Transport Mechanisms Across Cell Membranes
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Passive transport
Moves substances down concentration gradients using kinetic energy.
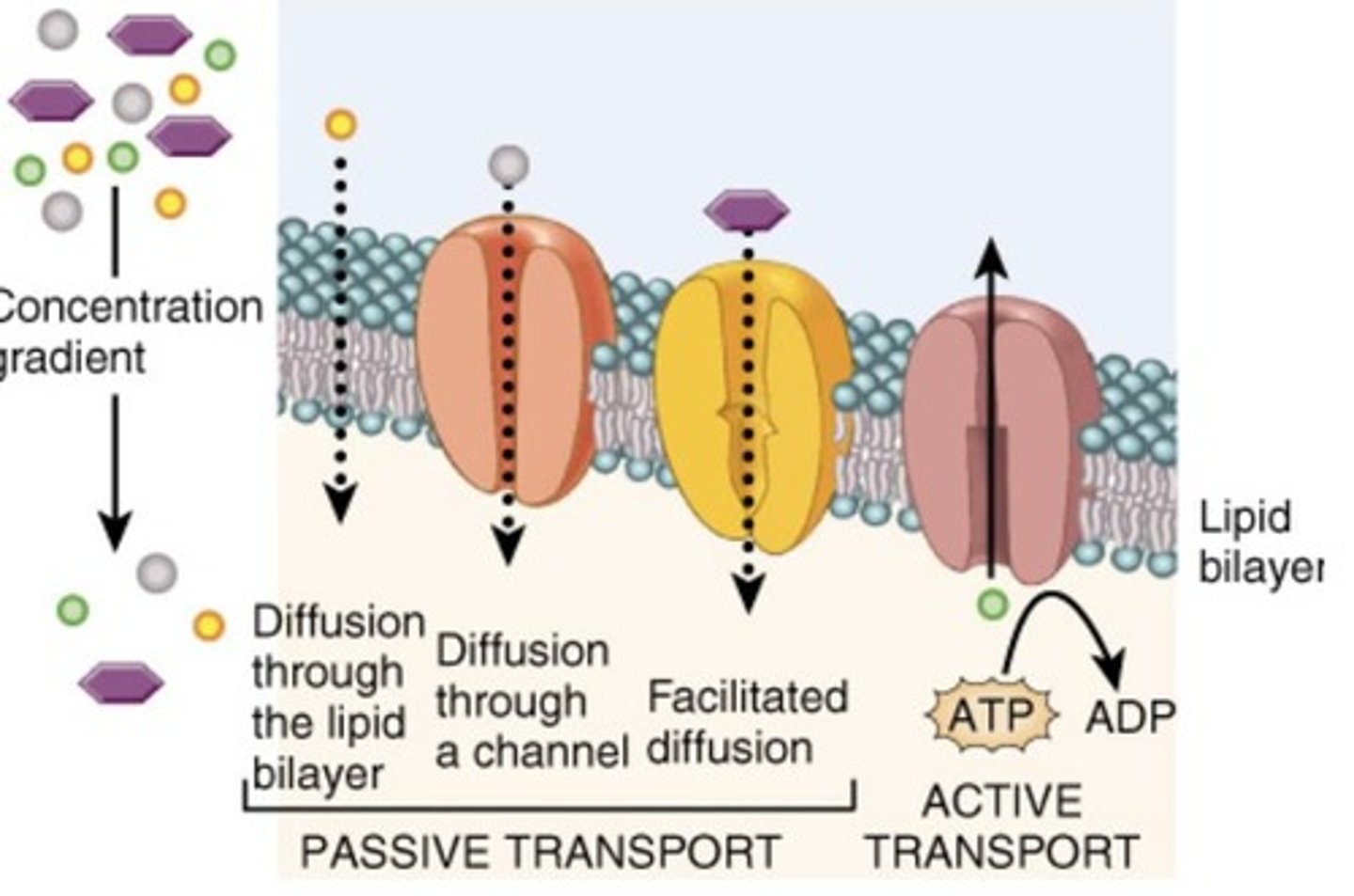
Active transport
Moves substances against gradients using energy.
Mediated transport
Requires transport proteins to move substances.
Non-mediated transport
Substances cross membranes without transport proteins.
