Unit 5 - The Heart and Fetal Circulation
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
What are the major components of the cardiovascular system?
heart, blood vessels, blood
What is the major function of the cardiovascular system?
Transporting nutrients, oxygen, waste products, hormones
Where is the heart located?
In the middle mediastinum. between the 2nd rib and 5th intercostal space
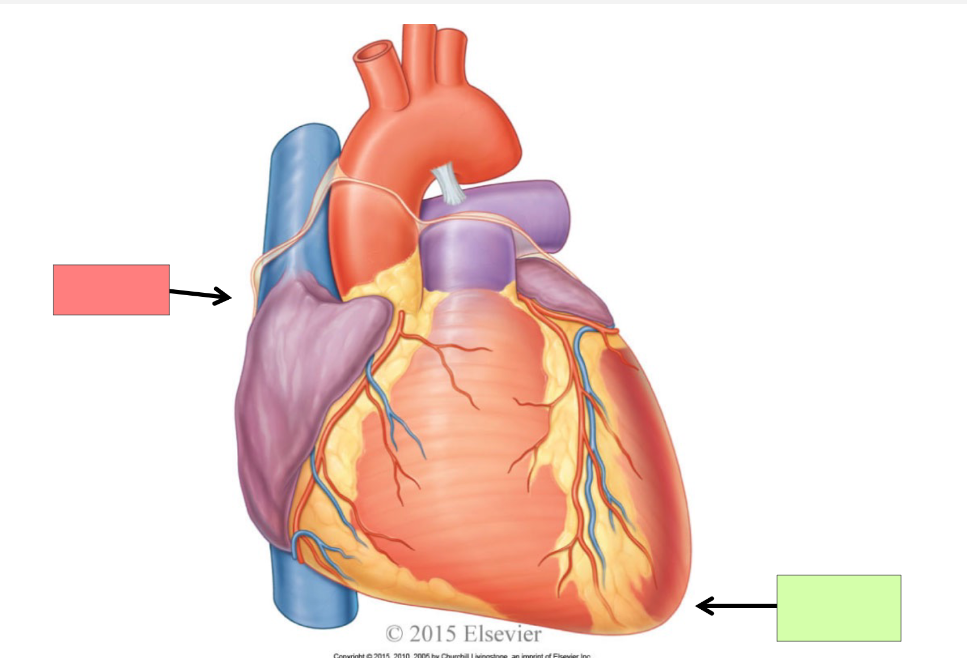
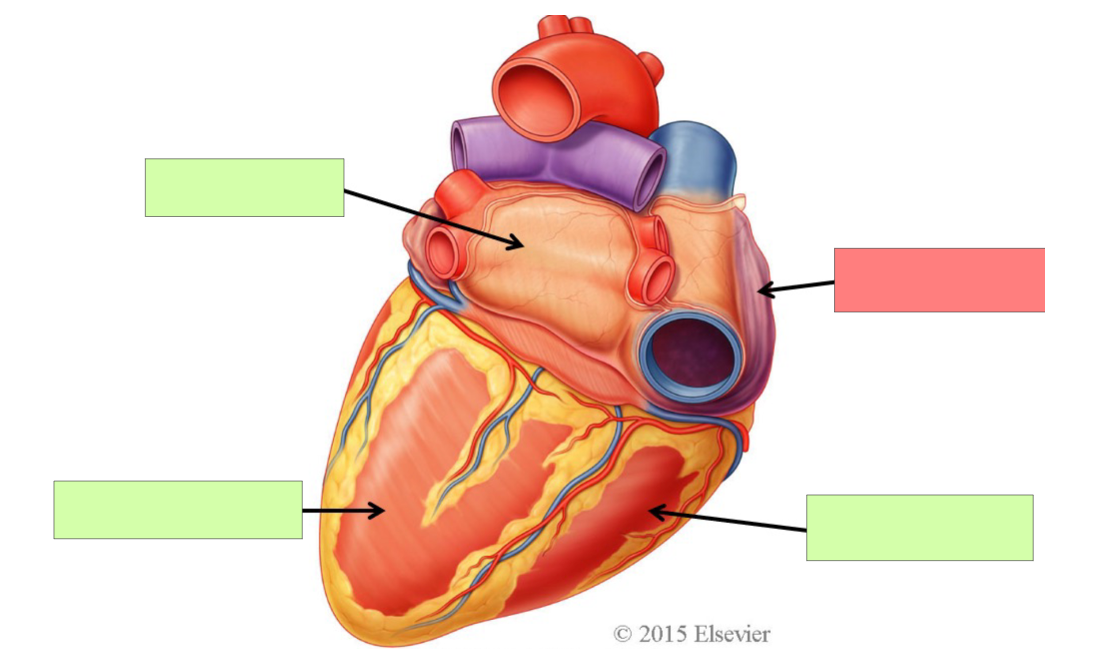
base
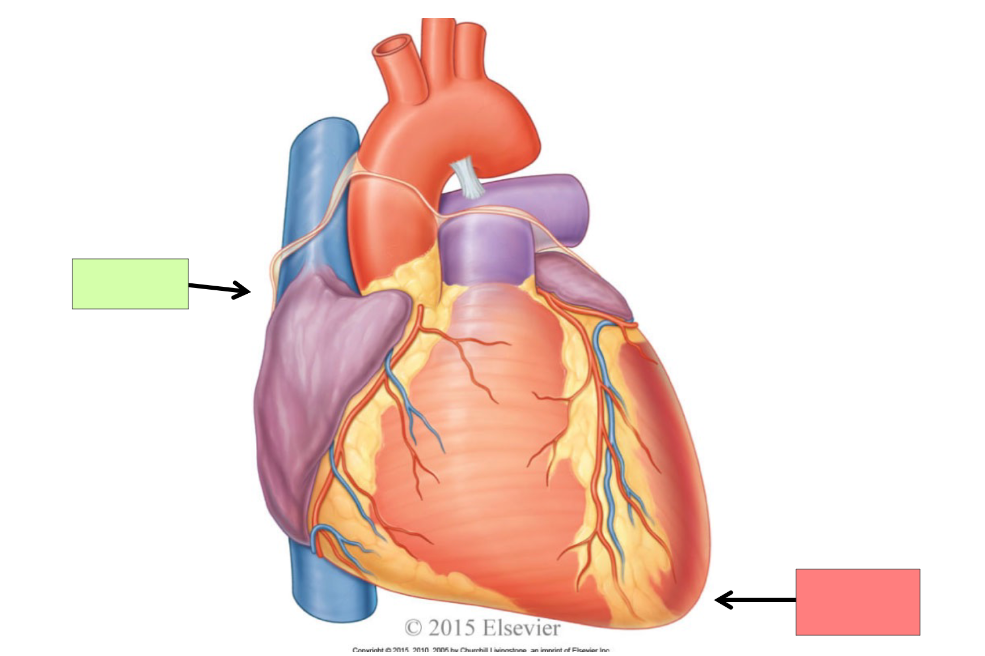
apex
left atrium
left ventricle
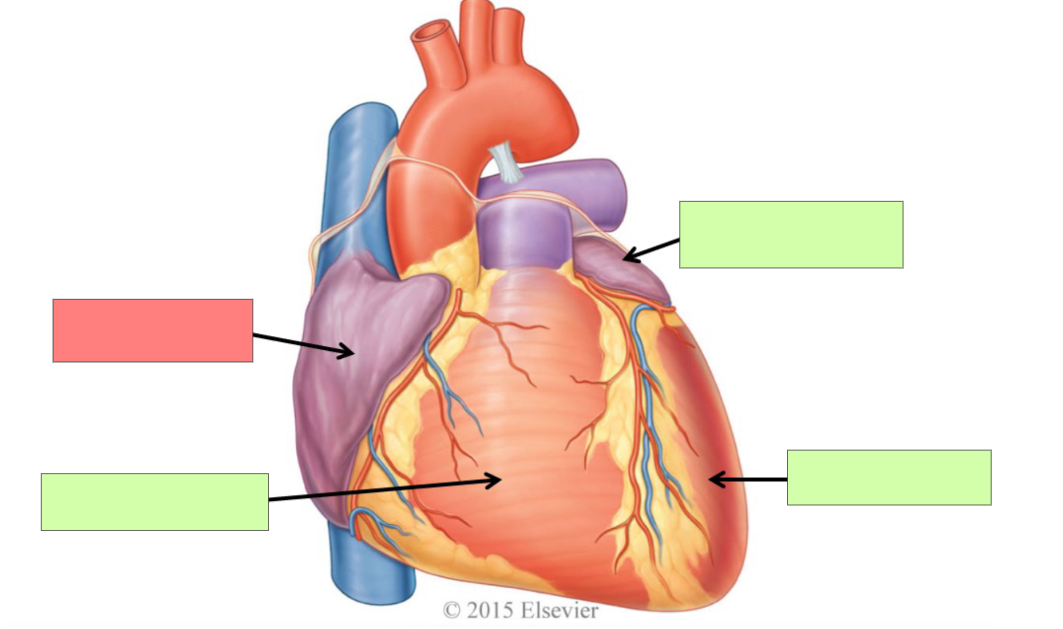
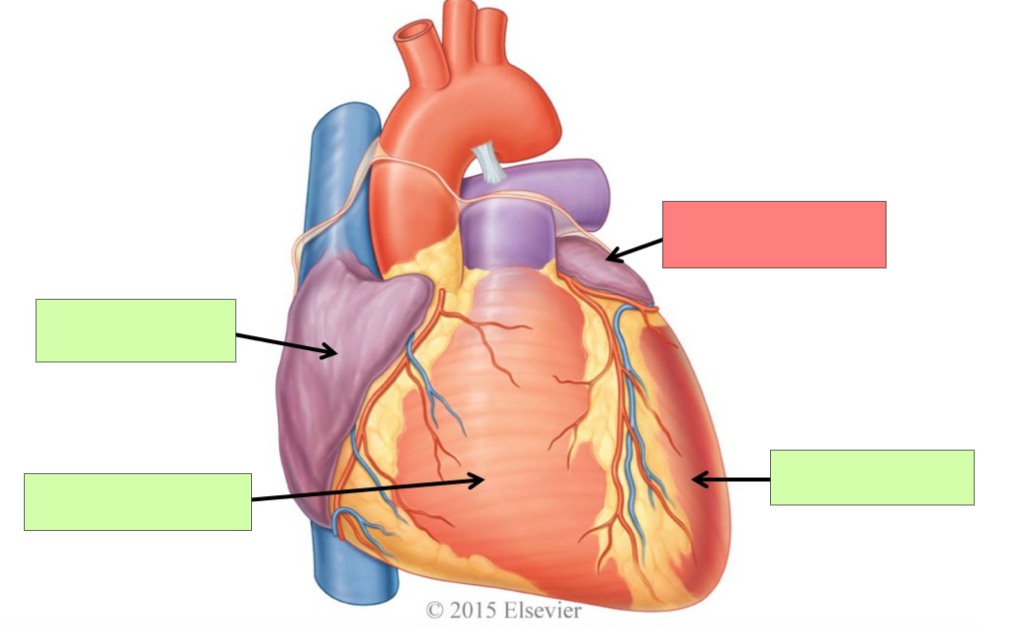
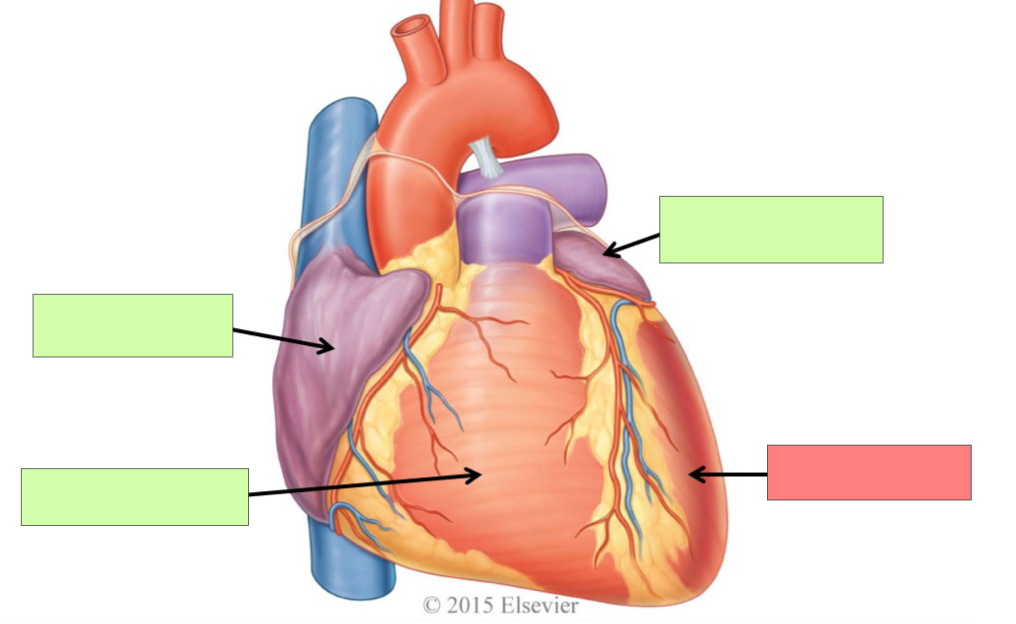
right atrium
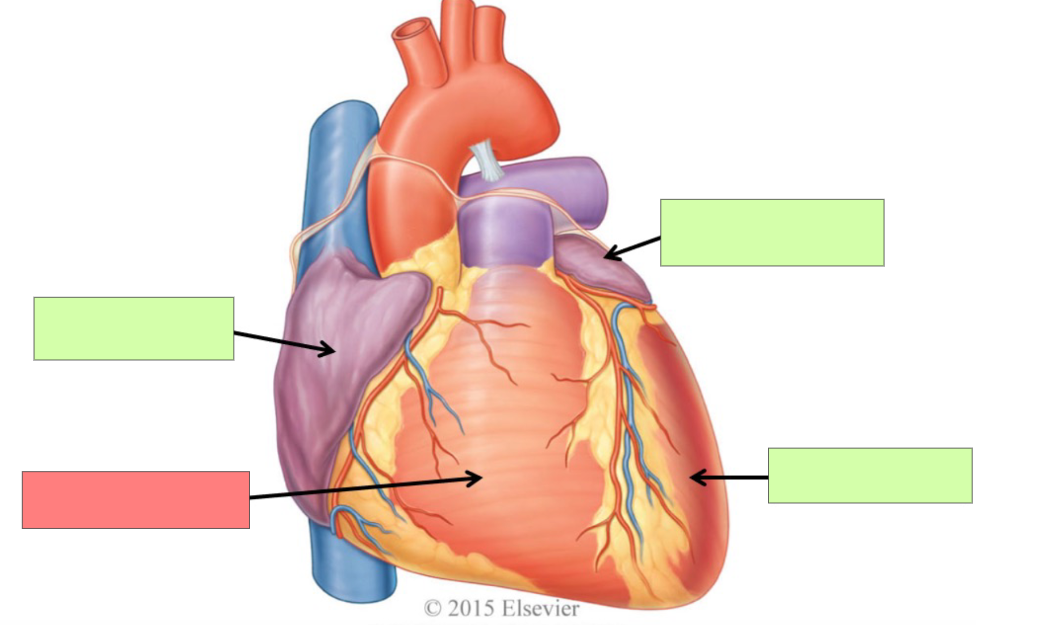
right ventricle
left atrium
left ventricle
right atrium
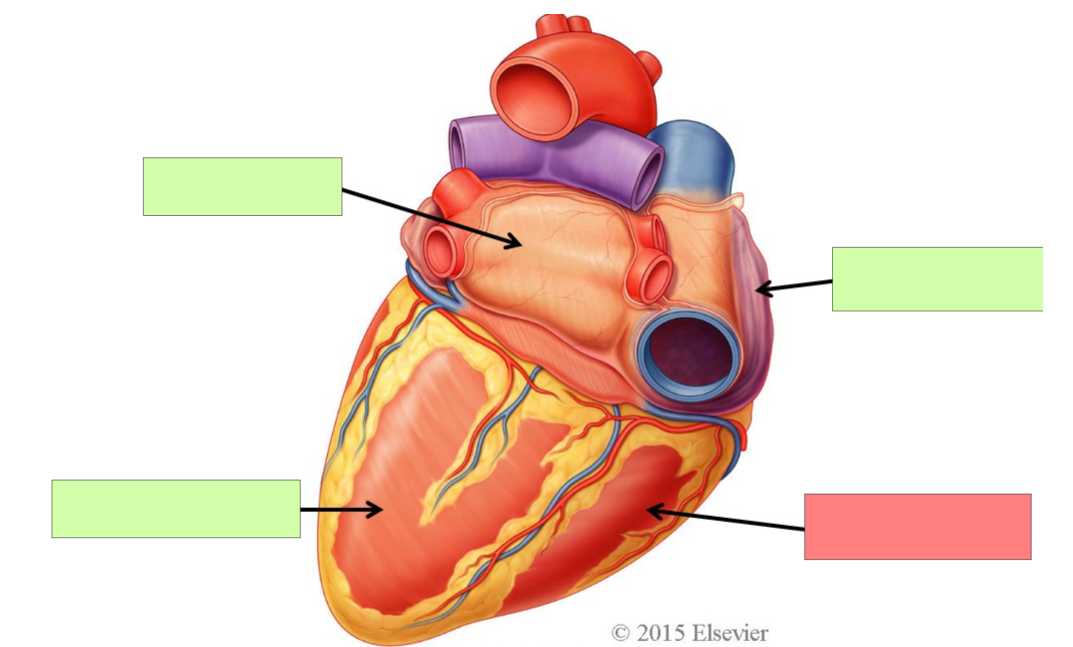
right ventricle
Describe the circuit on the right side of the body.
Pulmonary circuit. Right side of heart pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs and gas exchange occurs and oxygenated blood goes back to the left side of the heart
Why does blood need to go to the lungs?
To become oxygenated
Describe the circuit on the left side of the heart
