Cell Bio - Biomolecules Lectures 1
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
what is organic molecule?
An organic molecule is a compound primarily consisting of Carbon and Hydrogen bonds, and also other main atoms like oxygen and nitrogen.
Living organismes consist or carbon-based compounds bc 4 covalent bonds → large, complex, diverse molecules eg. proteins, dna, carbs
Carbon chains = skeletons of most org molecules
functional molecular groups
the 4 macromolecules
carbohydrates
proteins
nucleic acids
lipids (not polymers)
all living things are made of these macromolecules, that are covalently bonded and play essential roles in biological processes.
molecular stucture and function are inseparable
top 5 elements found in human body
CHO CHO CHON CHOP
molecules vs compounds
Molecules are groups of two or more atoms bonded together, while compounds are molecules that contain at least two different elements.
All compounds are molecules, but not all molecules are compounds.
eg. CH4 is a compound, H2 is a molecule (pure element)
Covalent Bonds
strong bonds between atoms, they share one or more pairs of electrons, usually between non-metals to form molecules.
They can be polar or non-polar
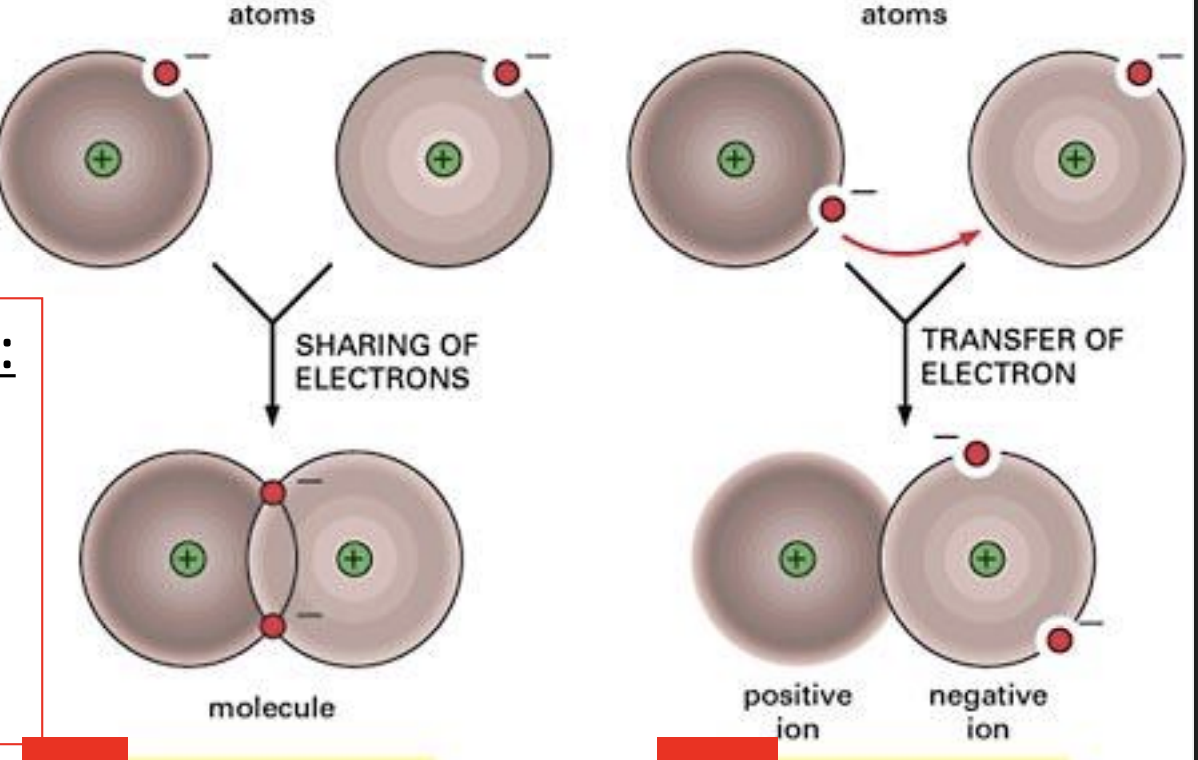
Ionic Bonds and what are ions?
