AP Gov- Political Participation
1/220
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Elections
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
221 Terms
Voter turnout
The percent of how many people voted compared to how many that could’ve voted. It serves as a crucial indicator of civic engagement and reflects the overall health of a democracy, influencing public policy and government responsiveness.
Ways that voter turnout can be affected
structural barriers
political efficacy
Demographics
type of election
Structural barriers and how they can affect voter turnout
A policy/law that can prevent people from voting/encourage people to vote.
Ex. voter ID laws
Political efficacy and how they can affect voter turnout
A citizen’s belief on whether their vote matters
ex. a republican thinking their vote will not matter cuz they are voting in a majority democrat state
how do demographics affect voter turnout
Certain groups of people are more likely to vote
Ex. Old people are more likely to vote
how do types of elections affect voter turnout
Some types of elections are more likely to have more people voting
ex. People more likely to vote in national elections
Factors that affect a voter’s choices
party identification/ideological orientation
candidate characteristics
political issues
demographic factors
First step in electing a president
Candidates have to first earn their party’s nomination through primary elections
Primary elections
A primary election is a preliminary election in which voters select candidates to run for office in the general election. This process plays a crucial role in determining which candidates will represent their political party on the ballot, influencing party dynamics and voter engagement leading up to the general elections.
primaries are handled differently for each state
Open primaries
held by some states, any registered voter can vote in either party’s primary, but not both
Closed primaries
only people who are registered with the party can vote in those primaries
Caucuses
meetings of members of a political party or faction to discuss and decide on policies, strategies, and candidate selections. They vote publicly.
2nd step in electing a president
Whoever wins the primary are presented by their party at the national convention
National convention
Party presents their candidate and their chosen vice president. Which opens to the beginning of the general election. This event is significant as it showcases the party's ideology, goals, and direction, reflecting the diverse interests within the party while also energizing supporters and establishing a unified front for the upcoming election.
Incumbent
A sitting president that is seeking for re-election. They typically enjoy advantages such as name recognition, established networks, and access to campaign resources, which can significantly enhance their chances of winning elections. Their existing position allows them to leverage their experience and accomplishments to appeal to voters, making them a critical factor in electoral politics.
incumbency advantage
incumbent has already won a election, so they know how it’s done
people already know how they will act as president
they already have a army of volunteers and fundraisers ready to help with another campaign
although these advantages are great, they may not guarantee another victory
3rd step in electing a president
general elections, very complex. Candidates from each party go against each other. Popular votes and electoral collage
Electoral college
a unique system established in the U.S. Constitution for electing the President and Vice President, consisting of 538 electors who represent the states. This mechanism was created to balance the influence of populous states with less populated ones and reflects the federal structure of government, where states play a critical role in national elections.
Faithless electors
a member of the Electoral College who does not cast their vote for the candidate to whom they are pledged. This phenomenon can occur in the presidential election process, where electors are selected to represent their state's popular vote but may choose to deviate from that decision. Faithless electors challenge the traditional expectations of the Electoral College system and raise questions about the accountability and authority of electors in the democratic process.
Minimum number of electoral votes a candidate needs to win inorder to be president
270 electoral votes
Super delegates
party leaders and elected officials in the Democratic Party who are given the freedom to support any candidate for the presidential nomination, regardless of the primary election results. Unlike regular delegates, who are pledged to vote for a specific candidate based on the outcome of primary elections, superdelegates can exercise their own judgment when choosing a nominee. This system allows party elites to have a significant influence on the nomination process, especially in closely contested races.
Most aspects of elections are under the control of the _____
states and state laws
Mechanics of primaries
States hold secret ballots to get votes for each politician. State by state contest, the competition is run by parties. Mechanics can be different for each state and party.
Mechanics of caucuses
-Members of a party show up in schools, religious buildings, community centers, and people's homes all across the state
-You need a certain number of people caucusing for you to be awarded a delegate
-As more candidates get eliminated for having too little people, their supporters have to choose to caucus for a new candidate based on the points they've heard from other supporters
-Caucuses are very participatory, and they tend to only draw people who are more committed to a candidate since they're more complex and time-consuming, unlike simply voting in a primary
lower voter turnout
Federal elections campaign act (FECA)
created a new federal commission called the federal election commission in 1972
FEC created to oversee and regulate the money being spent in political campaigns (How much money a person could give to candidate, and how much candidates should spend)
Buckley V Valeo
Court ruled that limits on individual and corporate contributions to campaigns were constitutional. But limits on how much a campaign can spend were unconstitutional. around 1976
Hard money
Contributions given directly to a candidate. Controlled by FEC
Soft money
Money donated to a party or interest group who can buy advertising on the candidate’s behalf. Not controlled by FEC
Bipartisan campaign reform act (BCRA)
2002, increased the amount of hard money that can be donated to a candidate, and regulate the amount of soft money that can be donated as well
“Stand by your Ad” provision

Citizens United V FEC
landmark Supreme Court case decided in 2010 that ruled that corporations and unions can spend unlimited amounts of money on political campaigns, under the premise that such spending is a form of protected speech under the First Amendment. This decision significantly altered the landscape of campaign finance in the United States, allowing for the rise of super PACs and leading to concerns over the influence of money in politics.
