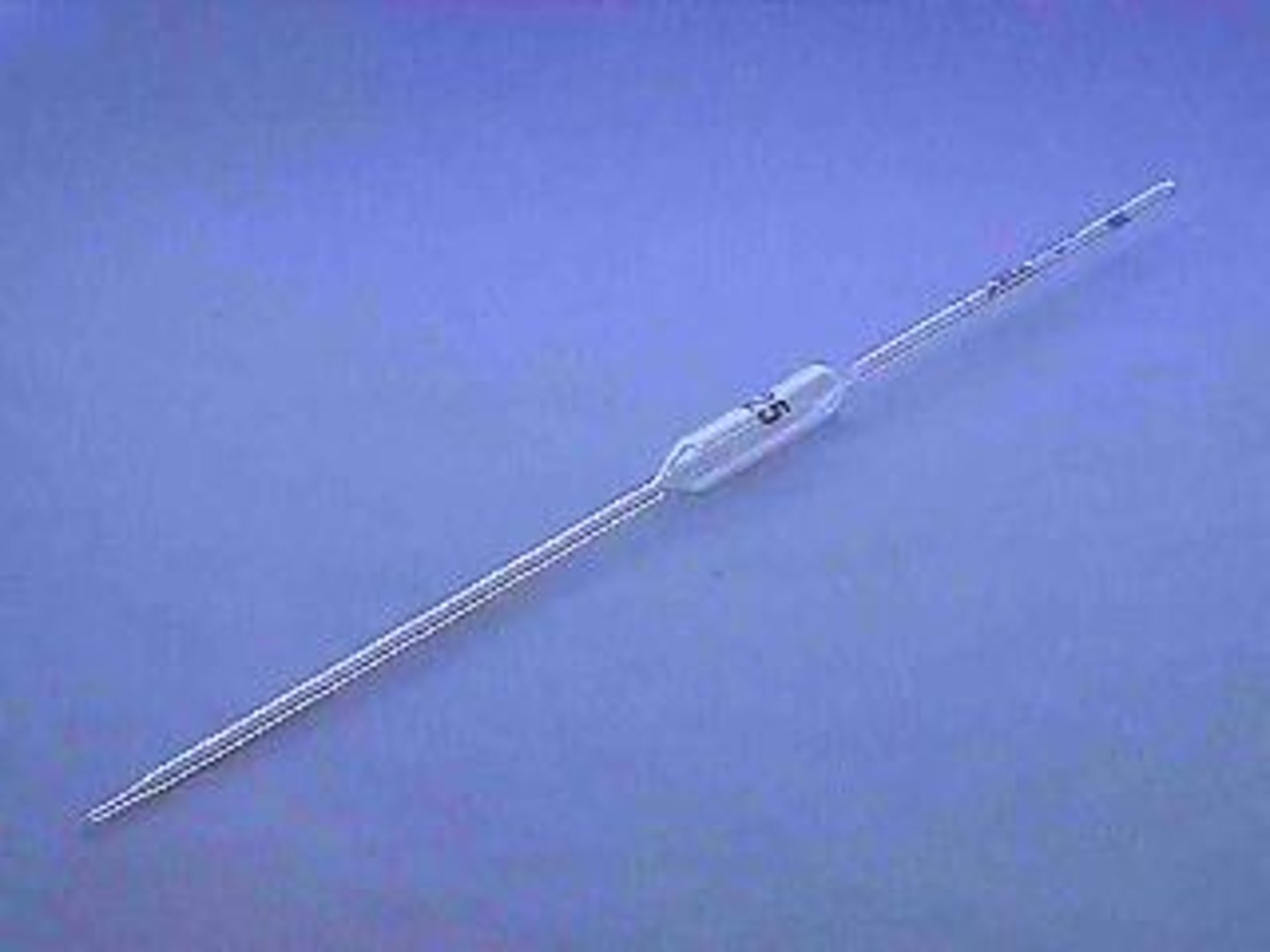
Volumetric pipettes
* are preferred for high precision work.
*calibrated to deliver accurately a fixed volume of a dilute aqueous solution.
*best used to measure small amounts of liquid.

Meniscus
the curve at a liquid's surface by which one measures the volume of the liquid
* can be concave, convex or flat depending on the properties of the liquid.
concave
curving inward ( upward)
Convex
curved outward ( downward).
SI Unit Prefixes
*Used to change SI units by powers of 10
*Kilo, Hecto, Deka, BASE, deci, centi, milli (acronym) King Henry Died By Drinking Chocolate Milk
Kilo (1000)
Value of prefix= One thousand/1000
Abbreviation- km= kilometer
Hecta (100)
Value of prefix= One hundred/ 100
Abbreviation- hm= hectameter
Deca( 10)
Value of prefix= Ten
Abbreviation- dam= decameter
Base SI Units (1)
Gram, liters, meter
deci (0.1)
Value of prefix=
Abbreviation
milli (0.001)
Value of prefix= One thousandth
Abbreviation- mm= millimeter
centi (0.01)
Value of prefix=
Abbreviation- cm=centimeter
micro
Value of prefix= One millionth
Abbreviation- = micrometer
Kilo, hecta, deca,
Multiply by 10
Centi , milli deci
Divide by 10
dimensional analysis
a technique of problem-solving that uses the units that are part of a measurement to help solve the problem
measuring instrument for mass
Triple beam balance and electronic balance.
Triple beam balance
instrument used to measure mass in grams
* measures in 1, 10, 100 gram increments.
Electronic balance
measures mass of an object in grams
analytical balance
*Measures small amounts of materials
*Used measure the mass of substances to +/-0.0001 precision.
*often called a "lab balance" designed to measure small mass in the sub-milligram range. The measuring pan of an analytical balance (0.1 mg or better) is inside a transparent enclosure with doors so that dust does not collect and so any air currents in the room do not affect the balance's operation
Sound waves or sonar
Are used to map ocean depths
Beams of light or electromagnetic radiation
Measures the distance planets.
The speed of sound
1500 meters per second
Distance equals
speed of sound x time