Economics (Economic Objectives + The Keys) - Year 12
1/52
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
What is Okun’s Law?
the relationship between economic growth and unemployment
What does Okun’s Law state?
For unemployment to fall, the rate of economic growth > productivity growth + labour force growth
What does NAIRU stand for?
Non-Accelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment
What is NAIRU?
The natural rate of unemployment after the elimination of cyclical unemployment. The remains of frictional, seasonal, structural and hardcore unemployment
What is full employment?
There is no cyclical or deficient-demand unemployment and all individuals seeking employment can find it. Also involves the full use of F.O.P.
What are the main long term objectives for an economy?
Full employment, price stability, economic growth, distribution of income and wealth, external stability, environmental sustainability
What is economic growth?
The increase in the volume of goods produced in an economy
How is Economic growth measured?
By the annual change in real GDP.
What is external stability?
Sustainability on external accounts so that economies can service their foreign liabilities in the medium-long term. Also includes acceptable levels of foreign debt and equity.
What is environmental sustainability?
Ecological and sustainable development to conserve the resources of an economy for now and future generations.
What objectives may the Govt. do to establish environmental sustainability?
Reducing green house gases or improve energy efficiency
What is the distribution of income and wealth?
The way the income and wealth of a nation is divided amongst its population
What does the distribution of income and wealth address?
The problem of poverty, inequality, the needs of people who are unable to provide for themselves or are socially disadvantaged
How is the distribution of income and wealth measured?
Lorenz curve and the Gini-coefficient
What is price stability?
Refers to keeping inflation at an acceptable rate
What is the RBA target band of inflation?
2-3% over the course of the business cycle.
What conflicts may arise form achieving all long-term economic objectives?
Price Stability (Inflation) VS Full Employment
Economic Growth VS External Stability
Economic Growth VS Environmental Sustainability
Economic Growth VS Inflation
Economic Growth VS Distribution of Income and Wealth
Full Employment VS Distribution of Income and Wealth
Would Govt. focus more on short term or long term objectives? Why?
Short-term, as they may gain more popularity with immediate benefits rather than long term objectives that may take substantial costs
What are the types of economic states an economy may be in?
Recessionary: high unemployment, low inflation
