Week 16: SBAS (Westburg)
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
What are the major pharmacist/pharmacy compensation framework?
- medication reimbursement/business incentives
- MTM services
- payment for services (E/M)
- unique pharmacy services (e.g., med sync, packaging)
What are examples of challenges in medication reimbursement and business incentives?
DIR fees and clawbacks, 340B changes, MAC pricing issues, and lack of strong incentives
Why are MTM services difficult to sustain financially?
not all payers cover MTM, definitions vary by plan/region, and reimbursement is inconsistent
What are unique pharmacy services that may generate revenue but not via MTM/E/M?
med sync, compliance packaging, and other individualized services (varies by pharmacy and payer)
Why is provider status important for pharmacists?
Determines the ability to bill medical plans
Medicare requires federal legislation, Medicaid depends on state law, and commercial plans decide individually
What distinguishes medical billing from pharmacy billing in process flow?
medical billing → EMR → health plan with slower processing
pharmacy billing → PBM → instant adjudication
What fee-for-service payment structures?
CPT codes, MTM codes, E/M codes, targeted service codes, facility fees
What value-based payment structures?
pay-for-performance, bundled payments, shared savings, risk-based contracts, and capitation
What infrastructure considerations differ across practice settings (community pharmacy, clinic/health systems, FQHC/RHC)?
- community pharmacies need software for medical billing plus contracting/credentialing systems
- clinics use existing EMR billing systems
- FQHC/RHC may use PPS encounter-based billing
HCPCS
Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System
What is HCPCS Level I vs Level II?
Level I = CPT (5-digit numeric)
Level II = supply/service codes (letter + 4 digits
In billing, what do HCPCS, ICD-10, and NPI/TIN each represent?
HCPCS = what service
ICD-10 = why (diagnosis)
NPI/TIN = who provides service
What are key characteristics of CPT codes?
AMA-maintained, uniform service descriptions, 5-digit, code existence ≠ payment guarantee, eligibility for billing varies by profession
What is the first step in the billing process?
define the service being rendered
What is Comprehensive Medication Management (CMM)?
as tandard ensuring each medication is appropriate, effective, safe, and taken correctly for each patient's conditions
What components are required for Medicare Part D MTM?
annual CMR + quarterly TMRs, with a written summary, med list, and patient to-do list
99605
New Patient , first 15 min
99606
Established patient, first 15 min
99607
each additional 15 min
What factors drive MN Medicaid MTM crosswalk levels?
# of meds, # of MTPs, complexity, and time requirements
How do you bill a 29-minute established patient MTM visit with 12 meds and 2 MTPs?
99606 + 99607 + 99607
3 multiple choice options
What defines E/M service billing?
increasing complexity levels based on total time or medical decision making (MDM)
What are the two ways to select an E/M code?
based on total time OR medical decision making
What are the four levels of medical decision making?
straightforward, low, moderate, high
Straightforward
99202/99212
Low
99203/99213
Moderate
99204/99214
High
99205/99215
What three components determine MDM?
problems, data, and risk
What is the time range for new patient E/M codes 99202-99205?