Citizens United v. FEC said corporations and unions have the same political speech rights as individuals and can spend unlimited money on independent political ads.
Problem of money in campaigning (politics)
Those with more money would have more influence, which can make it easier for them to direct political conversations
Political action committee (PACs)
Organizations that raise money for the sake of influencing the population to vote for their preferred candidate
Types of PACs
Connected PAC
non-connected PAC
Super PAC
Connected PACs
Formed by corporations or other entities like labor unions. Only collect funds from members of their organization, the money can be donated directly to candidates in limited quantities. Can raise unlimited amounts of money if the individual limits are followed
Non-Connected PACs
formed independently of an organization, usually around a specific public interest. Donations to non-connected PACs are limited by law, and can accept donations from the public → donate directly to candidates
Super PAC
Can be formed by anyone, accept unlimited donations but cannot be directly coordinated with the candidate. Very controversial, critiques say they have the potential to limited democracy and only give voice to the wealthy
Story of Buckley V Valeo
After the Watergate scandal, Congress passed the Federal Election Campaign Act (FECA) to clean up politics. It set limits on how much people could donate to candidates and how much candidates could spend on their own campaigns.
A group of politicians, including Senator James Buckley, sued — arguing that these limits violated their First Amendment right to free speech. They said spending money to spread political ideas is a form of speech.
Story of Citizens United V FEC
A nonprofit group called Citizens United made a movie criticizing Hillary Clinton before the 2008 presidential election. The (FEC) said the movie counted as an “electioneering communication” — basically, a campaign ad — and that it violated campaign finance laws banning corporations and unions from spending their money on political ads close to an election.
Citizens United sued, arguing that this ban violated their First Amendment right to free speech.
Campaign contributions
financial donations made to political candidates or parties to support their electoral campaigns. These contributions can come from individuals, organizations, or PACs.
plays a crucial role in the political process by enabling candidates to fund their campaigns, communicate with voters, and promote their messages. Understanding the impact of campaign contributions is essential for analyzing how public opinion can be shaped and influenced during elections.
Independent expenditures
political campaign communications (like ads, mailers, or social media posts) that advocate for or against a candidate but are not coordinated with that candidate or their campaign.
24th amendment
ratified in 1964, prohibits the use of poll taxes in federal elections. This amendment was a crucial milestone in the fight against voter suppression, particularly aimed at eliminating financial barriers that were used to disenfranchise African American voters and poor individuals, reflecting the broader goals of the civil rights movement during the 1960s.
15th amendment
constitutional provision ratified in 1870 that prohibits the federal and state governments from denying a citizen's right to vote based on 'race, color, or previous condition of servitude.' This amendment is significant as it aimed to secure voting rights for African American men following the Civil War and represents a crucial step towards ensuring broader voting rights and equality in the electoral process.
12th amendment
ratified in 1804, established the procedure for electing the President and Vice President. It aimed to prevent issues arising from the original electoral process, where the candidate with the most electoral votes became President and the runner-up became Vice President, which could lead to political conflicts and inefficiencies in governance.
The electoral college gives _________ slightly more power
smaller states, because
Every state automatically gets 2 electoral votes for its senators, no matter how small it is.
Since those 2 votes are a bigger share of a small state’s total, each voter in a small state represents more “electoral weight” than a voter in a big state.
open primaries usually have a ___ turn out rate than closed primaries and caucuses
higher
Caucuses usually have a ____ turnout rate than other primary methods
lower
How democrats usually award delegates in primaries
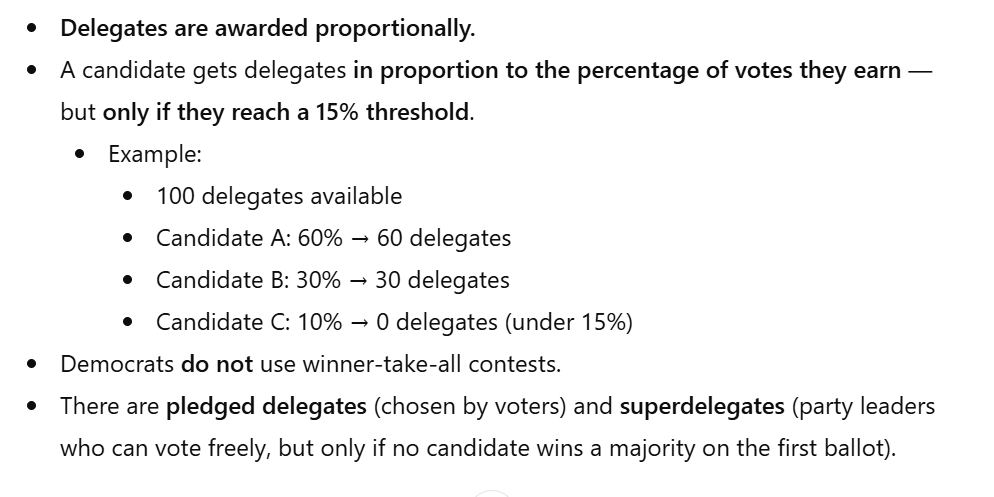
How republicans usually award delegates in primaries

The Media is a form of a ______
Linkage institution
Linkage institutions
Linkage institutions are the communication pathways that connect people to their government. They include political parties, elections, interest groups, and—perhaps most visibly—the media.
