D3.1 Reproduction
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Sexual reproduction
2 parents
Meiosis makes gametes
Genetically different (variation)
Gametes needed (sperm/egg)
Asexual reproduction
1 parent
No meiosis
Genetically identical (clones)
No gametes
Types of asexual reproduction
Binary fission - bacteria
Budding - yeast
Fragmentation - Starfish
Vertebrae clones
Occurs in all female species of whiptale
Offspring are formed as a hybrid of 2 other species
Eggs are formed by mitosis and develop without fertilising so can reproduce without males
Therefore eggs do not need to be fertilised
Difference between male and female sexes
Males produce sperm
large quantities increase likelihood of fertilisation
Sperm cells are very small
Females produce eggs
Fewer are produced
They are larger in size and have a more nutrient dense cytoplasm
The male reproductive system
Testes - responsible for production of sperm and testosterone
Epididymis - site where sperm matures and develops ability to be mobile. Matured sperm is stored here until ejaculation
Vas deferens - long tube connecting tube from testes to the prostate gland
Seminal vesicle - secretes fluid containing fructose (to nourish sperm), mucus to protect sperm and prostaglandin
Prostate gland - secretes an alkaline fluid to neutralise vaginal fluid
Urethra - connects sperm from prostate gland to outside the body via the penis
Female reproductive system
Ovary - where oocytes mature prior to release, also secretes oestrogen and progesterone
Fimbria - A fringe of tissue adjacent to the ovary. Sweeps an oocyte into the oviduct (or fallopian tube)
Fallopian tube - transports oocyte to uterus. typical site of fertilisation
uterus - where a fertilised egg implants and develops
Endometrium - mucus membrane lining of uterus. Thickens in preparation for implantation, otherwise lost in menstruation
Vagina - passage leading to the uterus by which the penis can enter
The 2 cycles in the menstrual cycle
Ovarian cycle - monthly preparation and release of an egg cell from ovary
Uterine cycle - Build up and shedding of the uterus lining (endometrium)
FSH
Released by the anterior pituitary
Stimulates follicle growth in ovaries
Stimulates oestradiol secretion
Oestradiol
Released by ovaries
Thickens uterus lining
Inhibits FSH and LH for most the cycle
Stimulates FSH and LH during pre-ovulation
LH
Released by anterior pituitary
Surge in LH causes ovulation
Thickens corpus luteum
Progesterone
Released by ovaries
Thickens uterus lining'
Inhibits FSH and LH
Positive feedback in the cycle
Oestradiol secretion - causes an increase in FSH receptors. This makes follicles more receptive to FSH so they produce more oestradiol
LH causes development of corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone
Negative feedback
Oestradiol levels (caused by FSH released) become so high that they inhibit FSH secretion
Another example - Inhibition of FSH and LH by rising progesterone levels
Fertilisation
Enzymes from acrosome digest the zona pellucida (jelly coat)
Sperm fuses with the egg membrane - head of sperm enters egg
Tail and midpiece are destroyed
Nuclear membrane of egg and sperm dissolve
2 sets of chromosomes join up and undergo joint mitosis
This forms a diploid nucleus
IVF
Woman is given drugs to suppress natural hormones
FSH is given in high doses - causes superovulation
HCG then given to cause eggs to mature
Eggs collected from ovaries and combined with sperm
Embryo starts to develop on a petri dish - can be screened
Progesterone taken to aid embryo implantation
Up to 3 embryo’s transferred to the uterus
What is gametogenesis
The process by which diploid pre-cursor cells undergo meiotic division to become haploid gametes
In males, sperm is made by spermatogenesis
