KINE 1020 Exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/294
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 10:34 PM on 4/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
295 Terms
1
New cards
Formula for Obesity
BMI = weight (kg) / height (m2)
2
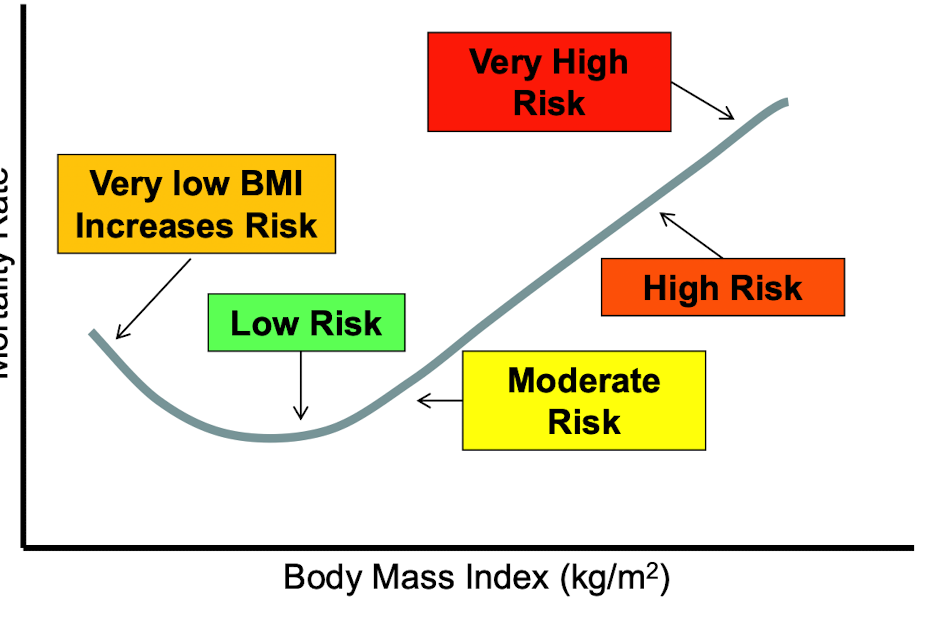
New cards
Relationship between Mortality Risk and BMI
3
New cards
Underweight (BMI)
4
New cards
Normal Weight (BMI)
18\.5-24.9 - least risk
\
\
5
New cards
Overweight (BMI)
25\.5-29.9 - increased risk
6
New cards
Obesity
>30
7
New cards
Class I
30\.0 - 34.9 - High risk
8
New cards
Class II
35-39.9 - Very high risk
9
New cards
Class III
>40 - Extremely high risk
10
New cards
What is body comp broken down into?
fat and fat free mass
* fat free is everything that is not fat
* bone, organs, muscles, etc.
* fat free is everything that is not fat
* bone, organs, muscles, etc.
11
New cards
densitometry
* Archimedes’ Principle
* Density = mass/volume
* Density = mass/volume
12
New cards
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
\
\
13
New cards
CT
Computed Tomography
14
New cards
Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA)
* how easy radiation passed through the body
15
New cards
Bioelectric Impedance Analysis
* how well body can conduct electricity
* more water = better
* affected by hydration
