Business Management - Topic 5
1/199
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
200 Terms
What is operations management?
The process of transforming resources/inputs into outputs by adding value (design, plan, direct, and improve the production of goods and services)
How is operations and marketing interrelated?
Marketing does research to discover needs, business will produce the necessary products to meet those needs, production methods chosen by operations will affect quality and USP, exclusively produced vs. mass produced products will be marketed differently
How is operations and HR interrelated?
HR recruits, trains, and motivates employees, operations need to decide on production methods (capital intensive or labor intensive) which influences how many employees are needed, what training is necessary, HR plans these trainings, hires the employees, and creates contingency plans for operational crises
How is operations and finance interrelated?
Finance ensures funds are in place to meet the needs of production, cost reductions could lead to inefficiencies and low quality
What is job production?
Creating an individual product from start to finish, the product is tailor-made to meet specific needs of a customer (one-off items like buildings, wedding dresses, movies, haircuts, and music instruments)
Why would job production be necessary?
Customers have a very specific requirement or there is a small number of customers and capital intensive labor is too expensive
What are advantages of job production?
Quality of production is high
Highly motivated employees as they enjoy their job and can use their expertise and skills
Products can be sold for higher prices due to unique specifications
Flexibility in designs and specifications allows for product to be adapted to customer needs, can improve relationships
What are disadvantages of job production?
Very labor-intensive, costs are high
Low production quantities so less EoS
Requires highly skilled workers
Time consuming
Long working capital cycle can cause cash flow problems, customers may pay a deposit and pay the rest after product is complete
What is batch production?
Producing similar items in groups, each batch is completed before moving to the next (Nike shoe made by sizes, bakery making batches of different flavored cookies )
When would batch production be used?
Amount of demand for a certain product in the market is unclear so batches are made to analyze the demand or business has a range of similar products that meet slightlydifferent consumer needs
What are advantages of batch production?
EoS from producing in larger quantities
Specialized employees for each batch can increase productivity
Tends to be an automated process with some employees
Wider product portfolio may increase sales and lower risks
Some flexibility allows each batch to be adjusted to meet a range of customer needs/expectations
What are disadvantages of batch production?
Inflexible once production starts
Storage costs may be high because of increased stock, work-in-progress, and resources for each batch
Repetitive work can lower motivation and lead to boredom
High production costs due to many machine parts and settings for each batch
What is mass production?
Manufacturing large amounts of a standardized product on an assembly line (ball bearings, phones, Legos, paper clips, pins, toothpicks)
What is flow production?
A type of mass production that keeps going forever, even more automated with even less workers, runs 24/7 to maximize output and eliminate waste
Why would mass or flow production be used?
Company is large, demand for products is high, product is standardized
What are advantages of mass/flow production?
Large-scale production due to use of machinery
Standardized quality
EoS due to high production quantities
EoS through capital-intensive (tech EoS) methods
Lower labor costs as employees are only at certain stations to fix, maintain, and assist machines
What are disadvantages of mass/flow production?
Low motivation due to boredom
Set-up, running, replacement, and storage costs are high due to captial-intensive production and a lot of held stock
Breakdowns in machines can cause major delays
Very little flexibility
What is mass customization?
Producing large quantities of goods through mass production but products can be tailored to a customer’s exact preferences (customizable shoes, cars with different colors, wheels, seats, etc.)
Why would mass customization be used?
EoS needed due to intense competition in the industry or the company wants to sell products which are adapted to customer specifications at a relatively lower price
What are types of mass customization?
Collaborative customiziation: close interactions between customer and business to adapt mass-produced products according to customer specifications
Adaptive customization: customers choose from pre-set customizations provided by the business
Cosmetic customization: changes to the face of the product, usually packaging, to suit customer needs
Transparent customization: personalized items are recommended to the customer based on their online data
What are advantages of mass customization?
Customers have some variety of options so businesses can target a larger customer base
Business maintains EoS of mass production due to large volumes and capital-intensive production
Business can charge a higher price due to customization
What are disadvantages of mass customization?
Hard to resell returned customized products
Higher costs due to a wider variety of stock and equipment needed
Customized products take longer to produce and can result in supply chain problems
What needs to be considered when choosing an appropriate operation method?
