Unit 1: Matter, Chemical Trends &Bonding; Wave Mechanical (Quantum) Model of the Atom chem ap
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Quantitative Measurements
Measurements in an experiment made using various tools to measure volume, mass, temperature, etc.
Continuous Data
Quantitative data with associated uncertainty, reflected in significant digits.
Discrete Data
Quantitative data involving counting, exact values with potential experimental error.
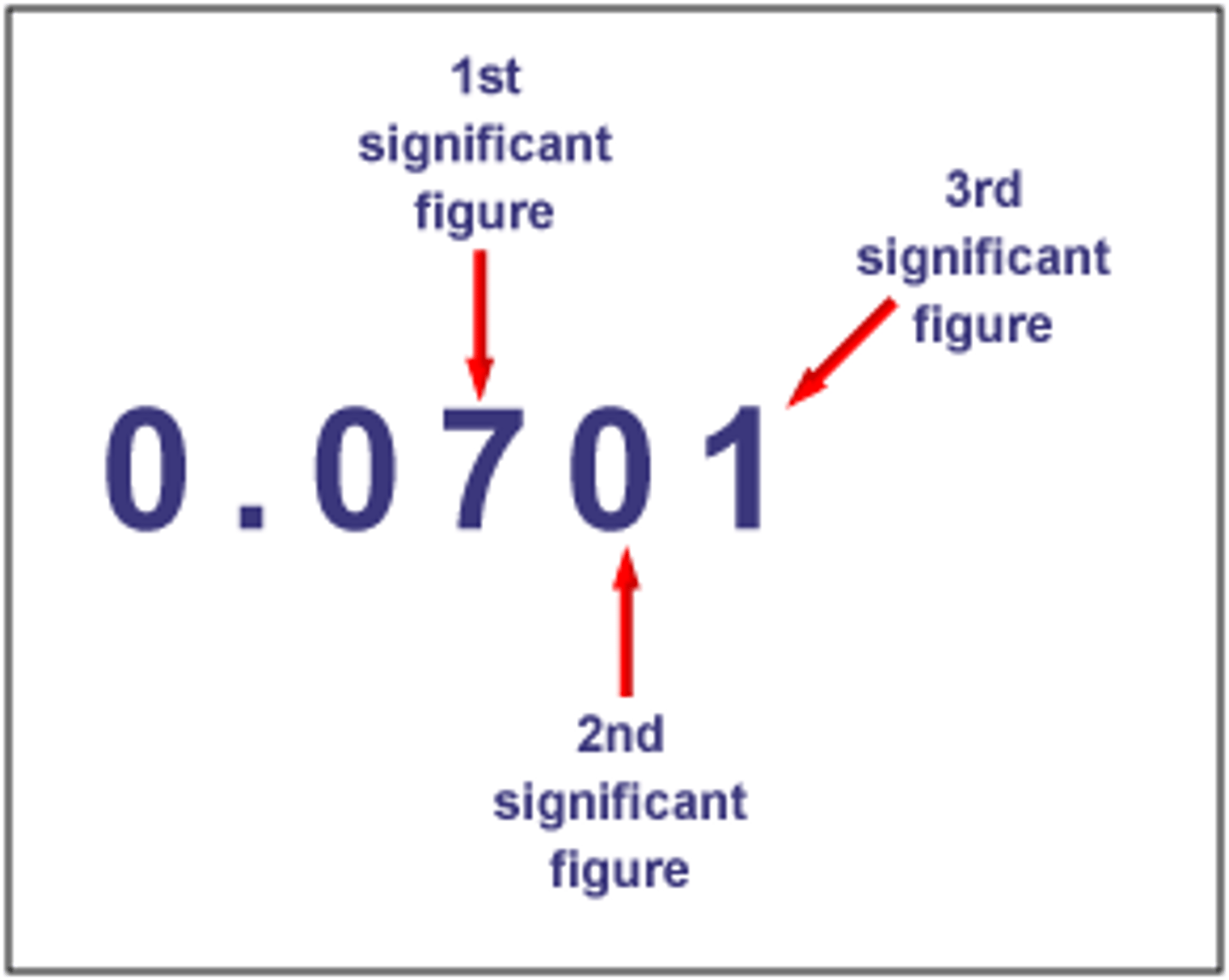
Significant Digits
Digits in a measurement that carry forward in calculations, determined by the precision of the measuring tool.
rules of significant digits
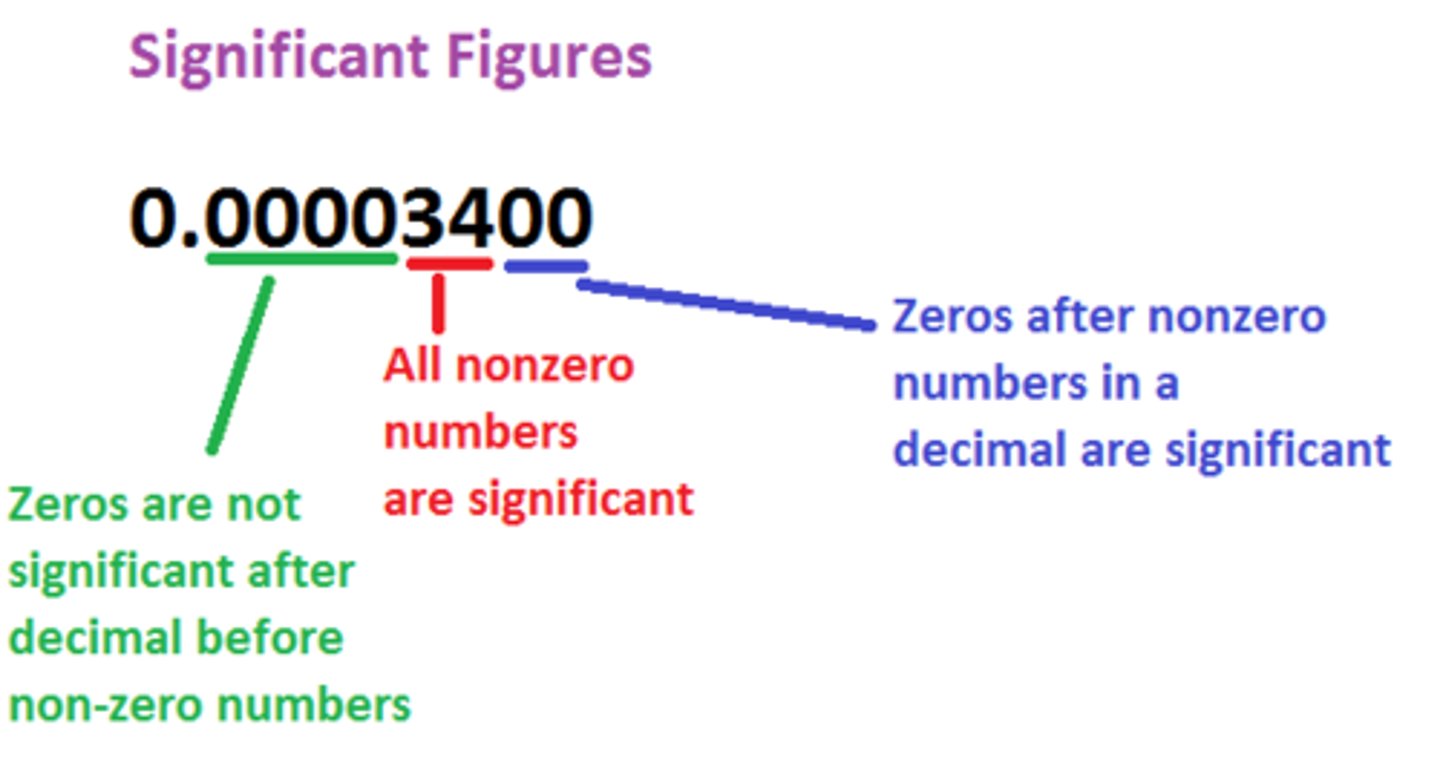
1. All nonzero numbers are significant
2. Sandwiched zeros (zeros between 2 nonzero numbers) are significant
3. Zeros after the decimal point are significant
4. Zeros used to locate the decimal point are not significant
addition and subtraction rule
the result carries the same number of decimal places as the quantity with the fewest decimal places

multiplication and division rule
the result carries the same number of significant figures as the factor with the fewest significant figures
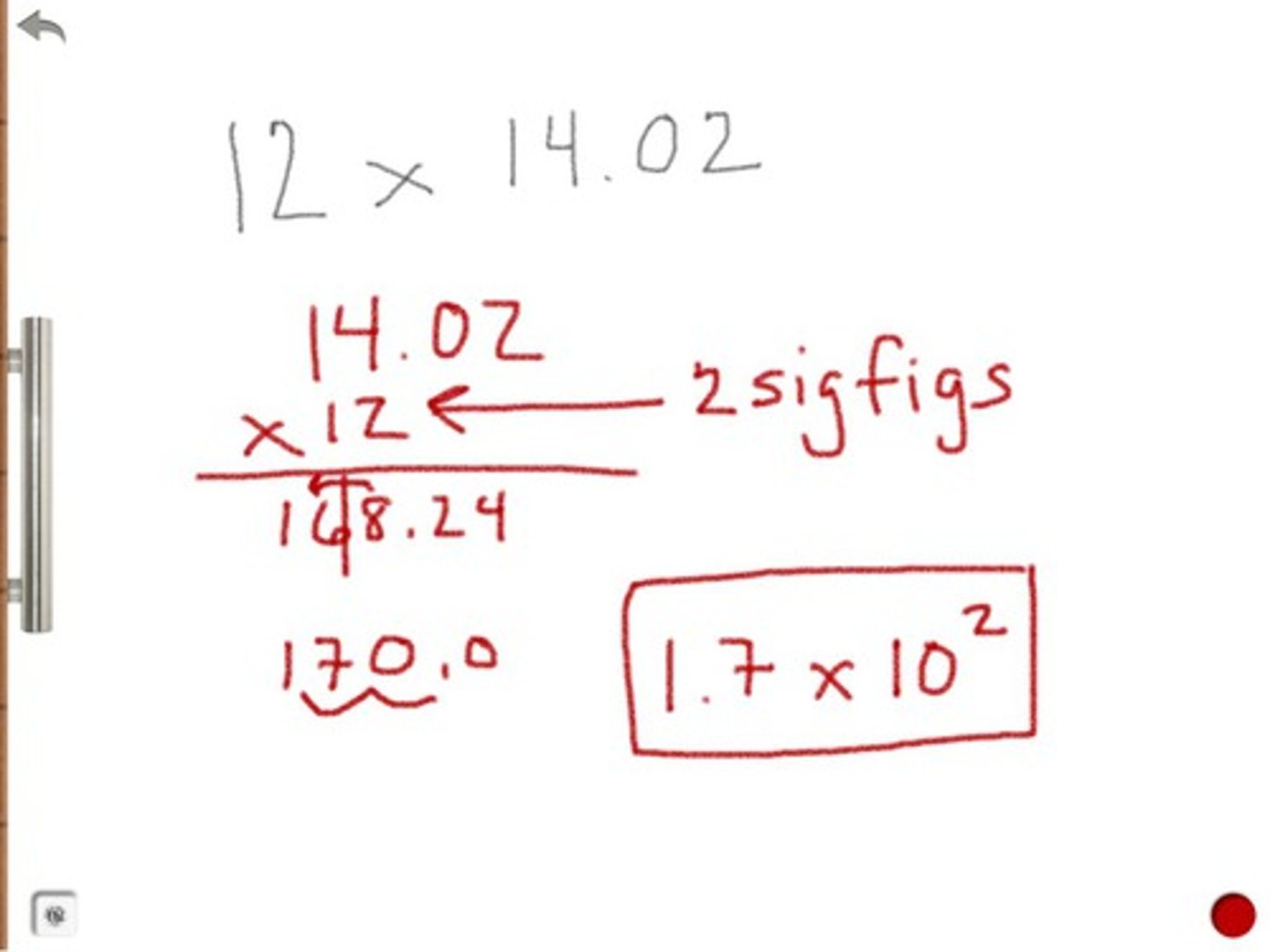
Accuracy
Closeness of measurements to an accepted true value.