Agenda Setting
The media has the power to highlight certain issues and bring them to the attention of the public.
Among the types of linkage institutions, the _______ plays a _____ role because it helps shape how people understand the political world.
Media; unique and powerful
How has the rise of digital media transformed the media’s role as a linkage institution?
It has increased the number of voices influencing the political agenda, allowing independent creators to shape public discourse.
One of the media’s most important traditional roles is_____
investigative journalism
investigative journalism
specialized form of journalism that involves in-depth research and analysis to uncover hidden facts, corruption, or misconduct. This type of reporting often requires significant time and resources, as journalists dig into complex issues, gather evidence, and interview various sources to produce stories that inform the public and hold those in power accountable. Investigative reporting plays a critical role in fostering transparency and democracy by exposing wrongdoing and providing citizens with the information necessary to make informed decisions.
ex. Muckrakers
examples of investigative journalism
reporting on the Watergate scandal and the publication of the Pentagon Papers.
Today, investigative reporting still exists, but it often _____ for attention with faster, more informal commentary on______
compete; social platforms
Social media has made political information more accessible and immediate. However, it also means that not all media content is equally _____
reliable
Media coverage of elections has also _____
evolved
Horse race journalism
the media's tendency to focus on the competitive aspects of political campaigns, emphasizing the 'who's winning, who's losing' narrative rather than substantive policy discussions. This type of coverage often treats elections like a sporting event, with candidates as the 'horses' racing towards the finish line.
very big esp in modern politics
Why might horse race journalism have a negative impact on democratic participation?
It emphasizes poll standings and campaign strategy rather than issues and policies, which can leave voters less informed about their choices.
social media ______ how people engage in politics, making the media a more______ space.
reshapes; interactive and participatory
While the media serves as a______between citizens and government, it doesn’t always___________.
vital connection;promote understanding or unity
Importance of media in politics
The media plays an influential role in how citizens learn about political issues and events. Media coverage also affects the formation of policy agendas by raising awareness of certain topics, which can increase public demand for government action.
"media as a gatekeeper"
The media’s role in setting the political agenda by drawing public and government attention to certain issues.
Why do social media platforms have such a powerful influence over public understanding of politics, even though they don’t produce content themselves?
They control what content users see through algorithms and platform design choices.
ideologically oriented programming
As Americans have become more politically divided, many media outlets have adapted, creating content that appeals to specific political beliefs.
Confirmation bias
the tendency to search for, interpret, favor, and recall information in a way that confirms one’s preexisting beliefs or hypotheses. This bias can significantly influence how individuals consume media, as they may gravitate towards sources that reinforce their views while dismissing those that challenge them.
What can confirmation bias do in politics
it is harder to have open and well-informed debates in a democracy.
Many modern news outlets are_______
consumer driven
credibility crisis
When people don’t know which sources to trust, and start to doubt the media as a whole
News media
the conventional forms of mass communication that have been used to disseminate news and information to the public, primarily through print (newspapers and magazines), broadcast (television and radio), and outdoor advertising. This type of media has historically played a crucial role in shaping public opinion, informing citizens about current events, and providing a platform for political discourse.
Social media
digital platforms that facilitate the creation, sharing, and exchange of content among users, enabling them to connect and communicate in real time. It plays a crucial role in shaping public discourse, influencing political behavior, and providing new avenues for political communication and engagement.
Mass media
Various means of communication that reach large audiences simultaneously, including television, radio, newspapers, and the internet. It plays a crucial role in shaping public perception and opinions, acting as a primary source of information and influencing the political landscape and socialization processes.
ex. the penny press
Broadcast media
the transmission of television programs and news through airwaves, cable, or satellite to a wide audience. This medium has played a crucial role in shaping public opinion, providing information, and influencing cultural norms by delivering news, entertainment, and educational content to viewers around the world.