Systemic circuit. Left side of heart pumps oxygenated blood to the body and then it goes back to the right side of the heart as deoxygenated blood
What is the function of the atria of the heart?
to receive blood
What is the function of the ventricles of the heart?
discharge blood
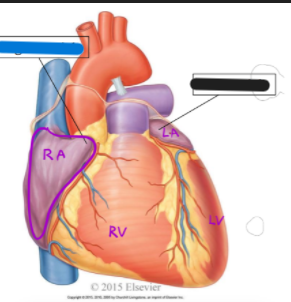
What is the blue structure?
right auricle
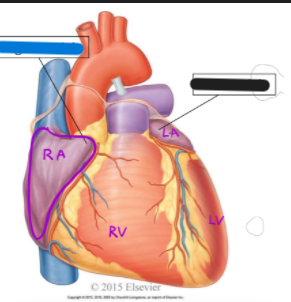
What is the black structure?
left auricle
What are the 5 great vessels of the heart?
Superior Vena Cava, Inferior Vena Cava, pulmonary veins, Pulmonary trunk and arteries, aorta
Which of the 5 great vessels are veins?
Superior Vena Cava, Inferior Vena Cava, pulmonary veins
Which of the 5 great vessels are arteries?
pulmonary trunk and arteries and aorta
What is the superior vena cava formed by?
Right and left brachiocephalic veins
Describe the flow of blood of the superior vena cava
SVC returns blood from thoracic wall, upper limb, head and neck to right atrium of the heart
What is the inferior vena cava formed by?
common iliac veins
Describe the flow of blood of the inferior vena cava
IVC returns blood from the abdomen, pelvis and lower limb to the right atrium
What blood does the right atrium receive?
deoxygenated blood
Where does the right atrium receive blood from?
superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, coronary sinus
What blood does the right ventricle receive?
deoxygenated blood
Where does the right ventricle discharged blood to?
pulmonary circuit
What does the right ventricle discharged blood via?
pulmonary trunk which splits into pulmonary arteries
Describe the flow of blood in the lungs.
Deoxygenated blood enters the lungs through the pulmonary artery and exits via the pulmonary veins into the left atrium
Describe the flow of blood on the right side of the heart
Superior Vena Cava, Inferior Vena Cava, Coronary Sinus —> right atrium —> right ventricle —> pulmonary trunk —> pulmonary arteries —> pulmonary veins
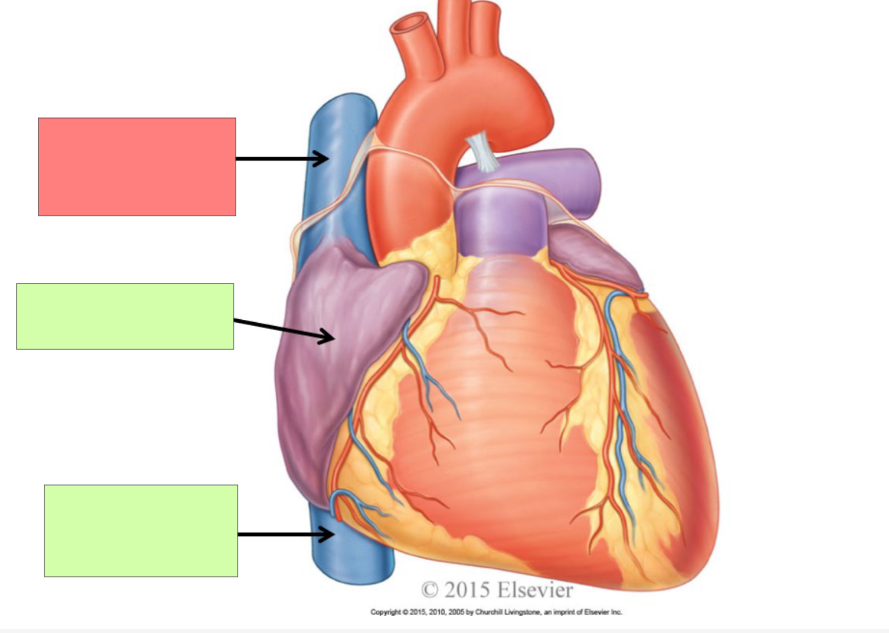
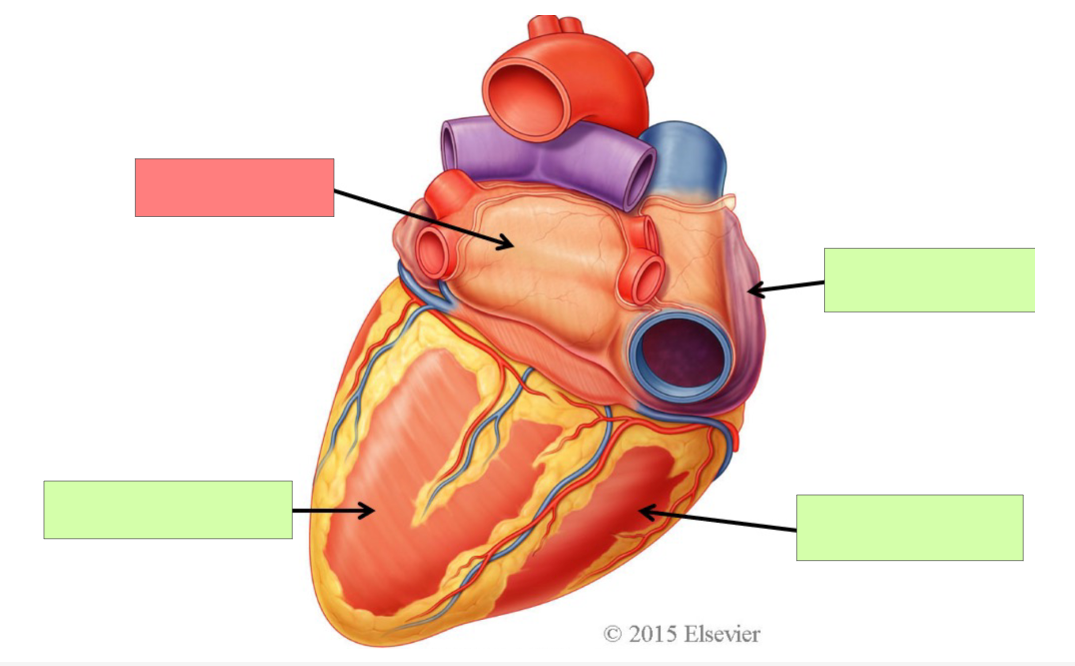
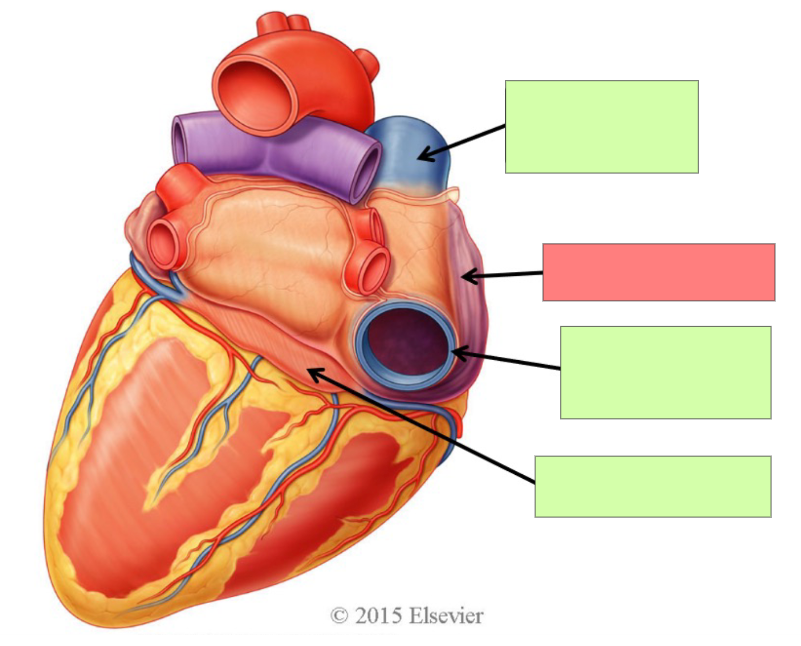
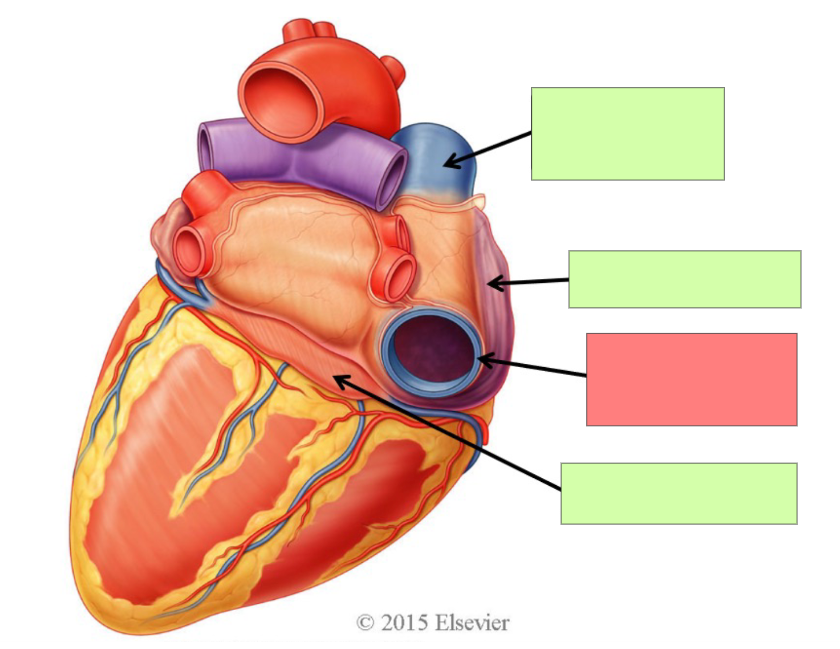
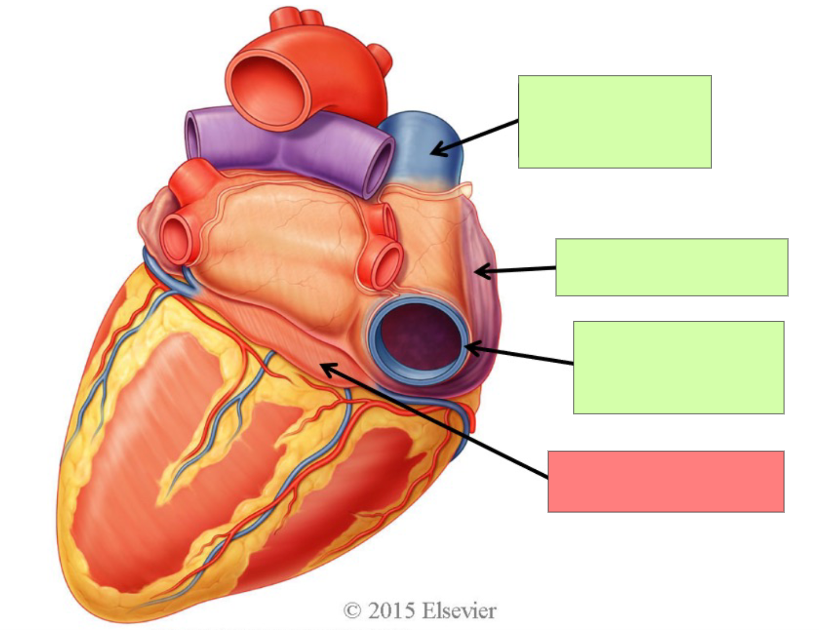
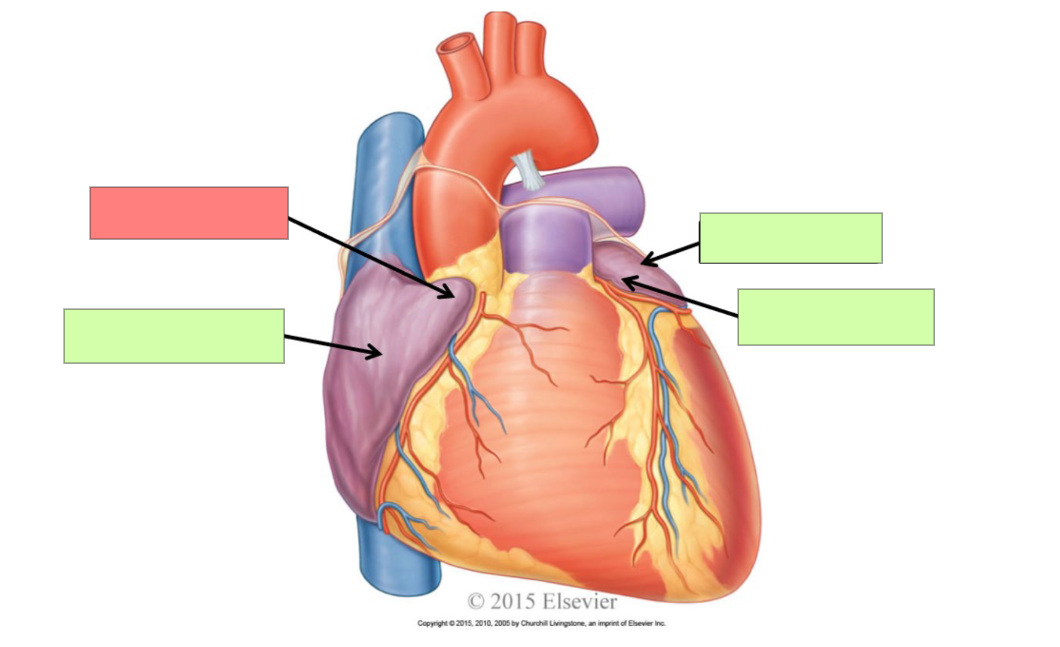
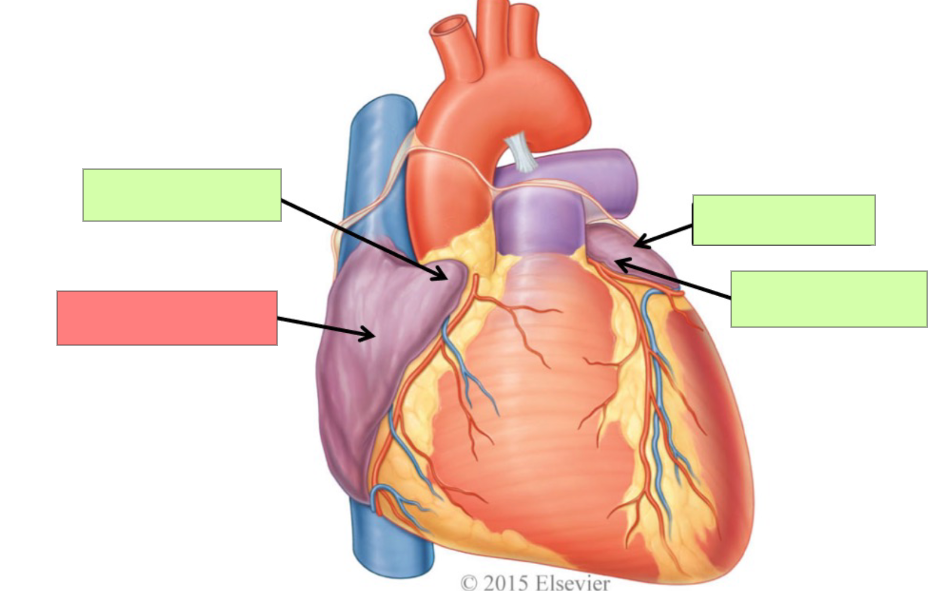
superior vena cava
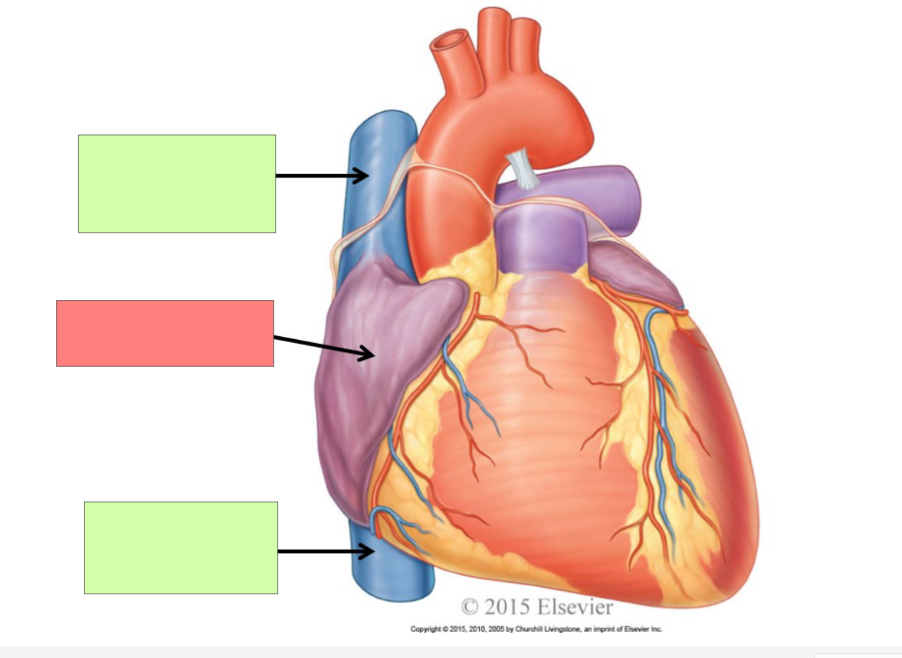
right atrium
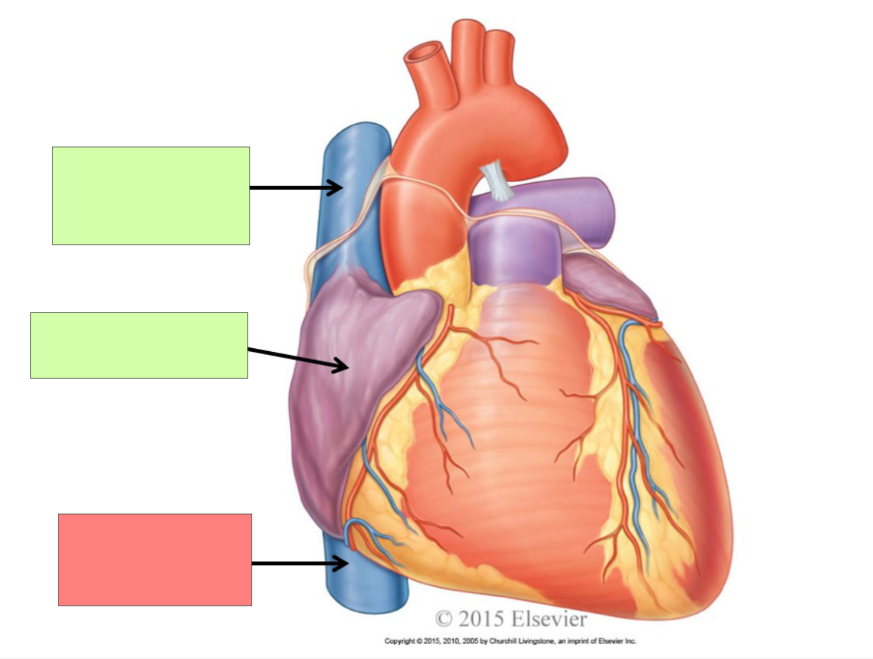
inferior vena cava
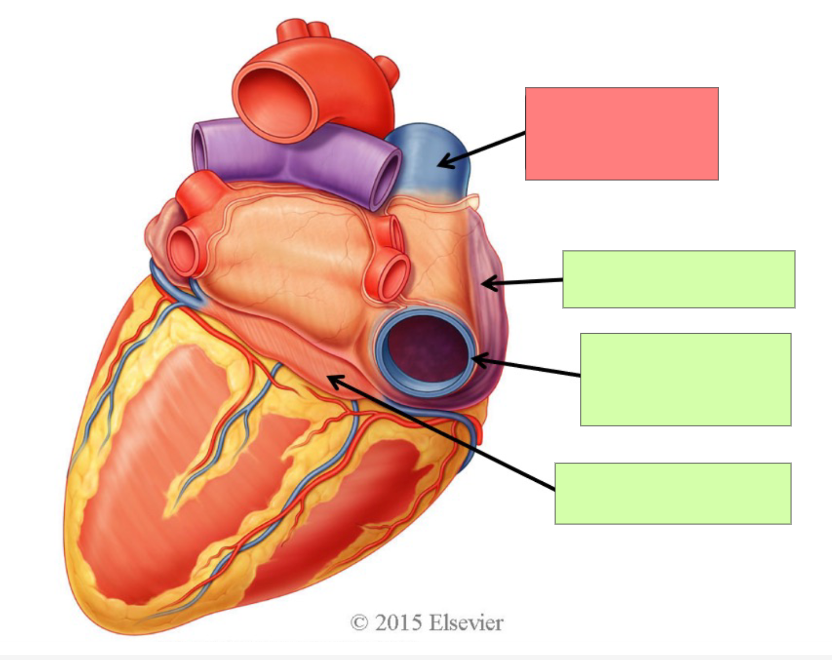
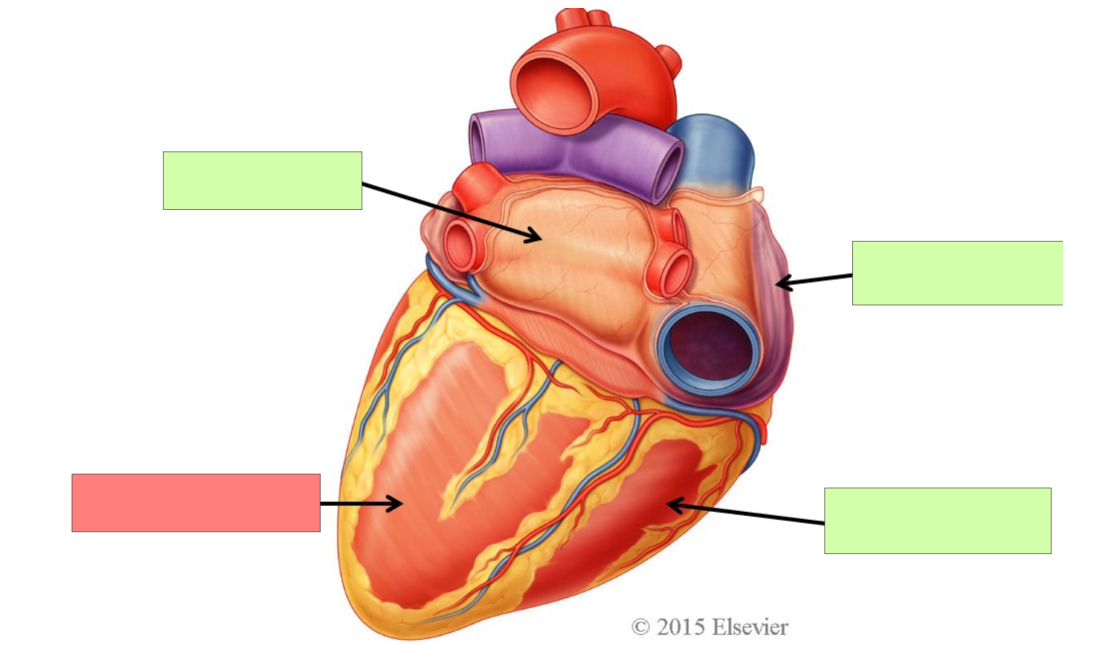
superior vena cava
right atrium
inferior vena cava
coronary sinus
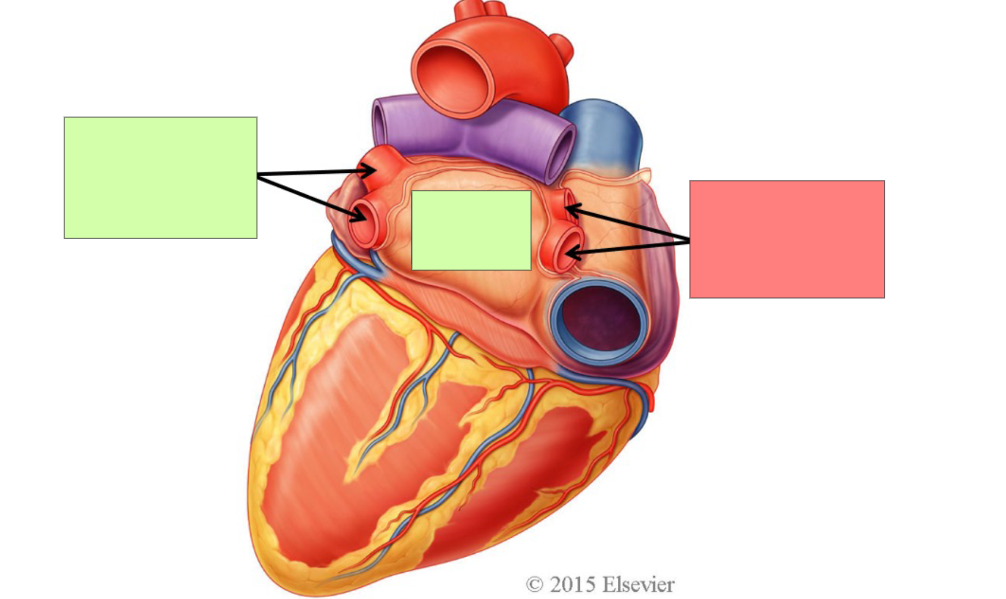