complete transfer of electron(s) → ions: an atom or molecules w 1 or more units of electrical charge
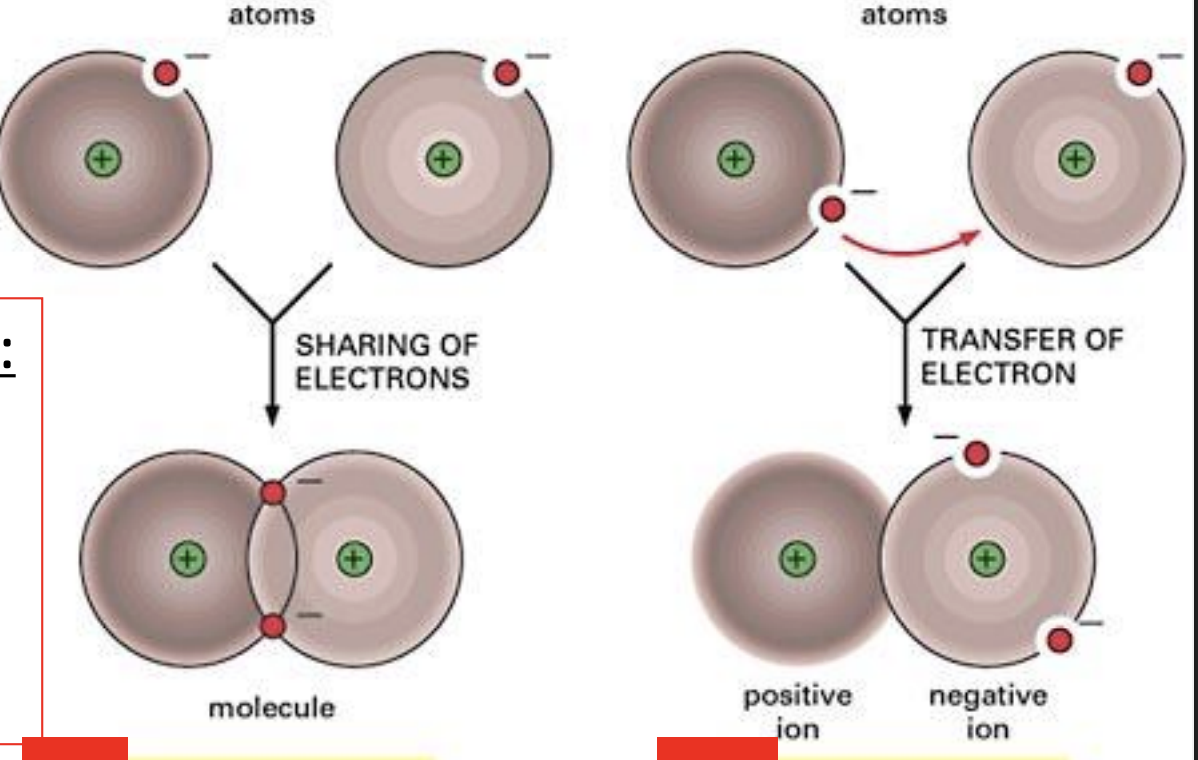
the types of chemical bonds and their function
Between atoms: covalent and ionic (strong bonds)
Between molecules: hydrogen (weak bonds)
Strong bonds want to complet outer shell (octet rule), either by sharing or transferring
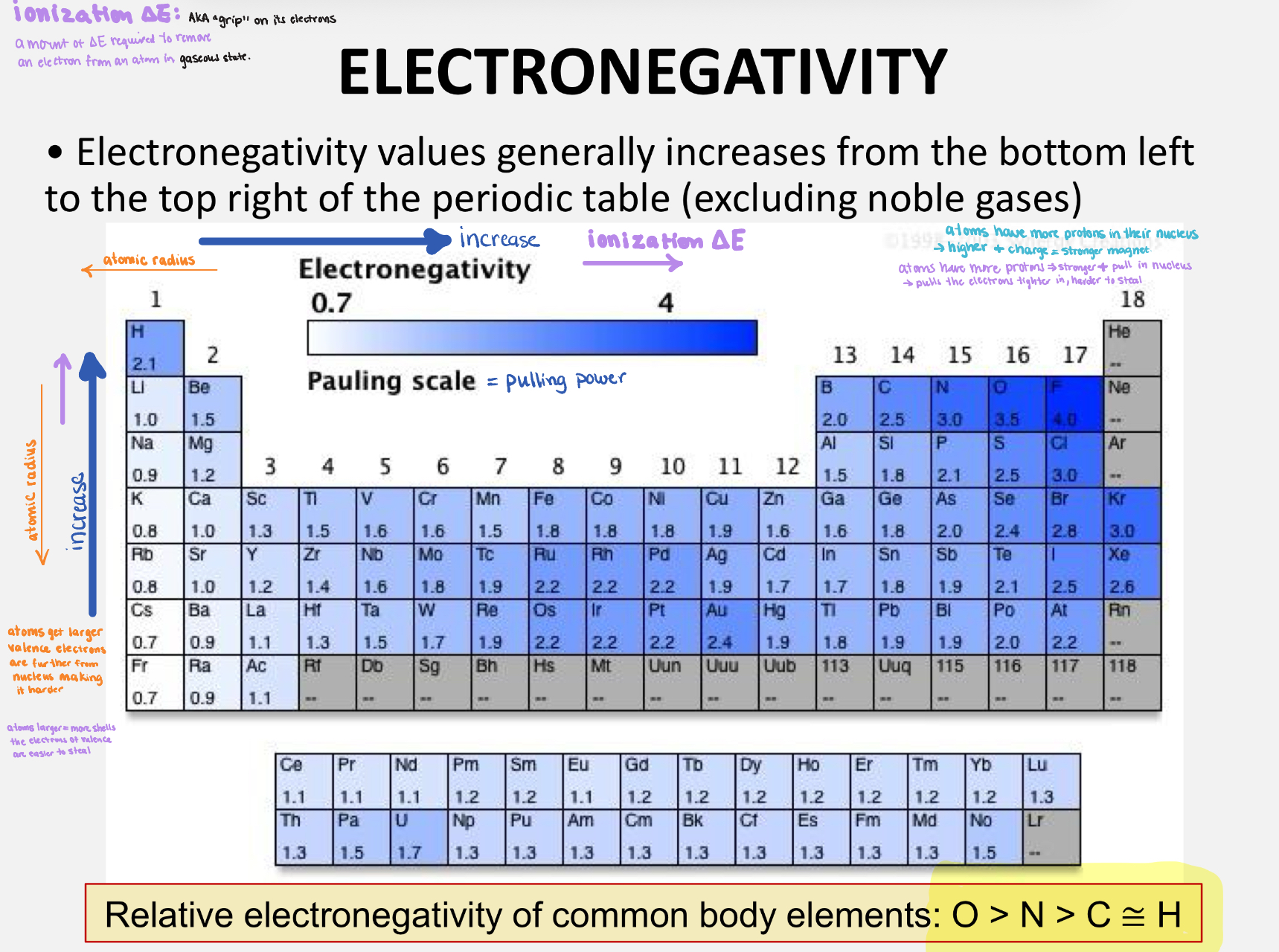
Polartiy and Electronegativity
Covalent bonds are strong so require lots of energy to break them, and they store a lot of energy (metabolism)
Covalent bonds are polar or non-polar depending on difference of Electronegativity of atoms (how greedy, how much attracts)
i- non-polar: electrons shared equally eg.CH4, lipids
ii- polar: atom > electronegativity pulls electrons closer→ poles
Molecule as a whole is neutral
O>N>C=H
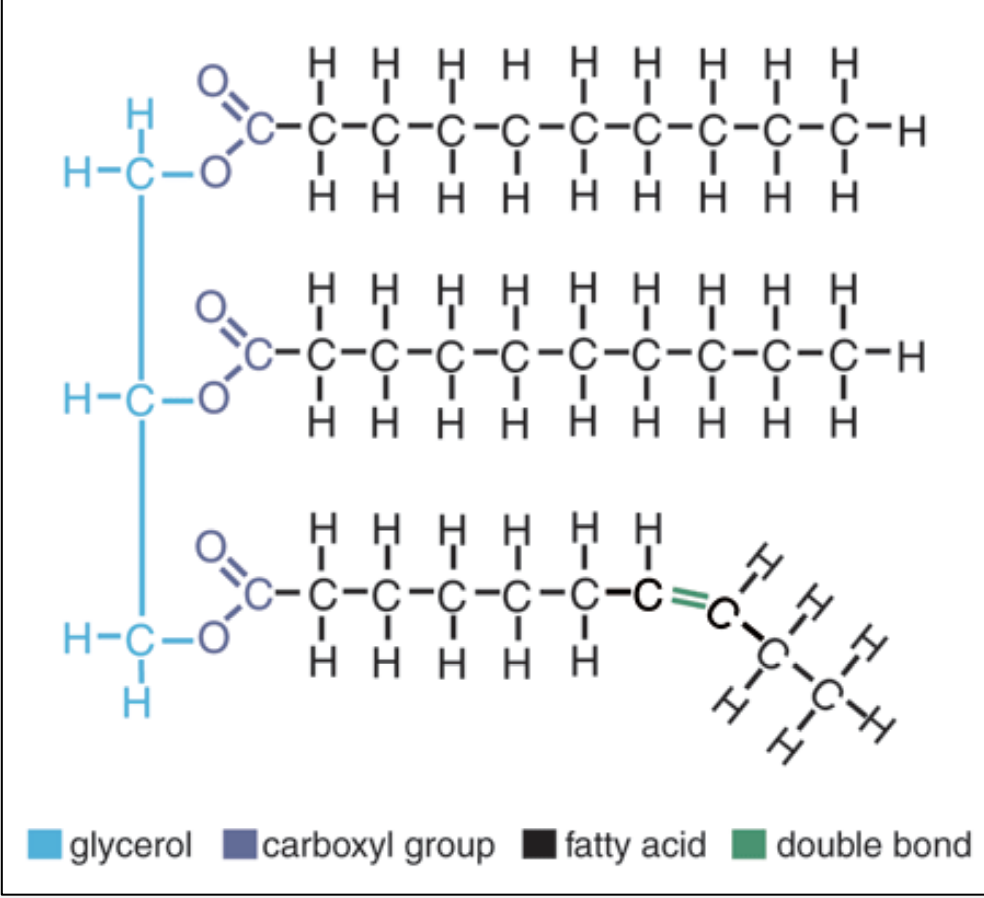
Table of elements, electronegativity, ionization, atomic radius
Lipids