Vesicular transport
Moves materials in vesicles via exocytosis or endocytosis.
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from high to low concentration.
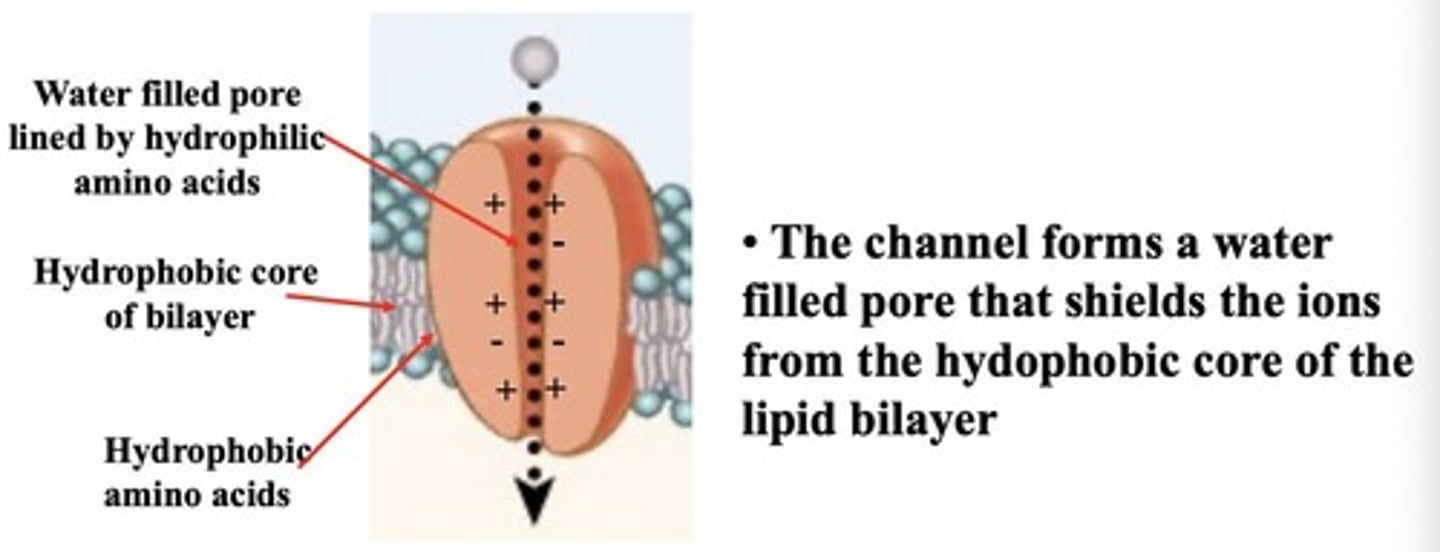
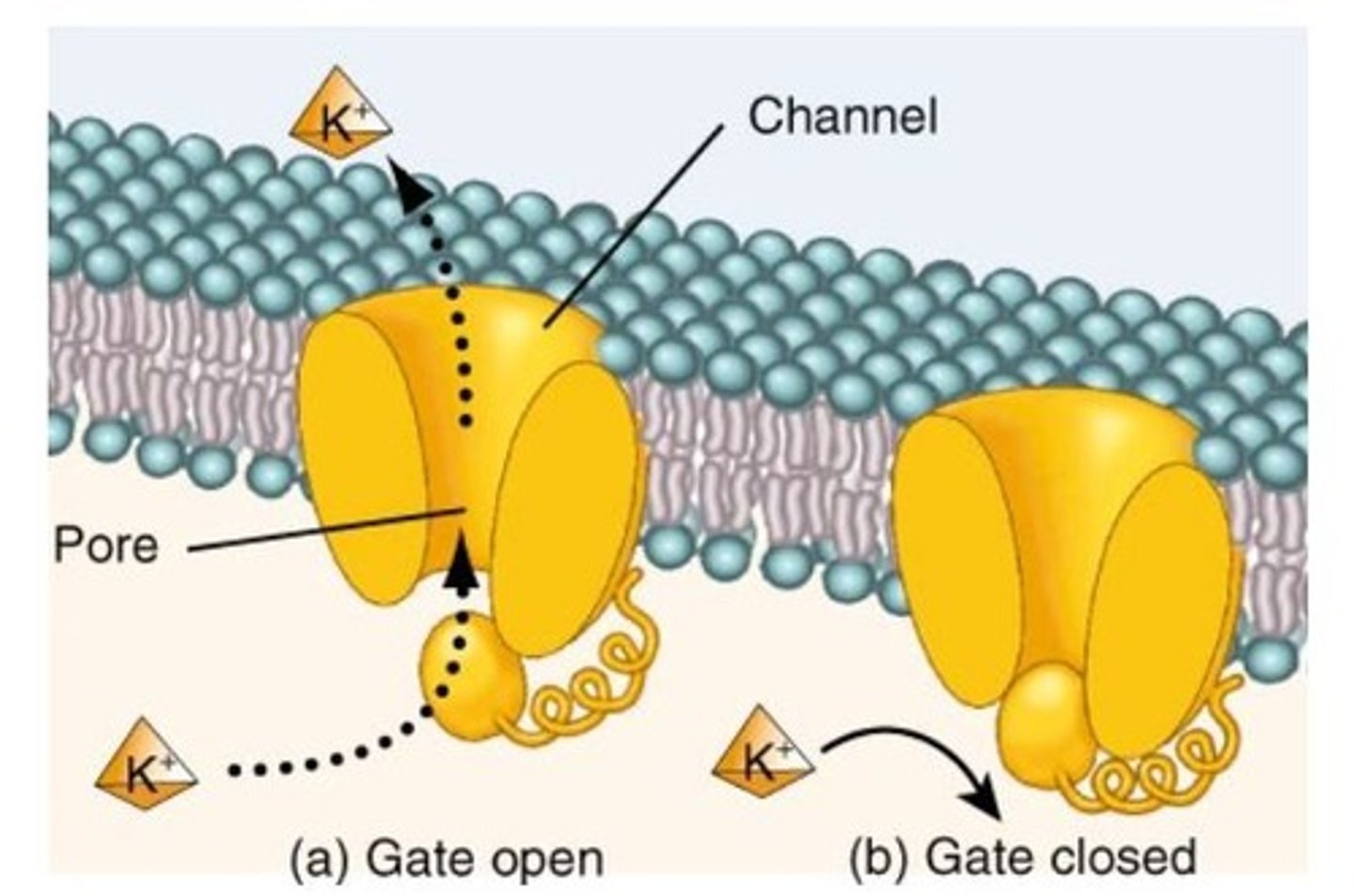
