CELL STRUCTURE AND DIVISION
1/100
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
What is the difference between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells
prokaryotic cells are smaller and simpler
or
eukaryotic cells are complex and larger
Give 4 examples of eukaryotic cells
animal cells
plant cells
algal cells
fungal cells
Give 1 example of a prokaryotic cell
bacteria
Name the 3 extra organelles in a plant cell than in an animal cell
cell wall
chloroplast
vacuole
In a plant cell, what is the cell wall made of
cellulose
In an algal cell, what is the cell wall made of
cellulose
In a fungal cell, what is the cell wall made of
chitin
What is the structure of the cell-surface membrane
found on the surface of animal cells
found inside the cell wall of other cells
mainly made of lipids and protein
What is the function of the cell-surface membrane
regulates the movement of substances into and out of the cell
has receptor molecules on it, this allows it to respond to chemicals like hormones
What is the structure of the nucleus
A large organelle surrounded by the nuclear envelope (double membrane) which contains nuclear pores
the nucleus contains chromosomes which are made from protein bound linear DNA
contains nucleolus which floats in the nucleoplasm
What is the function of the nucleus
controls the cells activities by controlling the transcription of DNA
DNA contains instructions to make proteins
the nuclear pores allow substance like RNA to move between the nucleus and the cytoplasm
the nucleolus makes ribosomes
What is the structure of the mitochondrion
oval shaped (usually)
double membrane
inner membrane is folded to form structures called cristae
inside is the matrix which contains enzymes involved in respiration
What is the function of the mitochondrion
the site of aerobic respiration
where ATP is produced
What is the structure of the chloroplast
A small, flattened structure in plant and algal cells
surrounded by a double membrane
contains membranes inside called thylakoid membranes which are stacked up in parts of the chloroplast to form grana
grana are linked together by lamellae
contains stroma in the middle (like a cytoplasm for the chloroplast)
What is the function of the chloroplast
the site of photosynthesis
some parts of photosynthesis occur in the grana and other parts happen in the stroma (a thick fluid)
What is the structure of the Golgi apparatus
a group of fluid-filled, membrane bound flattened sacs
vesicles are often seen at the edges of these sacs
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus
processes and packages new lipids and proteins
makes lysosomes
What is the structure of the Golgi vesicle
a small fluid filled sac in the cytoplasm
surrounded by a membrane
produced by the Golgi apparatus
What is the function of the Golgi vesicle
store lipids and proteins made by the Golgi apparatus
transports these lipids and proteins out of the cell membrane
What is the structure of the lysosomes
a round organelle
surrounded by a membrane
type of Golgi vesicle
What is the function of the lysosomes
contains digestive enzymes called lysozymes
these enzymes can be used to digest invading cells or break down worn out components of the cell
What type of cell is the 70S ribosome found in
prokaryotic
What type of cell is the 80S ribosome found in
eukaryotic
What is the structure of a ribosome
a very small organelle that either floats freely in the cytoplasm or is attached to the RER
it is made up of proteins and RNA it is not surrounded by a membrane
it is made of a small and large subunit
What is the function of the ribosome
site where proteins are made
What does RER stand for
rough endoplasmic reticulum
What does SER stand for
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
What is the structure of the RER
a system of membranes enclosing a fluid filled space
the surface is covered with ribosomes
What is the function of the RER
folds and processes proteins
What is the structure of the SER
a system of membranes enclosing a fluid-filled space
no ribosomes
What is the function of the SER
synthesises and processes lipids
What is the structure of the cell wall
a rigid structure that surrounds cells in plants, algae and fungi
in plants and algae the cell wall is made of cellulose
in fungi the cell wall is made of chitin
What is the function of the cell wall
supports cells and prevents them from changing shape
What is the structure of the vacuole
a membrane-bound organelle
found in the cytoplasm
contains cell sap- a weak solution of sugar and salts
the surrounding membrane is called the tonoplast
What is the function of the vacuole
helps to maintain pressure in the cell