four rings, consist of C - H covalent bonds→ non polar
b/c of this→ Hydrophobic
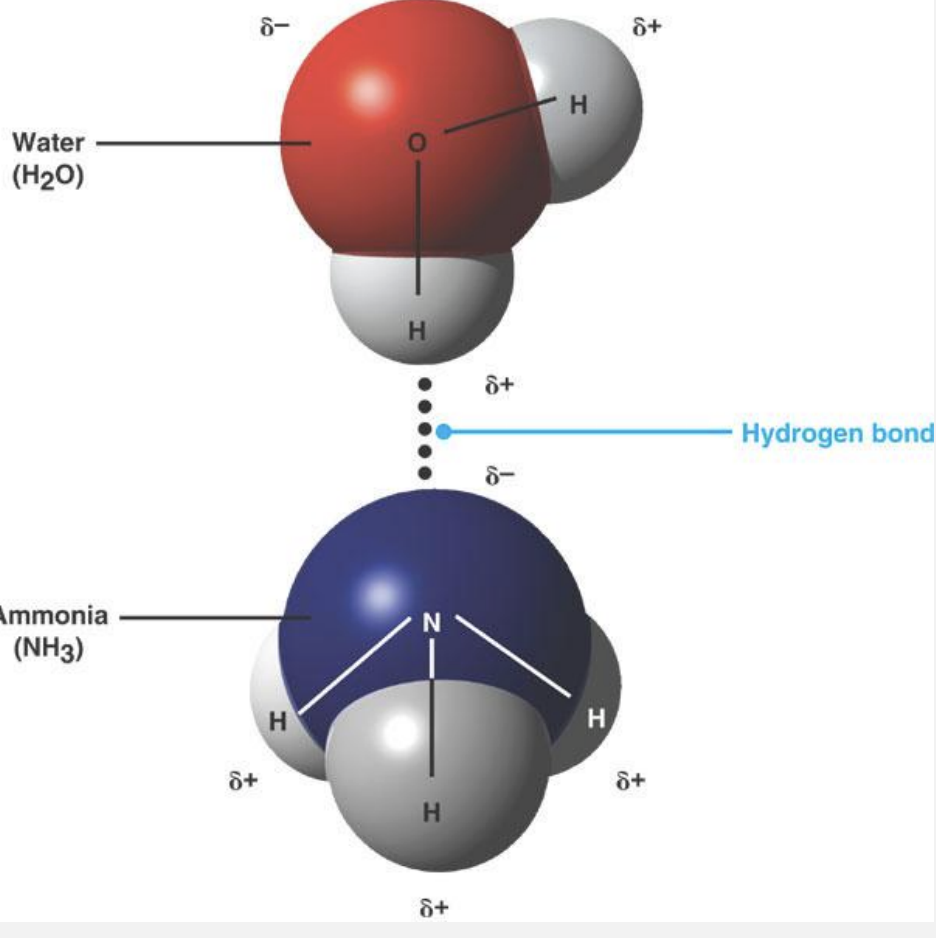
weak bonds
molecules to interact
-adhering molecules briefly when collide
stability within large molecules (proteins, dna)
hydrogen bonds
often -OH, -NH, -SH, very important in livings bc many water molecules
inter/intramolecular
individually they are weak, but strong in numbers (DNA)
molecular shape and function
molecules recognize, interact and respond based on shape
similar shapes → similar bio effects
shape based on electronegativity
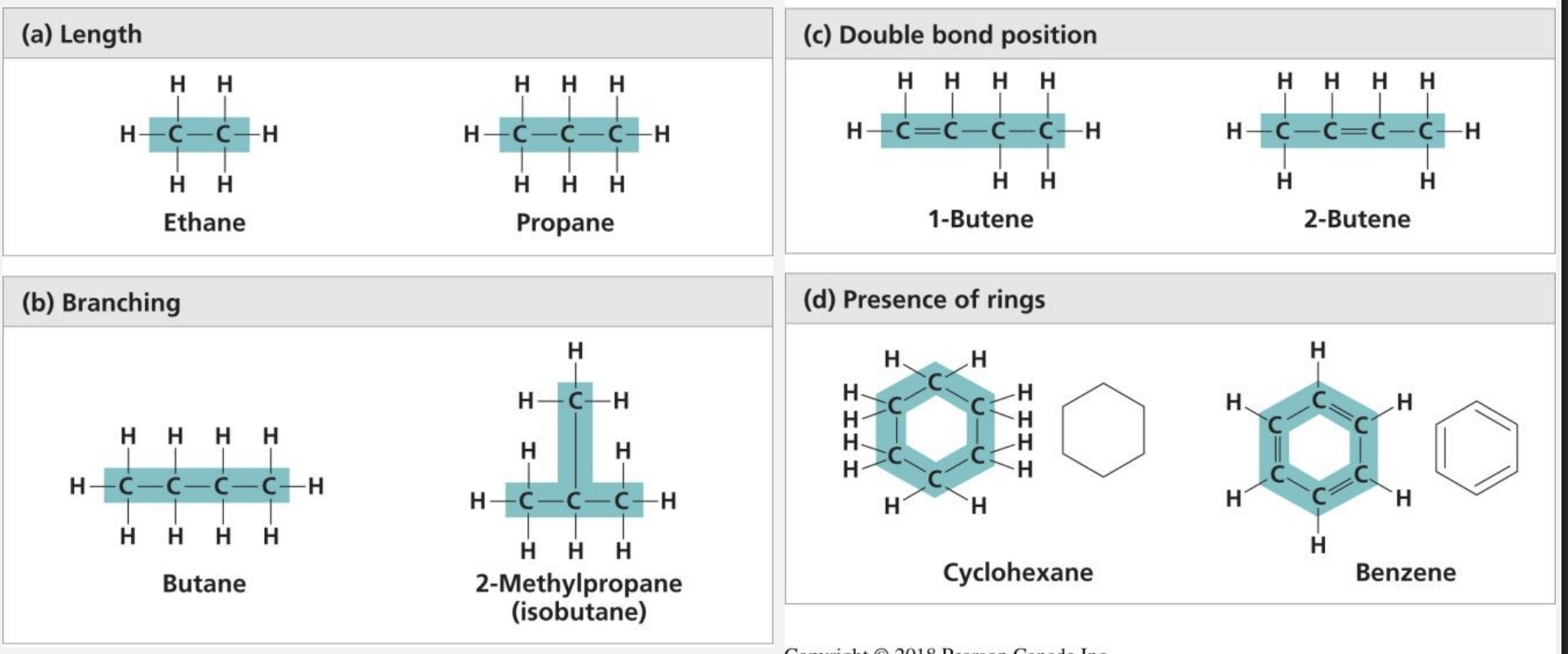
hydrocarbons
only C and H, many org molecules eg. fats
release a lot of energy (covalent bonds )
hydrophobic (bc non-polar)
functional groups
atom groups w function, attached to carbon skeletons, most form ionic and hydrogen bonds w other molecules
can cause hydrophilic properties (soluble)
non-polar → hydrophobic properties
macromolecules vs polymers