right pulmonary veins
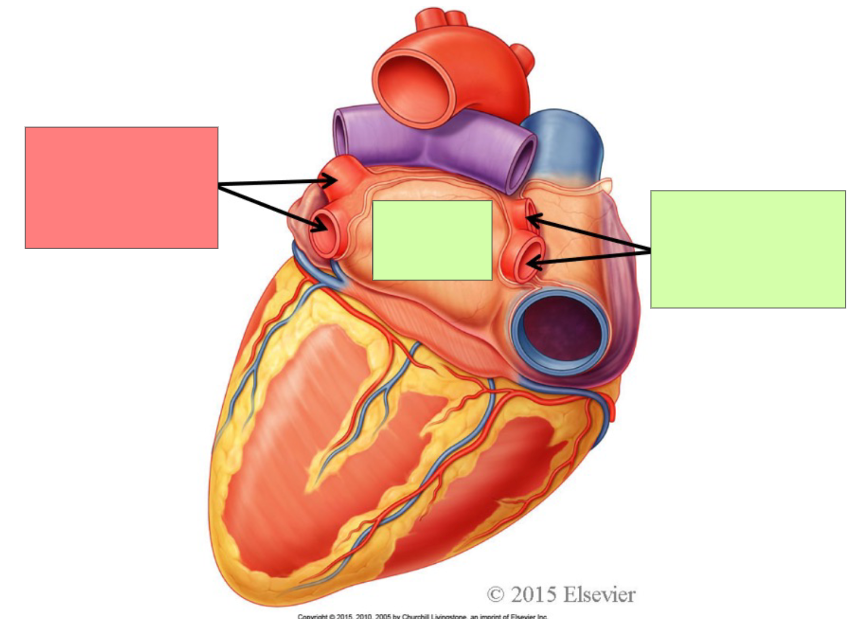
left pulmonary veins
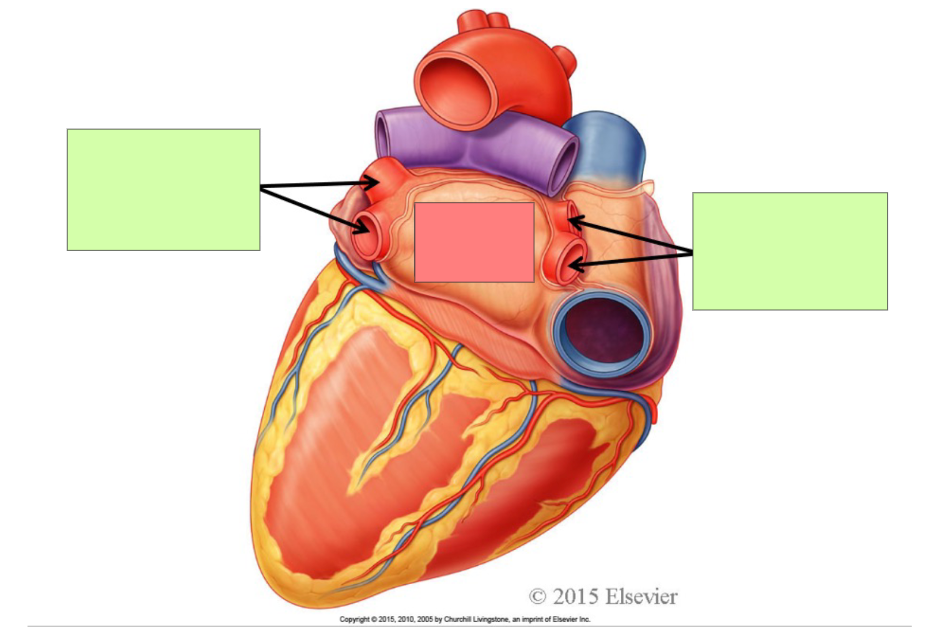
left atrium
right auricle
right atrium
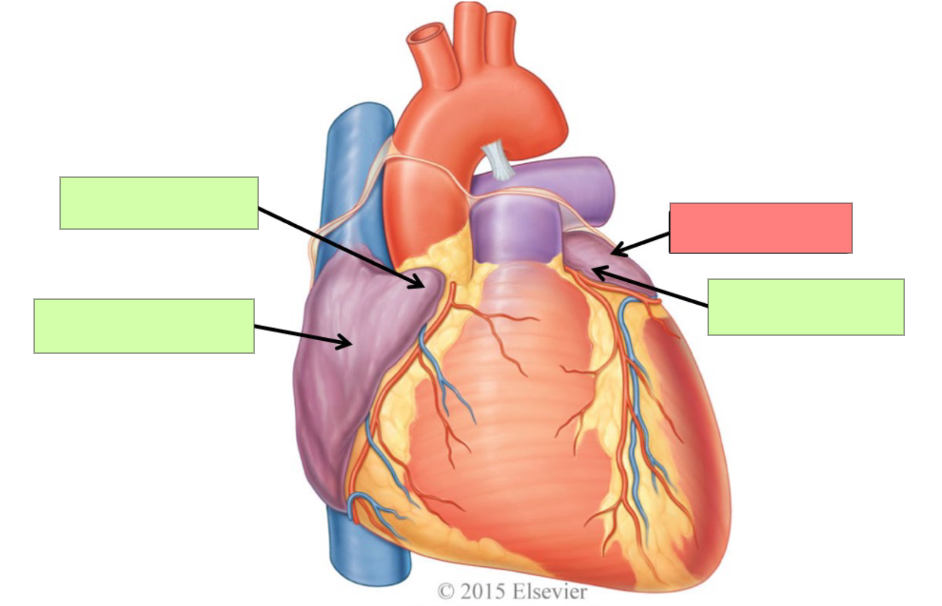
left atrium
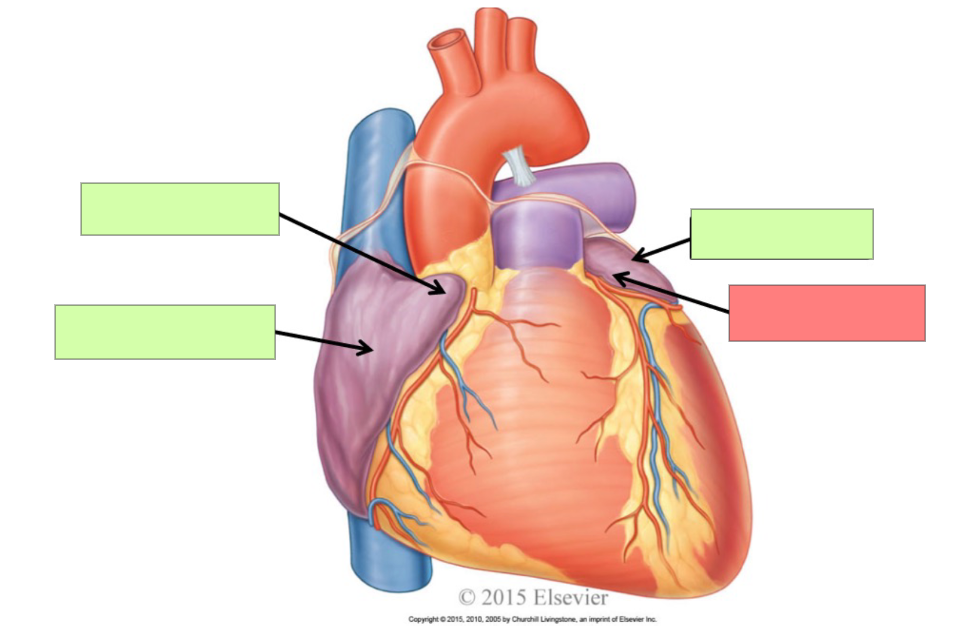
left auricle
What is the direction of the flow of blood in arteries?
away from the heart
What is the direction of the flow of blood in veins?
toward the heart
Describe the direction of the flow of blood in the right sides of the heart
The right side of the heart receives deoxygenated blood from the body and pumps it to the lungs
Describe the direction of the flow of blood in the left sides of the heart
The left side of the heart receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it to the body
How does the heart prevent backflow in the chambers?
valves
What are the two atrioventricular valves?
tricuspid valve and bicuspid/mitral valve
Where are the atrioventricular valves located and what are their functions?
Between atrium and ventricles. Prevent backflow into atria
Where is the tricuspid valve located?
between right atrium and right ventricle
Where is the bicuspid valve located?
Between left atrium and left ventricle
What are the two semilunar valves?
