COB 318 - Exam 2, Class 6 onward
1/340
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
341 Terms
Define Torts
Wrongful acts between private parties where the injured party seeks monetary compensation from the party that caused the injury
What’s the difference between crimes and torts?
Crimes → The State punishes the individual who causes the harm
Torts → The Private Party seeks compensation from the individual who caused the harm
Does the State/Government get involved when it comes to Torts?
No. Torts are only between private parties where the compensation is always money and never jail time.
Where does the term “Tort” come from?
It’s French for “injury” or “wrong”
What are the 2 Categories of Torts?
Intentional Torts and Negligence
What is the difference between the 2 categories of Torts?
Intentional Torts → Intended to commit the act that caused harm
Negligence → No intent to cause the harm, an accident that arose from carelessness.
What are the 2 Elements that make up an intentional tort?
The Intent to Act
The Damages or actual harm that was caused
In intentional torts, does the intent to act mean the intent to harm?
No. For example, I can be congratulating you, and give you a pat on the back.
My pat on the back could break your collar bone.
You could sue me for Tort, even though I didn’t intend to hurt you
When it comes to intentional torts, what is transferred intent?
An intentional act that sets off a “chain reaction” and causes indirect harm.
Example: I give Professor McCarthy a pat on the back, and he stumbles forward, knocking another student over, and breaking their nose.
If I give Professor McCarthy a pat on the back, and he stumbles forward, knocking another student over, which breaks their nose, who is responsible for the tort?
Me (the guy who patted Professor McCarthy on the back")
or
Professor McCarthy who stumbled into the person who broke their nose
I am responsible, not professor McCarthy
What are the 5 Types of Intentional Torts
Assault, Battery, False Imprisonment, Intentional Infliction of Emotional Distress (IIED), Defamation
What is the definition of Assault?
Intentional threat of immediate contact that will be harmful or offensive (Reasonable person standard)
What are some examples of assault?
Pointing a gun
Dragging finger across the neck (Suggesting I will kill you)
Fake punches
Pretending to throw basketball at your friend
Fake rubber band game
What is the definition of Battery?
Intentional contact with a person, or their attached belongings, that is harmful or offensive (reasonable person standard)
What are some examples of battery?
Shooting a rubber band in face
Push your finger into someone’s chest
Slap
Unwanted kiss
water gun
cigarette smoke in someone’s face
Knock hat off head
Kick someone’s umbrella they’re holding
Difference between assault and battery
Assault: Just the threat of the contact
Battery: The actual contact
Define False Imprisonment
Intentional confinement or restraint without justification
What are the 3 Types of restraints that count as false imprisonment
Physical Barriers (locked in a room/car)
Physical Restraints (Handcuffs, rope, tape)
Threat of immediate physical force (“If you get up from that seat, I will shoot you“)
What does NOT count as a physical restraint
Threat of future force
Example: If the person could go and get help, they are not restrained
“If you get up from that seat, I’ll hurt you at some point in your life.”
The threat has to be immediate
What is the shoplifting rule
If you’re a store owner, and you accuse someone of shoplifting
You can bring that person to an office, and essentially restrain them in a reasonable manner & for a reasonable time
This is NOT false imprisonment
Define Intentional Infliction of Emotional Distress (IIED)
Intentional extreme & outrageous conduct that causes emotional distress
Behavior must exceed the bounds of social decency
What is an example of Intentional Infliction of Emotional Distress (IIED)
The Westfield Watcher
He stalked a family, sent them letters in the mail that he knew what they were talking about in the house
This causing emotional distress, and the behavior exceeded that bounds of social decency
Define Defamation
Intentionally making false statements of fact that harm a person’s reputation
What constitutes defamation? AKA what must happen for the tort to be defamation
The statement must be a false statement of fact
The statement must be “published” aka communicated to a third party.
If I personally tell you I hate you, that isn’t defamation. I need to tell a 3rd party or a 3rd person about you and how much you suck
What are the 2 types of defamation?