polymer = macromolecules, consisting of similar, repeating building blocks = monomers
synthesis & breakdown of polymers
dehydration reaction : joining 2 monomers into polymer by removing water molecule
hydrolysis: water molecule is used to breakdown
these processes are facilliated and sped up in our cells by Enzymes!
carbohydrates
sugars and polymers of sugar
monomers: monosaccharides
macromolecules are polysacchrides→ polymers composed of many sugar
monosacchrides
multiples of CH2O
major fuel source, very easy to break (easier than protein and fats )
explain what happens when even one amino acid is substituted for another in a polypeptide
alters primary structure of protein
the new functional group will change Hydrogen bonding → 2 structures a helices and B sheets
if secondary changes→ 3rd (change in bonds=> hydrophobic interactions, ionic bonds and disulphide bonds) → quaternary structure too
Protein shape change = function altered
if a salamander relies on hydrogen bonds to cling to surfaces what surface would cause problems?
A surface made with carbon and hydrogen atoms covalently bonded: Hydrogen bonds needs to encounter Polar Molecules, H atoms bonded to highly electronegative atom like O or N.
What is needed to mimic effects of a hormone ?
a compound with same 3d shape as part of the hormone.
Hormone (compound)= key needs to fit into the lock = receptor for it to respond w same bio trigger reaction
Which group of biomolecules is not synthesized exclusively through dehydration?
Odd one out: Lipids (not polymer) Steroids are derivatives of cholesterol
Triacylglycerides are formed by dehydration (glycerol+fatty acids, but the fatty acids have multi-steps of reactions )
What helps absorb water into large intestines?
cellulose (fiber) isn’t branched so undigested→ bulk so intestines absorb water to soften stool and push it out
How do they make liquid oils into (semi)solid?