Pulmonary semilunar valve. Aortic semilunar valve
Where are the semilunar valves and what are their functions?
Between ventricles and outflow arteries. prevents backflow into ventricles
Where is the pulmonary semilunar valve located?
Between right ventricle and pulmonary trunk. Right heart to lungs
Where is the aortic semilunar valve located?
Between left ventricle and aorta. Left heart to body

Right AV valve. Tricuspid valve
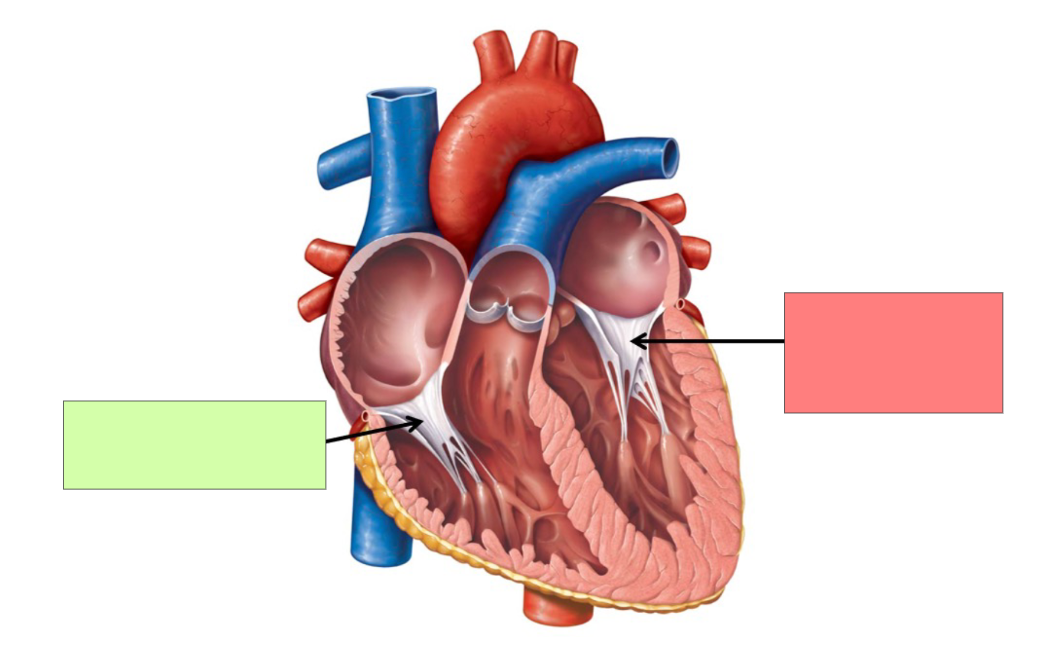
Left AV valve. Bicuspid/mitral valve
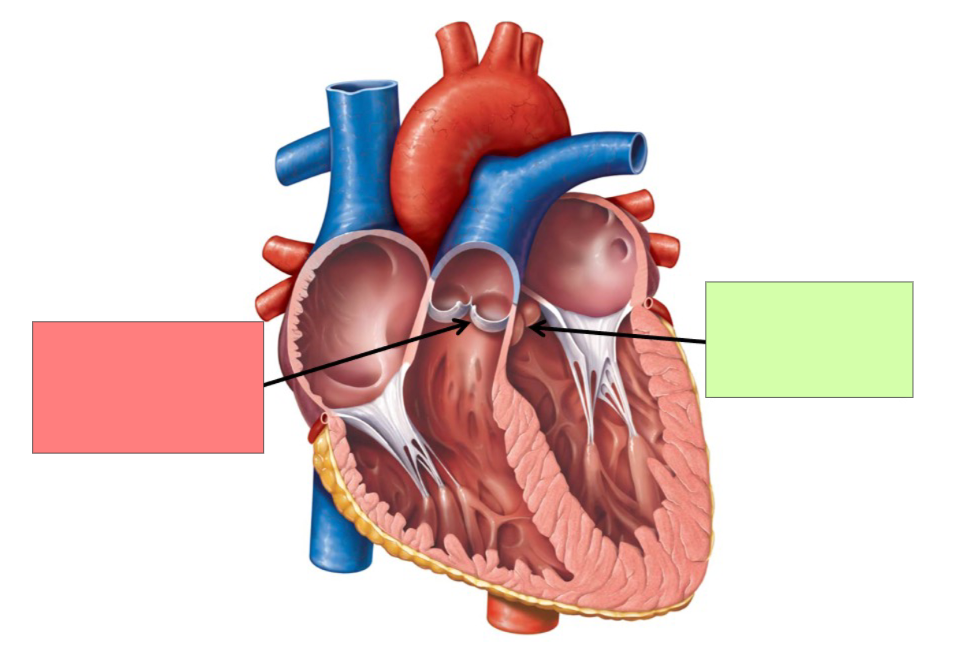
pulmonary semilunar valve
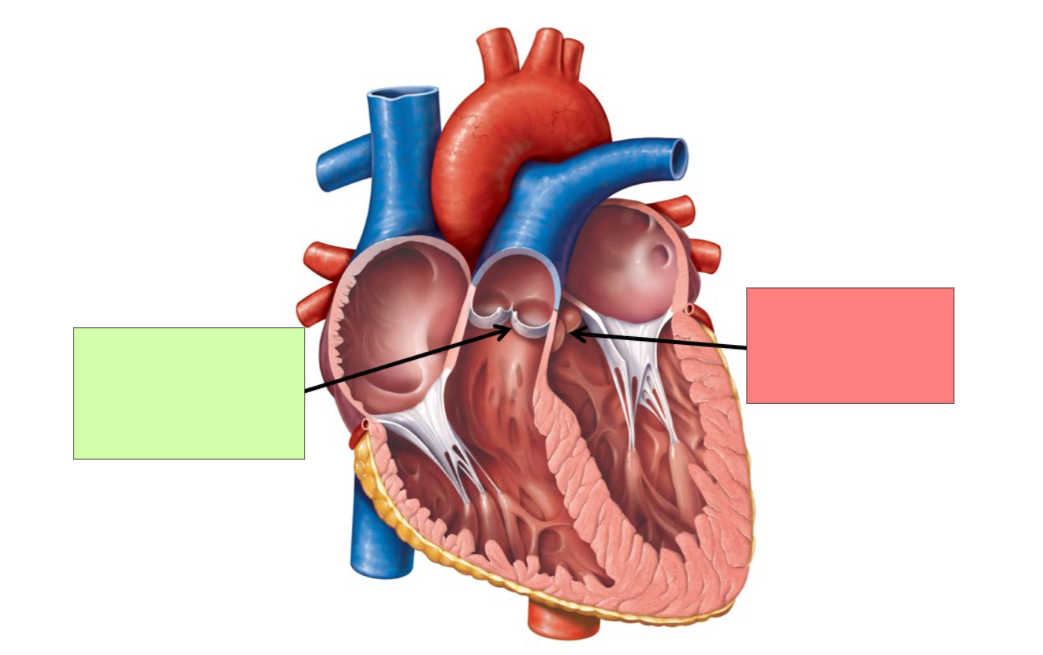
aortic semilunar valve

chordae tendinaea
What structures is the chordae tendinae attached to?
Tricuspid valve and papillary muscle
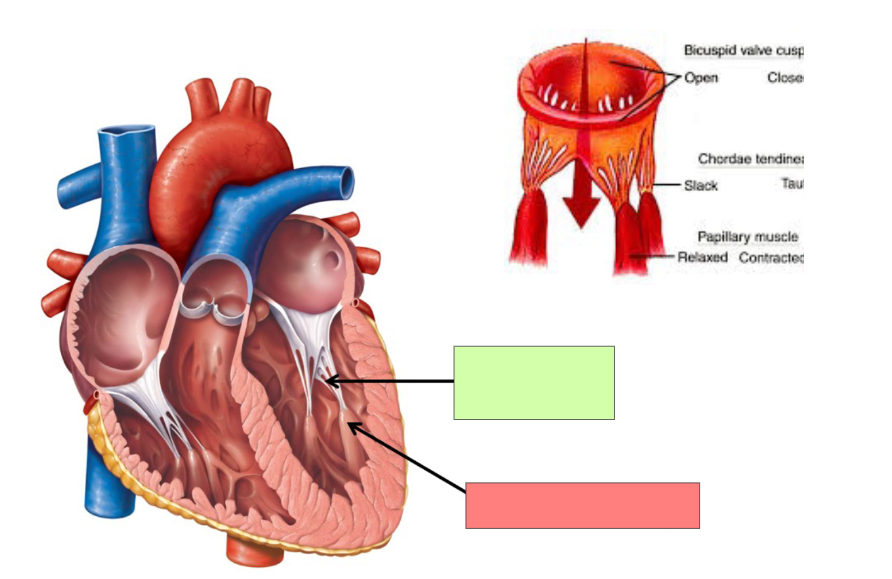
papillary muscle
How do the valves open and close?
through difference in pressure
What is systole?
Systole is the action when ventricles contract to pump blood out of the heart and there is high pressure in the ventricles. Atrioventricular valves close and semilunar valves open
what is diastole?
Diastole is the action when ventricles relax so blood can fill them again and pressure is low. Atrioventricular valves open and semilunar valves close
What are the sounds associated with contractions?
Systole - lub. Diastole - dub
Describe the flow of blood from the right atrium to the body.
SVC, IVC, coronary sinus —> right atrium —> tricuspid valve —> right ventricle —> pulmonary semilunar valve —> pulmonary trunk —> left and right pulmonary arteries —> lungs —> pulmonary veins —> left atrium —> bicuspid valve —> left ventricle —> aortic semilunar valve —> aorta —> body and coronary circulation
What are the layers of the heart superficial to deep?
epicardium, myocardium, endocardium
Why does the left side of the heart have thicker layers?