Inflationary: low unemployment, high inflation
Full Employment: lowest natural rate of unemployment
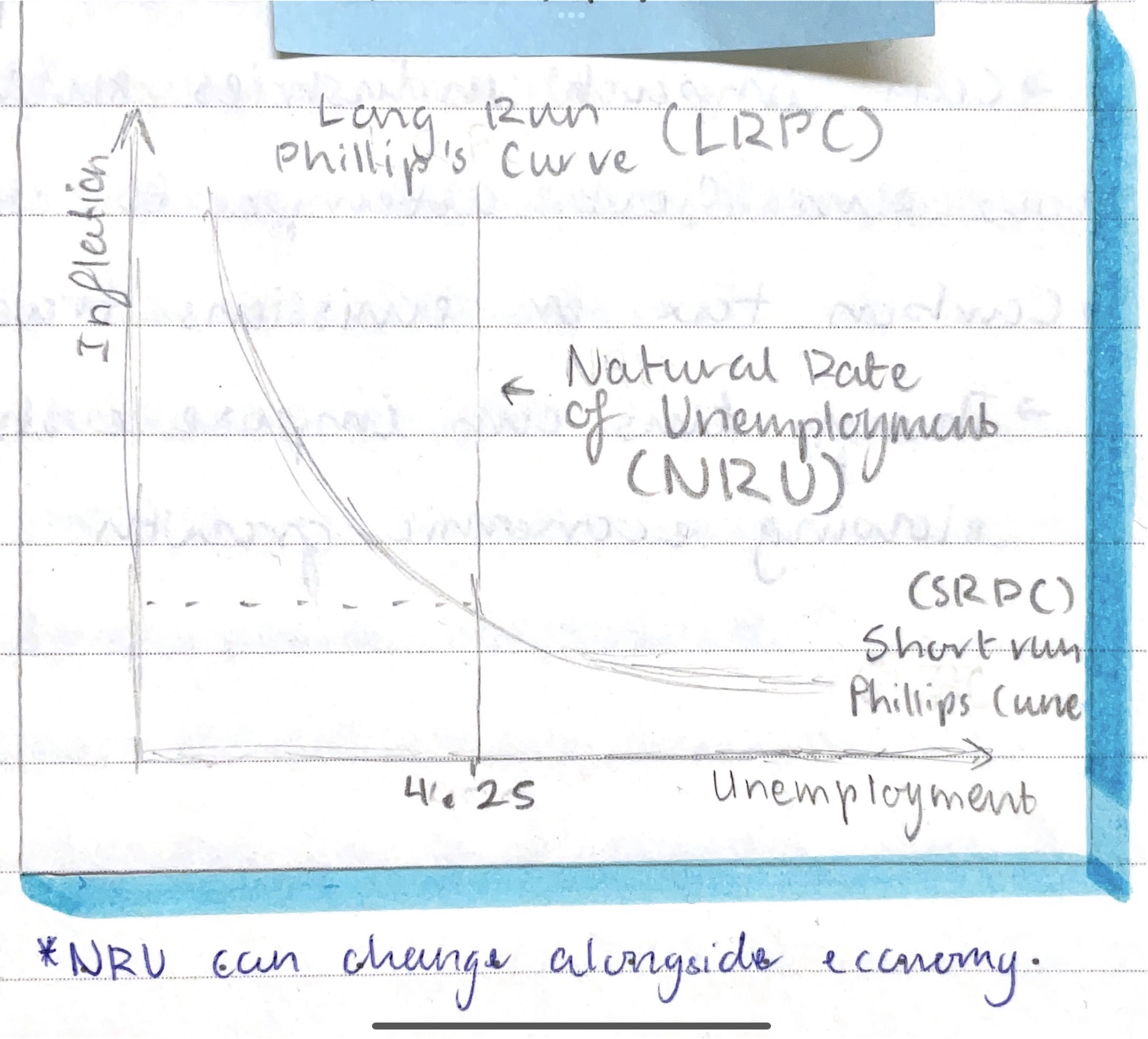
What is the Phillips Curve (PC)?
Demonstrates an inverse relationship between unemployment and inflation
What is a trade-off?
Opportunity cost, to gain more of something, something else must be reduced
Draw the Phillips Curve
.
What is the conflict between economic growth and external balance called?
Balance of Payments (BOP) constraint
What is the Balance of Payments (BOP)?
Record of Int. Transactions between an economy with the rest of the world through the Current Account (CA) and the capital and financial account (KA/FA)
What is the Current Account (CA)?
Records flow of G/S in and out a country (imports and exports, debits and credits)
Why does increase economic growth lead in the deterioration of the CA and the BOP?
Higher economic growth —> higher consumption and investment —> volume of imports begin to rise > exports
What practices lower environmental sustainability but increase economic growth?
Mining and certain agricultural practices
How can Govt. attempt to curb carbon emissions?
Carbon tax or emissions trading scheme
What is IBG and IBG+?
Individuals, Businesses, Governments and economic objectives
What is ADAS?
Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply (a tool to work out the impact of a change from objectives)
What is the key binary?
Trade flows and financial flows
What is the “big picture” of the global economy?
How globalisation works, is supported, and is impeded in higher trades and financial flows
What is IBG usually used for?
To analyse the impact of any economic change in an economy

In economics, what are the 2 most important objectives?
GDP growth (economic growth), Quality of life (economic development)
How do Govt. achieve economic growth and economic development?
Internal stability (Price stability, full employment) and external stability (Foreign liabilities, Terms of Trade, Exchange Rates, Int. Competitiveness)
How is quality of life/economic development measured?
By the United Nations (UN) Human Development Index (HDI)
What is the target goal of unemployment for full employment (Australia)?
4.25% unemployment rate
What is the formula for Aggregate Demand (AD)?
C + I + G + (X - M)
Consumption + Investment (capital) + Govt. Spending + (Exports - Imports)
What is the formula for Aggregate Supply (AS)?
C + S + T
Consumption + Savings + Taxation
What is the ADAS model?
Illustrates that GDP can increase through either or both AD or AS increasing
What does an increase in AD lead to in the ADAS model?
higher GDP —> lower Unemployment (more labour needed to produce more goods) —> higher Inflationary pressures
What does an increase in AS lead to in the ADAS model?
