[L1] Gauss' Law
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
electric flux
the measure of “flow” of electric field through a surface
gauss’ law
this states that there is a net outward or inward electric flux through a closed surface depending on the sign of the enclosed charge
sign of the enclosed charge
gauss’ law states that there is a net outward or inward electric flux through a closed surface depending on the ____
gauss’ law
this states that charges outside the surface do not give a net electric flux through a surface
do not
gauss’ law states that charges outside the surface ____ give a net electric flux through a surface
gauss’ law
this states that the net electric flux is directly proportional to the net amount of charge within the surface but is otherwise independent of the size of the enclosed surface
net electric flux
gauss’ law states that the ____ is directly proportional to the net amount of charge within the surface but is otherwise independent of the size of the enclosed surface
gauss’ law
this primarily states that the total electric flux through any closed surface (a surface enclosing definite volume) is proportional to the total/net electric charge inside the surface
total electric flux
gauss’ law’s main statement is that the ____ through any closed surface (a surface enclosing definite volume) is proportional to the total/net electric charge inside the surface
proportional
gauss’ law’s main statement is that the total electric flux through any closed surface (a surface enclosing definite volume) is ____ to the total/net electric charge inside the surface
total/net electric charge inside the surface
gauss’ law’s main statement is that the total electric flux through any closed surface (a surface enclosing definite volume) is proportional to the ____
carl friedrich gauss
he invented the gauss’ law
carl friedrich gauss
known for electromagnetism, number theory, statistics, non-euclidean geometry, cometary orbital mechanics
carl friedrich gauss
he is a founder of the german magnetic union which studies the earth’s magnetic field
gauss’ law
this is an expression of the general relationship between the net electric flux through a closed surface and the charge enclosed by the surface