through Hydrogenation process → replace double bonds in fatty acids with hydrogen atoms
the info in the DNA is contained in…
the sequences of nucleotides along the length of the 2 strands of the DNA molecule
explain dehydration process
joining 2 small monomers → polymer + H2O
Carbohydrates (blocks, functions, bonds, examples)
monossacharides, polysaccharides, fuel source/ structure + shape, glycosidic link
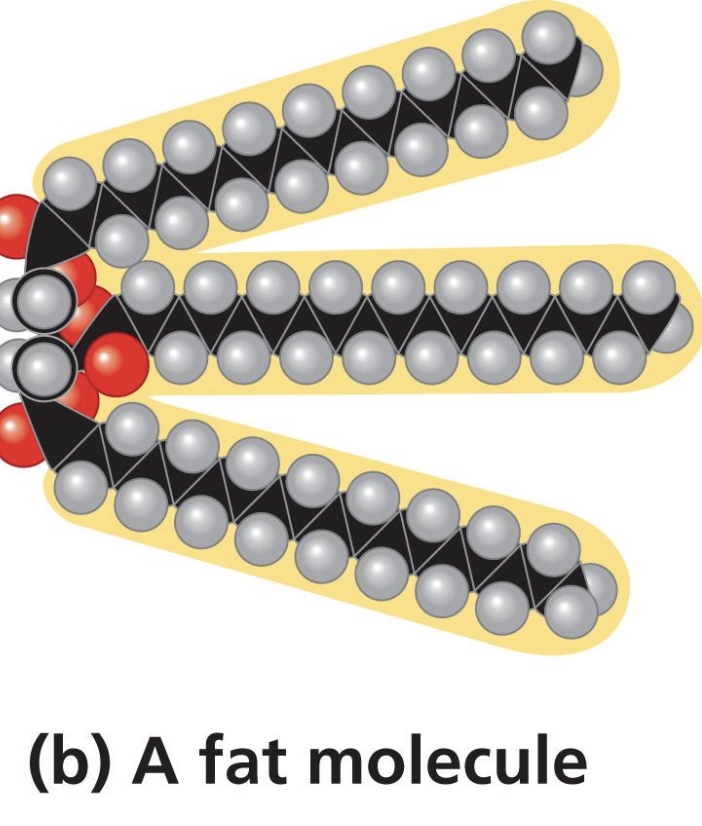
Lipids (blocks, functions, bonds, examples)
glycerol+ fatty acid chains (not polymer not polymerize),
Energy storage, form cells, insulation, regulation cell functions
ester linkage
Proteins (blocks, functions, bonds, examples)
amino acids → polypeptide, protein, peptide w peptide bond
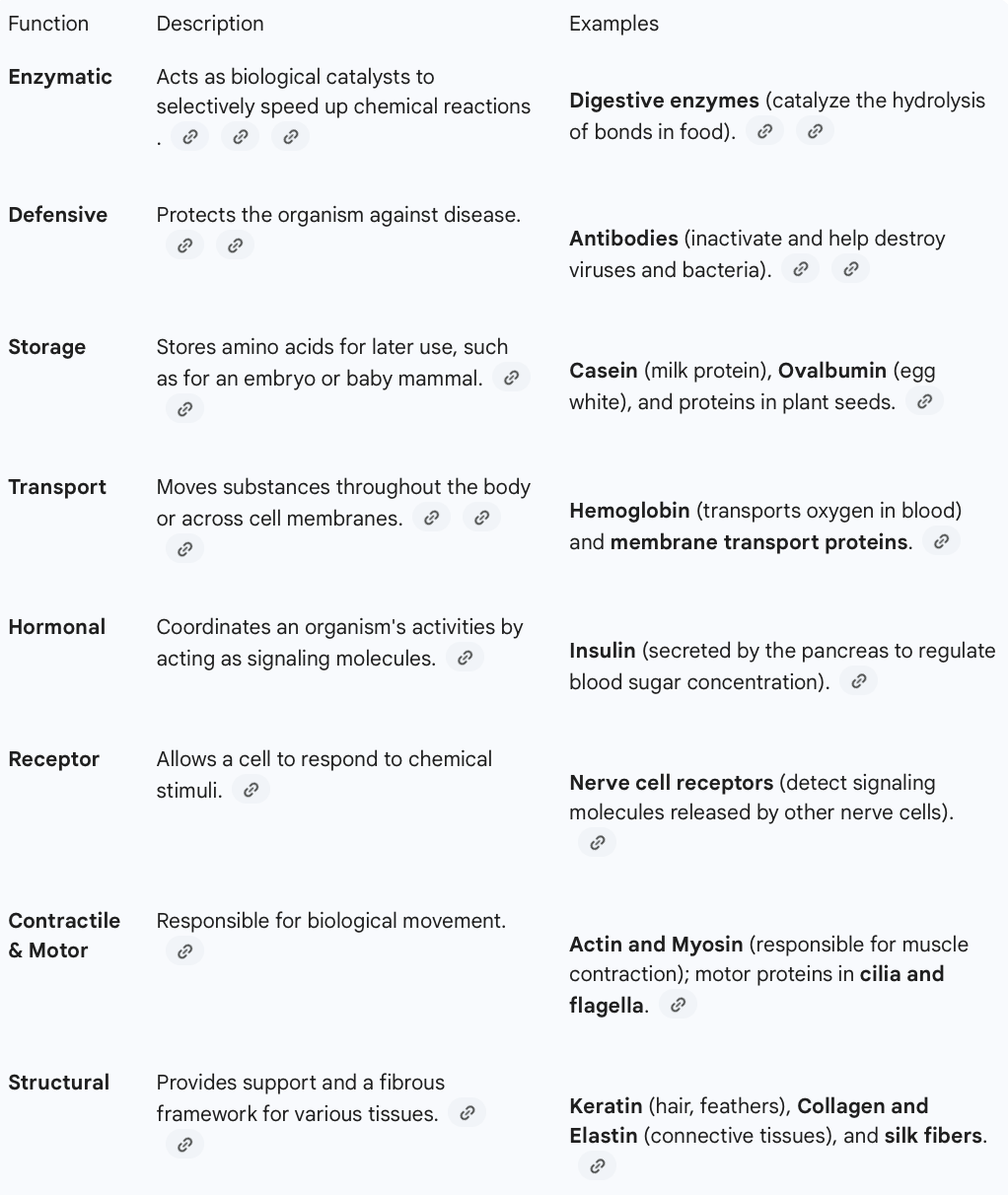
many diverse: catalyse, communication, storage, defensive, transport, hormonal, receptors, structural, contractile/motor
Nucleic Acids (blocks, functions, bonds, examples)
functions of proteins
transport: facilitate movement of substances (hemoglobin), protein channels
biological catalyst (amylase)
Hormonal : communication+coordination of activities (insulin)
defensive: protect by identifying and neutralizing (antibody)
mouvement within cells and tissue(myosin)
support and shape (collagen)
storage of AA (ovalbumin in eggs AA source for developing embryo)
receptors: of chem stimuli (built in nerve cells)
contractile/motor: actin and myosin → contraction of muscles, in the cilia and flagella
functions of proteins + examples
Glucose properties, functions, types
