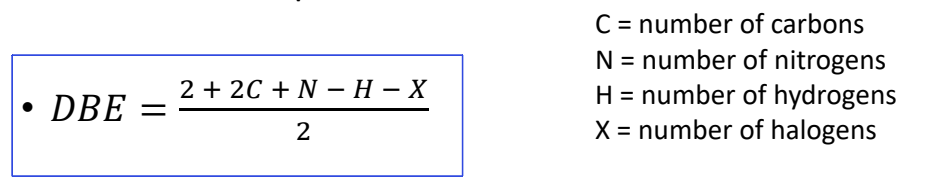mass spectrometry
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
how does a mass spectrometer work?
what is measured? what form does the sample need to be?
what is output?
molecular weight measured
ionise sample to create positive and negative ions from neutral sample
output is measurement of mass/charge ratio of ions
how are ions generated and in what phase
the source generates ions in gas phase
time of flight mass spectrometer diagram
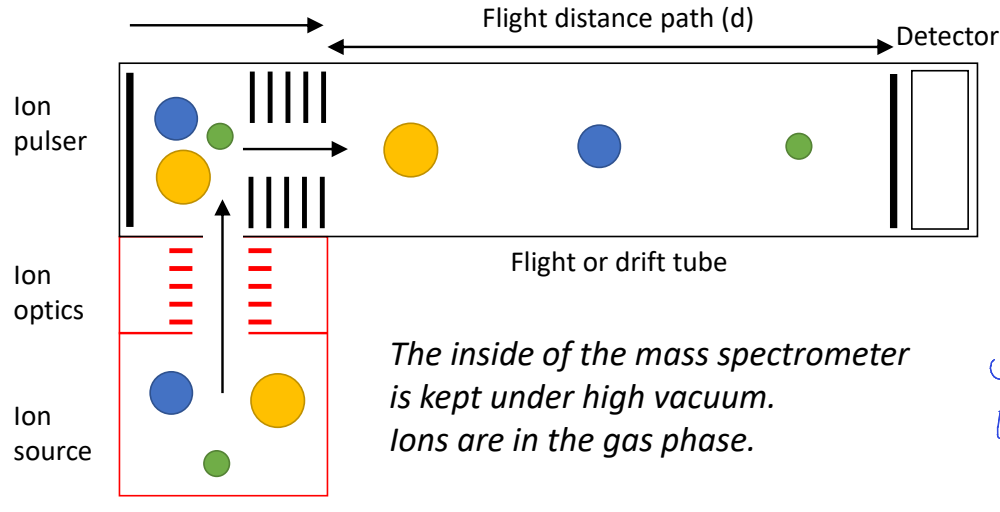
what is accelerating energy for time of flight?
E=zV
depends on charge and applied voltage
what are the 3 main ion sources
electrospray (ESI)
matrix assisted laser desorption/ionisation (MALDI)
electron impact (EI)
what are soft ionisation methods? 2 examples
what types of molecules are detected
ESI and MALDI
low energy to molecular ion is observed without breaking up
detection of large molecules eg proteins
what are hard ionisation methods? example
EI
imparts energy to molecule = extensive molecular fragmentation h
how does electrospray ESI work
what other analytical technique is it coupled with (think state)
generates ions from molecules in solution
coupled with liquid chromatography
how does matrix assisted laser desorption/ionisation MALDI work
generates ions from sample dried together with matrix on solid plate
electrospray ionisation ESI diagram
what state ?
