MicroEconomics Exam 1
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Markets
Interaction between buyers and sellers
may be local, national, or international
Price is discovered in the interactions between buyers and sellers
Demand
A schedule or curve that shows the various amounts of a product that consumers are willing and able to purchase at each of a series of possible prices during specified periods of time
Law of Demand
When other things are equal, as price falls, the quantity demanded rises, and as price rises, the quantity of demand falls
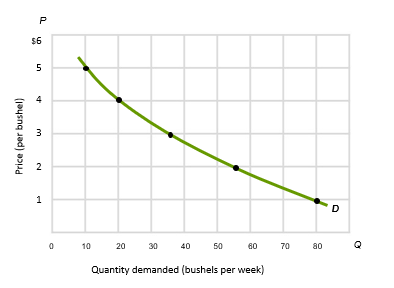
The demand curve
Determinants of demand
Change in consumer tastes and preferences
Change in number of buyers
Change in income
Change in prices of related goods
Change in consumer expectations
Law of Supply
When other things equal, as the price rises, the quantity supplied rises and as the price falls, the quantity supplied falls.
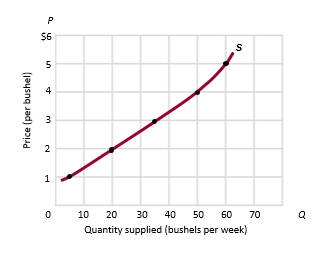
Supply Curve
Determinants of Supply
Change in resource prices
Change in technology
Change in number of sellers
Change in taxes and subsidies
Change in prices of other goods
Change in producer expectations
Rationing Function of Prices
The ability of the competitive forces of demand and supply to establish a price at which selling and buying decisions are consistent
Price Ceiling
Price cannot raise to where it needs to be
Set below equilibrium price
Rationing problem
Black markets
Rent control
Price Floor
Prices set above the market price
Chronic surpluses
minimum wage
Price Elasticity of Demand
Measures the buyers’ responsiveness to price changes
Elastic demand
Inelastic demand
Elastic Demand
Sensitive to price changes
Large change in quantity demanded
Inelastic Demand
Insensitive to price changes
Small change in quantity demanded
Midpoint Formula
Ensures consistent results of Elasticity
Inelastic: Ed < 1
Elastic: Ed > 1
Unit Elastic: Ed = 1
Absolute value
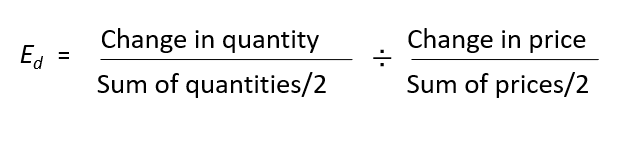
Total Revenue (TR)
Price x Quantity
Total Revenue test wit Elastic Demand
Elastic Demand: P and TR move in opposite directions
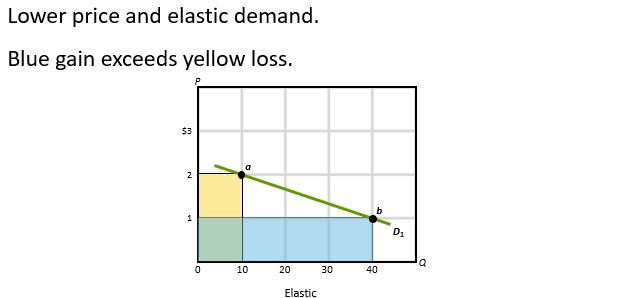
Total Revenue Test with Elastic Demand
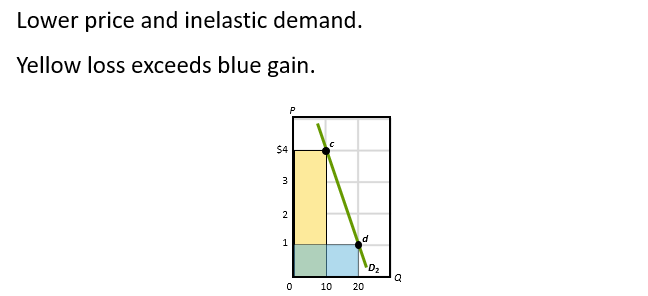
Inelastic Demand: P and TR move in same Direction
Substitutability
More substitutes, demand is more elastic
Proportion of income
Higher proportion of income, demand is more elastic
Luxuries Vs. Necessities
Luxury goods, demand is more elastic
Time
More time available, demand is more elastic
Law if Diminishing Marginal Utility
As consumption of a good or service increases, the marginal utility obtained from each additional unit of a good or service decreases.
Utility
The satisfaction a buyer will experience when consuming a good or service
Total Utility
Total amount of satisfaction gained
Sum of all marginal utilities
Marginal Utility
Extra satisfaction from an additional unit of a good or service
Consumer Equilibrium
Consumer allocates his or her income so that the last dollar spent on each product yields the same amount of marginal utility
Utility maximizing rule
Rational Behavior
Consumers try to use their income to derive the greatest amount of satisfaction, or utility
Preferences
Each consumer has clear-cut preferences for certain goods and services that are available in the market
Budget Constraint
At any point in time the consumer has a fixed, limited amount of income
Prices
Goods are scarce relative to the demand for them, so every good carries a price tag
Income Effect
The impact a price change has on a consumers’ real income
Substitution Effect
The impact a price change has on a product’s relative expensiveness
Economic Cost
The payment that must be made to obtain and retain the services of a resource
Explicit and Implicit
Explicit Costs
Monetary outlay
Implicit Costs
Opportunity cost of using self-owned resources
Includes a normal profit
Accounting Profit
Subtract Explicit costs from Revenue
Economic Profit
Subtract Implicit costs from accounting profit
Short Run
A period where at least one factor of production is fixed (factory size, major equipment, or the number of production facilities)
Some Variable Inputs (labor hours or raw materials)
Fixed plant
A Bakery in the short run might hire more workers or buy more flour, but can't expand its kitchen.
Long Run
A period where all factors of production are variable
Build new factories, buy or sell equipment, enter or exit the market entirely
A bakery could now build a second location or install new ovens
Total Product
The total quantity, or total output, of a particular good or service produced
Marginal Product
The extra output or added product associated with adding one unit of a variable resource (such as labor) to the production process.
change in total product or output / change in labor (or resource) input
Average Product
Also called labor productivity, is output per unit of labor input
Total Product / Units of labor
Law of Diminishing Returns
Beyond some point, the extra/marginal product of each additional unit of the variable resource will decline. Assumes that:
Resources are of equal quality
Technology is fixed
Variable resources are added to fixed resources
Fixed Costs (TFC)
Costs that do not vary with output
Rent payments, interest on debt, insurance premiums
Variable Costs (TVC)
Costs that vary with output
Payment for materials, fuel, power, transportation, labor
Total Cost (TC)
Sum of total Fixed cost and total Variable cost
Economies of Scale
Bring costs down
Labor specialization
Managerial specialization
Efficient Capital
Other factors
Diseconomies of scale
Drives costs up
Control and coordination problems
Communication problems
Worker alienation
Shirking
Minimum Efficient Scale (MES)
Lowest level of output at which long-run average costs are minimized
Can determine the structure of the industry
Natural Monopoly
Long-Run costs are minimized when only one firm produces the product