Ion channels
Proteins allowing rapid ion passage without binding.
Gating
Control of channel pore opening by stimuli.
Facilitated diffusion
Passive transport via specific transport proteins.
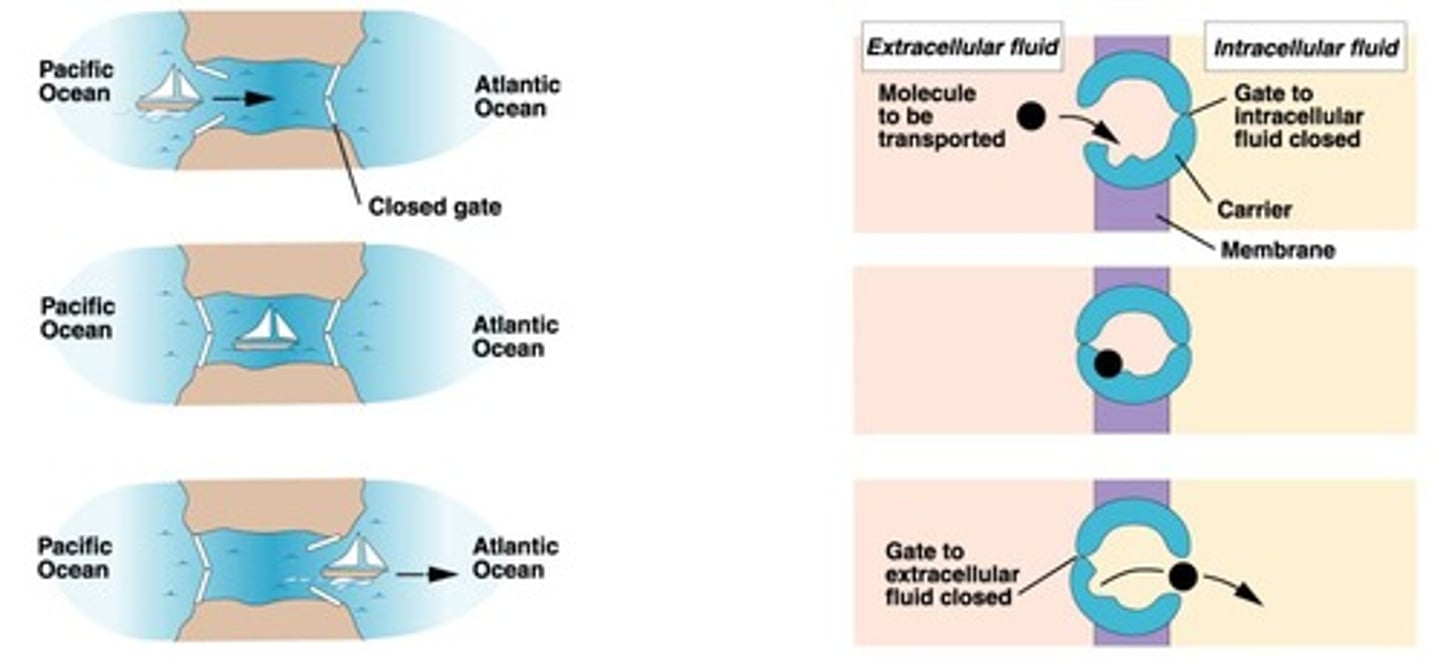
Carrier mediated transport
