AP Science Test Genetics
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
Alleles
Genes controlling a trait
Heterozygous
The Alleles for the trait are different (Bb)
Homozygous
The Alleles for the trait are the same (bb)
Genotype
The Genetic makeup of an organism
Phenotype
Physical traits of an organism
Punnet Square
Diagram used to predict the Genotype of an organism
Pedigree Chart
A chart showing the ancestors of a specific organism
Selection
The process of choosing organisms with the most desirable traits for mating
Inbreeding
The mating of closely related individuals to obtain desirable characteristics, decreases the variation in the population, which can be good or bad
Outbreeding
New mates are introduced outside the immediate gene pool
Mutations
A sudden change in structure or the amount of genetic material
Cloning
A group of organisms that have exactly the same genes. The cloning of plants is easier that animals or humans due to the simplicity of the genetic makeup.
Gene Splicing
The joining of D.N.A. from 2 different species.
Genetics
The branch of biology that study the way that hereditary information is passed on from parents to offspring
Gene
A unit of hereditary material found in chromosomes
R.N.A.
Ribonucleic Acid, Helps build D.N.A.
D.N.A.
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
Composition of D.N.A.
5 Sugar Deoxyribose
Phosphate Group
4 types on nitrogen bases
A
Adenine
G
Guanine
Purine
Adenine & Guanine
C means…
Cytosine
T means…
Thymine
Primidine
Cytosine & Thymine
Mitosis
Identical cell division, constantly happening in our body
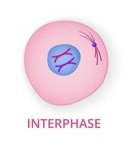
Interphase
Start/stop
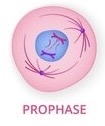
Prophase
Centrioles begin to move to opposite poles, spindle fiber replaces nucleus, Chromatin match up to become chromasones
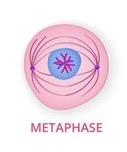
Metaphase (Middle)
The nucleus is gone, chromosomes meet in the middle and double.
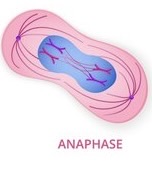
Anaphase
Chromosomes are pulled back to opposite poles, 2 cells begin to form
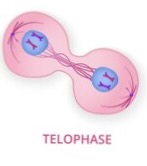
Telophase
Chromosomes revert to chromatin, Nucleus reforms, 2 identical daughter cells replace the old cell
Adenine goes with..
Thymine
Cytosine goes with…
Guanine
D.N.A. Structure
The strands are dioxi syra and phosphate. The genetic code is attached to the dioxi syra. The 2 strands are held together by weak hydrogen bonds. 3 pieces of D.N.A. make a nucleotide.
Hydrogen Bonds (weak)
Bonds are weak so the strands of D.N.A. can open and close repeatedly
Regeneration
The ability of an organism to grow lost body parts.
Vegetative Reproduction
The ability to grow from a bulb producing an identical offspring
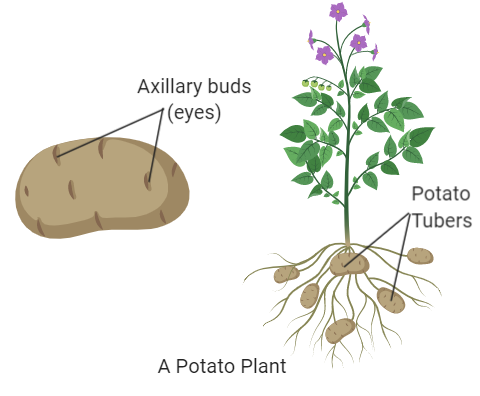
Tuber
an enlarged part of an underground stem. The eyes are tiny eyes for growth
Artificial Vegetative Reproduction #1, Cuttings
Any part of a plant, stem, leaf or root used to produce a new individual
Artificial Vegetative Reproduction #2, Layering
A stem is bent over into the soil and roots will develop
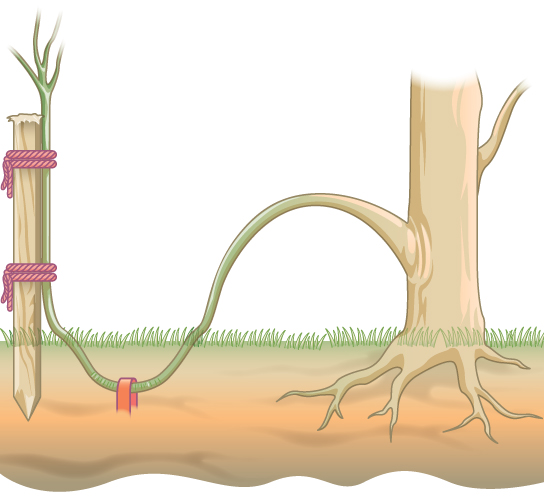
Grafting
A stem or bud is removed from one plant and attached to a new plant
Mutagens
Factors causing mutation
Chromosomal
Change in part of a chromosome, usually takes place during mitosis
Translocation
The transfer of the part of one chromosome to another (EX: ABCDEFG/XYZ)
Inversion
A piece of a chromosome that is inverted (EX:ABCEDFG)
Addition
A piece of a chromosome is added causing repeating in the pattern (EX:ABCABCDEFG)
Deletion
A piece of a chromosome breaks off (EX:ABC_FG)