Relative costs of labor and capital
Size of market
Corporate objectives (tailor for customers, provide large variety, provide high quality, produce in large quantity)
Capital vs. labor-intensive production
What are the benefit of labor-intensive operations?
Can offer more personalized services/customized goods
What are the benefits of capital-intensive operations?
Higher level of output, standardization in products
What is efficiency?
How well a business can transform physical, human, and financial inputs into outputs
What is waste/muda?
Any part of the production process that doesn’t add value
When is a business more efficient?
When more products are produced with the same or less resources or when quality, speed, and results increase and costs decrease
What are parts of muda?
Over-processing/when the business adds more features or functions to a product than necessary
Delays in production, delivery, and inefficient movement around the production facility
Sub-standard and defective output that will need to be re-worked
Waste of energy (lights, A/C, utilities) by leaving them on when not needed
Under or overproduction
Why is it important to reduce muda?
Reducing waste reduces costs, less waste means greater efficiency, more waste results in resources lost which can harm people and the planet
What is lean production?
The process of streamlining operations and processes to reduce waste and achieve greater efficiency which can lead to improved quality and reduced costs
What are the principles of lean production?
Waste minimization/removal of processes that don’t add value
Aim for no defects by identifying and resolving problems at the source (quality control)
Flexibility, resources are adaptable to the changing needs of the business
Continuous improvement to quality and efficiency in small steps (Kaizen)
Develop and maintain good professional working relationships in the supply chain
What is Kaizen?
Philosophy of making small and continuous improvement to increase efficiency and productivity
How is Kaizen implemented?
Small groups of employees are formed with the purpose of identifying changes and improvements to products, processes, and procedures
Can be motivating for employees as they are helping to improve the system
Why does Kaizen work?
Change is easier to manage in small, continuous improvements
People tend to be resistant to big changes
Focusing on quality often saves costs
Motivating for employees as they can contribute regardless of rank
What are the benefits of Kaizen?
Diversity of ideas from employees to make the best decision
Employees have a greater understanding of problems than managers and directors
Staff involvement improves motivation
What are the limitations of Kaizen?
Meetings and evaluations takes up, can reduce productivity
Staff may demand for higher wages due to increased responsibility
What is just-in-time (JIT) production?
Minimizing costs by reducing and eliminating stock as the absolute minimum levels of stock is held and finished goods are delivered as soon as they are done
The business places smaller, more frequent orders that are delivered just in time for use
What are the benefits of JIT production?
Reduces costs by reducing stock held, money can be used for other operations
Employees are more careful due to limited stock
Free space can be used for production
Successful JIT production means the business has good relationships with suppliers
Improves cash flow
Can reduce break-even point
Can be more flexible in times of changing demand
What are limitations of JIT?
Reduced purchasing EoS
Risk of delay is critical if supply chain breaks down
May be hard to adapt to changes in environment
Not suitable for business with seasonal demand
Huge reliance on external suppliers
Stock must be good quality
Relies on sophisticated technology
What is cradle-to-cradle (C2C) design and manufacturing?
A sustainable production model based on processes that benefit the environment (make products more durable, use recyclable material, choose less polluting production methods)
What is the opposite of cradle-to-cradle?
Cradle-to-grave (single use products that end up in land fills)
What is quality?
Characteristics of a product or service that meets customer needs and expectations
Good quality mans the product fulfill its purpose and meets customer expectations
How can customers percieve quality?
Physical appearance and design
Image and reputation of business
Reliability
Durability
Fit for purpose
Safety features
Customer service
After-sales service
What is quality management?
Controlling business activities to ensure products are fit for a purpose
What are 4 reasons why quality may be a priority for a business?
Increasing consumer awareness (ratings, reviews)
Increased competition
Government legislation makes certain quality standards mandatory
Increased customer income, customers can pay for higher quality
What is quality control?
The traditional approach to quality by inspecting, testing, and sampling the quality of completed work (reactive approach)
What are the advantages of quality control?
Cheaper, need to hire a few QC inspectors than train every employee
Prevents faults from reaching customers if not done in samples, safeguards reputation
Widespread issues and problems across the organization can be identified by inspectors
What are disadvantages of quality control?
Expensive to fix mistakes since products are complete
Root problem isn’t fixed
Lack of accountability for substandard work for individuals
Waste of resources if problem can’t be fixed
What is quality assurance?