Libel: Written Defamation (General Damages) Slander: Spoken defamation (Special Damages)
When it comes to Defamation, is it easier to prove someone guilty for libel or for slander?
Libel (Written Defamation):
I essentially just have to prove that you did it, and I can sue you for everything
Easier to sue because something written down is permanent
Slander (Spoken Defamation)
I have to prove that your slander was a direct reason why I lost my job for example
Harder to sue because something spoken is not permanent
When it comes to defamation, can you sue for embarrasment?
No. The defamation has harmed my reputation. If I’m just embarrassed, I can’t sue for that.
McKee v. Laurion (Case about Defamation)
Laurion (Patient) left negative reviews about McKee (Doctor) on a website
Laurion was upset at how McKee treated Laurion’s father
McKee made fun of Laurion’s father.
McKee sued for defamation claiming that the comments made on the website harmed his reputation
The court sided with Laurion saying that for defamation to occur, the claims made must be false statements.
McKee actually did what Laurion said on the website, McKee was essentially a jerk
IMPORTANCE
Truth (if you actually said/did it) is an absolute defense to defamation.
What is the Public Figure Exception to Defamation?
If the target of the defamatory statement is a public figure (athlete, politician, celebrity), then that public figure has to prove actual malice
Actual Malice: The person who made the statement knew it was false, or acted with reckless disregard for the truth.
-
Essentially If a celeb is going to be famous and put themselves out there, it’s much harder to win a defamation case.
What is Vicarious Liability aka Respondient Superior?
An employer is responsible for all of his/her employees actions
Define Fraud (Fraudulent Misrepresentation)
The intentional use of deceit for personal gain.
What are the elements of Fraud?
A material misrepresentation (omission): Lying by being silent about it
Intent to induce you to rely on that lie: They intend on tricking you
Justified Reliance: (A reasonable person would believe that lie. Nobody would believe a crazy lie)
Damages: The lie actually hurt you
Causal Connection: The damages that happened to u must be the direct result of those lies.
When it comes to fraud, what is an example of A material misrepresentation (omission)?
Sketchy Car Sale
“Has this car been in any accidents?”
“Nope, no accidents”
The car actually has accidents
When it comes to fraud, what is an example of puffery?
Car Sale
“This is the best car in the universe AND a good luck charm”
This actually doesn’t count as fraud. It counts as “marketing talk”
What are the 3 types of Business Torts
Fraud
Wrongful Interference with a Contract
Wrongful Interference with a Business Opportunity
Define Wrongful Interference with a Contract
Intentional interference with a valid contract
Define Tortious Interference
An intentional tort that interferes with a business scenario
What are the 2 types of Tortious Interference
Wrongful Interference with a Contract
Wrongful Interference with a Business Opportunity
What are the elements of the Wrongful Interreference with a Contract
Valid Contract: It’s an enforceable contract
Interfering Party Knew it was a Valid Contract: The interfering person knew it was valid
Interfering Party Induced a Breach of Contract: The interfering person induced someone to break it
What’s an example of Wrongful Interreference with a Contract
I tutor Ben for $20 an hour.
We have a contract that I will tutor you
Someone else comes in and convinces Ben to leave my tutor session for another person. If Ben leaves my tutor session, he’s breaking the contract
“Hey Ben, you should break that contract, and come get tutored by me, I’m cheaper and I know more of what I’m talking about”
Define Wrongful Interference with a Business Opportunity
Intentional Predatory Behavior to Steal Customer or Clients
What is an Example of Predatory Behavior of Wrongful Interference with a Business Opportunity
Standing right in front of a Burger King door, not letting people in, holding a sign that says “McDonald’s is better, we are down the road and to the right”.
What is the fine line between Predatory Behavior of Wrongful Interference with a Business Opportunity and just straight up Competition?
Predatory: Standing right in front of a Burger King door, not letting people in, holding a sign that says “McDonald’s is better, we are down the road and to the right”.