gauss’ law
states that the closed surface is often called a gaussian surface
gaussian surface
the closed surface is often called a ____
gauss’ law
this is of fundamental importance as it provides a different way to express the relationship of electric charge and electric field
electric charge, electric field
gauss’ law is of fundamental importance as it provides a different way to express the relationship of ____ and ____
flux
the ____ is independent of the radius of the sphere. it depends only on the charge enclosed by the su
radius
the flux is independent of the ____ of the sphere. it depends only on the charge enclosed by the sphere
charge enclosed by the sphere
the flux is independent of the radius of the sphere. it depends only on the ____
permittivity of free space
a measure of how much an electric field affects, and is affected by, a dielectric medium
the same (electric field decreases, area increases, cancelling each other out)
every field line passes through the smaller and larger sphere radii. the flux through these two spheres is ____
the same
the net electric flux is ____ through all surfaces
independent
net flux through any closed surface surrounding a point charge q is ____ of the shape of the surface
zero (since the field lines just passes through the objects surface. the field lines enter and leave through the surface (through imaginary holes)
if the charge is outside the closed surface with an arbitrary shape, the electric flux is ____
the charge is outside the closed surface with an arbitrary shape
if a field line enters the surface and leaves at another point, this means that
zero
electric flux through a closed surface that surrounds no charge is ____
symmetry
in choosing the right gaussian surface, always take advantage of ____ to make “electric field” same everywhere of a gaussian surface
electric field
in choosing the right gaussian surface, always take advantage of symmetry to make “____” same everywhere of a gaussian surface
gaussian surface
an imaginary closed surface used in Gauss's Law to calculate the electric field due to a charge distribution
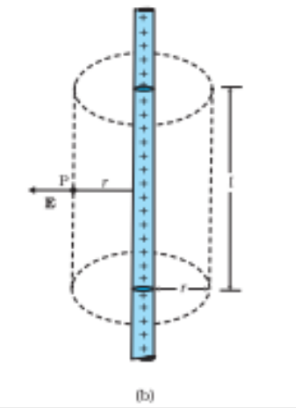
spherical gaussian surface (expressed as a cylinder)
this is the right gaussian surface for a uniform and symmetrical point charge