Hexose structure, form rings in aq solution, not hydrophobic, soluble
in cell. Resp → ATP
a glucose and B glucose: isomers = OH group at C1
stereoisomer is galactose at C-4
Explain 2 types of Diabetes mellitus
1: deficiency of insulin
2: body no response to insulin
explain what happens when blood sugar spikes
Pancreas (control center) secrets insulin (hormone)→ binds to receptors of fat, muscle and liver cells → promotes transport of glucose into cells
uptake in muscles,
adipose cells (store E as fat)
prevents breakdown of glycogen (liver)
explain what happens when blood sugar drops
pancreas secretes glucagon
stimulates glycogen → glucose (liver)
breakdown of protein→ amino acid (muscle)
breakdown of fats → release of fatty acids (adipose)
explain the formation of complex sugars
monosaccharides form → disaccharides + H2O with glycosidic linkage
polysaccharides

Fats (Triacylglycerol / triglycerides)

with dehydration, Esther linkage
what causes different fats?
different fatty acid chains:
length : number of C
location and number of C=C double bonds
Types of fats


trans fats elevate cholesterol→ plaque deposits abnormal blood flow (clog)
Hydrogenation: change the double bonds with H atoms to make liquid to (semi)solid.
phospholipids
amphipathic, main component of cell membrane
phosphate head + 2 fatty acids (different combinations )
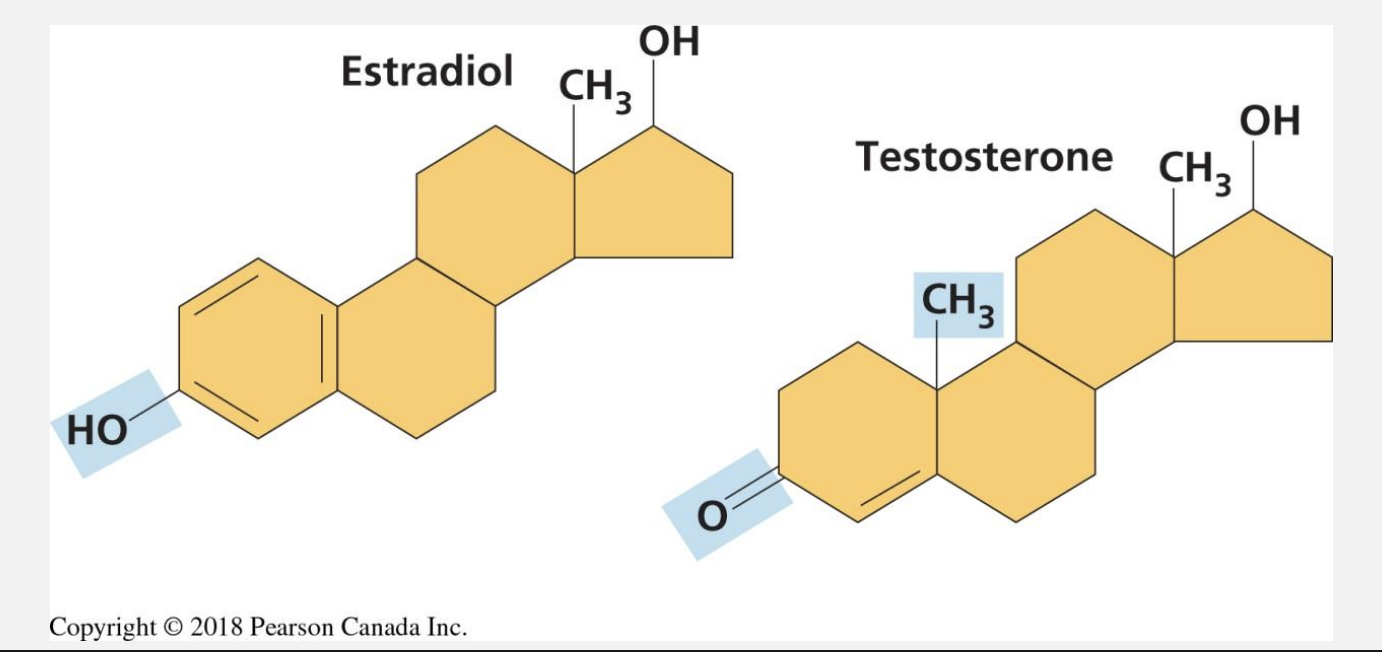
what is cholesterol
waxy substance produced by liver for building animal cell membranes. Produce hormones and vitamin D.