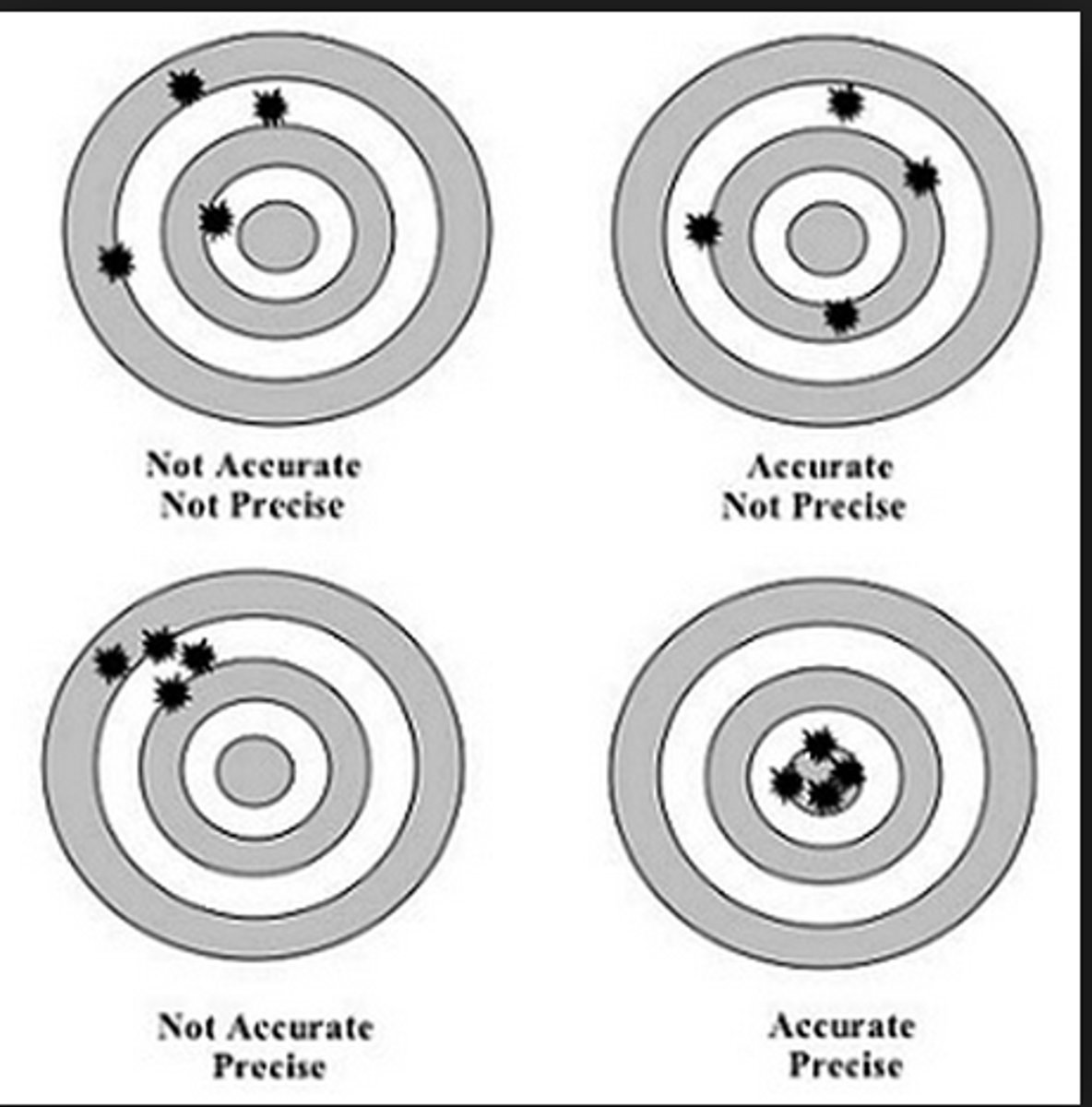
Precision
Reproducibility or closeness of measurements to each other.
Sensitivity
Ability of an analysis to detect positive cases correctly (true positive rate).
Specificity
Ability of an analysis to detect negative cases correctly (true negative rate).
Accuracy Rate
Percentage of correct results in an analysis.
Precision Rate
Percentage of reproducible results in an analysis.
Pure Substances
Homogeneous substances composed of a single type of atom or molecule.
element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom
Compund
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds
Mixtures
Substances with heterogeneous composition, composed of more than one type of pure substance.
Element
A pure substance consisting of only one type of atom.
Compound
A pure substance composed of two or more elements in a fixed ratio.
Atom
The basic unit of matter, indivisible and retaining the properties of an element.
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus.
Atomic Mass
The sum of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus, expressed in atomic mass units.
average atomic mass
the weighted average of the atomic masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element

Alpha Particles
Helium nuclei with a mass number of 4 and atomic number of 2, emitted during alpha decay.