* provides regions of body fat
* more water = better
* affected by hydration
* provides regions of body fat
16
New cards
Ultrasound
Subscious fat
17
New cards
Skinfold measures
* measures of skin and fat thickness at various sites
* can predict body fat
* can predict body fat
18
New cards
Common sites for Anthropometric Measures
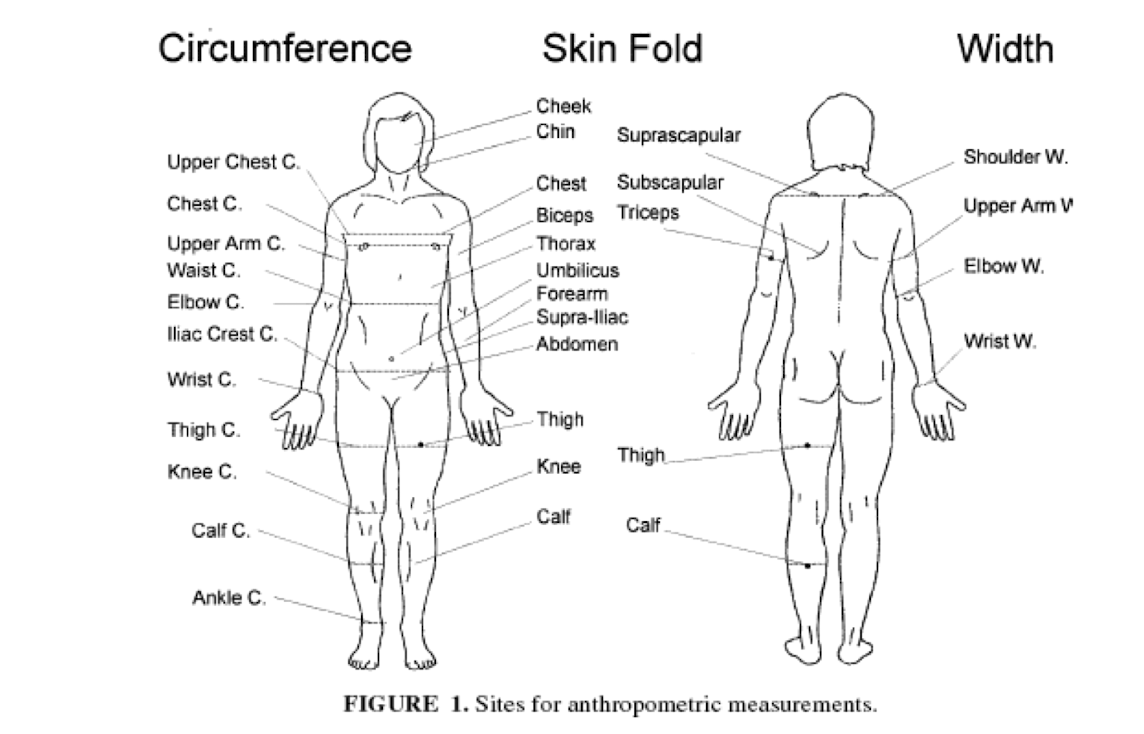
19
New cards
BF prediction - Yuhasz Male and Females

20
New cards
BF prediction - Durnin
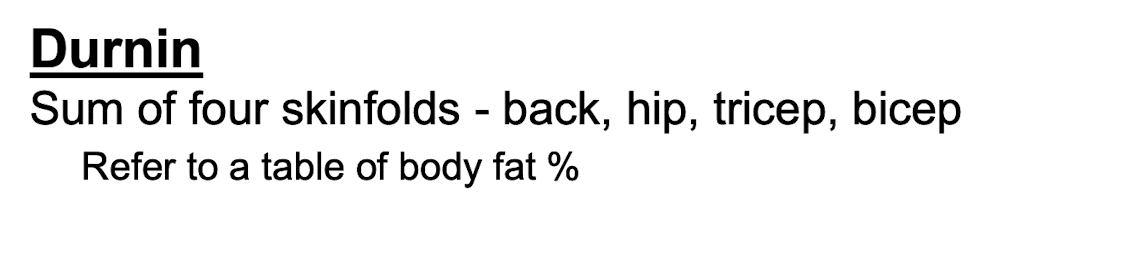
21
New cards
Female vs Male BF
females have higher body fat than males
22
New cards
Characteristics of Yuhaz formula
* 6 sites
* lower body site
* M/F diff in formula
* Age in formula
* lower body site
* M/F diff in formula
* Age in formula
23
New cards
Durnin formula characteristics
* 4 sites
* no lower body site
* M/F diff in formula
* Age diff in formula
* no lower body site
* M/F diff in formula
* Age diff in formula
24
New cards
Others BF formula
* up to 12 sites
* lower body
* M/F diff
* Age diff
* lower body
* M/F diff
* Age diff
25
New cards
Body Comp pros and cons
Pro - ese of use, protability, time
Cons - cost, radiation, testing requirement
Cons - cost, radiation, testing requirement
26
New cards
A body mass index:
from 18.5 to 24.9 has the lowest health risk
27
New cards
What body composition test uses magnetic properties of the body?