Process of assuring customers that everything is done “right first time”, prevents defects by checking the quality throughout production (proactive approach)
What are advantages of quality assurance?
Improves staff morale as QA includes employee participation and ownership of their work
New ideas for improving quality can be prevented from all employees
Breaks down the”them and us” culture as there is less rivalry between producers and testers
Less wastage as products are checked at every stage
What are disadvantages of quality assurance?
Time, energy, and training needed to nurture a total quality culture in the organization
Costs of implementing changes to establish the culture is high
What is a quality circle?
A small group of people taken from every department who meet regularly to discuss potential improvements to product quality
Members volunteer or are picked by senior managers. They also execute and manage solutions to quality issues
What are benefits of using a quality circle to manage quality?
Improved motivation as the employees who are part of the quality circle are engaged
Increase involvement can reduce mistakes, improves quality
Less quality inspectors are needed and less waste will reduce costs
What are limitations of using a quality circle to manage quality?
Takes time away from other tasks
Additional training costs
Only works in democratic leadership or flatter organizational structures
Employees may not enjoy this form of empowerment
What is benchmarking?
Comparison of products, operations, processes, and financial data with others in the industry, especially market leaders (inter-firm benchmarking), or with past performances of the business (historical benchmarking)
What are benefits of benchmarking?
Reduces performance gap with rivals
Simple way to determine quality rather than guessing
Informs company on competitor actions and customer needs
Improves quality by using examples and experiences of others, competitive advantage and reduce costs
Identifies which company has the best process or result and can replicate them
What are limitations of benchmarking?
Time consuming, expensive to collect relevant and up to date benchmarks
Replicating ideas and processes doesn’t create a USP
Processes may not work
Restrains creative and innovative thinking when relying on idas of others
Must select the right benchmark for their goal
What is total quality management (TQM)?
A process that requires the dedication of everyone in the org to commit to achieving quality standards, a culture of focusing on quality that is embedded throughout the whole company
What are the fundamental principles of TQM?
Focus on customers
Commitment by employees
Kaizen
Engagement in the process
Strategic and systematic approach
Data utilization
Communication
What are benefits of TQM?
Improved motivation from empowered employees
Reduces or eliminates waste, lowers production costs
Improved corporate image when reputation is associated with TQM
Competitive advantage due to customer-focused production process (TQM views quality from the perspective of the consumer rather than the producer)
What are limitations of TQM?
Cost of implementation and maintenance is high
Bureaucracy (lots of rules and regs) can hamper the TQM process
Staff training and development is necessary and can be expensive
TQM only works if there is full commitment by all employees
Time lag between implementation and results can take years and may upset shareholders
Only works if everyone is aligned
How can get approved national or international quality awards?
Apply for an inspection and evaluation of their product’s quality and quality assurance process to show certain quality standards are met
Why would a business want to get national/international quality awards?
Can use stamp of approval in promotional material
Some companies only use accredited suppliers
Promote quality awareness within the organization
Motivates workforce, recognizes quality achievements
Attracts high caliber employees
Why would a business not want to get national/international quality awards?
It is a long and expensive process that requires the business to produce comprehensive evidence of quality processes
What are types of quality symbols or logos?
CE Mark: EU award for products that meet health and safety standards
ASQ Award: American Society for Quality, dedicated to the promotion and advancement of quality in the US
BSI Kitemark: British Standards Institutions, responsible for setting quality standards in the UK
NSF: international organization that certifies products and services meet high standards of public health
What is location?
The geographical position of a business, where the business is positioned or sited
What are quantitative reason for choosing a location?
Availability, sustainability, and cost of land
City centers are expensive as demand is high
Inexpensive land is attractive but may not fit firm’s purpose
Availability, suitability, and cost of labor
Affects level of wages paid
Supply and quality of labor varies in different areas
Mass producing businesses may locate in highly populated countries with low labor costs
May want to be closer to customers like retail or service industries
Proximity and access to raw materials
Bulk-reducing industries will locate near sources of raw materials that are heaver and more costly to transport than the final product
Government incentives and limitations
May offer financial incentives to make a business more likely to locate in an enterprise zone (region that are granted special status by a government to encourage development and economic growth)
Feasibility of e-commerce
Businesses that must have physical stores will want to be in an area where customers can purchase items easily
What are qualitative reasons for choosing a location?