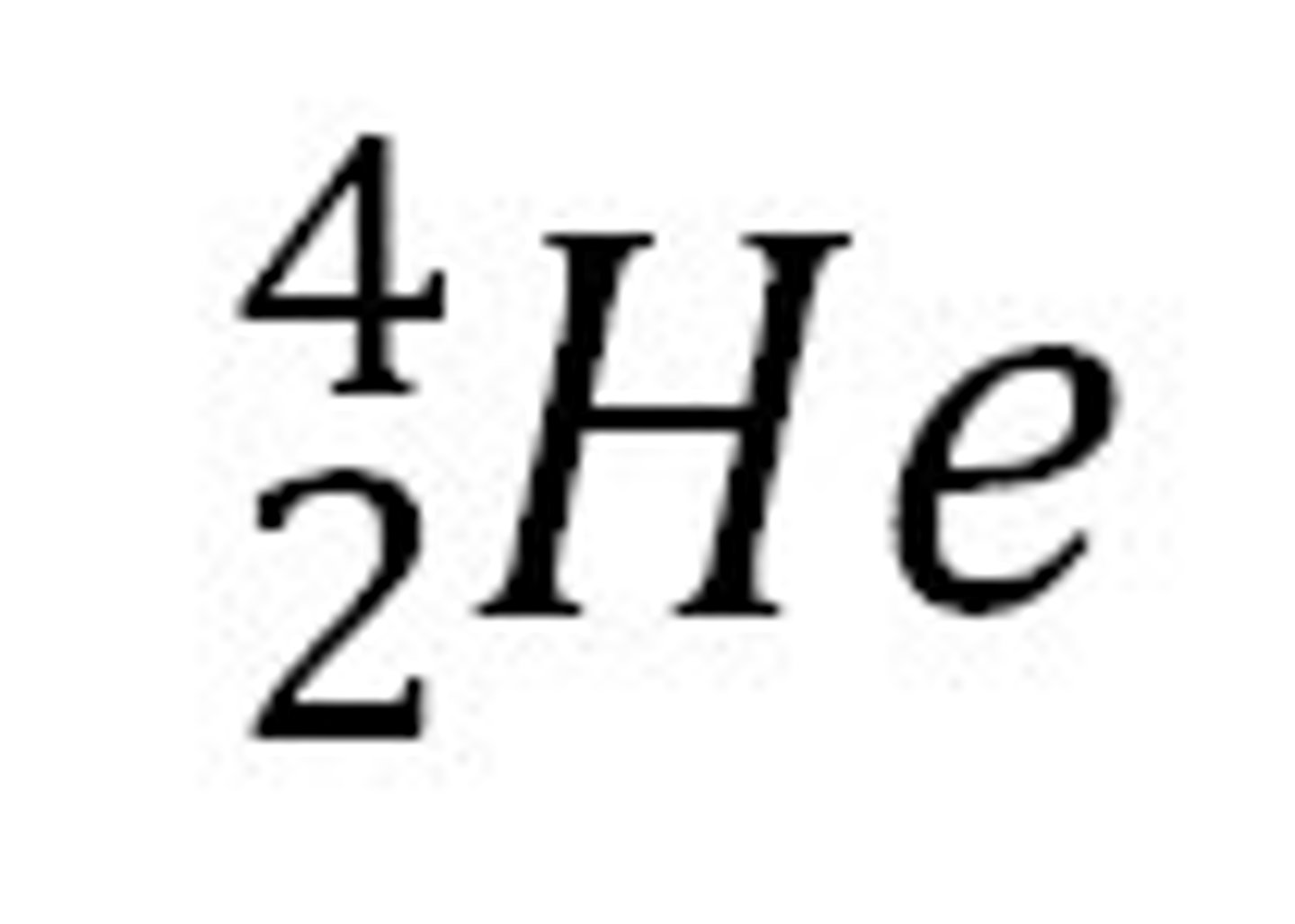
Beta Particles
High-energy electrons emitted during beta decay, causing the atomic number to rise by 1.
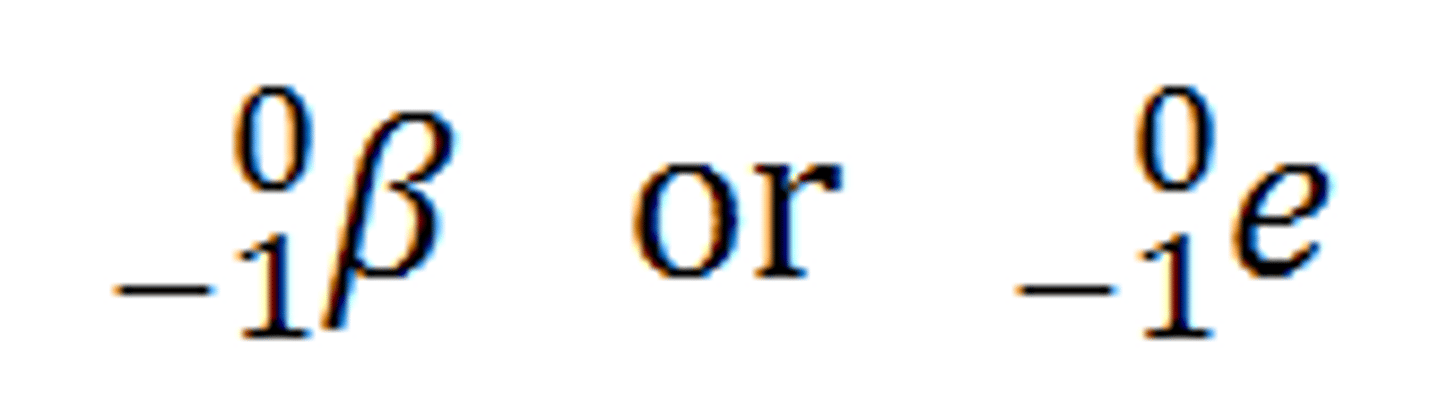
Positrons
Particles with the same mass as an electron but a positive charge, emitted during certain types of radioactive decay.
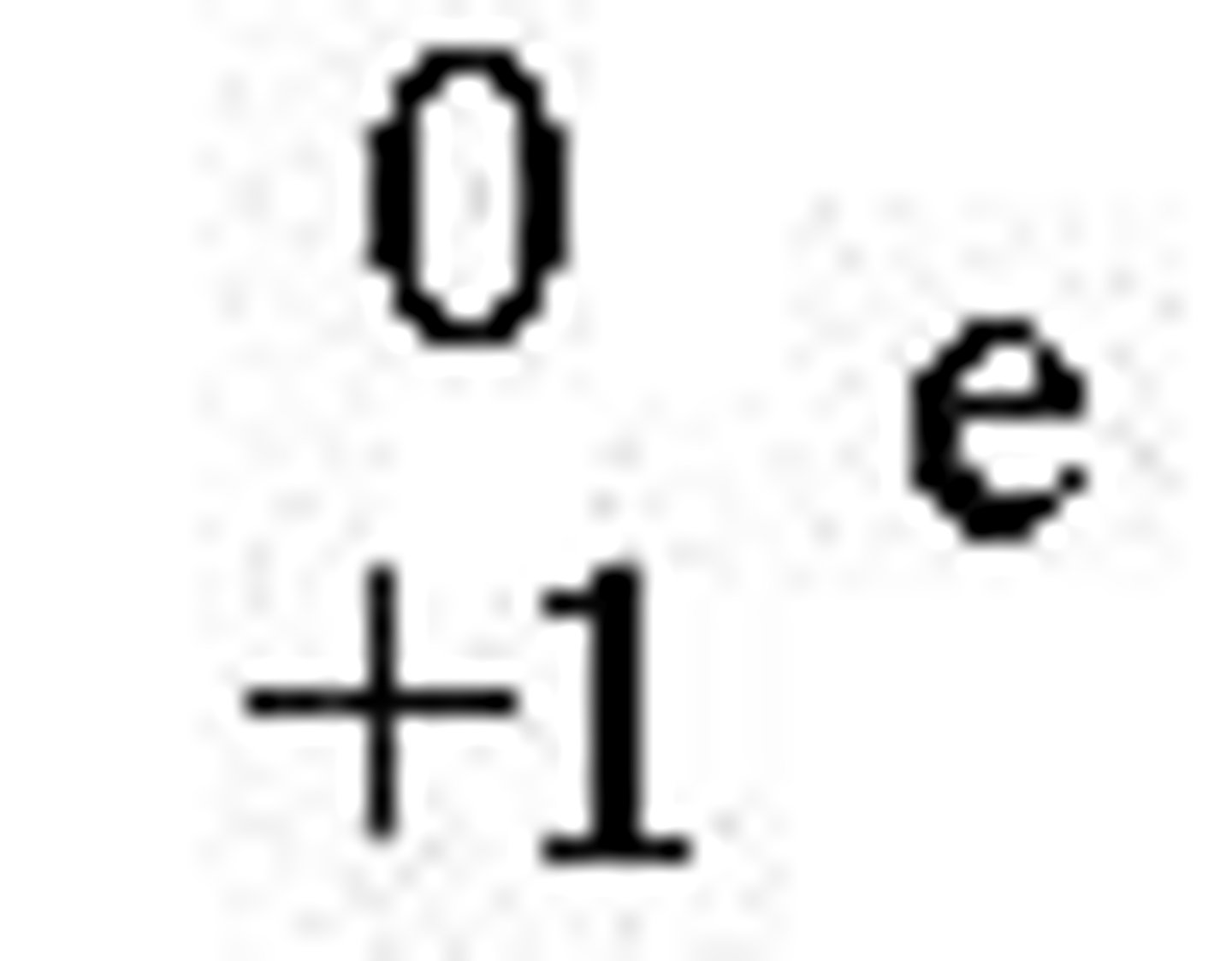
Protons
Nuclei of hydrogen atoms with a positive charge and a mass number of 1.
Neutrons
Neutral subatomic particles with a mass number of 1, found in the nucleus of atoms.
Gamma Rays
High-energy electromagnetic radiation emitted during nuclear reactions.