Transport proteins undergo conformational changes during transport.
Saturation
Transport maximum when all binding sites are occupied.
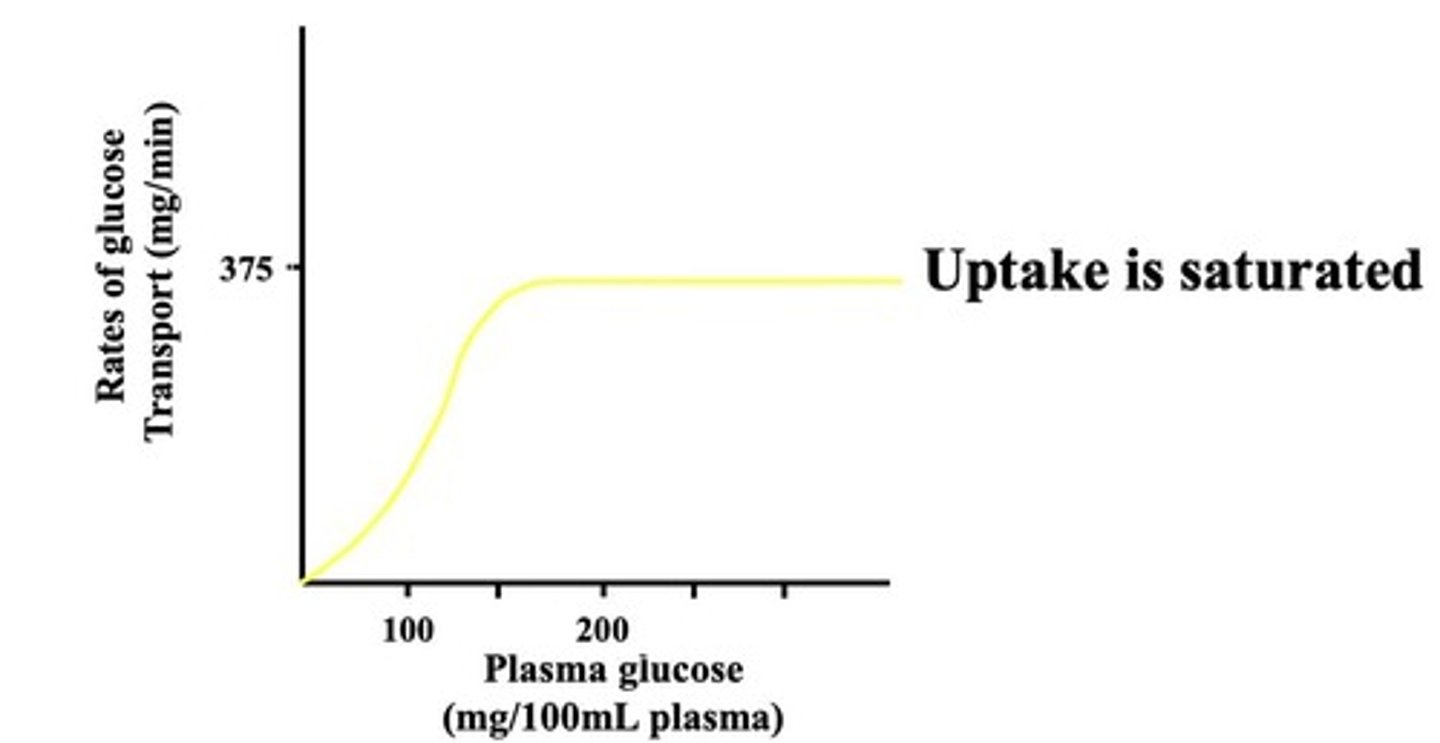
GLUT
Transport protein facilitating glucose entry into cells.