High levels → plaque buildup → cardiovascular disease
steroids
4 fused rings
derivatives of cholesterol→ they are stripped into steroids to make enzymes for steroid hormones
structure determines function
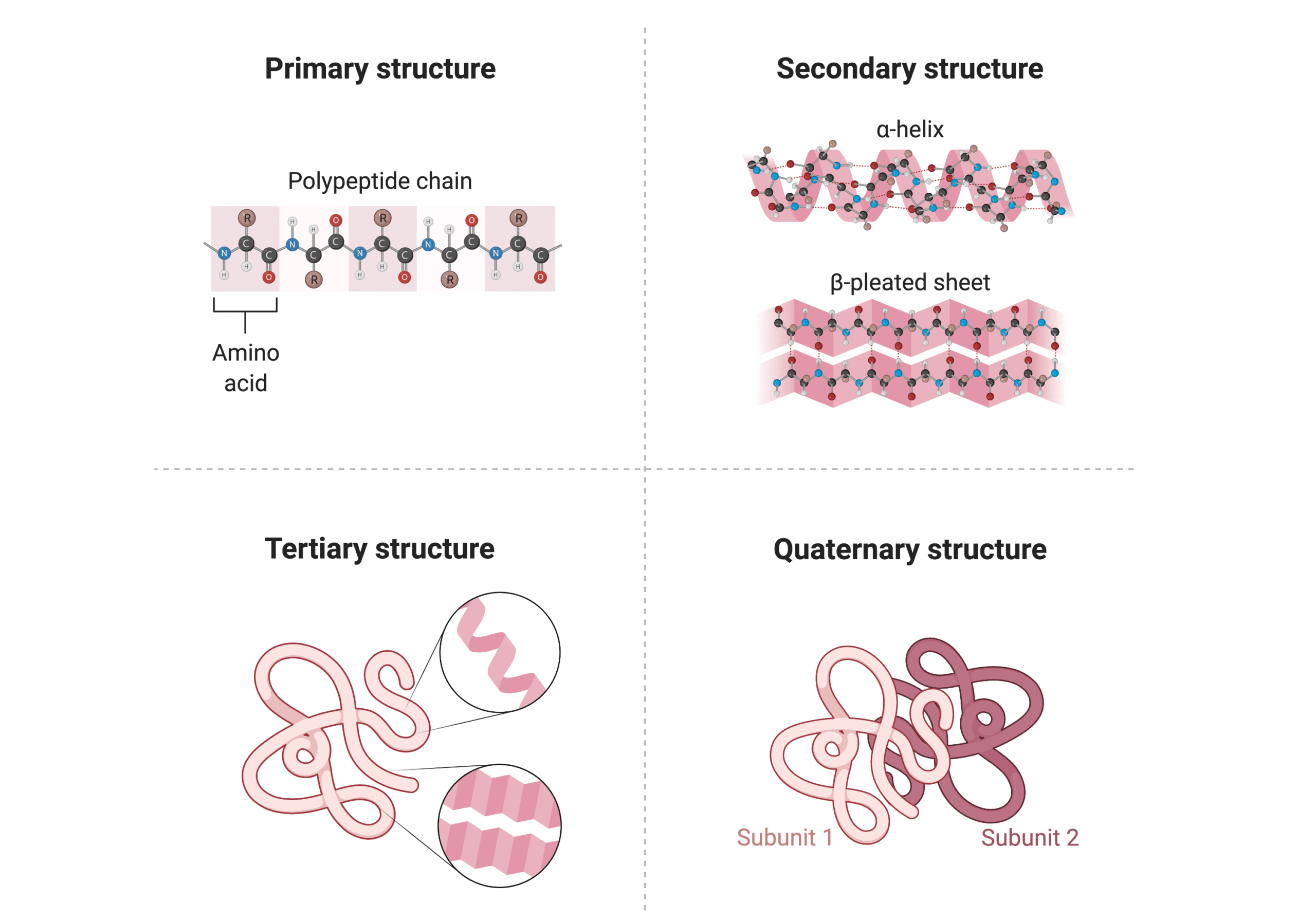
protein structure
amino acid, carboxyl acid, variable side chain, Central alpha C
depending on R, shape of protein changes→ structure determines function
Levels of protein structure
denaturation of a protein
heat and pH change protein’s structure & function
sometimes can renature
nucleotide struture
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nucleotide_base-5b6335bdc9e77c002570743e.jpg)
functions of nucleic acids
sequence determines sequence of amino acids for protein synthesis
DNA and RNA (information storage)
→ DNA: replication blueprint for cell growth
→ Instruction for mRNA
protein synthesis
DNA transcribed →mRNA → ribosome reads to make AA chain→ protein goes to rough ER