In females, eggs are made by oogenesis
3 stages of gametogenesis
Multiplication of precursor cells - occurs by mitosis
Growth of developing sex cells
Maturation phase - forms cells which differentiate to haploid gametes
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogonia - the male germ line cells that remain dormant until adolescence
Spermatogonia cells undergo mitosis and grow to form primary spermatocytes
Primary spermatocytes undergo meiosis division to form secondary spermatocytes
These undergo meiosis again to form spermatids
Spermatids differentiate to form sperm
Structure of testis
Contain many seminiferous tubules - make sperm
The sperm is then stored and matures in the epididymis
Seminiferous tubules contain sortoli cells, which nourish developing sperm until they are spermatozoa
Leydig cells make testosterone
Hormonal control of sperm production
Pituitary gland causes FSH to be released
FSH starts sperm production
Pituitary gland also causes LH production
LH causes leydig cells to produce testosterone
Testosterone and FSH maintain sperm production and growth of sortoli cells
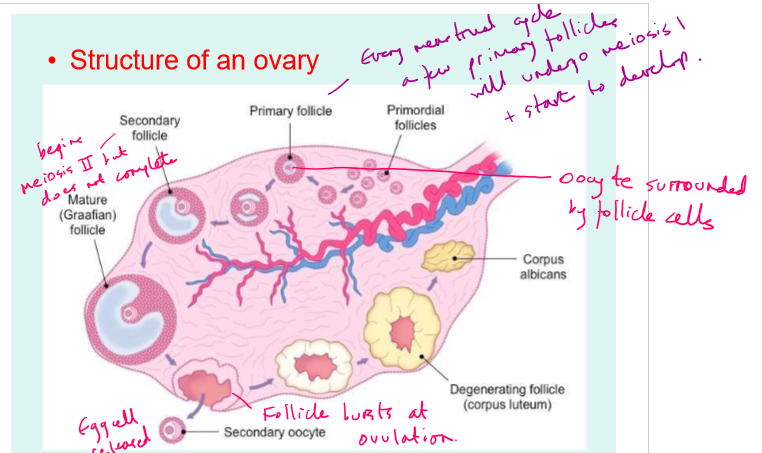
Oogenesis
Oogonia undergo mitosis and growth before birth to form primary oocytes
Oogonia production ceases during pregnancy
The primary oocytes start meiosis, but stop at prophase 1
During puberty, meiosis 1 is completed t form a secondary oocyte
The secondary oocyte is locked in metaphase 2
If fertilization occurs, the secondary oocyte completes meiosis 2 to form an ovum
Meiosis is only completed if the egg is fertilised
Ovary structure
Triggering puberty in males
Gonadotrophin releasing hormone (GnRH) is released from hypothalamus during puberty
This causes anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH
LH causes testosterone release
FSH starts spermatogenesis
Testosterone surge alters gene expression to trigger secondary sexual characteristics
Triggering puberty in females
GnRH released from hypothalamus
Causes anterior pituitary to release FSH and LH
This causes production of oestradiol and progesterone
Oestradiol → secondary female characteristics
Human fertilisation - capacitation
When released, sperm is protected by a cholesterol coat
Uterine chemicals direct the sperm and dissolve this coat
This increase sperms motility
Human fertilisation - acrosome reaction
Sperm binds to a docking protein on the zona pellucida
Enzymes are released from the acrosome
This digests the eggs jelly coat
The sperm nucleus enters the egg cell
Helps to reduce polyspermy
Human fertilisation - cortical reaction
Once the sperm nuclei enters the gg, the egg detects this and is depolarised
This causes cortical granules to rupture and release a chemical
This chemical removes attachment sites and hardens the jelly coat
Prevents polyspermy
Embryogenesis
Day 0 - Zygote - one diploid cell after fertilisation
Day 4 - Morula - Zygote divides to form a group of cells called morula
Day 7 - Blastocyst - contains 3 sections: inner mass that will become foetus, trophoblast layer that surrounds the blastocyst and will become the placenta and a fluid filled cavity called the blastocoele
Trophoblast cells bind and embed the blastocyst into the endometrium
HCG
A hormone that is in high levels in pregnant women
Maintains the corpus luteum
Maintains production of progesterone and thus the uterus lining
This occurs until the placenta is formed, which takes over progesterone production
Pregnancy tests - reactions site
Contains free antibodies attached to dye enzymes
The antibodies will bind to HCG if present
Pregnancy tests - test site
Contains a fixed antibody and dye substrate
The fixed antibody binds to the HCG attached to the free antibody + dye enzyme if pregnant
