A&P TEST 5- brain and spinal cord
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Function of cerebrum
Conscious thought, decision-making, and processing
frontal lobe: decision making, problem solving, voluntary movement, personality
parietal lobe: sensory processing, spatial awareness
temporal lobe: hearing, language comp., memory storage
Occipital lobe: Vision processing
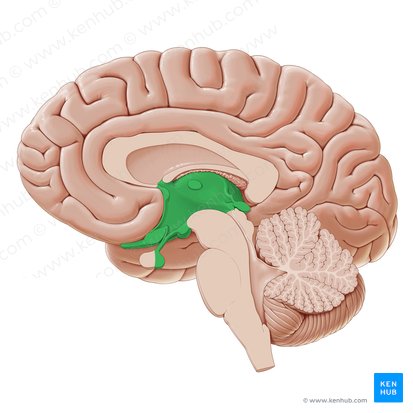
Diencephalon contains…
thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus,
Cerebellum
Major role in motor coordination
Pons
Contains respiratory centers to control breathing
“Bridge of the brain”
conveys info to and from the rest of brain
Thalamus
sorts most sensory information and sends it to cerebrum for perception
Hypothalamus
emotions, appetite, thermoregulation, and other homeostatic feedback loops
Temporal lobe
contains Wernicke’s, and auditory cortex
Parietal lobe
Contains primary sensory cortex
Visual reflex vs perception of vision
Visual reflex: midbrain
Perception of vision: visual cortex of occipital lobe
Primary sensory cortex
perception of general senses (Pain, touch, pressure, temperature)
Broca’s area
responsible for speaking and pronouncing words correctly
Wernicke’s area
language comprehension
Ependymal cells
part of choroid plexus
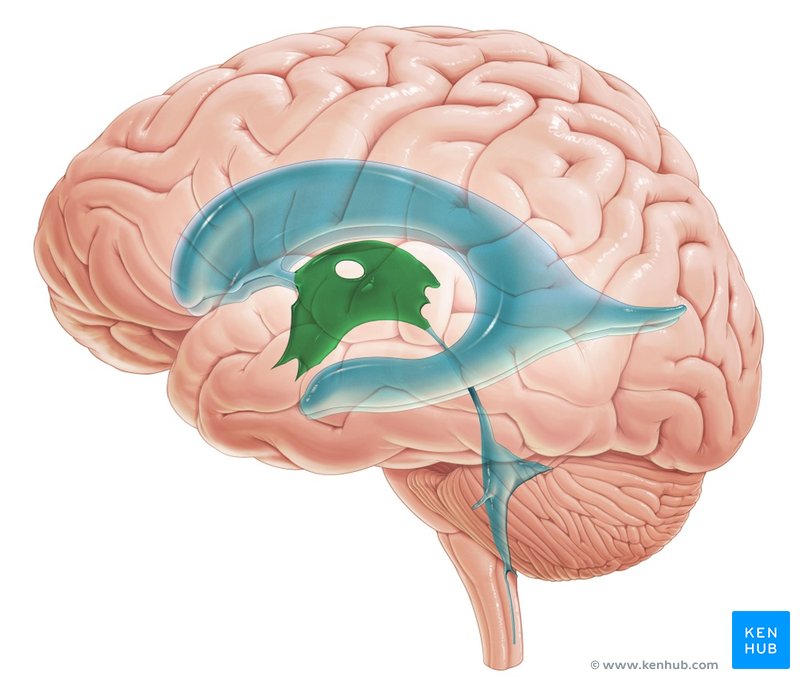
Choroid plexus
site for cerebrospinal fluid production
Lateral ventricle
contains cerebrospinal fluid