To have enough strength to pump to whole body
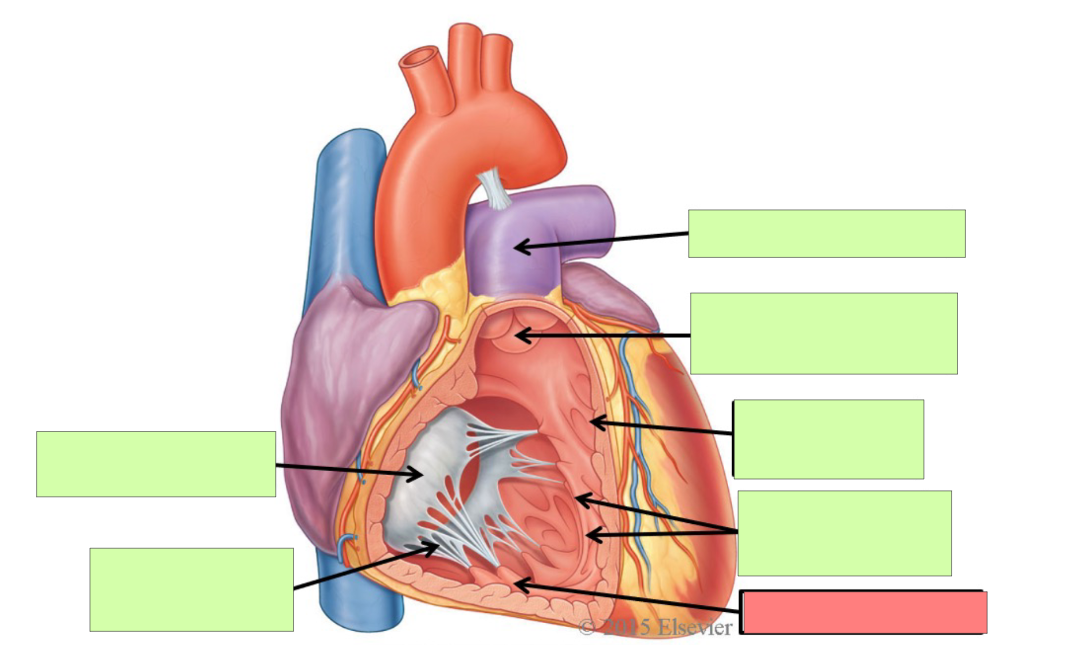
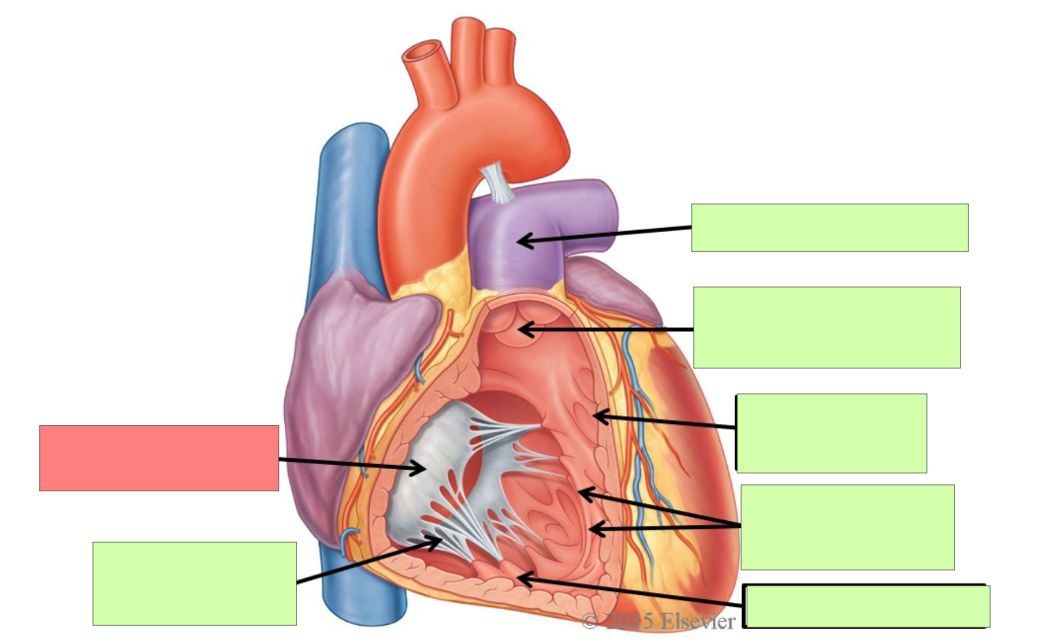
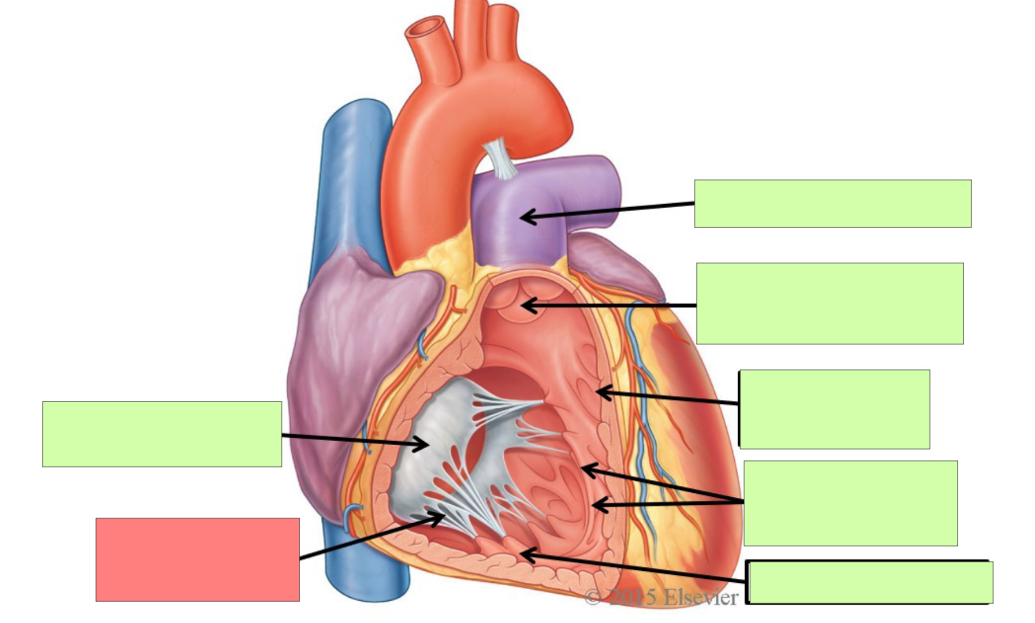
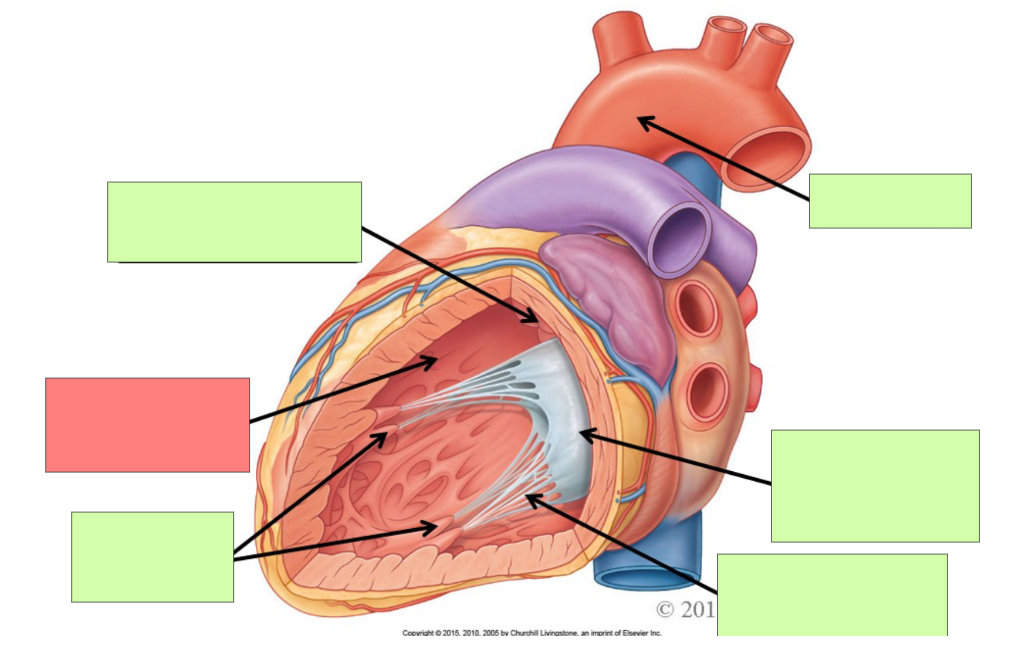
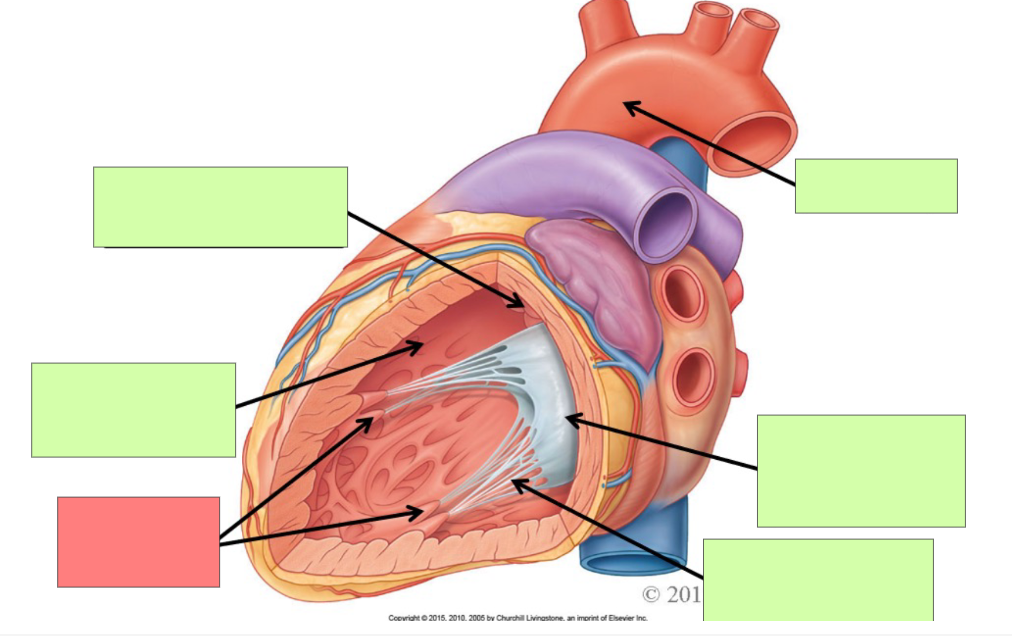
What are the internal features of the right atrium?
pectinate muscle, fossa ovalis, opening of coronary sinus
What are the internal feature of right ventricle?
Trabeculae carnae, chordae tendinae, papillary muscle, tricuspid valve, pulmonary trunk, pulmonary semilunar valve
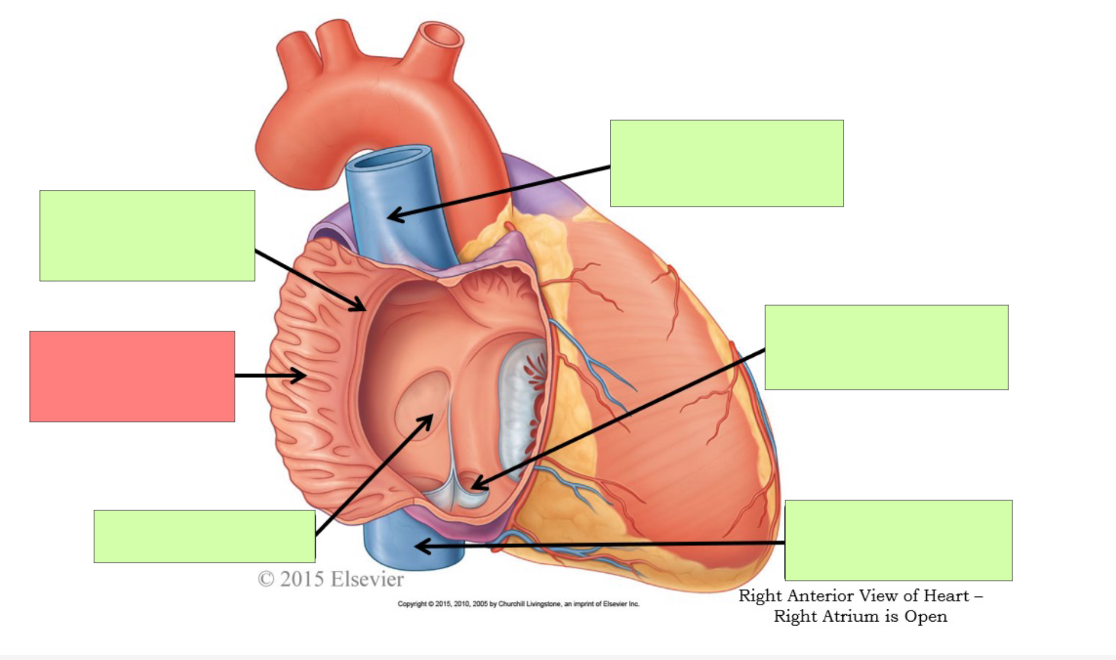
pectinate muscle
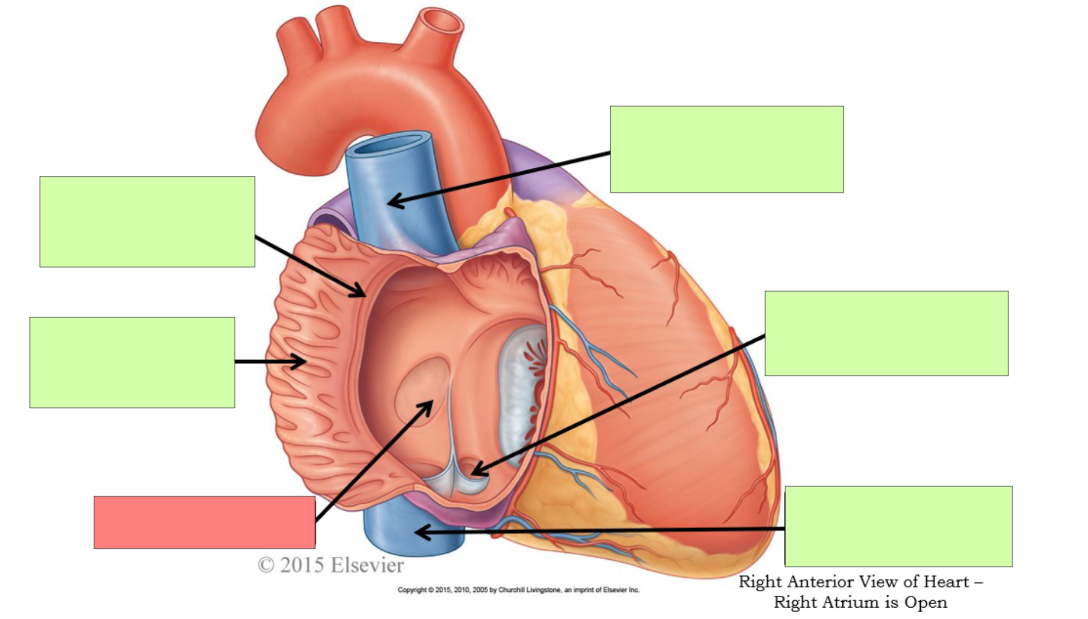
fossa ovalis
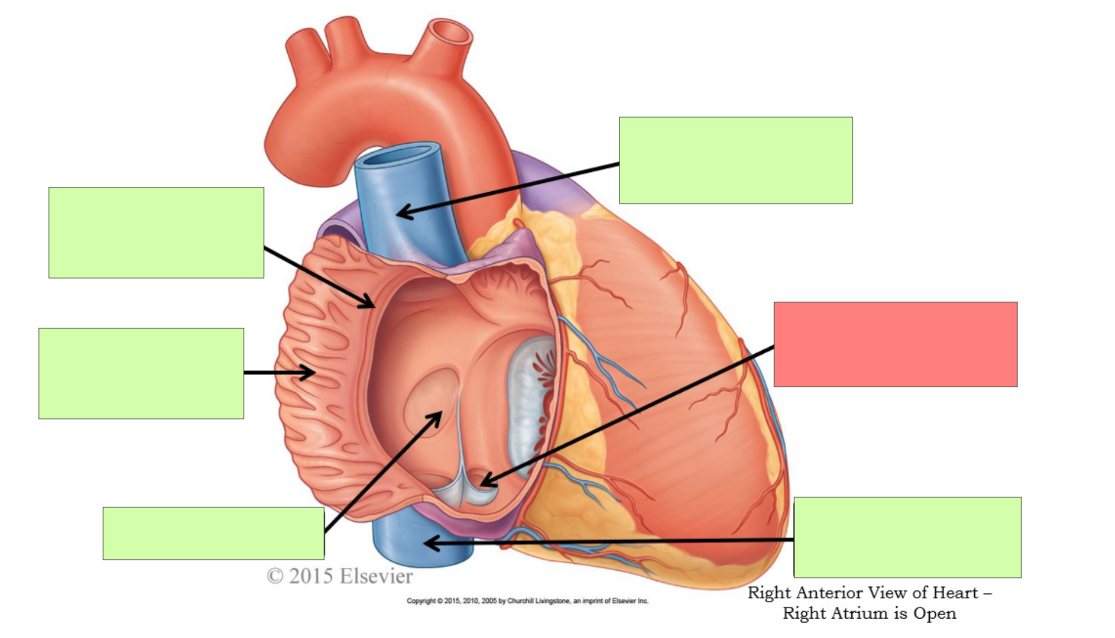
opening of coronary sinus