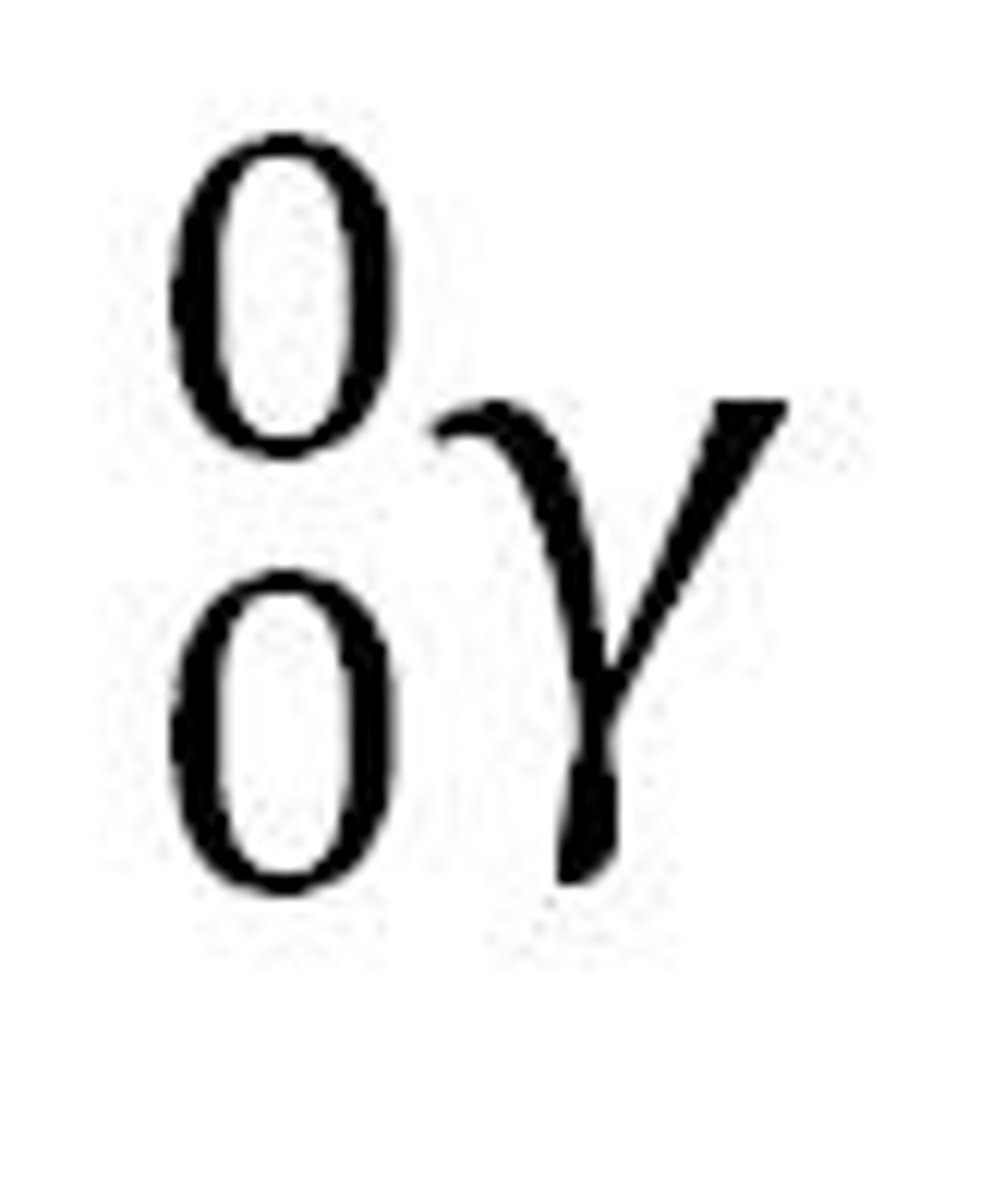
nuclear reactions
A reaction that involves splitting the nucleus of an atom or fusing two nuclei; these reactions produce much more energy then chemical reactions. balance atomic number and atomic mass
Alpha Decay
A type of radioactive decay where an alpha particle is emitted, reducing the mass number by 4 and atomic number by 2.
-most radioisotope atoms with an atomic number over 82 undergo alpha decay
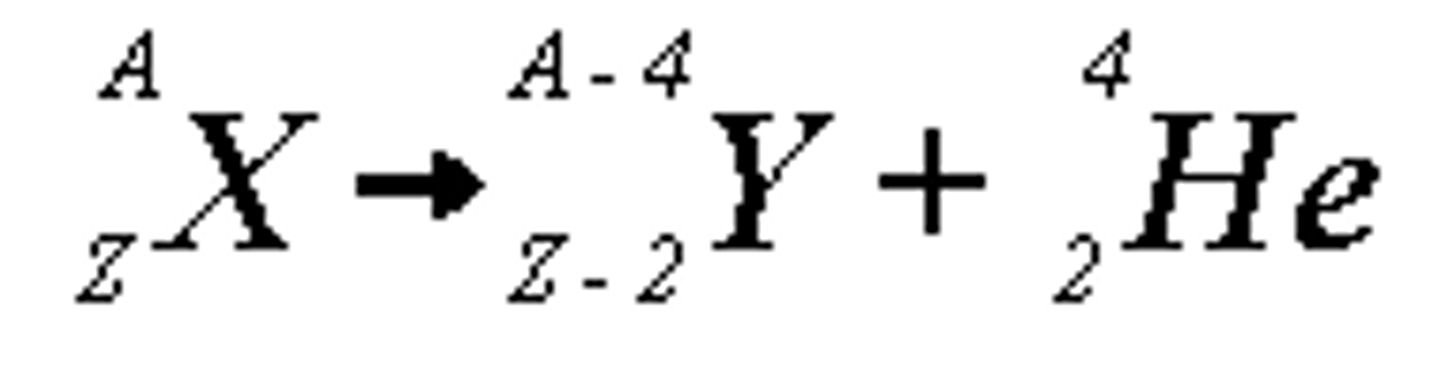
Beta-Decay
A type of radioactive decay where a neutron changes into a proton, increasing the atomic number by 1.
-happens if too many neutrons in nucleus
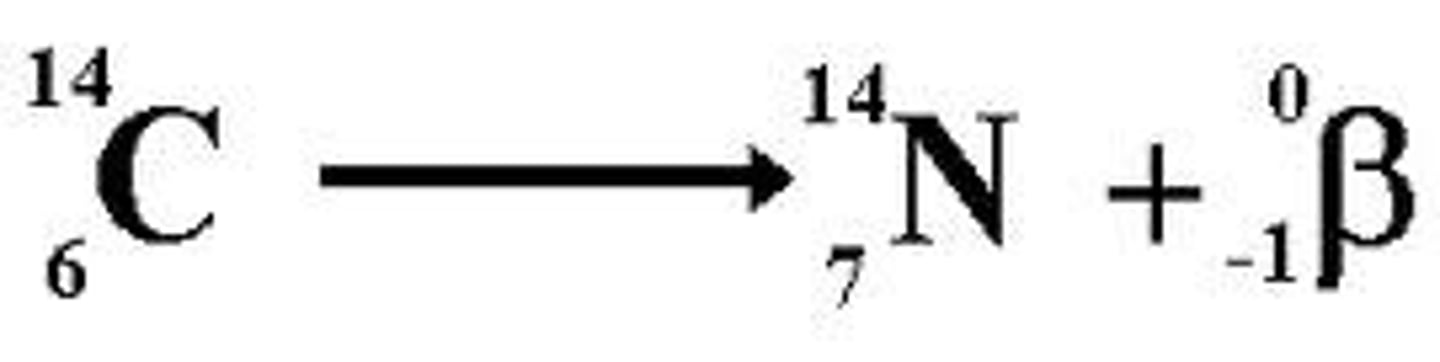
positron decay
a nuclear reaction in which a positron is emitted
-happens when too few neutrons compared to number of protons
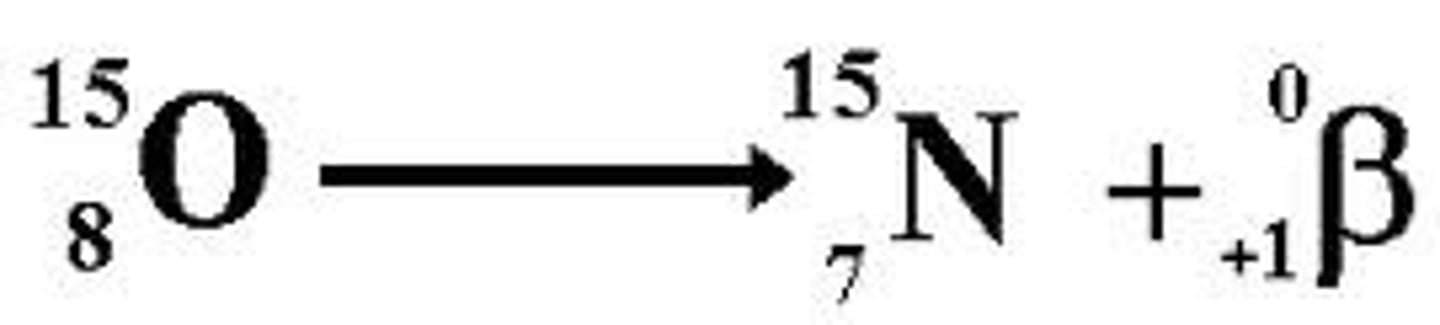
Fusion
A nuclear reaction where two nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing a large amount of energy.

Transmutation
The process of creating a new isotope by inducing a small particle to react with a starting isotope.