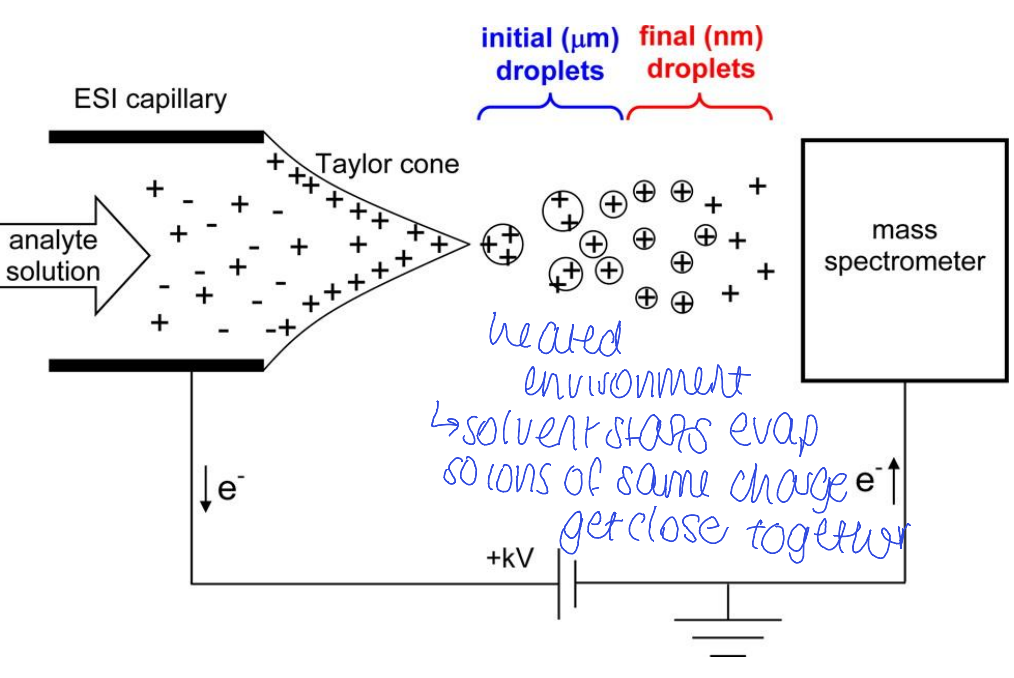
what ions are seen in ESI (think what type of ionisation is it?) 3
what isn’t seen
pseudo molecular ions - gained or lost H+
multiply charged ions
other adducts (e.g. Na+ or K+)
don’t see fragmentation
MALDI diagram
(think what states is it in, what is analyte held on)
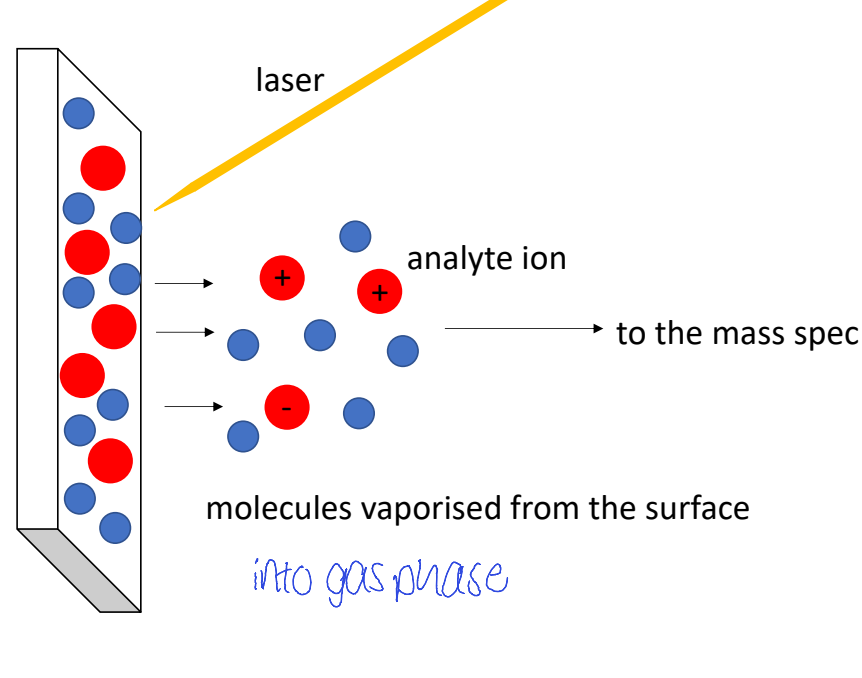
what ions are seen in MALDI (think what type of ionisation is it?) 2
what isn’t seen
molecular ion peak seen
multiple charged ions
don’t see fragments
how is matrix chosen in MALDI? how does this affect what ions are seen
don’t see fragments as matrix (e.g. c acid) absorbs laser energy
electron impact EI diagram
where do electrons come from, how do analyte molecule become charged
high energy electrons created by filament and accelerated towards analyte
electrons knock valence electron off to make analyte molecules charged
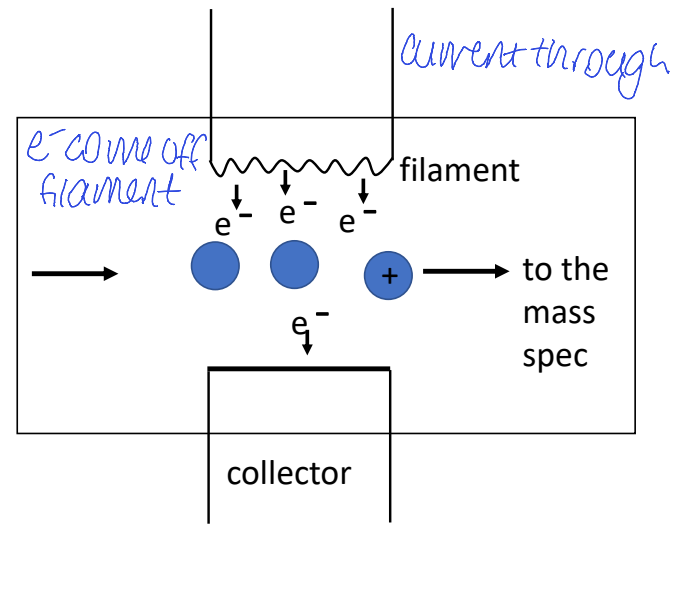
is fragmentation seen in electron impact? why or why not?