pulmonary trunk
pulmonary semilunar valve
trabeculae carneae
papillary muscle
tricuspid valve
chordae tendineae
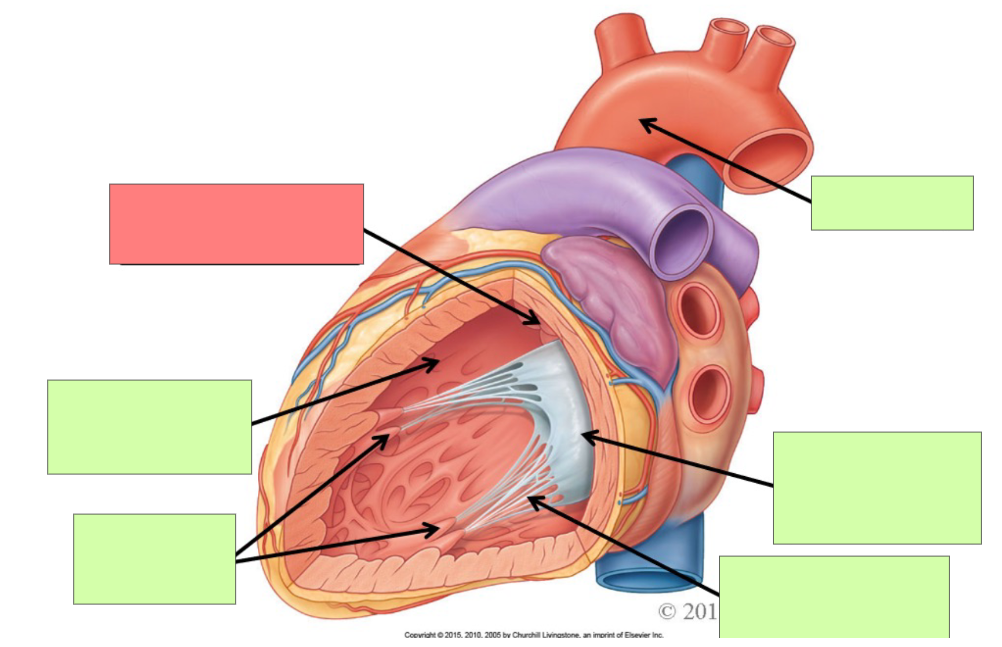
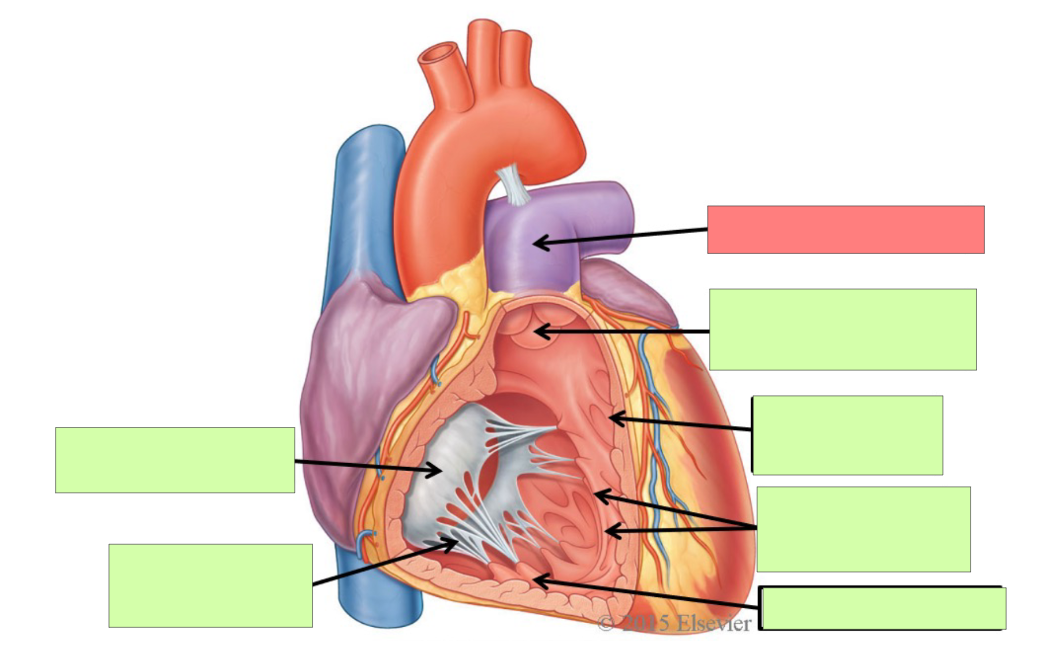
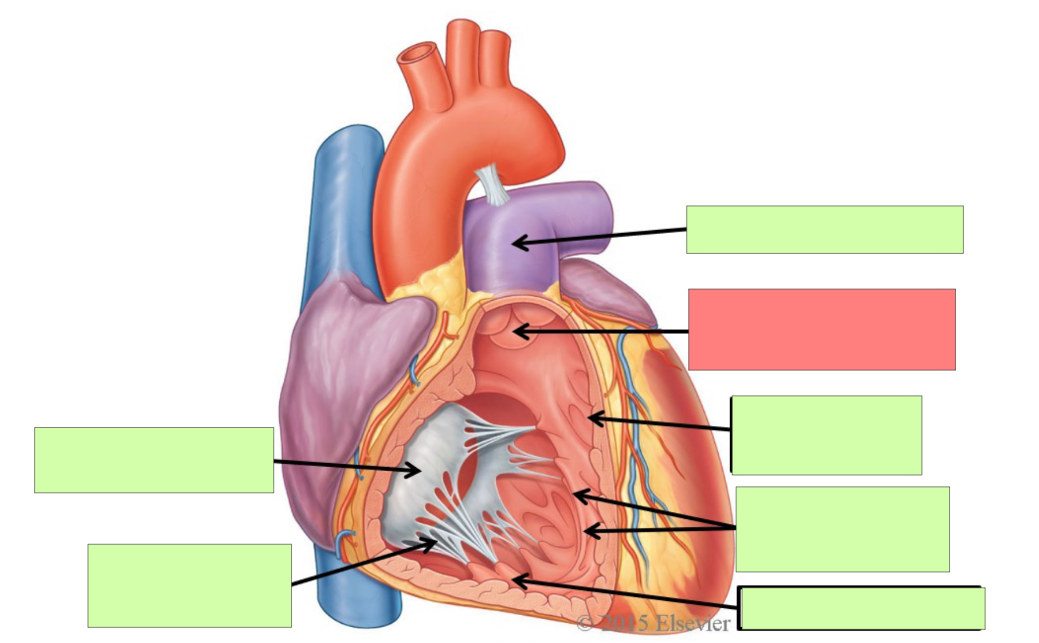
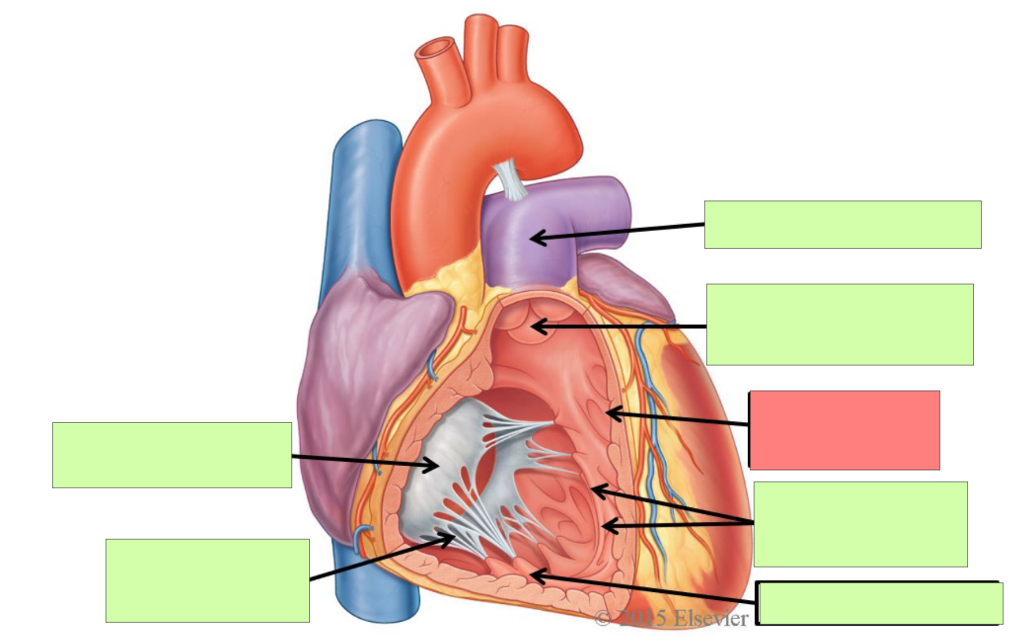
aortic semilunar valve
trabeculae carneae
papillary muscle
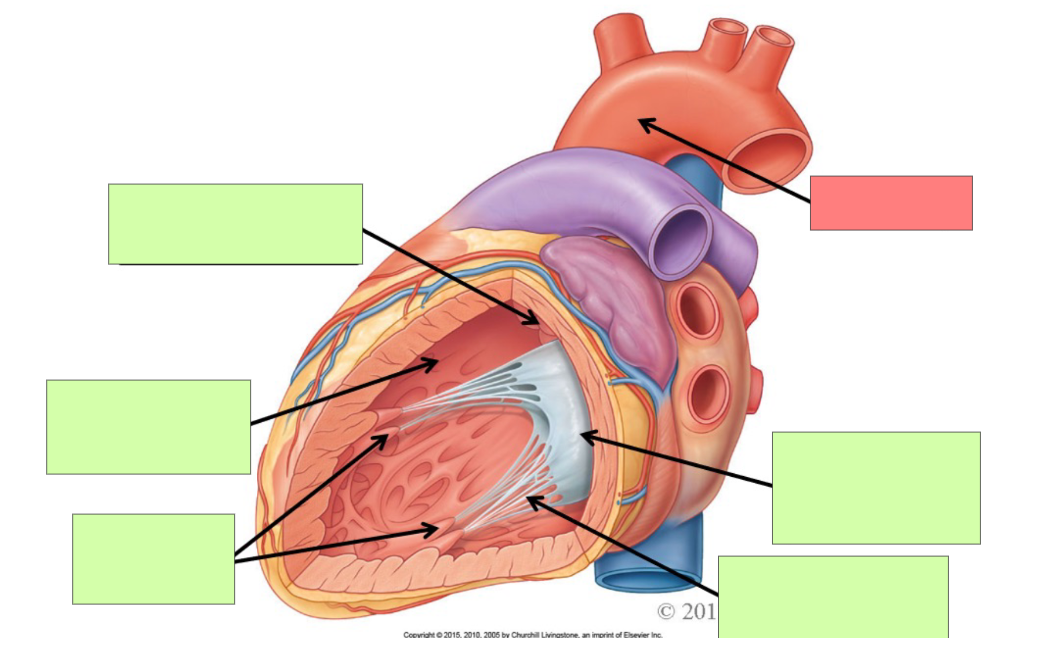
aorta
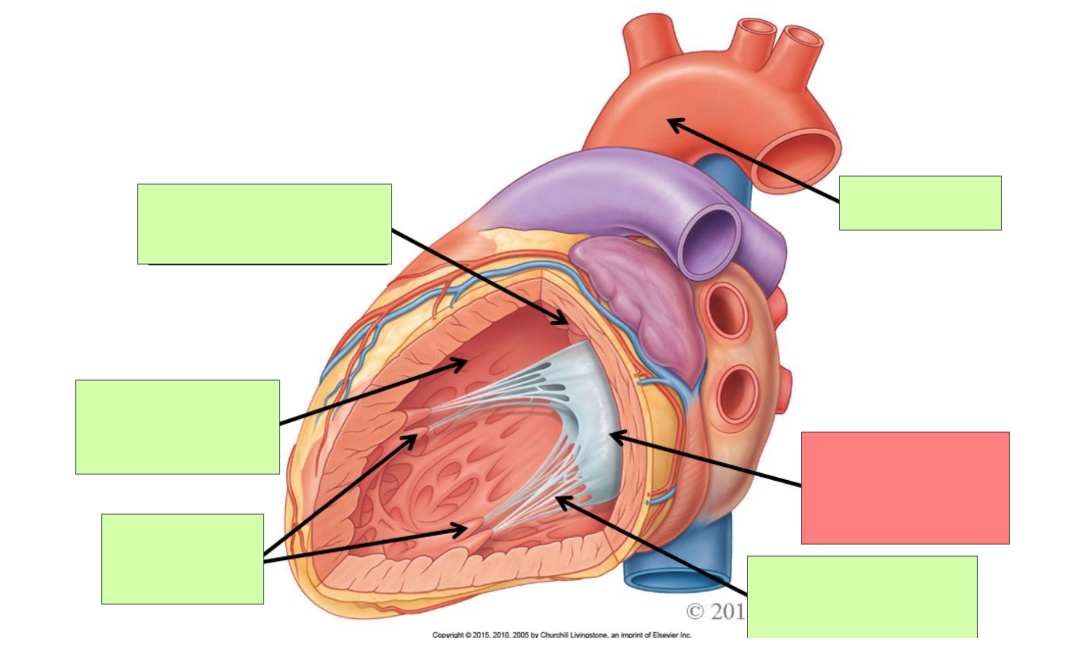
bicuspid (mitral) valve
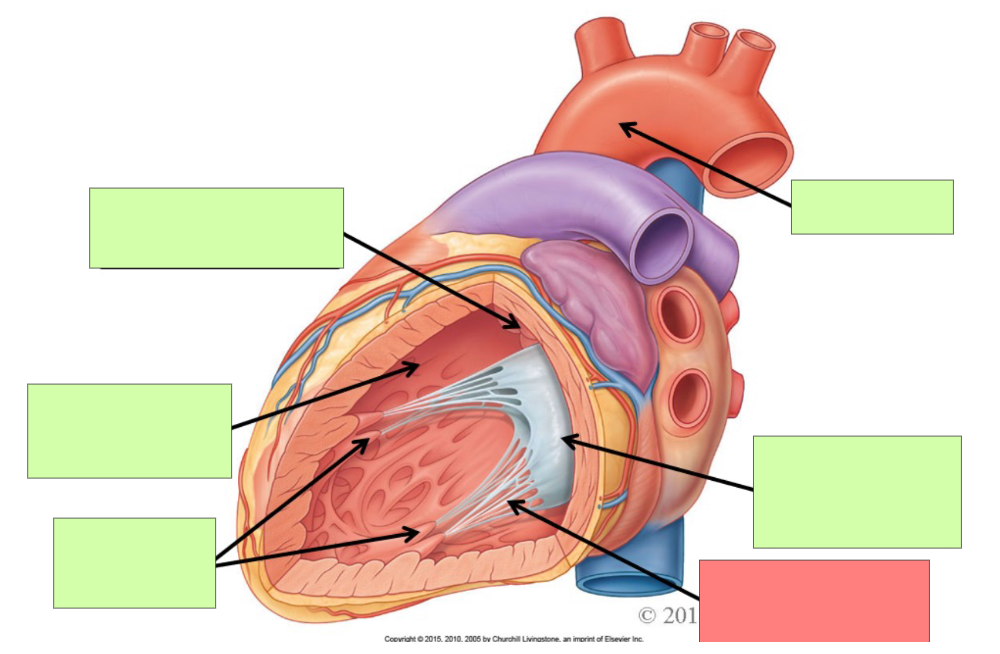
chordae tendineae
Describe arterial coronary circulation when the heart is relaxed (diastole)
maximum blood flow to the myocardium occurs when the heart is relaxed
Describe arterial coronary circulation when the heart contracts (systole)