Primary active transport
Directly uses ATP hydrolysis for transport.
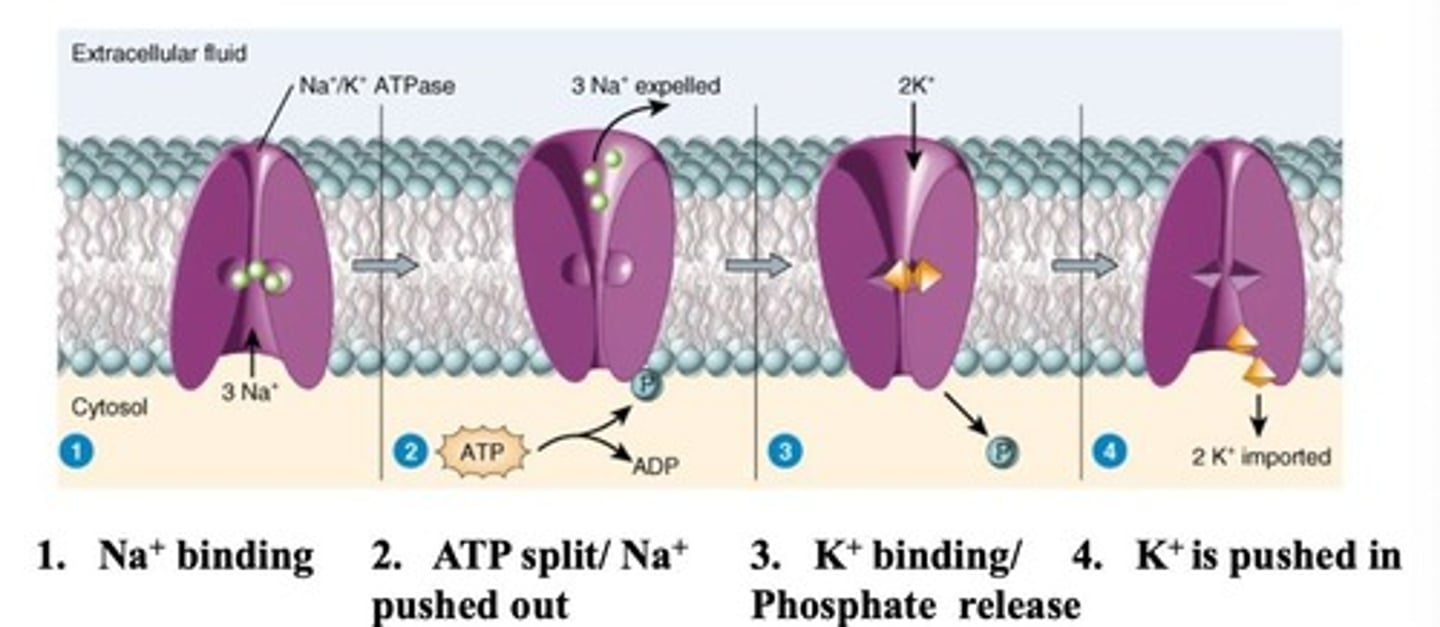
Na/K ATPase
Pumps 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ into cells.