MRI
28
New cards
What are factors that influence skinfold fat equations?
* age
* Sex
* Physical activity
* A and B above
* All of the above
* age
* Sex
* Physical activity
* A and B above
* All of the above
A and B
29
New cards
Obesity Trends
Obesity has been in an upward trend throughout the years
30
New cards
Parental Identification of Overweight
* 60% of mothers underestimate the weight of their child
* 80% do not see that their child is overweight
* 80% do not see that their child is overweight
31
New cards
Obesity in kids trend
going down throughout the years
32
New cards
Cons of too much fat
1. Serious health risks - hypertension, diabetes, cancer, etc
2. limited physical due to lack of movement
3. stress on bones and joints
1. hip and knee replacements but some people don’t qualify because they are overweight
4. psychologically damaging - stereotypes of overweight people
33
New cards
medical complications of increased weight
* COVID 19 & H1N1
* Gall bladder disease
* Gynecologic abnormalities
* Gall bladder disease
* Gynecologic abnormalities
34
New cards
Different types of fat
* visceral and subcutaneous
* not all fat is equal
* not all fat is equal
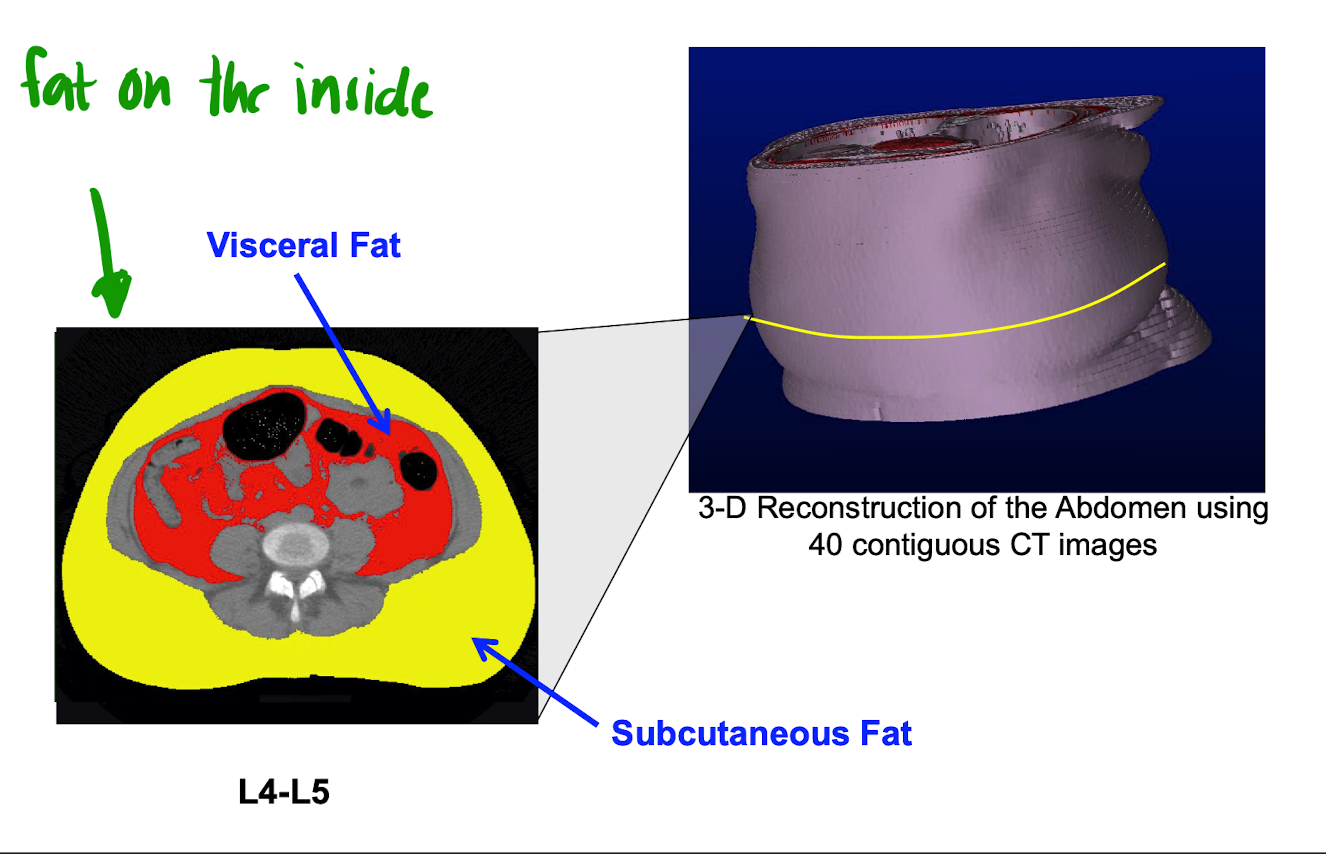
35
New cards
what is visceral fat
\
\
small contribution to total obesity but large contribution to obesity related disease
36
New cards
Absence of the effect of Lipo on insulin action and risk factors for coronary heart disease
* lipo = not helpful and does not target visceral fat
* 10-12 weeks post op results
* fat loss = 10 kg
* 13 cm waist circumference
* 44% abdominal sat
* 10-12 weeks post op results
* fat loss = 10 kg
* 13 cm waist circumference
* 44% abdominal sat
37
New cards
Waist Circumference - Gynoid
* not associated with health risk facts
38
New cards
Waist circumference - Android