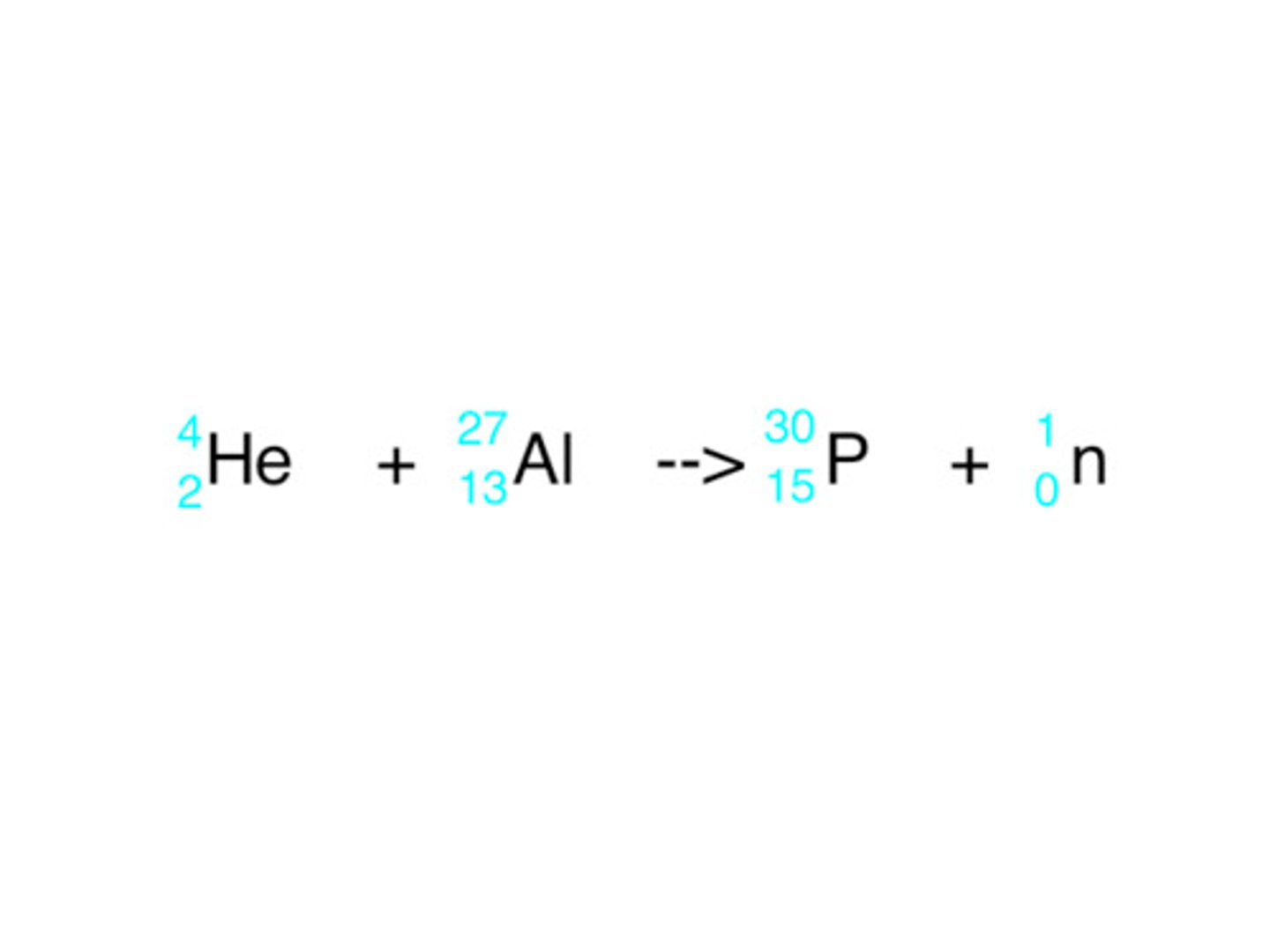
Gamma Emission
The release of gamma radiation from a nucleus without any change in atomic or mass numbers.
fission reactions
bombarding nucleus with small high energy particle to break nucleus into two isotopes
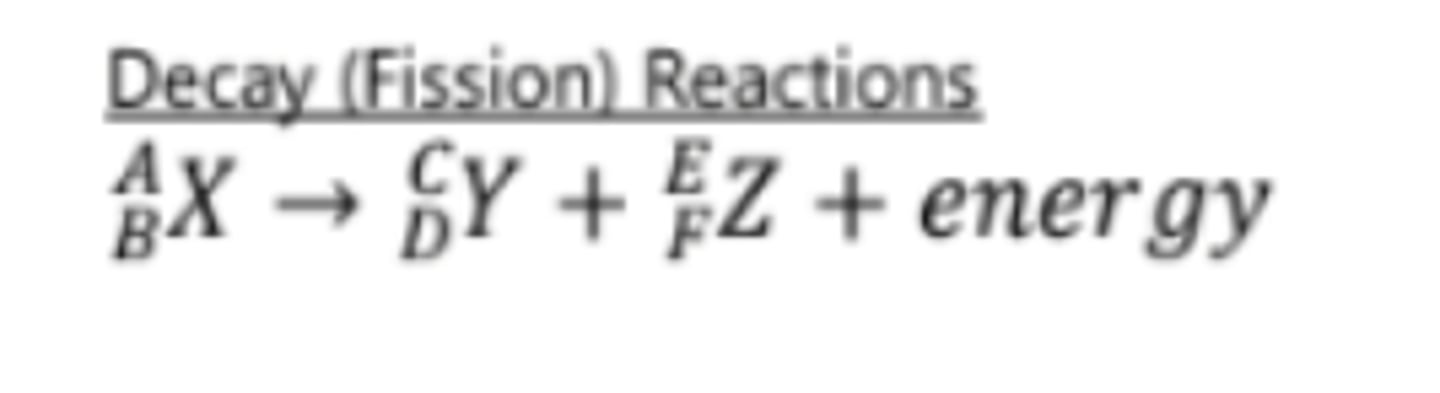
first identified radioactive element
polonium (Po)
Radioisotopes
Isotopes that exhibit radioactive decay and are used in various applications.
Half-Life
The time taken for half of the radioactive nuclei in a sample to decay.
unstable isotope
An isotope in which the nucleus is likely to break apart, nucleus is too big, weak electromagnetic force.
-elements over bismuth ((83)
Geiger Counter
A device used to detect and measure ionizing radiation.
Gamma Emitter
Emits gamma radiation, used in medical imaging
Alpha Source
Emits alpha particles, used for direct irradiation in cancer treatment
Beta Source
Emits beta particles, used in medical applications
Decay of Radioisotopes
Process of unstable isotopes spontaneously emitting radiation
John Dalton atomic theory (1803)
the "billiard ball" model of the atom
