EEB 321 - Vocabulary
1/21
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Ecological niche
Is a way of conceptualizing the ecology of a species (what it does, how it differs from other species)
Grinnelian (recess-role)
The niche of an organism is the habitat or environment it is capable of occupying. It is a Species’ “Address” in the environment. Organisms have traits that suit their address. Also Implies the Existence of ‘Ecological Equivalents’ and that niches can be ‘empty’.
Environment contains niches, occupied by species. Implies convergent evolution in similar environments & existence of ‘empty’ niches.
Eltonian (functional attributes and impact)
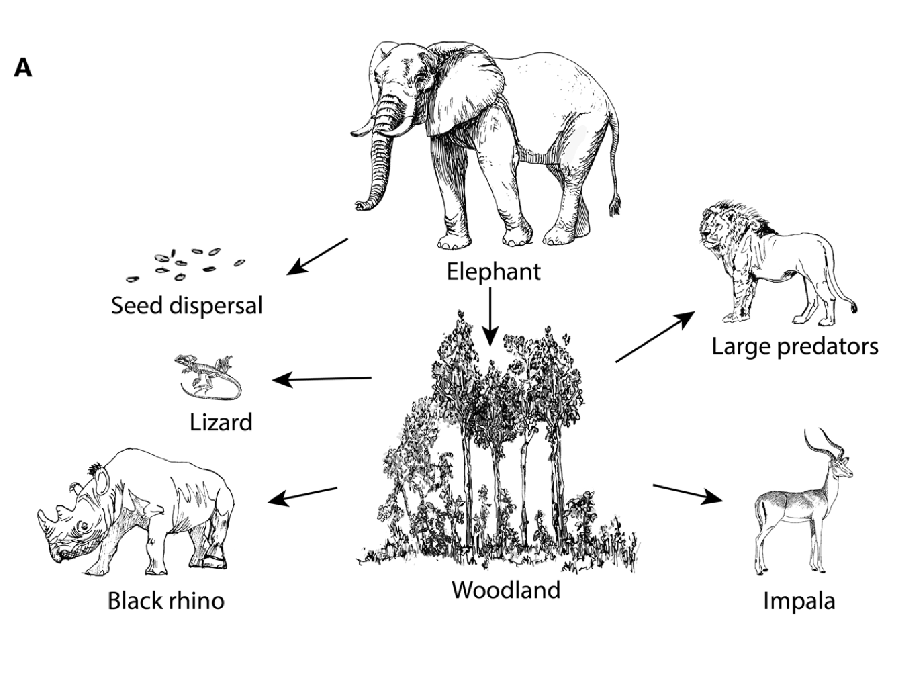
The niche of an organism is the role the species plays in the community, it’s ‘job’. Refers to species’ functional roles in ecological processes and their effects on other species. Ex. Two rhinoceroses, different mouths, different jobs (and impacts).
Niche is a species’ profession, describes its functional role and impact on other species.
Hutchinsonian (population-persistence)
Conceives the niche in terms of both the species’ environment (resources available) and what it does (how it uses them). It is precisely defined and quantifiable in 2D and 3D. Also created definitions of realized (actual) vs fundamental (capable without constraints) niches. Problems: Too many niche dimensions.
Niche is defined in terms of any number of axes—the range of values for a set of environmental variables—that enable population to persist.
Guild
A group of species that have similar requirements and play a similar role within a community. Co-occurring species that use the same types of resources.
MacArthur-Levins (resource-utilization)
Focusing on a few key axes, can quantify niches in terms of resource utilization distributions and develop theory on limiting similarity.
Limiting Similarity
Specifies the minimal niche difference between two competing species that would allow them to coexist. Ex. Character displacement in Darwin’s finches.
n-dimensional hypervolume
Hutchinson showed how we might quantify an organism’s niche, including both biotic and abiotic dimensions of the environment, as axes of an…
niche axes/dimensions
The different dimensions, or plot axes, of a niche represent different biotic and abiotic variables. These factors may include descriptions of the organism's life history, habitat, trophic position (place in the food chain), and geographic range.
(interspecific) competition
The struggle between individuals of different species for the same limited resources within an ecosystem, like food, space, or mates, where the presence of one species negatively impacts the survival or reproduction of the other species.
Life History
Schedule & duration of key events in a lifetime (e.g., growth, reproduction, aging, death). Life-history theory assumes animals evolve strategies to maximize fitness (offspring production and survival of those offspring). This leads to predictions about organisms’ behavior & ecology.
Trade-Off
Getting or doing one thing requires sacrificing another; Physiology constrains life-history strategy: a Jill of all trades are masters of none... But a master of one trade has limited flexibility...
Ex. Hindgut fermenters vs. ruminants (Zebra can eat less nutritious food, but must eat constantly. Gazelle may eat less, but require more nutritious foods).
Performance
Fitness. Performance breadth = range of temperatures in which animals can sustain some threshold level of function.
Energetics
Energy is fuel (the breaking of chemical bonds, etc.).
Metabolic Rate
The rate at which an organism consumes, processes, and expends energy. (expensive). Energy expenditure per unit time.
Thermoregulation
The ability of an organism to maintain a stable body temperature in response to changes in its environment. (expensive).
Importance of Body Size
Allometry
Survivorship
The percentage of a population that survives to a specific age.
Net Reproductive Rate
The average number of offspring a female individual is expected to produce throughout her lifetime.
Semelparity
Reproducing only once in a lifetime. Ex. Salmon.
Iteroparity
Reproducing many times over a lifetime.