Chemistry - Data Test
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Effect of increasing Pressure
Shifts the equilibrium position of the gas-phase reaction towards the side with fewer moles
Effect of decreasing Pressure
Shifts the equilbirum position of the gas-phase reaction towards the side with more moles
Effect of increasing temperature in an exothermic reaction
Shifts the equilibrium position towards the reactants as there is an increase products
Effect of decreasing temperature in an exothermic reaction
Shifts the equilibrium position towards the products as there is an increase of reactants
Effect of increasing temperature in an endothermic reaction
Shifts the equilibrium position towards the reactants as there is an increasing of products
Effect of decreasing temperature in an endothermic reaction
Shifts the equilibrium position towards the products as there is an increase of reactants
Effect of increasing concentration
Shifts the equilibrium position towards the opposite side to counteract the change
Equilibrium Expression
Name of the products on the numerator
Name of the reactants on the denominator
Equilibrium Constant
Number of moles of products to the power of the constant over number of moles of the reactants to the power of the constant.
Effect of a Catalyst on Equilibrium
Only increases the reaction rate towards equilibrium. Doesn’t affect equilibrium position.
Reaction Quotient
Same as the equilibirum constant
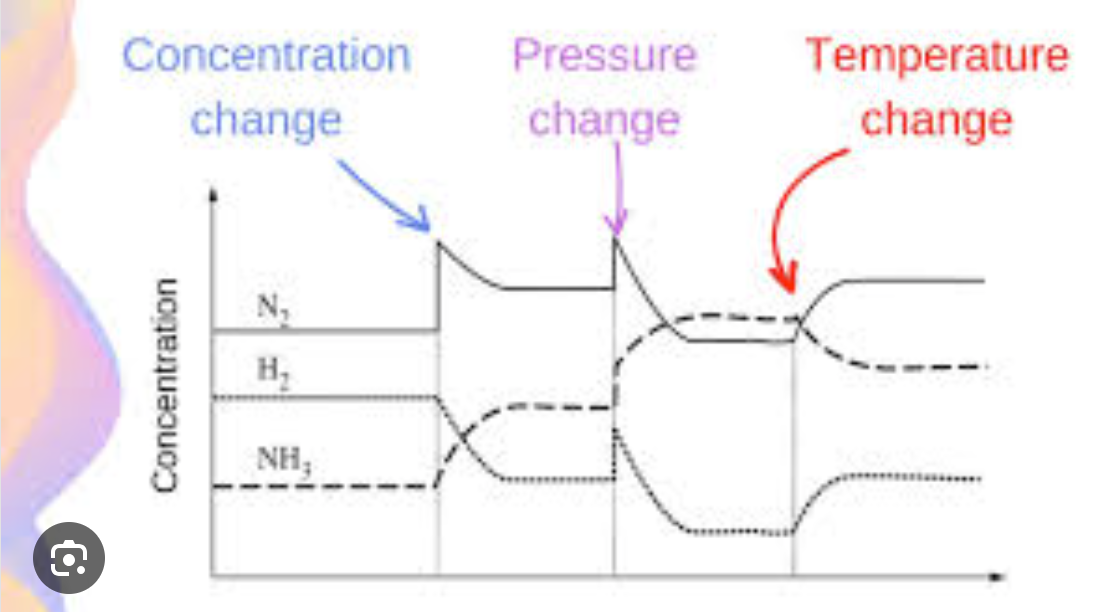
Predicting yield from graphed information
Pressure
Temperature
Concentration
Refer to the Graph
Calculating concentration of an unknown mole
Using formulas: n=cv and n=Mm/m
First calculate number of moles for known
Compare Rations by dividing unknown by known
Calculate number moles of unknown
Calculate concentration