different atoms were represented by different spheres that could be joined to make molecules in specific ratios; atoms are indivisible
chemical reactions were rearrangments

jj thomson (1904)
discovered that atoms consist of smaller particles (pos + neg)
cathode ray experiment: particles ejected from neutral material between two plates, and were attracted to the negative plate
-plum pudding model
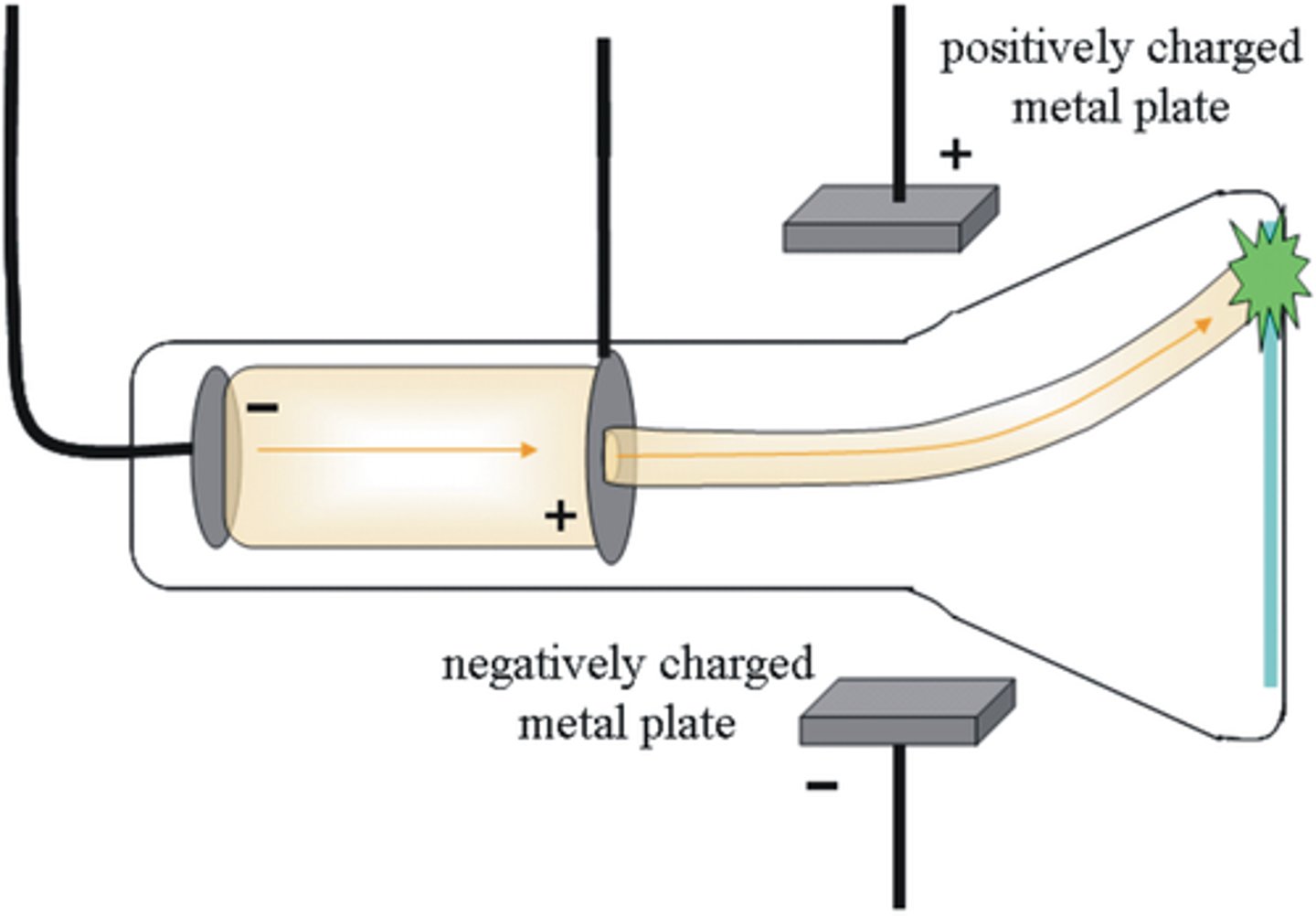
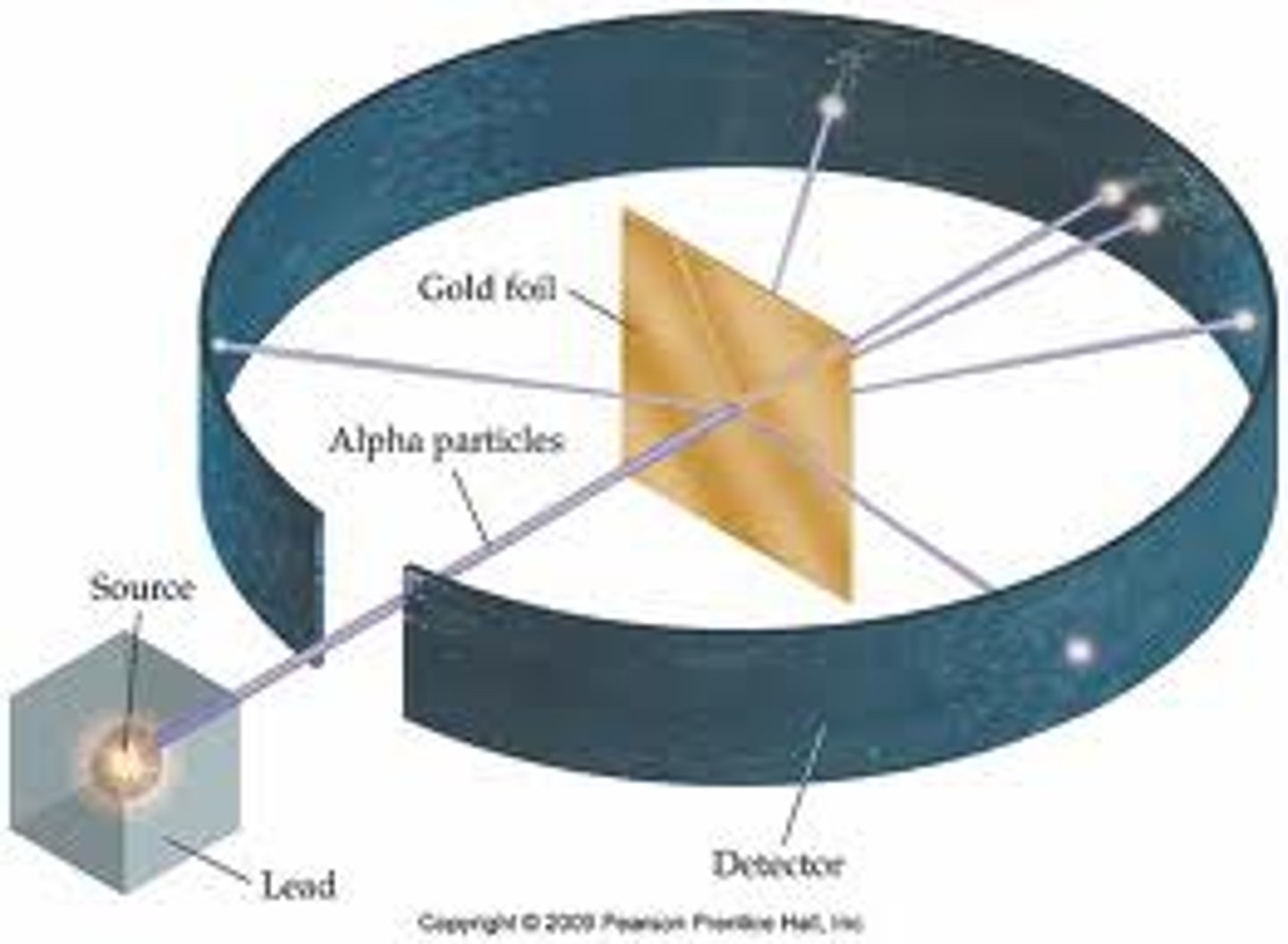
Ernest Rutherford (1911)
found the nucleus; gold foil experiment, used (positive) alpha particles and a narrow beam of particles directed at a sheet of gold foil, most particles went through undected by few bounced back randomly with high energy.
-atom is mostly empty space
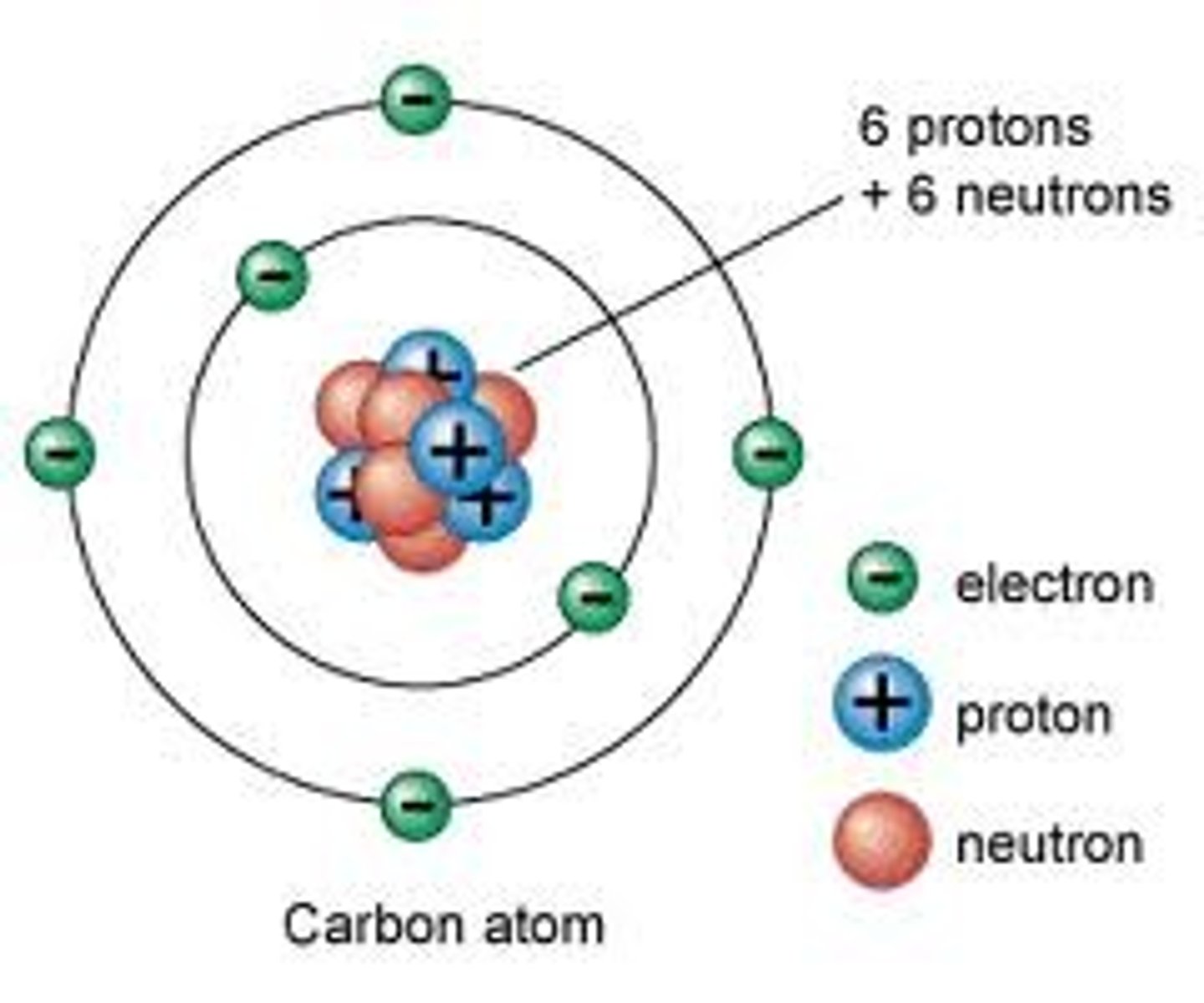
Bohr(1913)
planetary model of the atom
-Extended rutherfords model
-discovered electrons exist in specific orbits around nucleus
-birth of quantum mechanical model
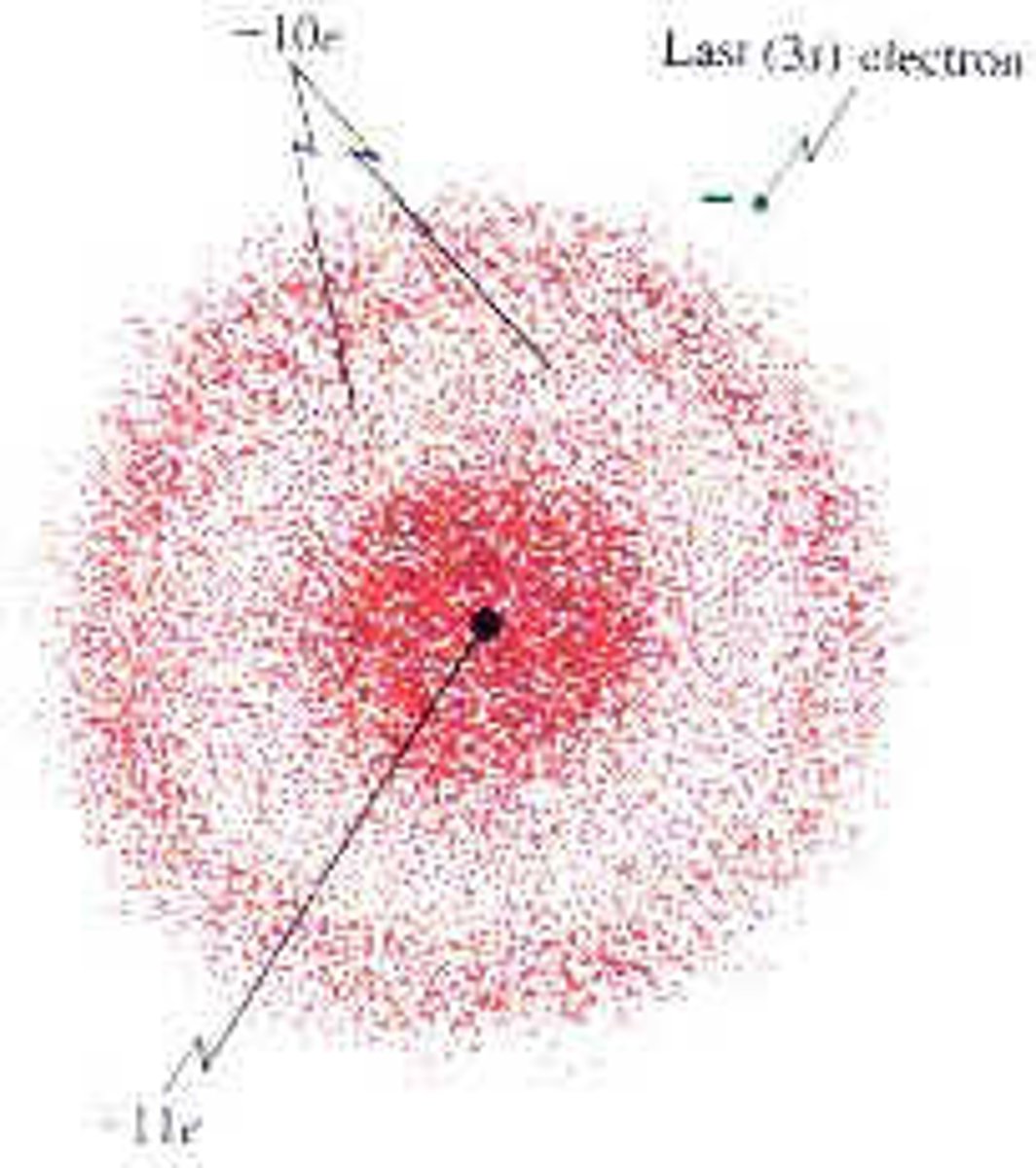
Schrodinger
-electons exist in region of space around nucleus according to specific mathematical wave functions.