This causes dye to be released
If not pregnant, fixed antibodies cannot bind to free antibodies so no dye is released
Pregnancy tests - control site
Contain a fixed antibody that traps the free antibody even if no HCG is present
This proves the test has worked
The Placenta
Delivers nutrients to a developing baby, facilitating exchange between mother and foetus
Also secretes hormones to maintain pregnancy
Chorionic villi
A large surface area of foetal blood vessels and chorionic villi extend into intervillous spaces
This enables exchange to take place between foetus and mother
The placenta enables the foetus to be retained int he uterus until later stages of development
Positive feedback when giving birth
Baby pushes against the cervix, causing it to stretch
Nerve impulses are sent to the brain
Stimulate the posterior pituitary to produce oxytocin
Oxytocin causes smooth muscle lining in the uterus to contract
Hormonal control of birth
Oxytocin - stimulates uterus contractions
A drop in progesterone and oestradiol causes childbirth
A high level of oxytocin causes labour
The menopause
Menopause = caused by a drop in oestradiol and progesterone
Symptoms:
Changes in body temp
Increase heart rate
Joint and muscle stiffness
Excess sweat
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
Can help some menopause symptoms
Low levels of oestradiol and progesterone
Evidence from epidemiology studies of reduced risk of heart disease if taking HRT
Clinical studies did not support this - there was no cause and effect relationship
New hypothesis - those on HRT tend to have higher socio economic status
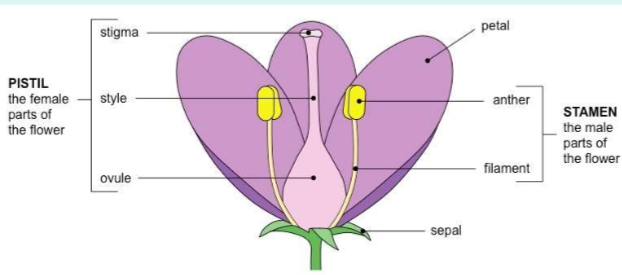
Structure of the flower
Pollination
The transfer of pollen from the anther to stigma
A mutualistic relationship - insects drink nectar from plants, insects transfer pollen to other plants stigma
Stages of plant reproduction
Pollination
Fertilization
Seed dispersal
Self pollination
When the pollen is produced and transferred to the stigma of the same plant
Advantage - preserves good genomes suited to the environment
However, reduces variation, decreases genetic diversity, greater chance of 2 recessive alleles combining that may not be desirable
Cross pollination pros and cons
Pros - increase variation, good if there is environmental changes (natural selection)
Cons - less change of pollen reaching stigma, dependent on insects/wind
Mechanisms to encourage cross pollination
different male and female flowers
Stigma and anther far apart or at different heights
Stigma and stamen mature at different times
Self incompatibility mechanisms
Stigma rejects any pollen with protein markers that show it is from the same flower
prevents in breeding
Seed stucture
Largely contains a cotyledon - contains food reserves
Hard case around the outside called a tesla - protects the seed
Contains a radicle, has an embryo stem and root
Formation of seeds after ferilisation
Zygote grows by repeated mitotic division
Produces cells that form an embryonic plants, embryo root, stem and single/2 cotyledons
Formation of stored food reserves - absorbed into cotyledons
As seed matures, outer layers form protective coat (tesla)
ways of seed dispersal
Wind
Water
Animal
Seed germination conditions
Water uptake so seed is hydrated
Oxygen present for aerobic respiration
suitable temperature for enzymes involved in mobilisation of food reserves
Seed germination process
Water is absorbed by seed
Water activates gibberellic acid
This activates gene expression of hydrolytic enzymes
Starch is broken down into glucose, food reserves are mobilised, used for respiration
Proteins are broken down to amino acids and used for growth
When food reserves are gone, plant uses photosynthesis to survive