Local knowledge
Less risky in familiar areas, market knowledge and experience make it easier to run a business
Management preference for location
Infrastructure availability
Political and economic stability
Government restrictions and regulations that may make it easier or harder to run a business
Ethical issues (eg. business with a lot of noise pollution shouldn’t locate themselves in quiet residential areas)
Comparison shopping (clustering)
Locating near other businesses that are in related or similar markets (eg. Akihabara for anime, Garment District in NYC)
What is outsourcing/subcontracting?
Transferring business functions to an external firm within the same country
Eg. Bank with HQ in Sydney outsources customer services to a call center in Perth
What is outsourcing typically used for?
Recruitment of employees, cleaners, call centers, accounting, ICT maintanance, customer service
What is offshoring?
Transferring business functions to a different country
Eg. Bank in Sydney offshored their banking maintenance to an ICT firm in India
What is offshore outsourcing?
An extension of outsourcing where business functions are transferred to an external firm overseas
What is insourcing?
Use of a firm’s own people and resources to accomplish a certain function or task which would have otherwise been outsourced, bringing outsourced operations back
What is reshoring?
Bringing functions that were offshored back
What are advantages of outsourcing and offshoring?
Improved quality output
Reduced production and labor costs
Allows the business to concentrate on core activities as non-core activities are outsourced
Improved workforce flexibility with the use of part-time employees
What are disadvantages of outsourcing and offshoring?
Sub-standard quality output may occur without close supervision
Quality management can be difficult
Time spent supervising quality of sub-contractors will increase
Redundancies may occur, negatively impact staff motivation
Historically negative associations with unethical practices (eg. child labor and dangerous working locations)
What is supply chain management (SCM)?
The sequence of activities from a production of a good or service to being delivered, the art of managing and controlling logistics so that it is efficient and cost effective to stay profitable
What are key functions of SCM?
Stock control, quality control, supplier networks, transportation
What are costs of holding stock?
Expensive storage costs
Wasteful if not sold
Working capital cycle issues
More insurance and security costs to protect loss and damage of stock
Product can become obsolete
Opportunity cost of space
What are costs of holding not enough stock?
Can’t provide to customers immediately
Loss of reputation or brand image
No EoS from buying in bulk
Can’t respond to sudden increase in demand
No buffer stock in case of delays in supply chain
Special orders can be difficult and expensive to produce
What is just-in-case (JIC) stock control?
Keeping more than enough stock to ensure that the necessary parts and products are available at all times
What are advantages of JIC?
Business can meet sudden changes in demand
Increased flexibility
Can speed up production if necessary
Benefit from EoS
No wait for delivery of stock
What are disadvantages of JIC?
Higher cost of storage
Perishable stock can be wasted
Greater chance of damage or theft
Purchasing large volumes can be detrimental to cash flow
What is stockpiling?
Holding excess stock
What are stock-outs?
Holding insufficient stock
What are drawbacks of stockpiling?
Storage costs
Vulnerable to fires, damage, and theft
Perishables may deteriorate
Stock is illiquid
Stock can become obsolete if demand changes
Changing fashion and tastes of the market
What are drawbacks of stock-outs?
Loss of sales and customers to rivals
Halted production leading to inefficiencies
Damaged corporate image
Higher costs due to fixed costs still needing to be paid
What are the steps in creating a stock control chart?
