End of Outsiders Test Review
4.9(8)
4.9(8)
Card Sorting
1/22
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
1
New cards
Analysis
A thorough study of something (such as a poem or a piece of literature)

2
New cards
Foreshadowing
To show or indicate beforehand
3
New cards
Flashback
A conversation, an episode, or an event that happened before the beginning of the story. Often interrupts the chronological flow of a story to give the reader information to help in understanding a character's situation.

4
New cards
Point of View
the perspective from which a story is told
5
New cards
First Person Point of View
Told from the viewpoint of one of the characters using the pronouns "I" and We"

6
New cards
Second Person Point of View
the narrator addresses the reader directly using the pronoun "you"

7
New cards
Third Person Point of View
is narrated by the author. (He, She, It)

8
New cards
Simile
A type of figurative language. It is a comparison of two unlike things using like or as

9
New cards
Metaphor
A type of figurative language. It is a comparison, not using the words like or as.

10
New cards
Moral
A lesson (life lesson) that is taught in a literary work
11
New cards
Author's Purpose
His or her reason for creating a particular work. The purpose may be to persuade the reader to do or believe something, inform, or entertain (PIE), or to express an opinion. An author may have more than one purpose for writing, but usually one is the most important
12
New cards
Character Traits
Traits that are found on the inside of a character

13
New cards
Physical Features/physical traits
are traits that are on the outside

14
New cards
Conflict
A struggle between opposing forces or characters. Without conflict a story would be boring. A story can have several conflicts, the main conflict is central to the plot and is usually resolved by the resolution.

15
New cards
Internal Conflict
Takes place in a character's mind or heart. Sometimes this involves a decision.

16
New cards
External Conflict
Takes place between a character and something outside the character. The outside force could be nature, an event or situation, or another character.

17
New cards
Theme
The truth or central idea a story reveals about life. Any theme can be considered valid if you can support it with text evidence.

18
New cards
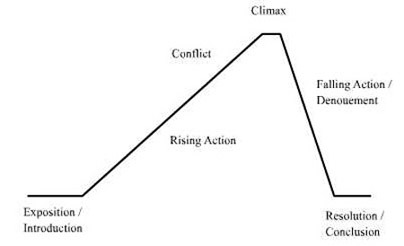
Plot
Stages of the story: Exposition, Rising Action, Climax, Falling Action, Resolution
19
New cards
Exposition
Introduces the characters and the setting, provides background information, conflict is usually introduced.

20
New cards
Rising Action
The story becomes more complicated as the conflict develops

21
New cards
Climax
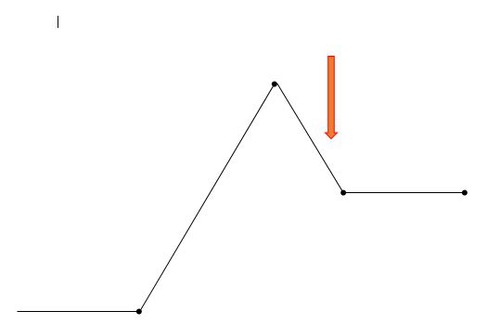
The turning point in the story, the most exciting part when the outcome of the conflict is decided.

22
New cards
Falling Action
The loose ends are tied up as the story comes to an end. (This is sometimes combined with the resolution).
23
New cards
Resolution
The conflict should be resolved. The story ends.