Electrogenic pump
Generates net current due to ion movement.
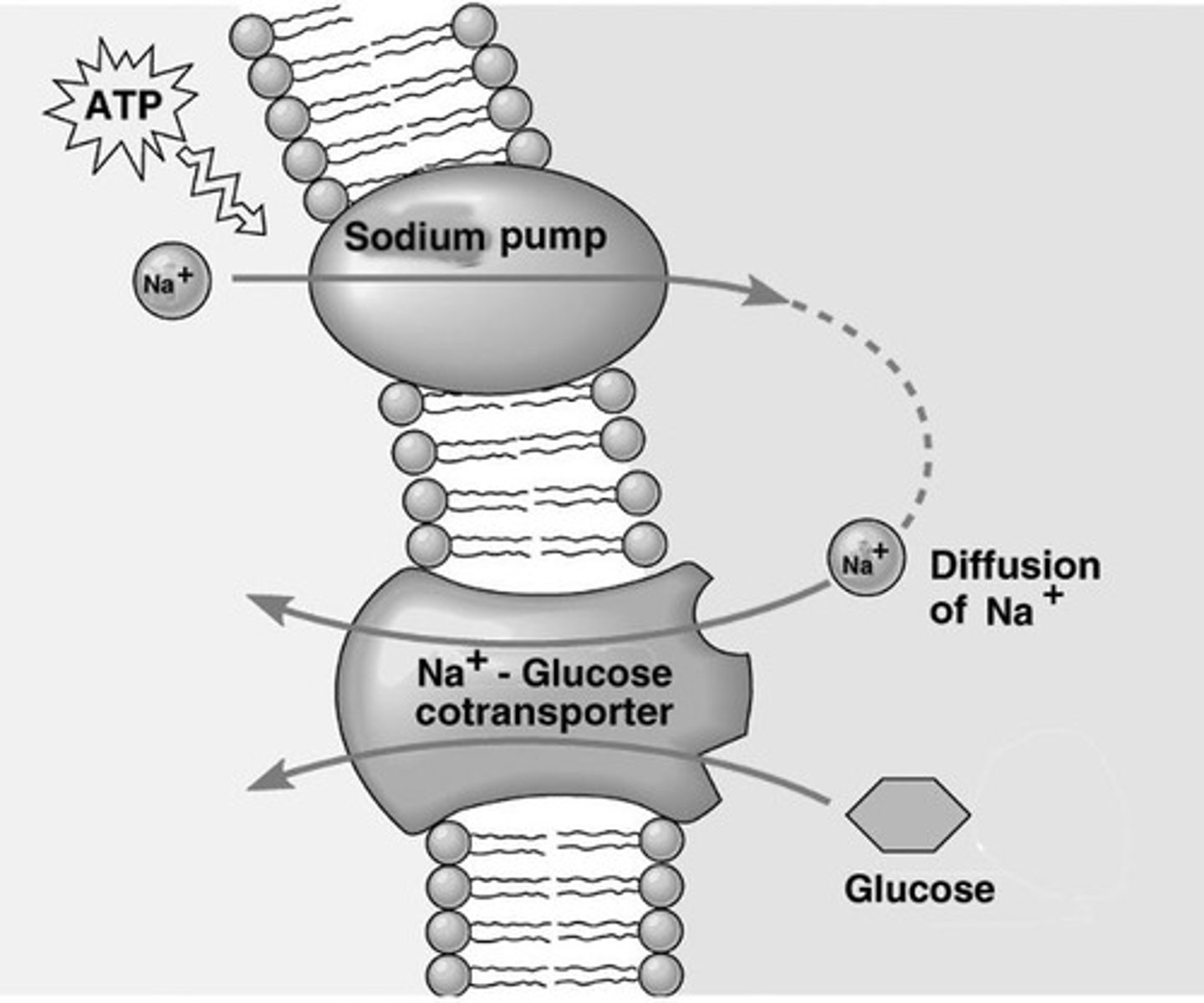
Secondary active transport
Uses ion gradients to move substances against gradients.