15-29, 30-44, 45-59, 60-74 minutes
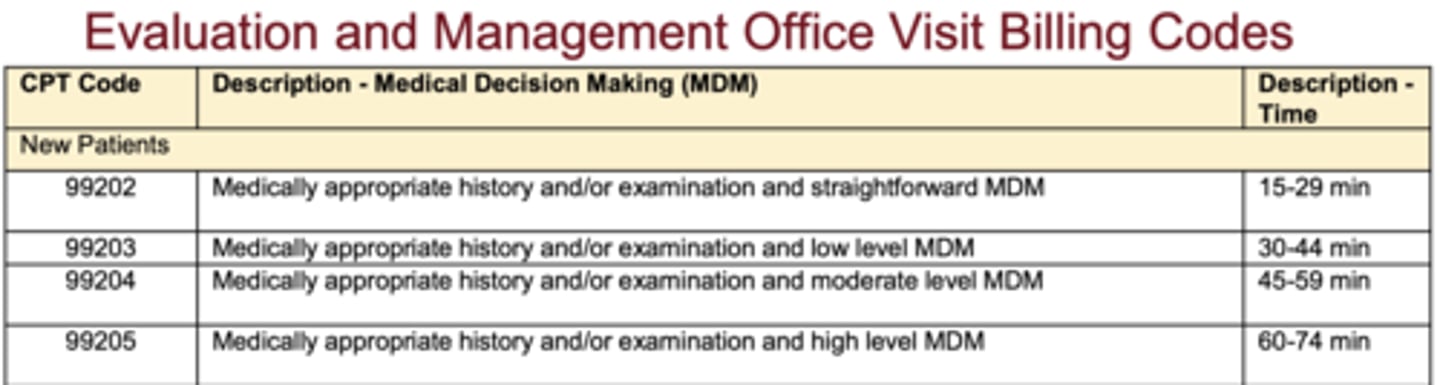
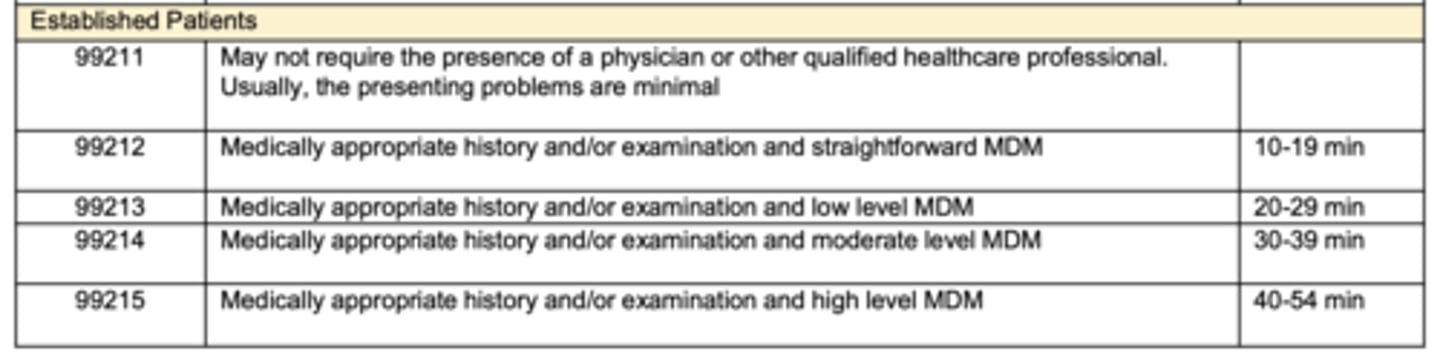
What is the time range for new patient E/M codes 99212-99215?
10-19, 20-29, 30-39, 40-54
What E/M code applies to a 47-minute new patient visit?
99204
3 multiple choice options
What is the E/M code for a 15-minute established patient visit?
99212
3 multiple choice options
What is a key difference between E/M billing and MTM billing?
E/M uses the same codes as other HCPs but requires copays
MTM may avoid copays but is less consistently covered
What is "incident-to" billing?
billing under a physician's supervision; pharmacists typically only bill 99211 unless state/payer allows higher levels
What types of targeted service CPT codes can pharmacists bill?
transitional care, CGM start/interpretation, chronic care management, diabetes education, annual wellness visits

Which preventive counseling codes correspond to 15 minutes?
99401
Which preventive counseling codes correspond to 30 minutes?
99402
Which preventive counseling codes correspond to 45 minutes?
99403
Which preventive counseling codes correspond to 60 minutes?
99404
What chronic care management codes cover physician/qualified practitioner time?
1. 99424-99425
2. 99491-99437
What chronic care codes involve clinical staff time directed by a physician?
1. 99426-99427
2. 99487-99489
3. 99490, 99439
What is CPT 98960-98962 used for?
patient self-management education using standardized curriculum (individual or group)
What is CPT 96372 used for?
billing for injection administration (intramuscular or subcutaneous)
What are examples of other areas with specific billing codes pharmacists may use?
anticoagulation, COPD/asthma, CKD, CHF, obesity counseling, hypertension, mental health, HIV prevention, naloxone, contraception prescribing
Why is follow-up essential in billing processes?
to manage denied claims, handle audits, and continuously improve revenue processes
What is pay-for-performance (P4P)?
a value-based model linking financial incentives to quality metrics, best practices, and patient satisfaction
How do value-based payment strategies vary across practice settings?