electrons accelerated to high energy, much more than needed to ionise
so excess energy is rumbling around leading to significant bond breaking = fragmentation
what is mono isotopic mass?
exact mass value for most abundant isotope
what is nominal mass?
integer mass value for most abundant isotope
what is average/chemical mass?
average atomic mass value taking into account isotope abundance
how to work out ppm error?
what value do you want for it to be considered a match?
within 5ppm

what are the ratios for Cl isotopes
ratios of peaks?
75% 35Cl
25% 37Cl
1:3 ratio
why is 13C containing ion peak smaller
much less abundant
about 1%
what are the ratios for Br isotopes
ratios of peaks?
50% 79Br
50% 81Br
1:1 ratio
how do peaks from molecules with different isotope compositions differ?
differ in mass by 1 unit (neutron)
what is m/z gap for doubly charged species
what if mass is +4 gap?
0.5 gap
0.25 gap
which fragmentation pathways are favoured for EI?
what does this mean about peaks
generation of stable cations and radicals are favoured
means molecular ion peak may not be most intense
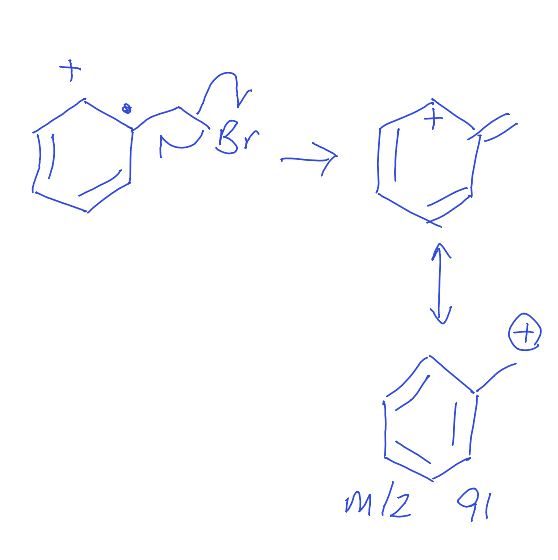
show benzylic group fragmentation to give 91 m/z peak
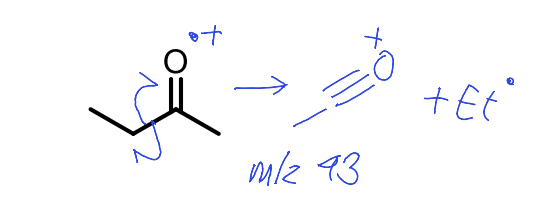
show carbonyl fragmentation to give m/z 43
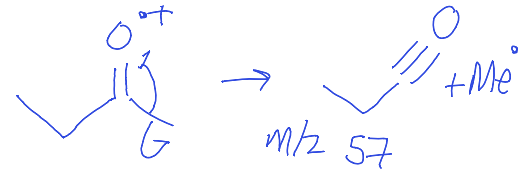
show carbonyl fragmentation to give m/z 57
O positively charged
show carbonyl fragmentation to give m/z 15
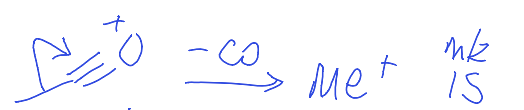
show carbonyl fragmentation to give m/z 29
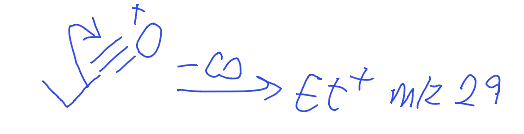
what is alpha cleavage?
when bond next to O broken
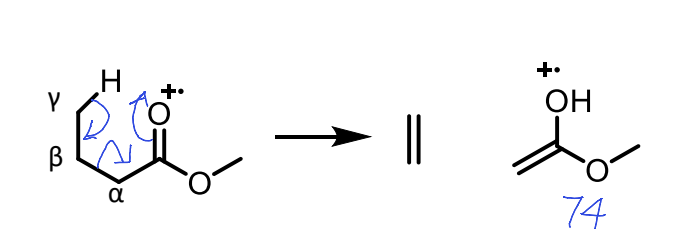
what is the mclafferty rearrangement?
what does a mass analyser do?
filter or sorter - only allows ions of specific m/z through
what are double bond equivalents equation? what does high DBE suggest?
suggests there may be aromatic ring