Fourth ventricle
Cavity located between brain stem and cerebellum- contains cerebrospinal fluid
Dorsal root GANGLION
contains sensory neuron cell bodies
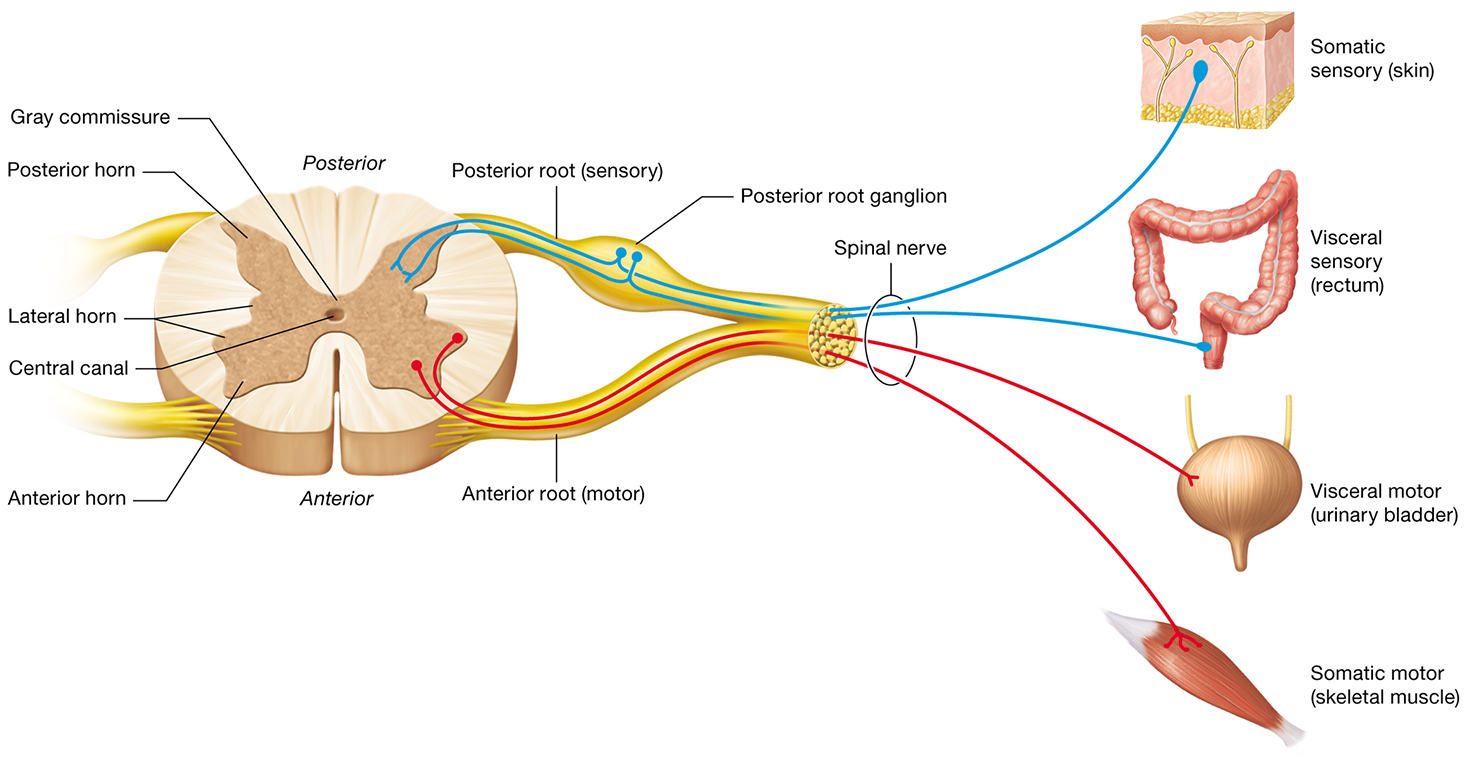
Dorsal(back) grey horn
Contains sensory neuron cell bodies
Ventral(front) grey horn
Contains motor neuron cell bodies
Ventral root
Contains motor axons
Dorsal root
Contains sensory axons
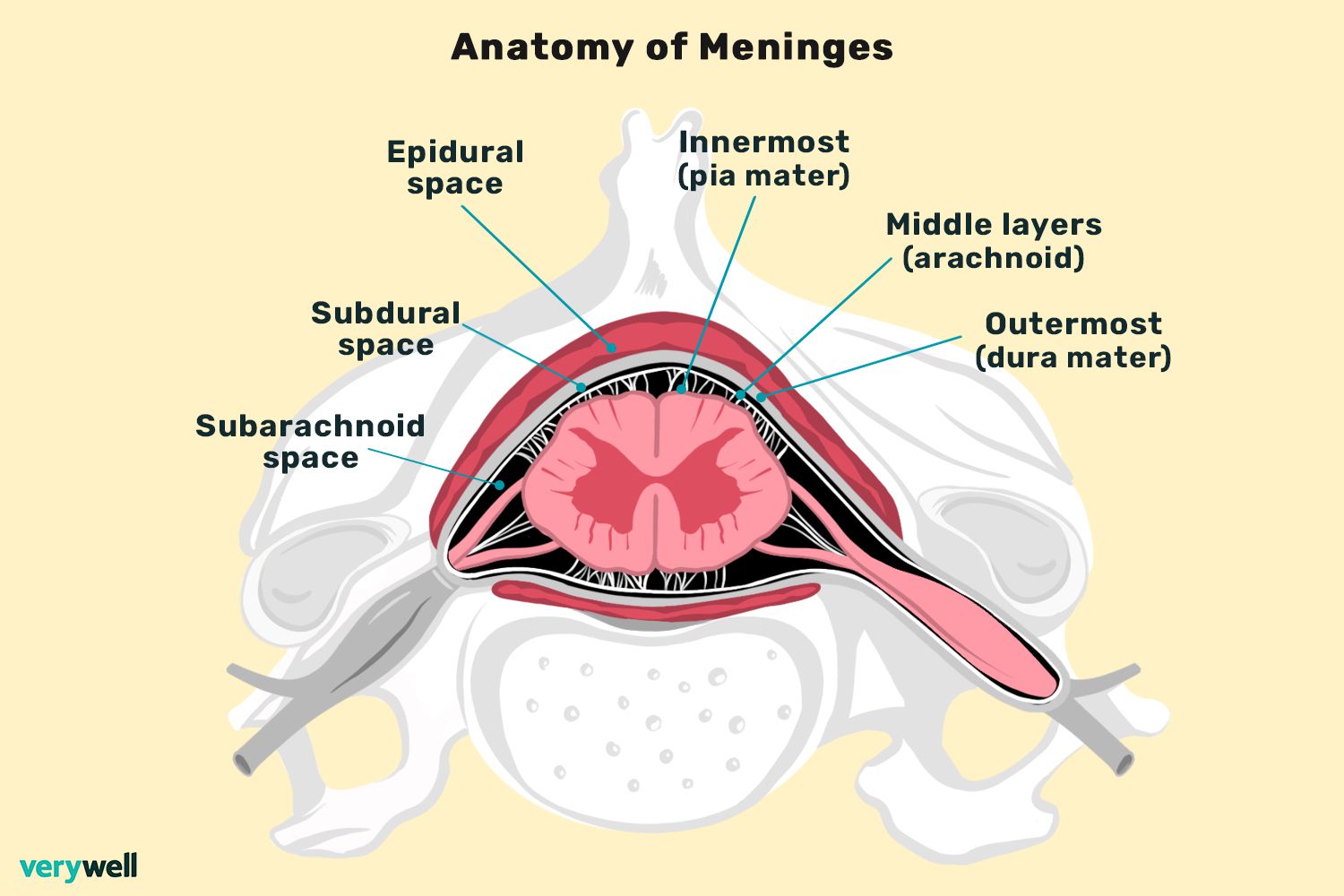
Spinal meninges superficial to deep
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater
Pia mater
Tendon reflex..
Golgi tendon organ is the receptor, and the response is muscle relaxation
Stretch reflex..
The muscle spindle is the receptor and the response is muscle contraction.