Business Competition (not breaking the law): Standing on the sidewalk, in front of Burger King, not letting people in, holding a sign that says “McDonald’s is better, we are down the road and to the right”.
Define Negligence (The Vast Majority of Tort Law)
The failure to use a reasonable level of care to prevent a foreseeable harm
What’s the difference between Negligence and an intentional tort?
Negligence is an Accidental Harm
Intentional Torts mean there was intent
What are the 5 elements of Negligence?
Duty of Care (You have a duty to be careful)
Breach of the Duty of Care (You weren’t careful and an accident happened)
Cause in Fact (If it didn’t happen, would I still be injured)
Proximate Cause (Was my injury the direct result of the breach of duty of care)
Damages (What damages were caused to me)
When it comes to Negligence, define Duty
Duty: We each owe society a duty to behave with reasonable care
What is the Reasonable Person Standard?
A person that sets the Duty of Care.
How would a Reasonable person (in the same circumstances and with the same abilities) have behaved in that moment?
Imagine if a European person came to America. There are different expectations
Weirum v. RKO (Case about Negligence → Duty of Care)
Radio show game to find “The Real Don Steele” in a red car
People were speeding and being dangerous, eventually, a Woman was driven off the road and killed
Importance: A reasonable radio manager should have foreseen the risk of getting high school students to speed through LA, since that can lead to an accident.
What are the 3 “Special” Duties of Care
Business Owner Duty of Care
Heightened Duty of Care
Lessened Duty of Care
What is the Business Owner Special Duty of Care
Business owners have a duty to discover and remove hidden dangers
“Clean up on Aisle 3”
What is the Heightened Special Duty of Care
Certain professionals have to be more careful than others. These professionals have expertise and you have personal trust in them.
Accountant, Architect, Doctor, Engineer, Lawyer
What is the Lessened Special Duty of Care?
Certain situations where you don’t have to be as careful
If that’s the case, there is normally an assumption of risk
When it comes to Duty, what is the Assumption of Risk?
By engaging in this activity, you’re assuming a certain level of risk.
Taylor v. Baseball (Case about Negligence → Duty of Care → Special Duty of Care)
Importance: Baseball fans assume the risk of a ball entering the stands and that a ball could hit you in the face when you go to the game
Baseball hits a woman in the face
She sues
She loses because she assumed the risk when she attended the baseball game
Remember these things about Duty (1/5 elements of negligence)
Special duties (Business Owner Special Duties Heightened Duties, Lessened Duties),
Weirum vs RKO CASE,
Taylor v Baseball CASE
Define Breach (Element 2/5 that constitutes negligence)
Failure to fulfill the duty of care
Give an example of Breach (Element 2/5 that constitutes negligence)
Speeding + texting while driving + brake lights not working
Define Cause In Fact (Element 3/5 that constitutes negligence)
The “But For” Cause
But for this breach of duty, the damages would not have occurred
Simple “cause and effect” analysis
Give an example of Cause in Fact (Element 3/5 that constitutes negligence)
Before you were texting while driving, you wouldn’t have crashed into my car
Define Proximate Cause (Element 4/5 that constitutes negligence)
No unexpected act intervened in the chain of events leading up to the accident
Give an example of Proximate Cause (Element 4/5 that constitutes negligence)
A train is going on a track and is emitting smoke like a train does
A seagull flies above the train, catches fire, and lands on your house and burns the house down
That is such an unexpected intervening event, than it cuts off the chain of liability
Cyr v. Adamar Associates (Case about Negligence → Proximate Cause)
A woman was at a hotel bar
While she’s outside for a moment, she gets raped by a sex offender
She sued the hotel
Her case didn’t win because the rapist in the hotel was an unexpected intervening event that cut off the chain of liability
The hotel can’t screen every person who walks into the bar to see if they’re rapists
Define Damages (Element 5/5 that constitutes negligence)
The victim suffered some quantifiable economic loss
Give an example of Damages (Element 5/5 that constitutes negligence)
If someone backs into your car, you have to show that your car actually suffered damages and it would cost money to get it repaired
What is the Negligence Policy
Tort law provides each of us with a financial incentive to make society safer.