keeps the cell rigid
stops plants wilting
involved in the isolation of unwanted chemicals in the cell
What are epithelial cells in the small intestine specialised for
food absorption
What is a tissue
a group of cells working together to perform a specific function
What is an organ
A group of different tissues working together
Name the parts of an animal cell
cell surface membrane
nucleus
nucleolus
nuclear envelope
nuclear pores
nucleoplasm
mitochondria
cytoplasm
Golgi apparatus
Golgi vesicle
lysosome
RER
SER
ribosome
Name the parts of a plant cell
cell surface membrane
nucleus
nucleolus
nuclear envelope
nuclear pores
nucleoplasm
mitochondria
cytoplasm
Golgi apparatus
Golgi vesicle
lysosome
RER
SER
ribosome
chloroplast
vacuole
cell wall
Name the parts of a bacterial cell
slime capsule
cell wall
plasma membrane
plasmids
circular DNA
flagellum
cytoplasm
ribosomes
In bacterial cells what is the cell membrane made of
lipids
proteins
In bacterial cells what is the cell wall made of
murein - a glycoprotein
What is the function of the slime capsule in bacteria
helps protect it from attack by the immune system
What are plasmids
small loops of DNA
contains genes for things like antibiotic resistance
Do prokaryotic cells contain membrane bound organelles
no
What type of ribosomes do bacterial cells contain
70S
What is the job and structure of the flagellum
rotates to make the prokaryotic cell move
its a long hair-like structure
Name 3 parts of a virus
core of genetic material (DNA or RNA)
protein coat around the core called a capsid
attachment proteins stick out from the edge of the capsid. These let the virus cling onto a suitable host cell
How do prokaryotic cells replicate
binary fission
What are the 4 steps of binary fission
circular DNA and plasmids replicate (plasmids can replicate more than once)
cell grows and the DNA loops move to opposite poles of the cell
cytoplasm begins to divide
cell wall forms and two daughter cells are produced
Describe how viruses replicate
they use their attachment proteins to bind to complimentary receptor proteins on the surface of host cells
they inject their DNA/RNA into the host cell
the host cell uses its machinery to replicate the parts of a virus
the virus assembles and leaves the cell
Explain why some viruses can only infect one type of cell
different viruses have different attachment proteins
therefore they require different receptor proteins on the host cell so some viruses can only infect one type of cell
Define magnification
how much bigger the image is than the specimen
Define resolution
how well a microscope can distinguish between two points that are close together
What is the equation for working out magnification
magnification= image size / actual size
What are the two types of microscope
light
electron
What is the maximum magnification on a light microscope
X1500
What is the maximum resolution on a light microscope
0.2 micrometres
Name 2 types of electron microscope
transmission electron microscope
scanning electron microscope
How do TEMs work
uses electromagnets to focus a beam of electrons which is transmitted through the specimen
denser parts of the specimen absorb more electrons which makes them look darker on the final image
Give 1 advantage of TEMs (transmission electron microscopes)
very high resolution so you can see the internal structure of organelles like chloroplasts
Give 1 disadvantage of TEMs (transmission electron microscopes)
can only be used on thin specimens
How do SEMs work
they scan a beam of electrons across the specimen. this knocks off electrons from the specimen which are gathered in a cathode ray tube to form an image
Give 2 advantages of SEM (scanning electron microscopes)
images can be 3D
can be used on thicker specimens
Give a disadvantage of the SEM (scanning electron microscope)
it has a lower resolution than the TEM
What method is used to separate out different organelles in a cell
cell fractionation
What are the 3 steps of cell fractionation
homogenisation
filtration
ultracentrifugation
Within cell fractionation, describe homogenisation
the process of breaking up the cells
this can be done by vibrating them or by grinding them in a blender
this breaks the plasma membrane and releases the organelles into solution
When breaking up the cells during homogenisation, the solution that the organelles fall into have to have 3 important conditions what are they
cold - this is to reduce the activity of enzymes that break down organelles
isotonic - this means it has the same concentration of chemicals and water as the cell being broken down to prevent damage to the cells through osmosis causing the cell to burst.