there is very little blood flow through the coronary circulation when the heart contracts
Why is there little blood flow when the heart contracts?
Contraction of myocardium compresses coronary arteries and entrances into the coronary circulation are partially blocked by the cusps of the open aortic semilunar valve
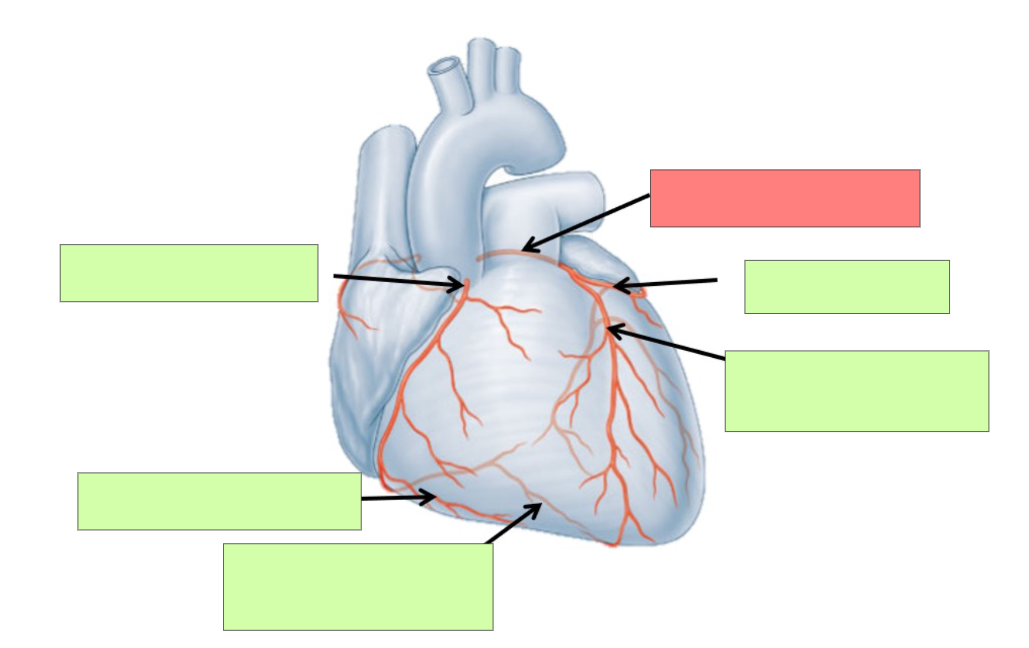
left coronary artery
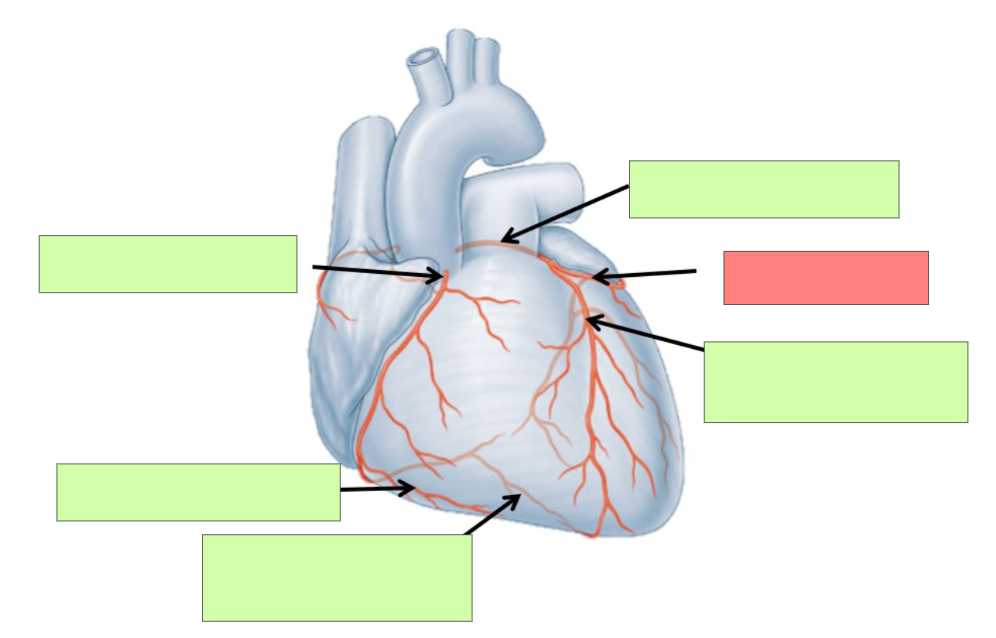
circumflex artery
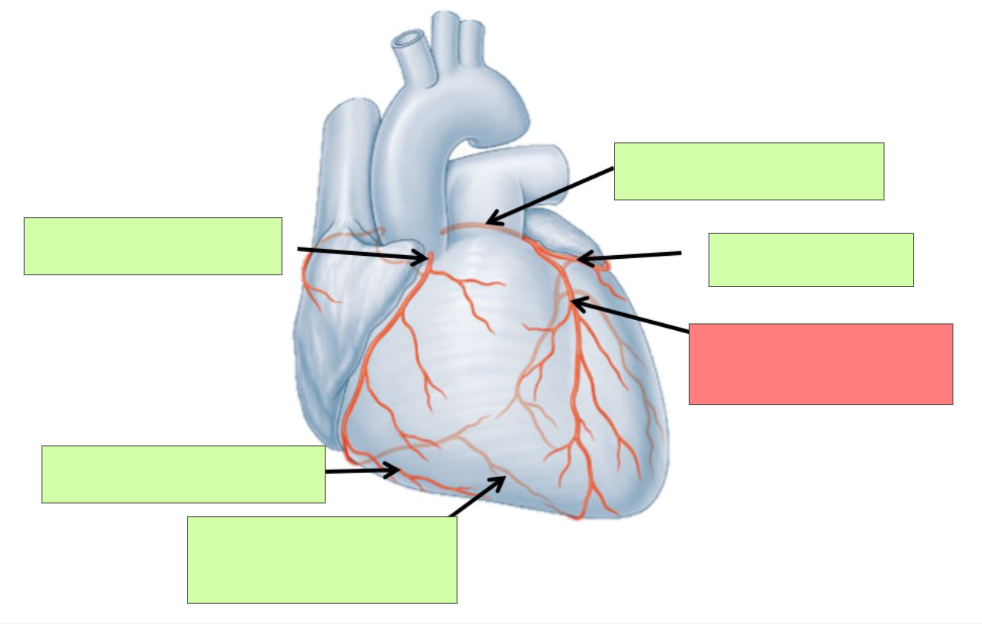
anterior interventricular artery
What is significant about the anterior intraventricular artery?
most common site for plaque build up
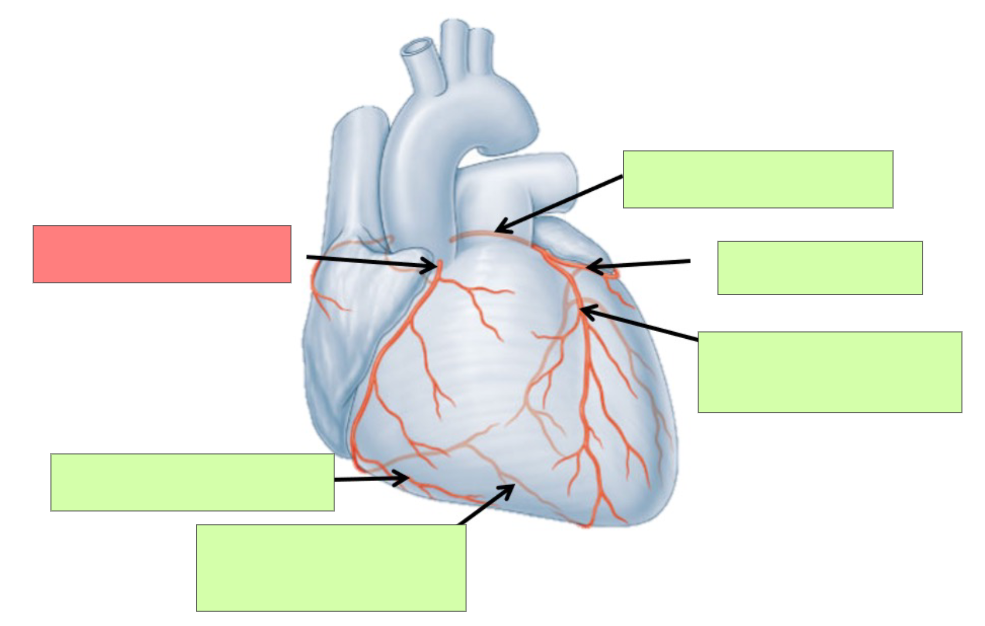
right coronary artery