If you are not careful, you will pay the price
What level of care does negligence demand?
A reasonable level of care
Essentially just do enough to be safe
Turn on your blinker when turning, look both ways when crossing the road
What is the Foam Suit Phenomenon
Essentially, JMU doesn’t want you to be spritning around campus, potentially colliding with people,
But JMU also doesn’t want you to walk around slowly with a foam suit on
Just be a reasonable person and make good judgement when deciding how safe to be
Does the Negligence Policy change over time?
Yes. It changes day to day, and it changes year to year
Taylor v. Seattle Baseball Club (the Negligence Policy changing over time) 2006
Baseball fans assume the risk of a ball entering the stands and that a ball could hit you in the face when you go to the game
Baseball hits a woman in the face
She sues
She loses because she assumed the risk when she attended the baseball game
Importance: She lost back then, but now, since everyone is on their phones looking down, she probably would’ve won the case because the reasonable standard has changed
What are the 4 defenses aka how can you defend yourself if you get sued for an intentional tort
Discipline (Smacking your child)
Necessity (Was it necessary for a greater cause? Like running away from an attacker but bumping into a civilian)
Duress (Someone puts a gun to my head and tells me to do something)
Consent (Did I consent to it? Like you’re a football player)
When it comes to consent (Element 4/4 that constitutes tort defenses), what is informed consent?
Having full knowledge of the risk + Agreeing in advance
Lugenbuhl v. Dowling (Case about Defenses to Intentional Torts → Informed Consent)
Importance: Performing surgery without using the mesh aka the informed consent is battery (harmful or offensive contact)
Guy needs surgery for a hernia
Agrees with Doctor to get the surgery done but only if the doctor uses a mesh
Doctor didn’t use the mesh
Guy sues cuz that isn’t what he agreed to
What are the 3 defenses to negligence aka how can you defend yourself if you get sued for negligence
Failure to meet the burden of proof
Comparative Negligence
Contributory Negligence
When it comes to defenses against negligence, what is the preponderance of Evidence?
The burden of proof, aka you are guilty if you meet the preponderance of evidence
More likely than not (50.1%)
When it comes to defenses against negligence, define Comparative Negligence
The jury assigns a percentage of fault, and the defendant pays according to that level of fault
When it comes to defenses against negligence, what is an example of Comparative Negligence
There was a car crash
Victim seeks $100,000
jury determines victim is actually 40% responsible for the crash
The Victim will win only $60,000 instead of the total $100,000
When it comes to defenses against negligence, define Contributory Negligence
If the victim is even 1% at fault, the victim receives nothing
Very strict rule and very rare rule
When it comes to defenses against negligence, which 5 states use Contributory Negligence? (if the victim is only 1% liable for the accident, the victim gets nothing)
Alabama
DC
Maryland
North Carolina
Virginia
When it comes to Damages, what are the 2 types of damages?
Compensatory Damages (most common)
Punitive Damages
When it comes to Damages, define Compensatory Damages
Compensating the victim for economic losses
When it comes to Damages, what is the policy for Compensatory Damages?
Return the victim to their pre-accident financial condition
Essentially only paying what needs to be paid to fix the problem.
No extra payments
You lost $20,000? Here’s $20,000
When it comes to Damages, define Punitive Damages
To financially punish a defendant who engages in extreme, reprehensible, or antisocial behavior
When it comes to Damages, what is the policy for Punitive Damages?