doesn’t match the symmetry of the electric field
no one will stop you from choosing any gaussian surface, but a gaussian surface that ____ is not very useful
zero
when electric field is 0 everywhere in the gaussian surface, gauss’ law requires that the net charge inside the surface is ____
electrostatic (charges not in motion)
under ____ conditions, any excess charge on a solid conductor resided entirely on the conductor’s surface
excess charge
under electrostatic conditions (charges not in motion), any ____ on a solid conductor resided entirely on the conductor’s surface
solid conductor
under electrostatic conditions (charges not in motion), any excess charge on a ____ resided entirely on the conductor’s surface
conductor’s surface
under electrostatic conditions (charges not in motion), any excess charge on a solid conductor resided entirely on the ____
surface of conductor
where does the excess charge (qc) within the conductor reside in electrostatic conditions
zero
what is the electric field within a conductor in electrostatic conditions
outside (by the surface of the conductor)
in electrostatic conditions, excess charge inside conductors is ____ the gaussian surface
gaussian surface
if there is no charge within the cavity of the conductor, we can use a ____ to show that the net charge on the surface of the cavity must be zero, because electric field is zero everywhere on the gaussian surface
zero
if there is no charge within the cavity of the conductor, we can use a gaussian surface to show that the net charge on the surface of the cavity must be ____, because electric field is zero everywhere on the gaussian surface
electric field
if there is no charge within the cavity of the conductor, we can use a gaussian surface to show that the net charge on the surface of the cavity must be zero, because ____ is zero everywhere on the gaussian surface
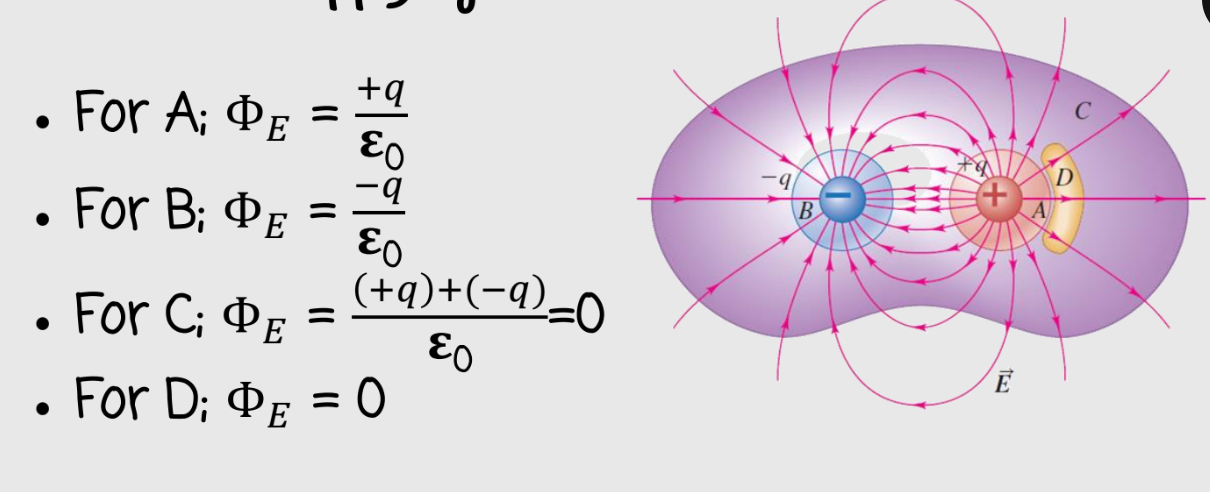
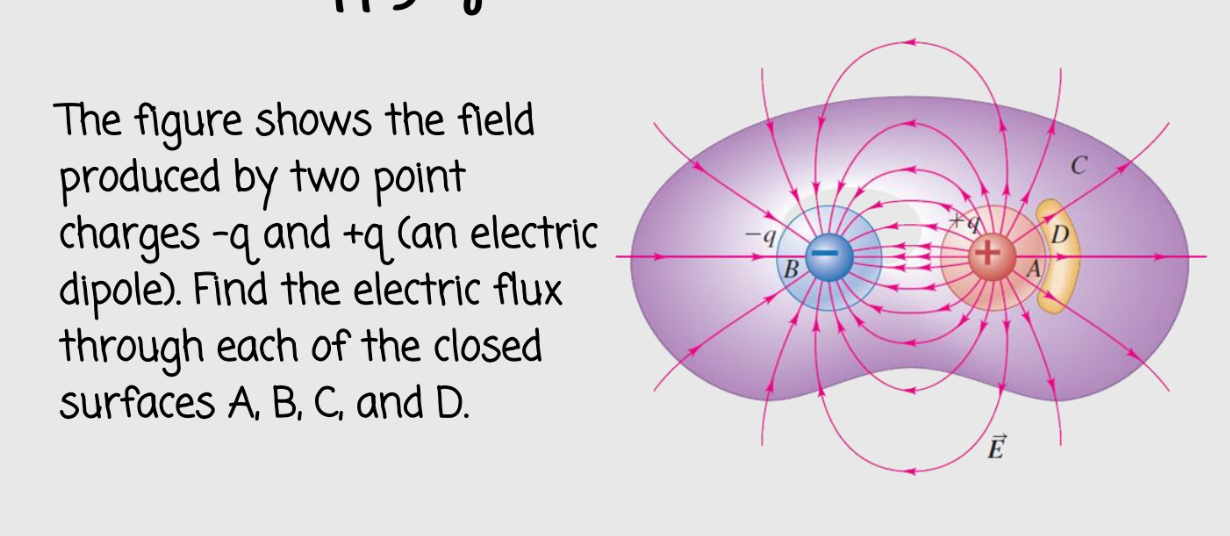
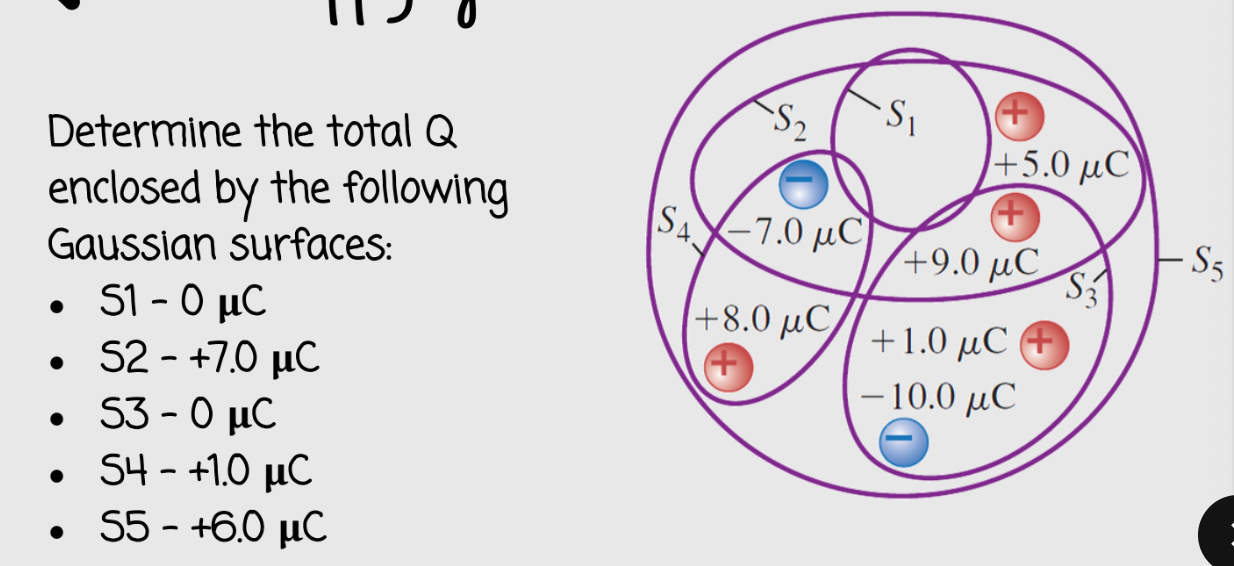
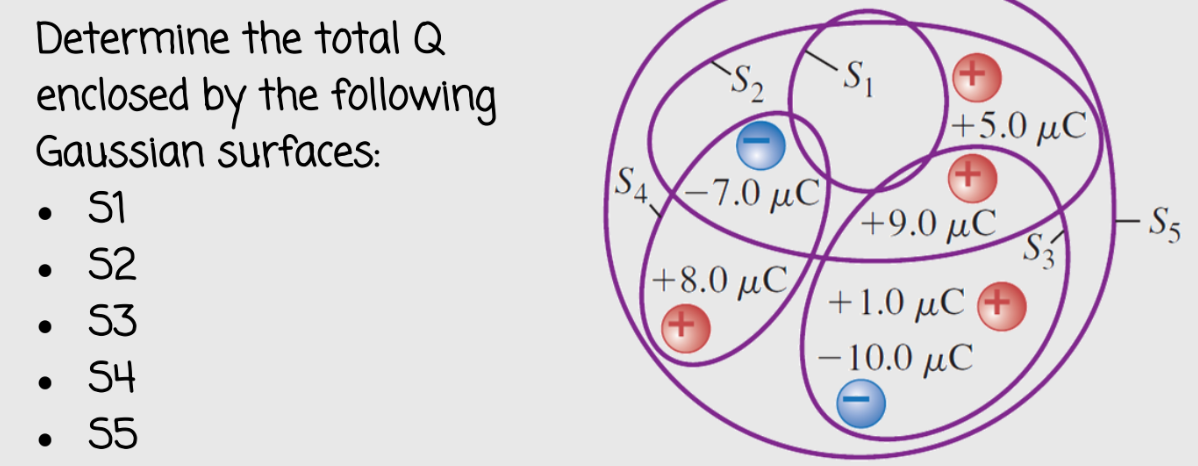
the flux will remained unchanged
if all the dimensions of the box are increased by a factor of 3, what effect will this change have on the electric flux through the box?