Anatomy: Nervous System- Neurons + Glia
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What does the nervous system do?
It is the body’s master control and communication system/
What are the primary functions of the nervous system?
Sensory Input — detect changes (internal & external)
Integration and Coordination — process and decide
Motor Output — respond via muscles or glands
What are the key properties of the nervous system?
Excitability – ability to respond to stimuli
Conductivity – ability to transmit electrical signals
Secretion – release neurotransmitters at synapses
What are the major divisions of the nervous system?
CNS
Brain
Spinal Cord
Integration & Decision-Making Center
PNS
Everything outside the CNS
More prone to injury (less protection)
What are the functional divisions of the PNS?
Sensory (afferent)
Motor (efferent)
What do afferent (sensory) signals do?
They carry info to the CNS
What do efferent (motor) signals do?
They carry out the commands from the CNS
What are the motor subdivisions?
Somatic Nervous System (SNS)
Autonomic (visceral) Nervous System (ANS)
What does the SNS involve?
They use skeletal muscles to carry out voluntary movements/actions.
What does the ANS involve?
They use smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and glands to carry out involuntary movements/actions.
What divisions is the ANS further broken down into?
Sympathetic Nervous System: fight-or-flight
ex. increase HR, BP, and alertness while slowing digestion
Parasympathetic Nervous System: rest-and-digest
calms the body down
lowering HR and helping with digestion
Enteric Nervous System
network within the GI tract that controls digestion
works somewhat independently
What are the two neural tissue cell types?
Neurons: conduct electrical signals
Neuroglia: support, protect, insulate neurons
50% neurons / 50% glia by volume
What are the characteristics of neurons?
Specialized for communication
Do not divide
Poor at repair
Require glial support
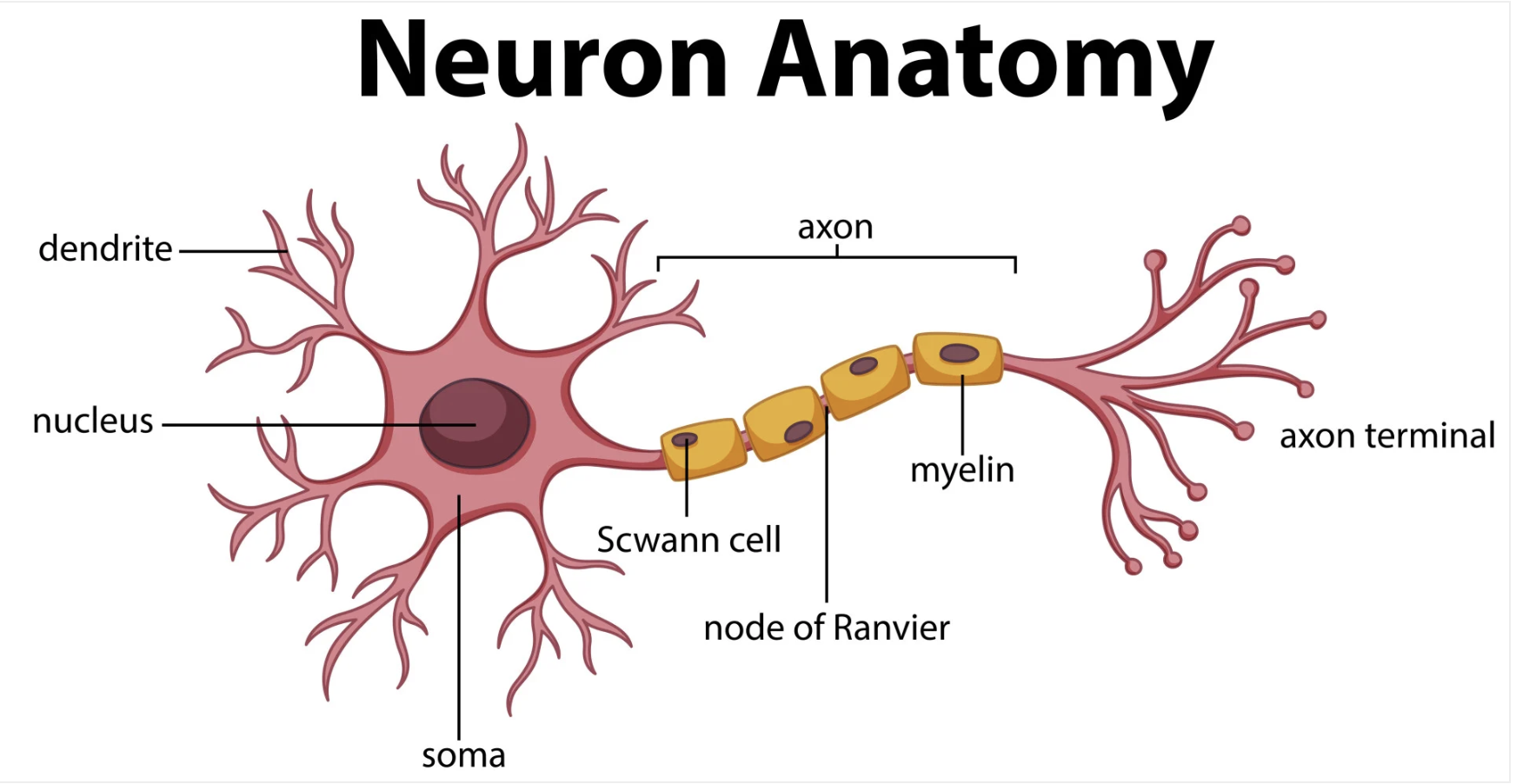
What is the structural anatomy of a neuron?
Dendrites: Receive signals
Soma (cell body): Integrates signals