To deter similar behavior in the future
Ford Motor Co. v. Stubblefield (Case about Damages → Punitive Damages)
Importance: Ford was fined EXTRA money (punitive damages) on top of what they already owed (compensatory damages) to deter them from doing the same thing in the future
Ford knew there was a design impact in the car that made it explode on minimal impact
Many people were injured
Whats the difference between Punitive Damages and Compensatory Damages
Compensatory: You repay the victim exactly what they lost in the damage
Punitive: You repay the victim exactly what they lost in the damage but then MORE money on top of that to deter this behavior in the future
What are the 4 Special Tort Doctrines
Res Ipsa Loquitur (the thing speaks for itself)
Good Samaritan Laws
Social Host / Dram Shop Laws
Strict Liability
When it comes to special tort doctrines, give an example of Res Ipsa Loquitur (Thing speaks for itself) (1/4 Special Tort Doctrine)
A guy walks down a sidewalk
A barrel rolls out of a building and hits the guy
Nobody was in the building at the time
No person directly committed negligence
Guy sues company
Importance: Flips the burden of proof onto the defendant
AKA the company has to prove that they weren’t being negligent
Normally, the guy has to prove that the company was being negligent
When it comes to special tort doctrines, What does Res Ipsa Loquitur translate to, and what does it mean? (1/4 Special Tort Doctrine)
The thing speaks for itself
Sometimes things happen that are so obviously a by-product of negligence, that you can’t prove it was negligence from your POV.
If a barrel rolls out of a building SOMEONE had to be negligent, but if nobody was in the building at the time of the injury, who was negligent?
When it comes to special tort doctrines, what are Good Samaritan Laws? (2/4 Special Tort Doctrine)
Some states require bystanders to assist at the scene of an accident
Minnesota, Rhode Island, Vermont
When it comes to good Samaritan laws, how do all states protect aka “insulate” good Samaritans? (2/4 Special Tort Doctrine)
If a good Samaritan helps, the state will remove any and all liability that the good Samaritan created when trying to help
Encourages kindness
When it comes to Special Tort Doctrines, what is the Social Host / Dram Shop Law (3/4 Special Tort Doctrine)
If you overserve someone alcohol, and they drive home and get in an accident, the injured person can not only sue the driver, but also the bar that overserved them.
This is why bartenders will sometimes cut people off
When it comes to Special Tort Doctrines, what is the Strict Liability Doctrine (4/4 Special Tort Doctrine)
Some things are so intrinsically dangerous, that if a company injures a person, that person doesn’t have to prove that the company was negligent, that person immediately wins.
When it comes to Special Tort Doctrines, what is the Policy for Strict Liability Doctrine (4/4 Special Tort Doctrine)
So dangerous that if you choose to do it, you have to pay all injuries for all parties
When it comes to Special Tort Doctrines, give examples of Strict Liability Doctrine (4/4 Special Tort Doctrine)
Toxic waste leakage
Missile test hitting civilians
Nuclear power plant explosion
When it comes to Special Tort Doctrines, does Virginia allow you to sue someone for Social Host / Dram Shop Law (3/4 Special Tort Doctrine)
No. In VA, if you drive home from a bar, and hit a driver. The driver can only sue you, not the bar as well.
When it comes to criminal law, define crime
The government’s power to deprive a person of life, liberty, and property as punishment for engaging in prohibited conduct
Life
Death Penalty
Liberty
Prison
Property
Fines & removal of assets (house)
When it comes to criminal law, define the Burden of Proof
The Government must prove a defendant’s guilt beyond a reasonable doubt
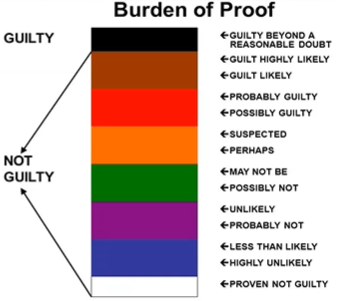
What is the difference between the Criminal Law Burden of Proof & the Tort Law Burden of Proof
Criminal Law Burden of Proof
The Government must prove a defendant’s guilt beyond a reasonable doubt
99.5% sure
Tort Law Burden of Proof
The victim must establish a defendant’s liability by a preponderance of evidence
50.1% sure
What are the 2 elements that all crimes have.
Actus Reus: Engaging in a forbidden act
Mens Rea: Having criminal intent
It is not a crime if only 1 or none of these are present, both must be present