18 Rates of Reactions
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
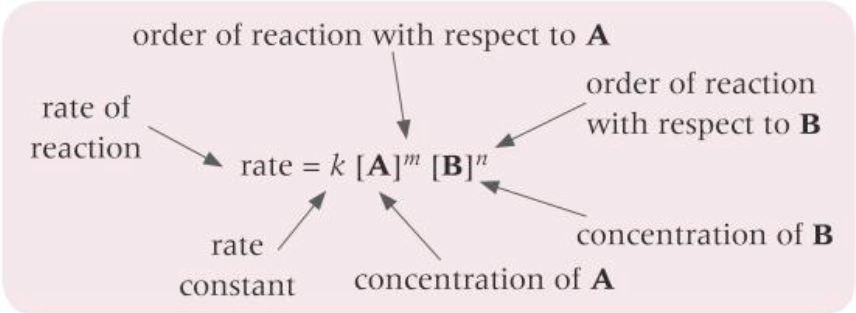
rate equation
rate = Δ[] / Δt
![<p>rate = <span>Δ[] / Δt</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/2c9a36d7-bf8d-4a32-a114-659205097536.png)
rate units
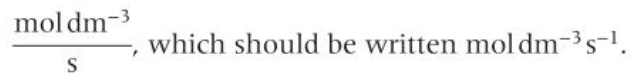
rate equation
overall order

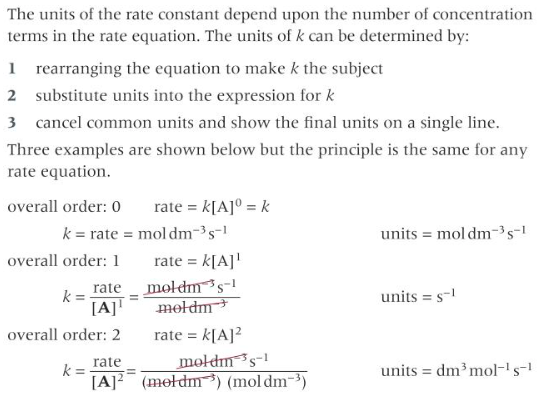
finding units of rate constant k
continuous monitoring def
continuous measurements taken during the course of a reaction
monitoring by gas collection
monitoring by mass loss
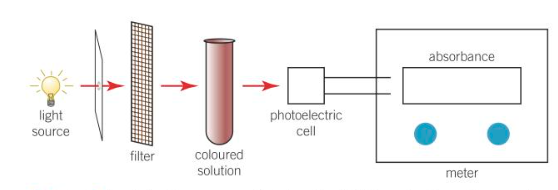
monitoring w a colorimeter
how does a colorimeter work
the wavelength of the light passing through a coloured solution is controlled using a filter
the amount of light absorbed by a solution is measured
what does the gradient of a []/t graph show
the rate of reaction
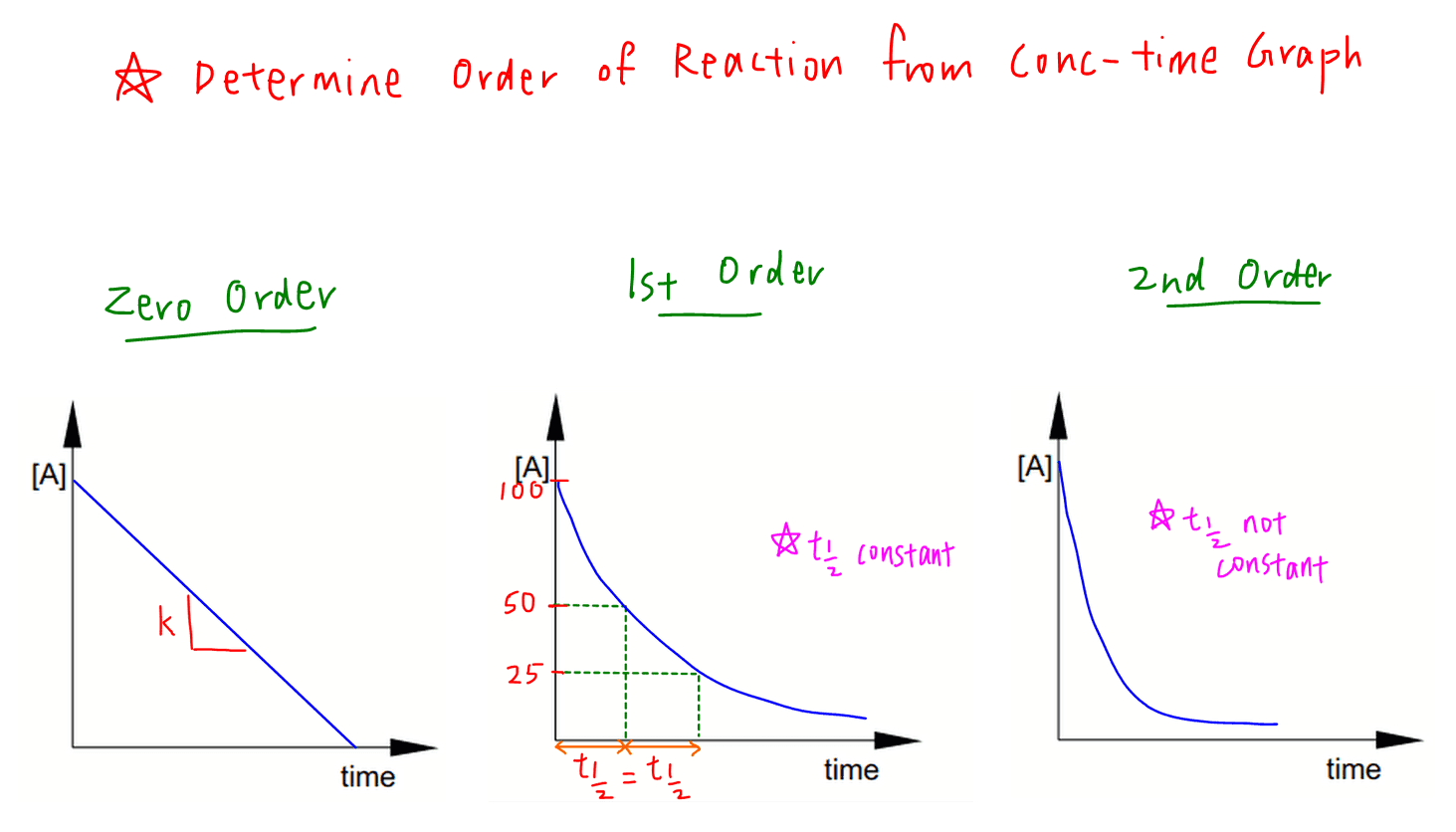
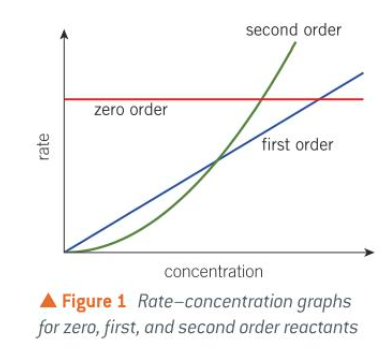
zero and first order on a []/t graph
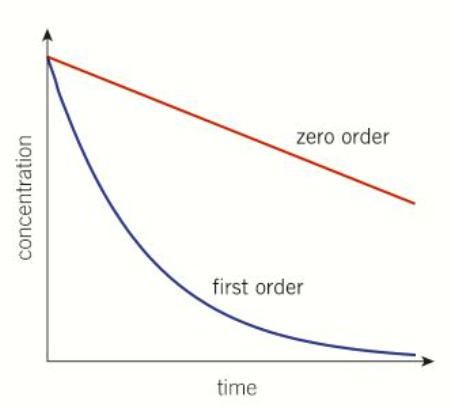
second order on a []/t graph
half life def
time taken for half of a reactant to be used up
first order reactions have a CONSTANT half life w the [] halving each time