More Productivity —> higher AS —> higher GDP —> lower inflationary pressures (if change in productivity > GDP, less labour will be in demand and may increase unemployment)
Draw the ADAS model
-
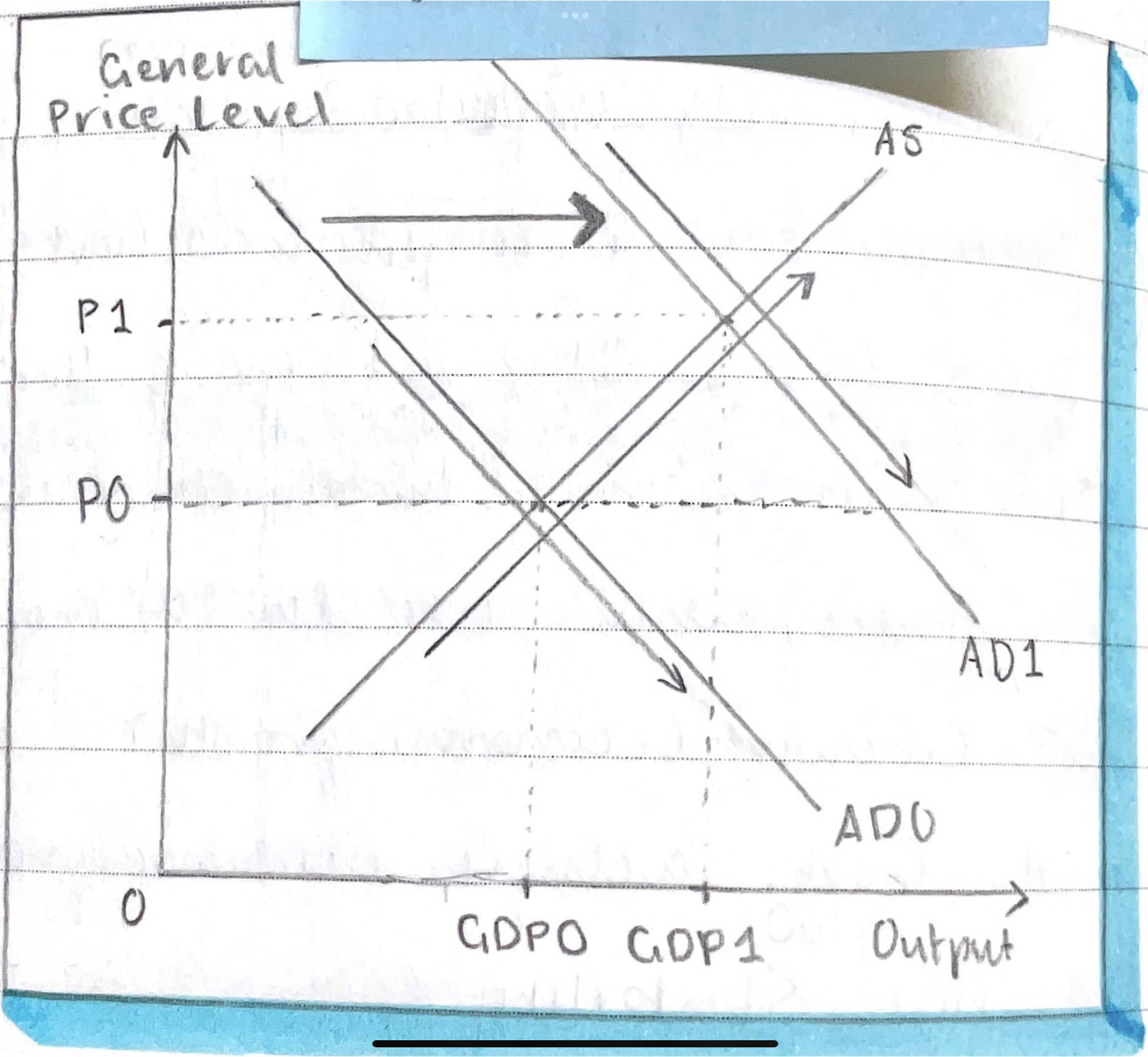
How is the ADAS model useful (what is it used for)?
Provides answers to what happens to full employment and price stability as a result in the change of AD
What is the Gross Domestic Product (GDP)?
Total monetary or mkt. value of all finished G/S produced within an economy over a period of time
What is another term for macro policy?
Demand side economics (it impacts Aggregate Demand)
What are the key micro reforms in the global economy?
Trade liberalisation and financial deregulation
What is trade liberalisation?
The removal or reduction of barriers on the free exchange of goods between nations
what is financial deregulation?
The process of removing Govt. rules controlling the way financial organisations operate
What are the financial flows and trade flows in AD?
In the AD formula, financial flows (debt, equity and liabilities) are in I (investment) whereas trade flows (exports and imports) are in X (exports) and M (imports)
What are the short term impacts of trade liberalisation?
Lower barriers protecting domestic producers, imports may rise in supply (with no impact on exports) —> short term lower AD, AD curve will shift left —> lower GDP —> higher Unempolyment —> lower Inflationary pressures
What are the long term impacts of trade liberalisation?
Higher Labour Productivity —> labour moves to competitively advantaged industries —> higher AS (from increased productivity) and higher AD (as higher X and higher C) —> higher GDP
How do the economic policies regarding globalisation impact an economy?
Capital Controls (lower potential financial flows) and Protection Policies (lower potential trade flows) will increase or reduce the effect of globalisation on a given economy