potential conflicts between economic objectives
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
prices stability and full employment
policies to promote eco growth and full employment may put upward pressure while policies aimed at reducing inflation may lead to rising unemployment
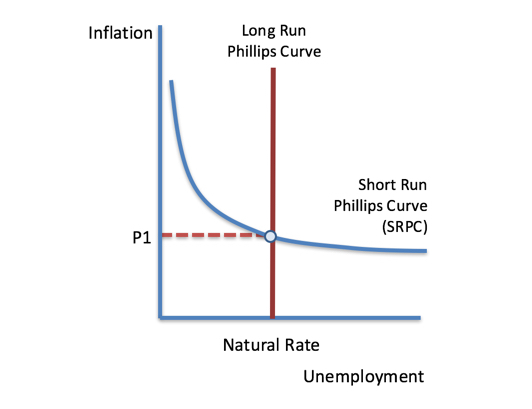
short run phillips curve
The Short Run Phillips Curve illustrates the inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment, suggesting that policies targeting economic growth can result in higher inflation and lower unemployment in the short term.
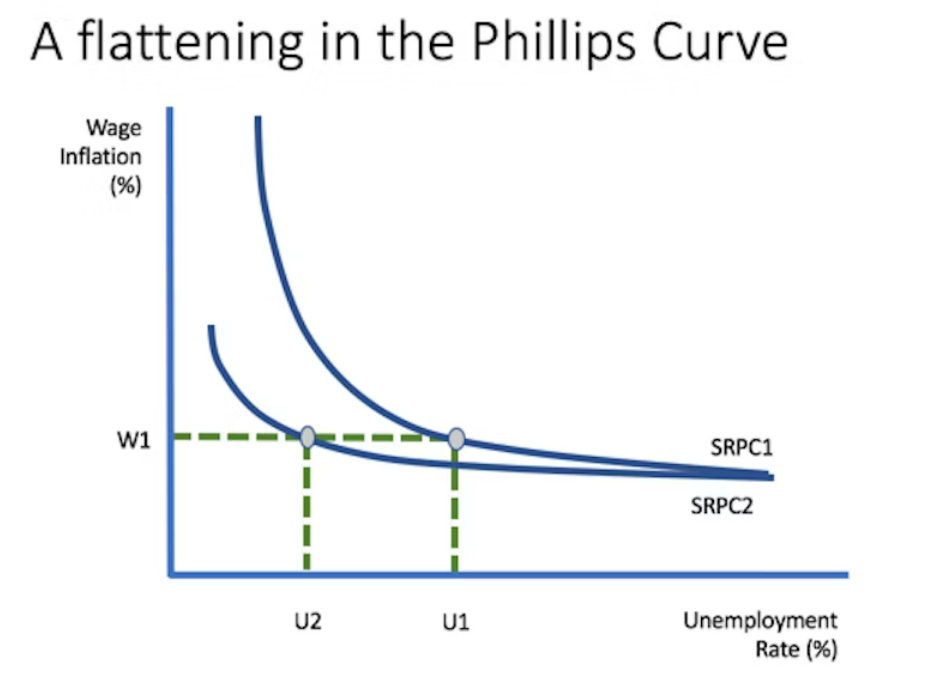
flattened phllips curve
a decrease in unemployment now causes a smaller rise in inflation, inflation targetting has weakened the inverse relationship
long run phillips curve
no apparent relationship between inflation and unemployment in the long term, stagflation that occured in 1970-80s where u/e reached 10% and inflation reached 17%
economic growth and external stability conflict 1
in the short run, an unsustainable rate of economic growth may increase import spending causing a worsening current account which threatens external stability (known as the BOP constraint)
conflict with economic growth and external stability example
seen during the Mining Boom when eco growth rates averaged 4.3% yet the BOGS deteriorated from 1% to -3%
economic growth and external stability conflict 2
increased economic growth also leads to an increase in business profits and greater debits on the net primary balance in the form of equity services
economic growth and full employment
the pursuit of microeconomic reform in order to increase economic growth in the long term may lead to an increase in structural unemployment in the short term, however in the long term, an increase in in eco growth through structural reform leads to the generation of new jobs
economic growth and environmental sustainability
if economic growth is ecologically unsustainable, it may conflict with maintaining environmental quality, firms prioritise profits driving them to pollute the environement and deplete natural resources, ultimately undermining long-term sustainability.
other economic growth and environmental sustainability
environmental policies may come at a cost to the government, reducing economic growth
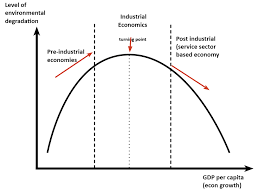
kuznet’s curve - economic growth and environmental sustainability
is a hypothesised relationship between economic development and environmental quality, suggesting that initial stages of growth may lead to environmental degradation, but after a certain income level is reached, sustainability improves.
economic growth and equitable distribution of income
theoretically economic growth improves living standards for everyone, however, in reality, the benefits flow disproportionately to asset owners and high skilled workers
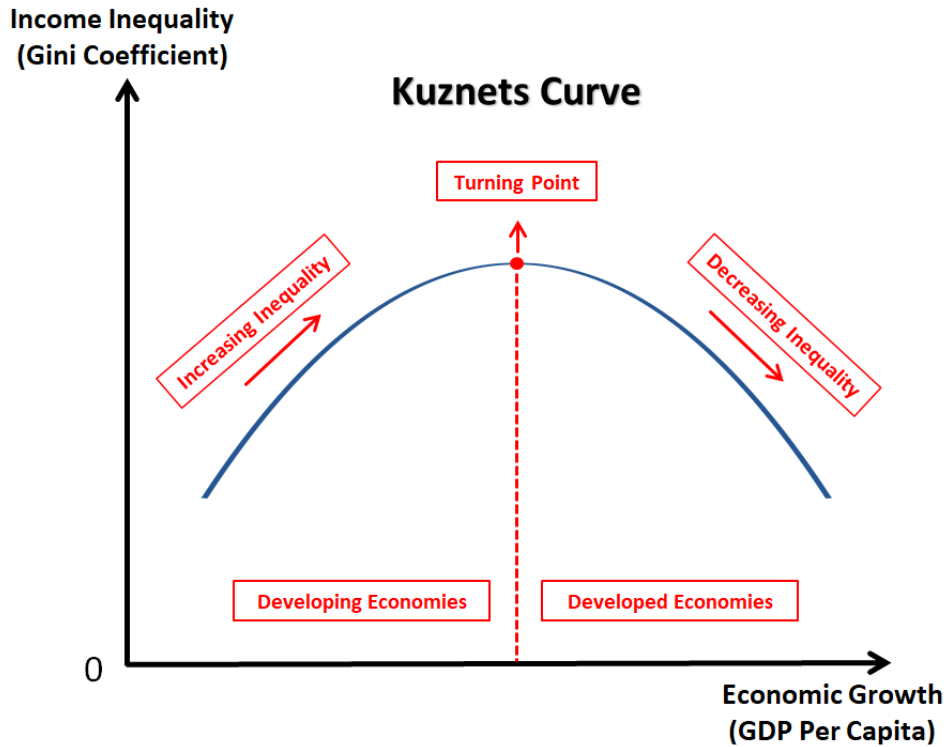
kuznet’s curve - distribution of income
At a low level of GDP per capita, most economies are agrarian-based. As they industrialise, there is a significant shift of labour from rural to urban areas, resulting in a large income gap. Once the turning point is reached, the economy has sufficient resources to implement welfare policies to reduce the income gap