A buffer solution added - to maintain the pH
Within cell fractionation, describe filtration
the solution is filtered through a gauze to separate any large cell debris or tissue debris
Within cell fractionation, describe ultracentrifugation
you have a solution containing organelles
to separate a particular organelle from the others, you use ultracentrifugation
the cell fragments are poured into a tube
the tube is put in a centrifuge and is spun at a low speed
the heaviest organelles collect at the bottom of the tube forming a thick sediment called the pellet
the rest of the organelles are suspended above the sediment - supernatant
supernatant is drained off
centrifuge is spun faster and the next heaviest organelle collects
this is repeated at higher and higher speeds
After being in the centrifuge, a thick sediment forms at the bottom of the tube. What is this called
the pellet
After being in the centrifuge, a thick sediment forms at the bottom of the tube and there is a solution containing the rest of the organelles on top. What is this called
supernatant
During ultracentrifugation, in what order do the organelles get separated
nuclei
chloroplast
mitochondria
lysosome
ER
ribosomes
What are the 2 types of cell division
mitosis
meiosis
What is mitosis needed for
growth
repair
The cell cycle consists of a period of growth and DNA replication. what is this called
interphase
Interphase is separated into 3 stages. what are these called
G1 or gap phase 1
synthesis
G2 or gap phase 2
What happens during gap phase 1
cell grows
new organelles and proteins are made
What happens during the synthesis stage of interphase
cell replicates its DNA
What happens during gap phase 2
cell grows
proteins needed for cell division are made
What are the 4 stages of mitosis
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
What joins two chromatids
centromere
What is one strand of a chromosome called
chromatid
Describe prophase
chromosomes condense getting shorter and fatter
tiny bundles of protein called centrioles start moving to opposite ends of the cell forming a network of protein fibres across it called the spindle
the nuclear envelope breaks down and the chromosomes lie free in the cytoplasm
Describe metaphase
the chromosomes line up down the middle of the cell and attach to the spindle fibres by their centromere
Describe anaphase
the centromeres divide separating each chromatid
spindles contract
this pulls the chromatids to opposite poles of the spindle
this makes chromatids appear to be V shaped
Describe telophase
the chromatids reach opposite poles on the spindle
they uncoil and become long and thin again
they are now called chromosomes again
nuclear envelope forms
this forms 2 nuclei
division of the cytoplasm (cytokinesis) occurs
this results in 2 genetically identical daughter cells
What is cytokinesis
division of the cytoplasm
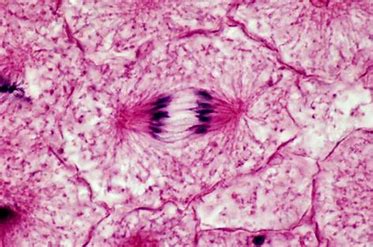
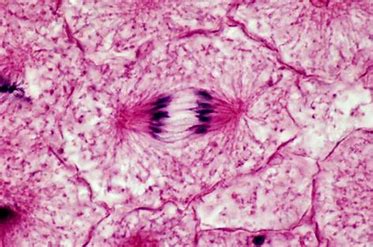
What stage of the cell cycle is this
anaphase
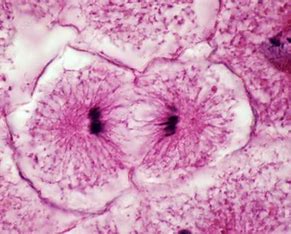
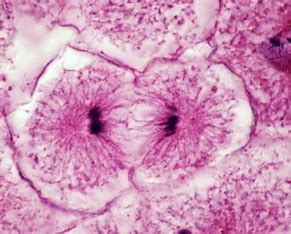
What stage of the cell cycle is this
telophase
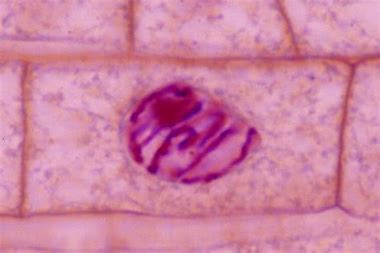
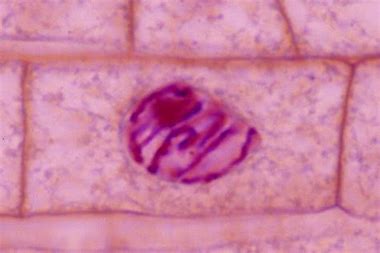
What stage of the cell cycle is this
prophase
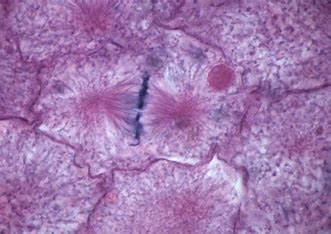
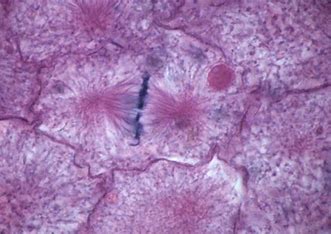
What stage of the cell cycle is this
metaphase
Explain what is cancer the result of
uncontrolled cell division
due to a mutation in a gene that controls cell division
this causes cells to keep dividing which causes a tumour
cancer is the result of a tumour that invades surrounding tissue
What controls mitosis and the cell cycle
genes
What part of the cell cycle does chemotherapy disrupt and how
G1
this prevents the synthesis of enzymes needed for DNA replication
this disruption to the cell cycle forces it to kill its self
What part of the cell cycle does radiation disrupt and how
Synthesis
radiation damages DNA at several points in the cell cycle (before and during S phase) the DNA in the cell is checked for damage
if there is damage, the cell will kill itself
what is the advantage of light microscopes
cheap
What is the advantage of electron microscopes
high resolution and magnification