![<p><span>time taken for half of a reactant to be used up</span></p><ul><li><p>first order reactions have a CONSTANT half life w the [] halving each time</p></li></ul>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a4d950b1-62d3-4e09-a872-deb945547634.png)
exponential decay def (and which order is this)
when the [] halves every half life
first order
![<ul><li><p>when the [] halves every half life</p></li><li><p>first order</p></li></ul>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/bde4a804-78e3-4257-85ad-8a9e6edde847.png)
two ways of determining k from a first order rxn
calculating rate constant from rate
calculating rate constant from the half-life
how to calculate rate constant from rate
draw tangents to curve at particular []
gradient of tangent = rate
rearrange rate eqn + sub in values of rate (gradient of tangent) and [] from where the tangent was drawn
how to calculate rate constant from half-life
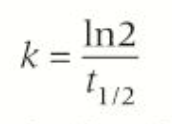
orders of rxn from shape of rate/[] graph
initial rates method
the initial rate is the instantaneous rate at the start of a rxn when t=0
can be found by measuring grad of a tangent at t=0 on a []/t graph
a clock rxn is a more convenient way of obtaining initial rate from a single measurement
the time t from start of an experiment is measured for a visual change to be observed (a colour of ppt)
initial rate proportional to 1/t
iodine clocks
common clock rxn is formation of iodine
starch usually added (blue-black colour)

rate determining step def
in multi-step reactions, the steps take place at different rates
the slowest step in the sequence is the RDS
effect of temp on k
as T increases, rate increases and value of k will also increase
for many rxns, each 10°C rise doubles k and rate
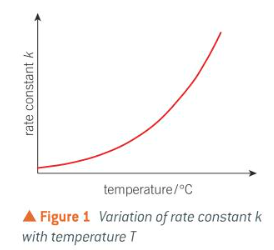
how does temp increase affect rate
increasing temp shifts Boltzmann distribution to right - proportion of particles that exceed Ea increases
as temp increases, particles move faster and collide more frequently
more particles colliding with sufficient Ea and correct orientation
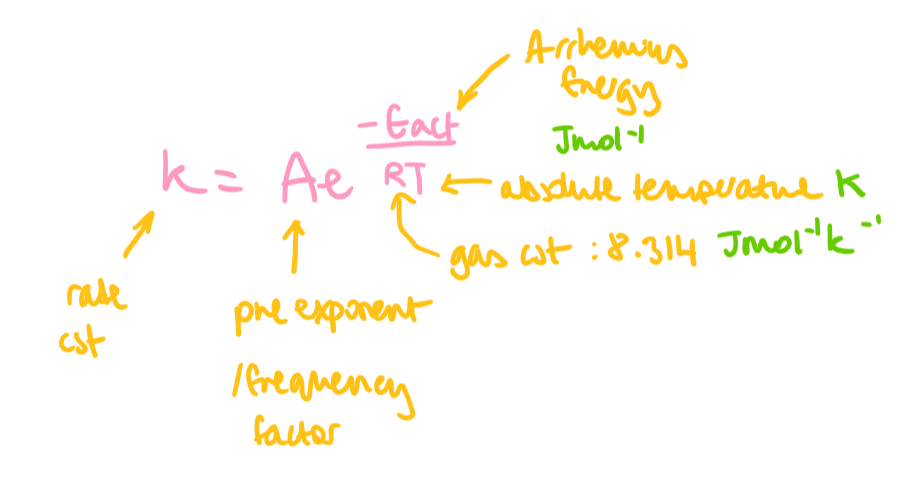
Arrhenius equation
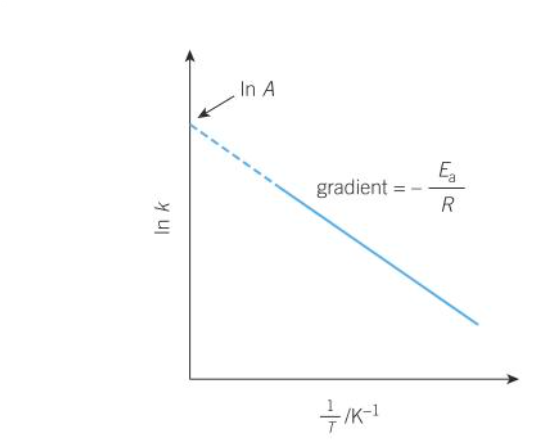
logarithmic form of arrhenius equation
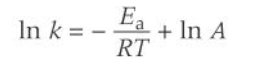
how does the logarithmic form of arrhenius eqn relate to graphs
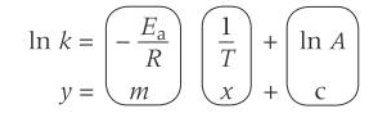
on a lnk and 1/T graph what does the gradient show
-Ea/R
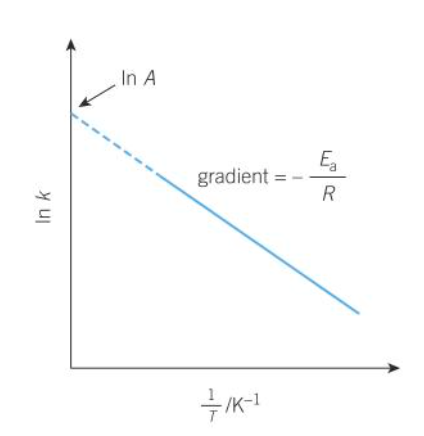
on a lnk and 1/T graph what does the y-intercept show
lnA