Community pharmacies may initiate payer contracts; clinics coordinate through contracting departments; FQHCs must follow state-specific rules
Which of the following describes an advantage for pharmacists to use Evaluation and Management CPT codes to bill for patient care services?
These claims are the same used by other health care providers, including physicians and nurse practitioners.
3 multiple choice options
Which of the following is an example of value-based payment?
A network of community pharmacies will be paid a bonus incentive if 60%
of the Type 2 diabetes population achieves an A1C of <7% in a year
3 multiple choice options
What four domains interact to define pharmacist practice authority?
1. Scope of Practice
2. Standard of Care
3. Provider Status
4. Payment for Services
How does the Federation of State Medical Boards define "scope of practice"?r
rules, regulations, and boundaries allowing a trained practitioner to practice, governed by continuing education and professional accountability
What major activities are included in Minnesota's statutory definition of the practice of pharmacy?
interpreting/evaluating prescriptions, compounding, labeling, dispensing, clinical monitoring, C-LIA waived tests, drug/device selection, drug administration, regimen reviews, and CPA-based therapy management
What is Standard of Care regulation?
a regulatory model where pharmacists practice to the level consistent with their education, training, experience, and setting, judged by peers under similar circumstances
Which states currently use Standard of Care regulation for pharmacy?
Idaho, Alaska, Iowa; California's version effective 2026
What is a key difference between Standard of Care and Bright Line regulation?
Bright Line regulation uses explicit, objective, specific rules
Standard of Care uses professional judgment evaluated case-by-case
What is an example of Bright Line regulation from pharmacy?
pharmacists must complete 15 CE hours each calendar year (Idaho example)
Why is Standard of Care considered more flexible than Bright Line rules?
it adapts to evolving practice guidelines, tech changes, and expanding pharmacist training without needing constant statutory updates
How does "entry barrier vs. legal ceiling" explain scope of practice?
Minimum competency sets the entry barrier; the legal ceiling may limit pharmacists from practicing to their individual training, which Standard of Care looks to correct
What are the two types of collaborative prescribing agreements?
patient-specific CPA and population-specific CPA
What defines a patient-specific CPA?
a signed agreement for each patient involving the patient, provider, and pharmacist; typically for chronic disease management
What defines a population-specific CPA?
agreement between provider and pharmacist allowing services for broad patient groups regardless of prior provider-patient relationship
What are the two types of Autonomous Prescribing?
Statewide Protocols and Unrestricted (Independent) Authority
What does Independent Prescribing allow pharmacists to do in Minnesota?
independently prescribe opioid antagonists, nicotine replacement therapy, self-administered hormonal contraception, and HIV PrEP/PEP (starting 2026)
How is a Collaborative Practice Agreement defined in federal literature?
an agreement allowing pharmacists to assume responsibility for assessments, ordering labs, and initiating, modifying, monitoring, and adjusting drug regimens under a defined protocol
What does Minnesota statute require pharmacists to do when making therapy changes under a CPA?
document changes and notify or report them to the practitioner responsible for patient care
What historical milestone in 1952 shaped pharmacist practice limitations?
APhA Code of Ethics prohibited pharmacists from discussing therapeutic effects or drug composition with patients
When did Minnesota adopt pharmacist CPA authority?
around 1999
What is Provider Status in pharmacy?
recognition by a payer that a pharmacist can bill for and be reimbursed for healthcare services
Why is Medicare Part B provider status difficult to achieve for pharmacists?
it requires federal legislation to amend the provider list
What was the significance of Minnesota Medicaid covering MTM starting in 2006?
minnesota became one of the first states to reimburse pharmacists for MTM services, defining pharmaceutical care in statute
What 2024 Minnesota law expanded pharmacist coverage beyond MTM?
health plans must reimburse pharmacists for services within their scope if they reimburse physicians for the same services (effective Jan 1, 2025)
What types of targeted services might now be reimbursable under Minnesota's 2024 legislation?
vaccine assessments, strep test-and-treat, hormonal contraception prescribing, and other focused clinical services within pharmacist scope