-electron cloud model wave functions represents probability of locating electrons
Heisenberg uncertainty principle
it is impossible to know exactly both the velocity and the location of a particle at the same time
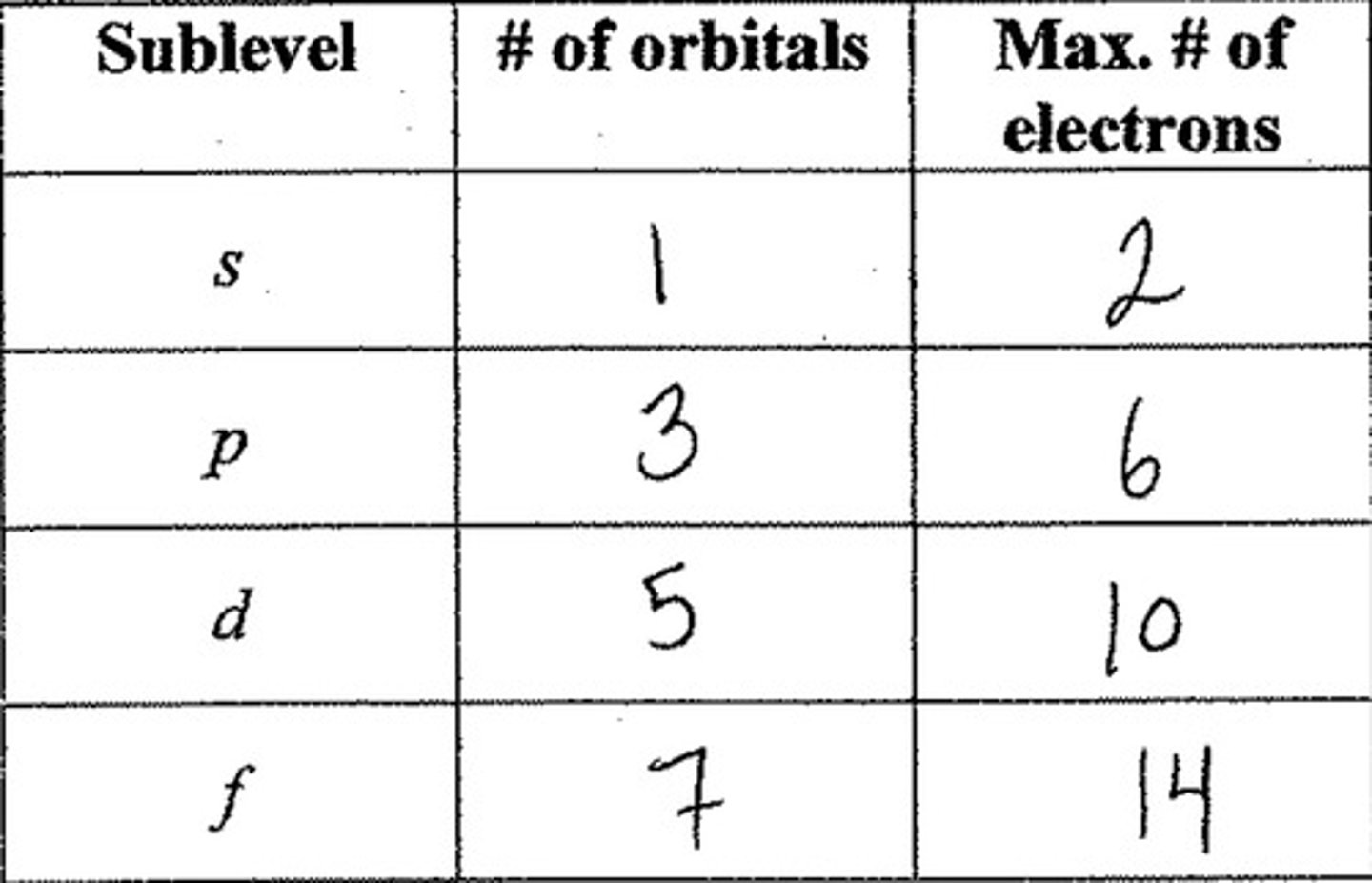
electron configuration

orbitals
regions around the nucleus in which given electron or electron pair is likely to be found
(s, p, d, f** g,h,i,etc)
Aufbau Principle
An electron occupies the lowest-energy orbital until full, then fills next sublevel
pauli exclusions principle
each orbital can hold max 2 electrons with opposite spins
Hund's Rule
electron in the same sub level (ex. 2s) will be added 1st with one spin direction in each orbital, and then filling the orbitals with electron of opposite sign
quantum numbers
Set of numbers used to completely describe an electron
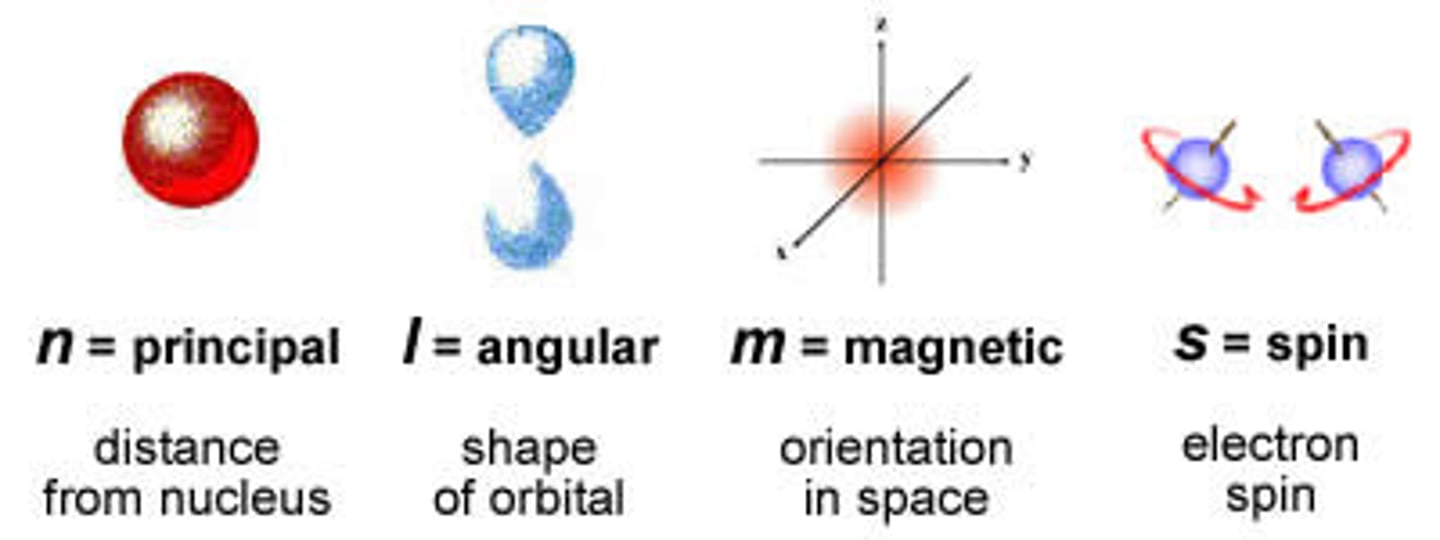
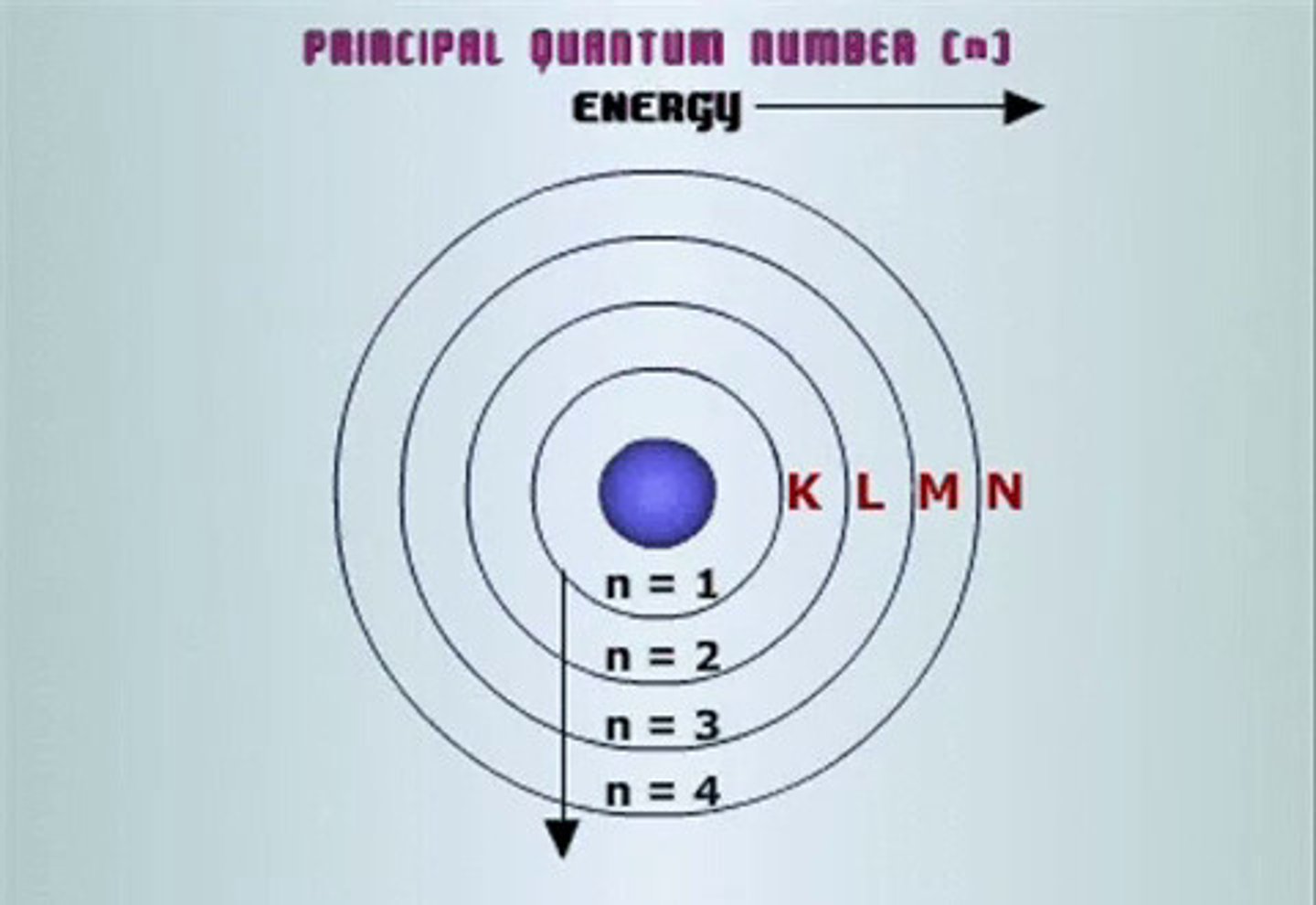
principal quantum number (n)
symbolized by n, indicates the main energy level occupied by the electron
secondary quantum number (l)
the quantum number that describes the shape and energy of an atomic orbital, with whole-number values from 0 to n-1 for each value of n
magnetic quantum number (m sub l)
magnetic Orientation of electron in 3d orbital (from +l to -l)
-magnetic quantum number represents numbers of orbitals