Axon: Transmits signal
Axon Terminals (boutons): Release neurotransmitters
What are the functional classes of neurons?
Type | Direction | Location |
|---|---|---|
Afferent (sensory) | To CNS | PNS → CNS |
Interneurons | Within CNS | CNS only |
Efferent (motor) | From CNS | CNS → PNS |
What are the structural classes of neurons?
Type | Description |
|---|---|
Multipolar | Many dendrites, one axon (most common) |
Bipolar | One dendrite, one axon (special senses) |
Unipolar | One process splits → CNS & PNS (sensory neurons) |
What neuroglia (glial cells) are located in the CNS?
Astrocytes
Microglia
Ependymal Cells
Oligodendrocytes
What neuroglia (glial cells) are located in the PNS?
Schwann Cells
Satellite Cells
What are the functions of astrocytes?
Structural support, blood-brain barrier, scar formation
What are the functions of microglia?
Immune defense, phagocytosis
What are the functions of ependymal cells?
Produce & circulate CSF
What are the functions of oligodendrocytes?
Form myelin in CNS
What are the functions of schwann cells?
Myelin in PNS (1 axon segment each)
What are the functions of satellite cells?
Support neuron cell bodies in ganglia
What is myelin, and what does it do?
Lipid-rich insulating sheath
Increases conduction speed
Creates white matter
CNS | PNS |
|---|---|
Oligodendrocyte | Schwann cell |
One cell → many axons | One cell → one axon |
What are the Nodes of Ranvier?
Gaps in myelin
Enables saltatory conduction (jumping signal)
Impulse speed of conduction depends on:
Axon diameter
Presence of myelin (not stimulus strength)
What is a synapse (chemical)?
Junction between neurons or neuron → muscle/gland
What are the steps of a synapse?
Action potential reaches axon terminal
Vesicles release neurotransmitter
Neurotransmitter crosses synaptic cleft
Binds postsynaptic receptors
Signal is excitatory or inhibitory
What are the neural circuits (neural pools) and their purpose?
Circuit Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
Divergence | One neuron → many targets (motor control) |
Convergence | Many inputs → one neuron (sensory integration) |
Reverberating | Feedback loop (breathing) |