x-axis is time and y-axis is stock level (units)
Draw maximum stock level line
Draw minimum stock level line, should be above 0
Identify buffer stock (JIC)
Draw re-order level line (amount of stock remaining where you order more so that you have enough time for delivery)
Draw stock quantity line (zig-zag line to show decrease in stock and when new stock arrives)
Label the lead time (how much time is needed for the order to be delivered)
Label re-order quantity (squiggly bracket on the left of the y-axis)
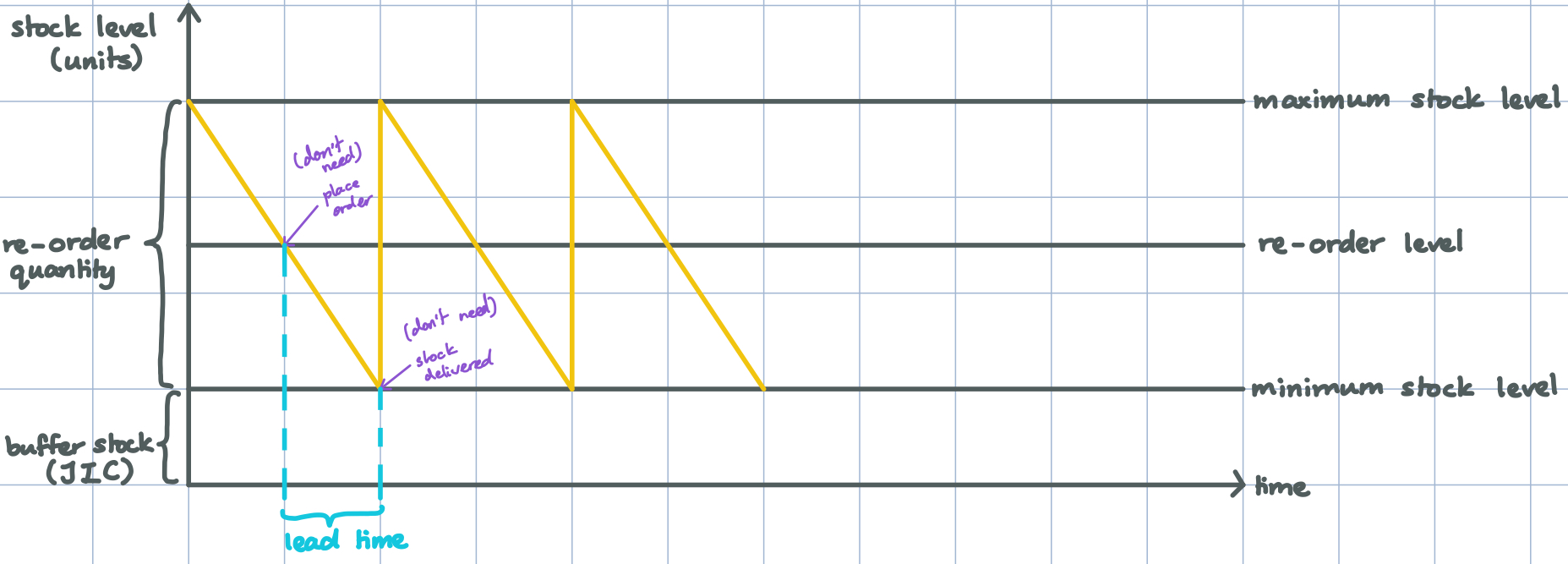
What factors influence the amount of stock held?
Type of product sold
Fast-moving consumer goods (FMCGs) need more stock held due to high stock turnover
Consumer durables are purchased less frequently so less should be held
Consumer perishables must not be overstocked to avoid spoilage
Forecasted level of demand
Peaks season requires more stock
Low season demand will have less sales so less stock held
Longer lead times means larger volumes of stock would need to be reordered
Cost of holding stock
Luxury goods are too expensive and risky to stockpile (high opportunity costs)
Low-cost FMCGs with high stock turn over will have a lower opportunity cost of holding stock
What is capacity utilization rate?
A measure of a firm’s output level as a percentage of its potential output, measures efficiency and the extent to which there are idle resources
What is the equation of capacity utilization rate?
Capacity utilization rate = actual output ÷ productive capacity x 100%
Higher the value the better
What is high capacity utilization important?
Can help lower average costs for businesses with high fixed costs
Businesses with low profit margin must sell a lot to be profitable
High capacity utilization will help reach the BEP faster
If extra costs of providing a particular product to 1 more customer is close to 0, high capacity utilization will mean a much greater profit
What are drawbacks of high capacity utilization?
Minimal time for maintenance repairs
Stress on workforce can result in problems with quality
Not a substitute for growth as growth is limited by the maximum capacity
What is a defect?
When the quality of a particular product is unacceptable, it represents waste and inefficiency
What are 2 ways to calculate defect rate?
Defect rate if all products are tested = defective output ÷ total output x 100%
Defect rate if a sample of all products are tested = defective output ÷ number of units tested x 100%
What is productivity?
How well resources are used in the production process to generate outputs
What is capital productivity?
How well a firm uses its physical resources (machines)
How is capital productivity calculated?
Capital productivity = total output ÷ number of capital hours
What is labor productivity?
Efficiency of workforce