spin quantum number (m sub s)
either +1/2(clockwise) or -1/2(counter-clockwise), indicating the spin orientation of an electron
atomic radius trend
increases down a group, decreases across a period
-more protons: more attraction from electrons, decreases radius
-more electrons: repulsions, increases radius

ionization energy trend
decreases down a group,increases across a period
-amount of energy required to remove outermost electron
-as atomic radius decreases, ionization energy increases
-as atomic radius increases, effective nuclear charge lessens, ionization energy decreases
electron affinity trend
decreases down a group increases across a period,
-measure of energy that is either released or absorbed during addition of an electron
-more negative energy indicates increased electron affinity
-main group non-metals except noble gases have high electron affinity
electronegativity trend
decreases down a group, increases across a period
-measure of atom's ability to attract electrons in a chemical compound
-elements with greater effective nuclear charge will display higher electronegativity
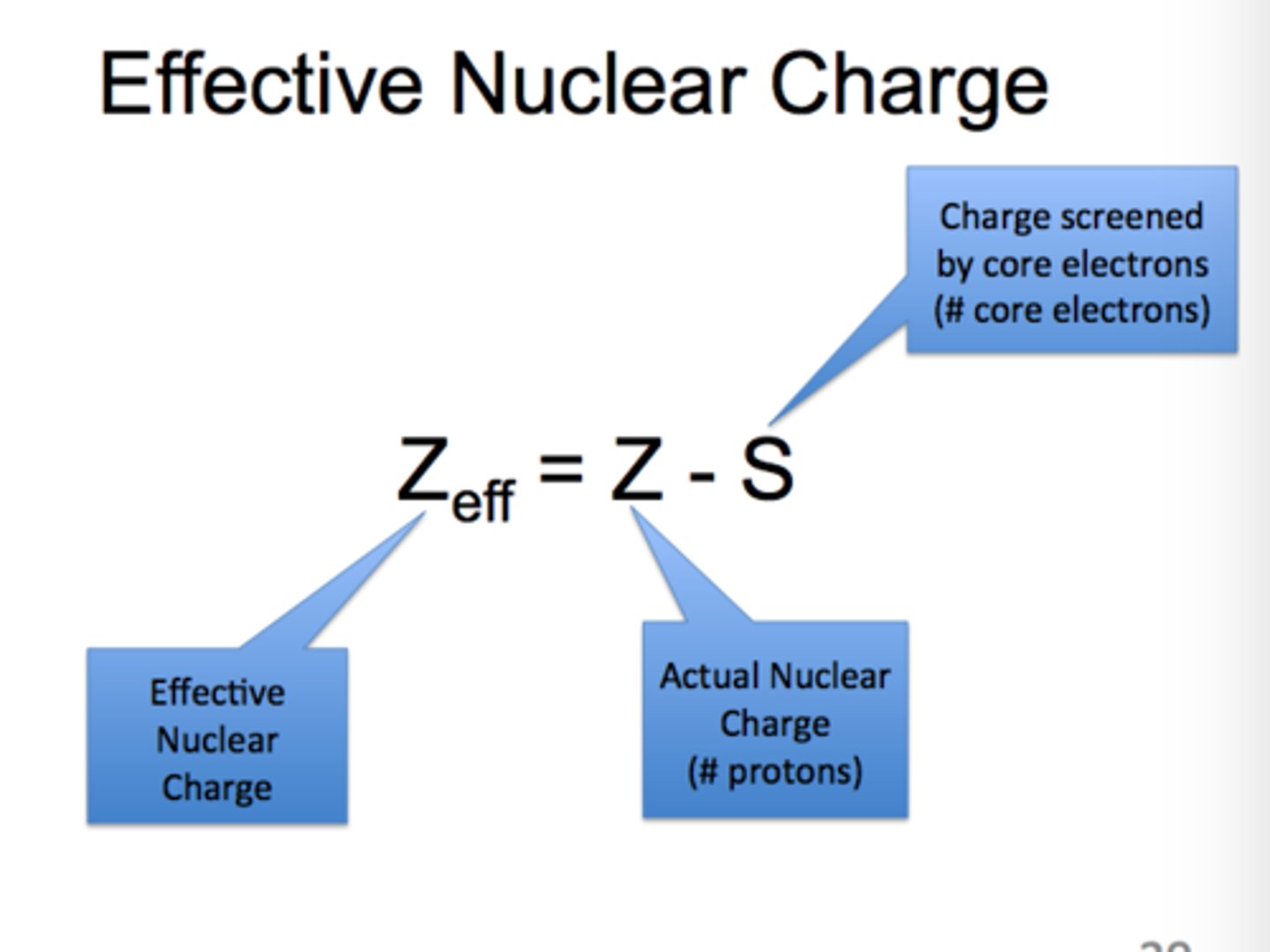
nuclear effective charge
a representation of average electrical field experienced by a single electron. average environment created by nucleus and other electrons in molecule