Media consolidation
News corporations buy other companies and eliminate competition between outlets. This makes less diverse sources of information and less groups of competing interests. More partisan media, media shows only one thing
New york times V US
(1971) established the principle of prior restraint (when the government tries to stop the media (like newspapers, TV, or websites) from publishing something before it comes out.) in relation to freedom of the press. The ruling reinforced the First Amendment's protection of press freedom and underscored the importance of a free and open discourse in a democratic society.
How did New york times V US happen
The case arose when the government attempted to prevent the New York Times from publishing the Pentagon Papers, a classified document detailing U.S. political and military involvement in Vietnam.
Partisan bias
the practice of media outlets providing news and information that reflects a specific political bias or agenda, favoring one political party or ideology over another. This type of coverage can shape public perception, influence political debates, and affect the checks on presidential power by framing narratives that align with particular political interests.
Narrow casting
the practice of targeting specific audiences with tailored media content, as opposed to broadcasting, which aims at a broader audience. This approach allows for the delivery of specialized information, opinions, and entertainment that caters to the interests and demographics of particular groups, enhancing engagement and influence. The rise of narrowcasting is significantly influenced by advancements in technology and changes in media consumption habits.
ex. Fox News tends to attract a conservative audience, while MSNBC appeals more to liberal viewers.
Wire service
an organization that gathers and reports on news and then sells the stories to other outlets
Some political scientists worry that ideologically driven news _____ and leads people to support____
increases polarization; more partisan policies
How can media be politically polarizing?
allows people to select information and political news, shutting down other viewpoints
The radio act
established the Federal radio commission and required broadcasters to obtain a license to broadcast on specific frequencies (1927)
Communications act
expanded fed gov's role in regulating the nation's broadcast media, creating the federal communications commission (1934)
FCC (federal communications commission )
independent U.S. government agency responsible for regulating interstate and international communications by radio, television, wire, satellite, and cable.
The FCC plays a crucial role in the establishment of rules and regulations that govern communication industries, ensuring that all citizens have access to reliable communication services while balancing the interests of the public and private sectors.
what concerns does the regulation of media raise?
How to balance between the constitutional right of freedom fo the press and the gov's need to protect liberty and order?
deregulation of media led to_____as news firms tried to ____in the face of declining sales and advertising revenue
increasing consolidation ; maximize their profits
political candidates who are also celebrities can obtain ______ based on their celebrity status
disproportionate attention
ex. Trump
Telecommunications act
significantly raised the % of a national audience a corporation was allowed to reach. Also raised limits on the number of media outlets one company could hold. (1966)
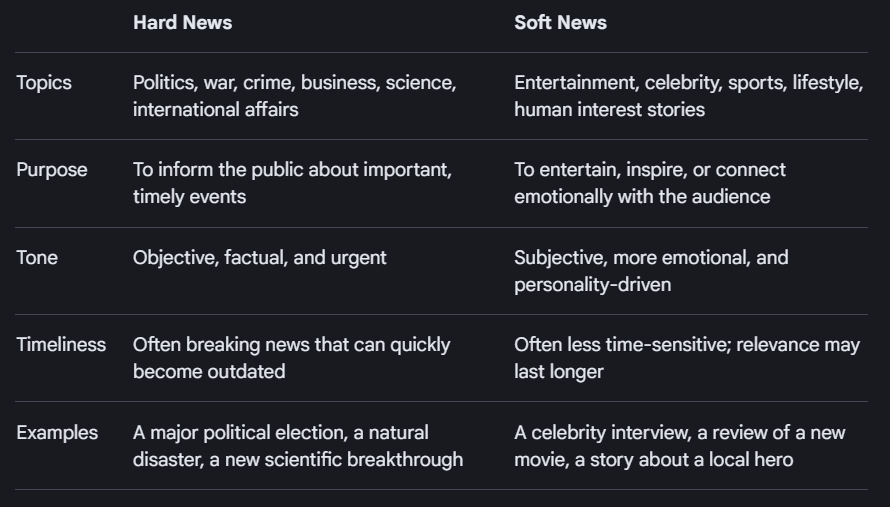
Hard news Vs Soft news
Interest groups
Voluntary associations of people who come together with the goal of getting the policies that they favor enacted
Social movements
Diffuse groups that educate the public and put pressure on policymakers in an effort to bring about societal change
besides how factions are formed around a number of issues, what is prolly the greatest concern that Madison had about factions
Although people might form factions around a number of issues, inequality of wealth posed the greatest danger
Theory of participatory democracy
citizens impact policymaking through their involvement with civil society
civil society
groups outside the gov that advocate for policy
pluralist theory
political power is distributed among many competing groups, no single group can grow too powerful
Fed 10
Madison argues that the constitution reduces the negative consequences of faction by creating a large, representative republic
The theories of interest group formation
Participatory democracy
Pluralist democracy
Elitist democracy