Reciprocal inhibition
Relaxes antagonists when primary muscles contract
Contralateral reflex
Occurs in opposite side of body from where stimulus is detected
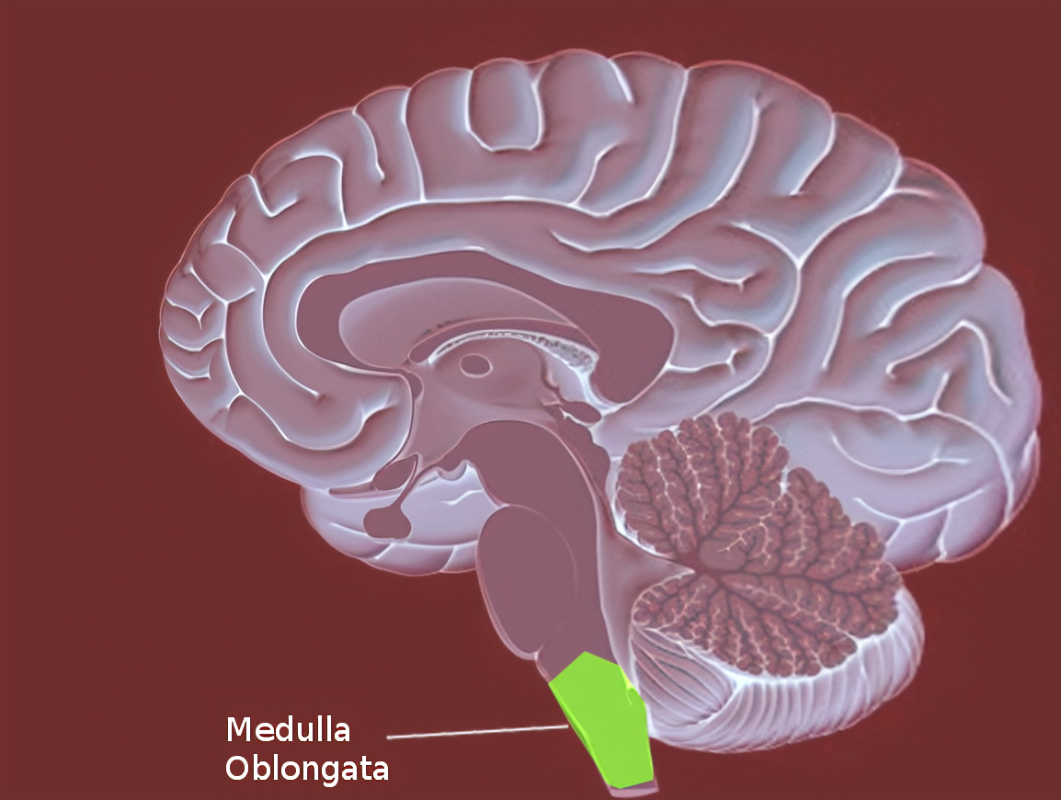
Medulla oblongata
Location for cardiovascular center
controls heart rate, bp, and swallowing
innervates muscles for breathing
What part of brain has role in memory?
Limbic system
contains hippocampus-learning and memory
and amygdala- fear, emotion
Flexor reflex(withdrawal)
helps to quickly pull away from painful stimulus (ex: hand on stove)
Resting membrane potential
neuron has negative charge because of sodium potassium pump (3 Na+ ions out and 2 K+ ions in) cell more negative
(-70mV)
Depolarization (rising phase)
stimulus reaches neuron- voltage-gated sodium channels open= Na+ ions rush in causing inside to become more positive
triggering action potential if threshold is reached(-55mV)
Perception occurs when sensory info reaches what part of the brain?
Primary sensory cortex
Repolarization (falling phase)
brings neurons down from peak at (+30mV) to -70mV
voltage-gated potassium channels open= K+ ions exit the neuron= restores negative charge in neuron
Hyperpolarization and return to resting state
Neuron becomes briefly more negative than resting state due to excess K+ LEAVING cell
(-80mV to -90mV)
Sodium potassium pump restores original ion balance= neuron goes back to resting potential(RESTING STATE) by restoring balance in the sodium-potassium pump
Threshold potential
(-55mV)
stimulus triggers voltage-gated sodium channels to open
action potential generated here
Which neurotransmitter is used in the sympathetic nervous system and causes bronchodilation (dilation of the bronchioles, or airways)?
also increases heart and breathing rates
Epinephrine and norepinephrine
Which neurotransmitter inhibits contraction in cardiac muscle?
(and contracts skeletal muscle)
Acetylcholine
Loss of this neurotransmitter in skeletal motor pathways leads to the tremors seen in Parkinson's.
dopamine
What term refers to a group of neuron cell bodies found in the CNS (central nervous system)?
nuclei
What term refers to a group of neuron cell bodies found in the PNS (peripheral nervous system)?
ganglia
The resting potential of a neuron is maintained by what 2 types of transport for sodium and potassium?
Leak channels and exchange pumps
Reticular activating system (RAS)- medulla
Maintains alertness(consciousness)
lets you sleep
What lobe contains the primary motor cortex? also associated with personality. contains Broca’s area
Frontal lobe
Multipolar neuron
CNS and ANS
control all skeletal muscles
most common
Bipolar neuron
rare
sensory pathways
Unipolar
one process extending from cell body