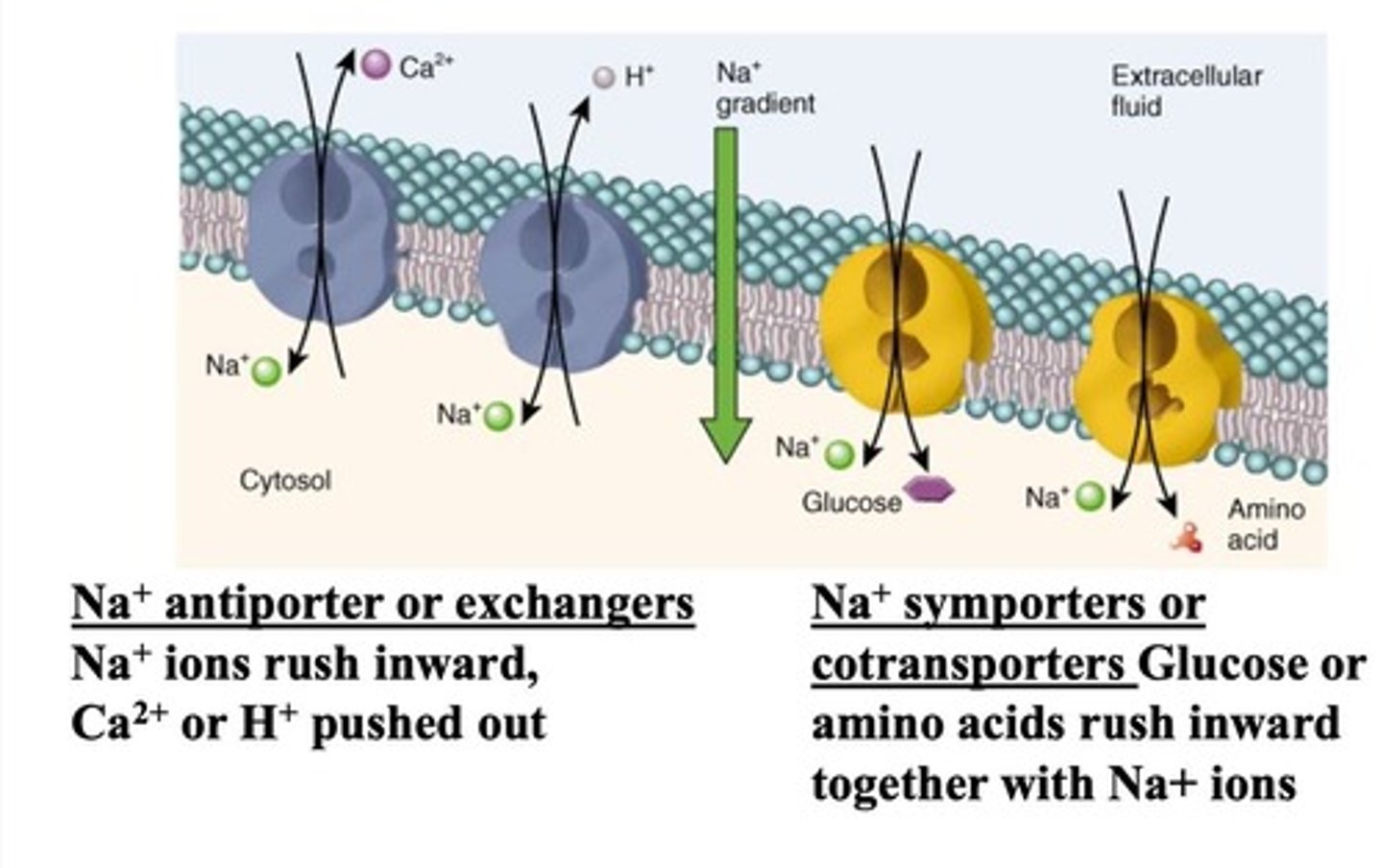
Pump-leak hypothesis
Continuous operation of Na/K pump due to ion leakage.
Concentration gradient
Difference in ion concentration across a membrane.
Hydrolysis of ATP
Energy release from ATP breakdown for transport.
Transport specificity
Transport proteins selectively bind specific substrates.
Transport inhibition
Reduced transport efficiency due to competitive binding.
Electrical excitability
Ability of cells to respond to stimuli via ion movement.
Intracellular pH maintenance
Regulation of pH through ion transport mechanisms.