* enhances risk for high BP, CVD, diabetes and abnormal blood lipids
39
New cards
BMI and WC
Increased BMI + Increased WC = Increased health risk
40
New cards
Components of Energy Expenditure
* Resting metabolic rate (RMR, 60-75%)
* # of calories needed on a daily to stay alive
* Thermic effect of food (TEF, 10%)
* eating, chewing, digesting
* Non exercise activity thermogenesis (NEAT, 15-50%)
* leisure, shopping, talking
* Exercise related activity thermogenesis
* negligible or zero in developed countries
* # of calories needed on a daily to stay alive
* Thermic effect of food (TEF, 10%)
* eating, chewing, digesting
* Non exercise activity thermogenesis (NEAT, 15-50%)
* leisure, shopping, talking
* Exercise related activity thermogenesis
* negligible or zero in developed countries
41
New cards
BW and shape
40-70% genetics
42
New cards
genetics of obesity
>140 genetic regions that influence obesity traits
43
New cards
Higher risk of obesity
* platics
* pests
* textiles
* air pollution
* immigration
* etc.
* pests
* textiles
* air pollution
* immigration
* etc.
44
New cards
Obesity Triggers
usually pregnancy or there is no specific trigger
45
New cards
Prenatal weight gain
mothers to be that had a bmi of 27 and over are 4 times more likely to have an overweight child at age three
* dietary traits to children
* diet iin the womb
* dietary traits to children
* diet iin the womb
46
New cards
Canada’s pregnancy weight gain guidelines
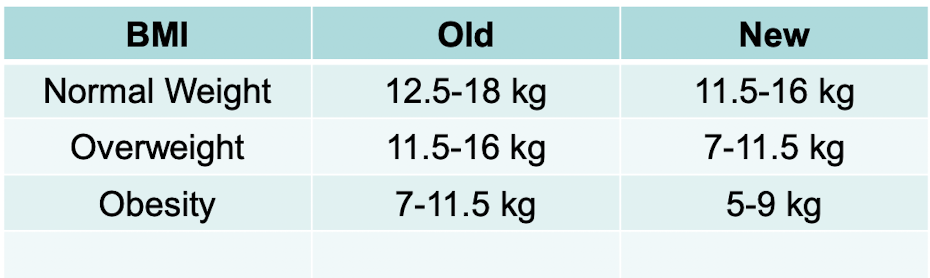
47
New cards
Advantages of Fat
* energy storage
* insulation
* sports: swimming
* appearance - limited amount is desirable
* improved survival rates for chronic and infectious disease
* insulation
* sports: swimming
* appearance - limited amount is desirable
* improved survival rates for chronic and infectious disease
48
New cards
Body Energy stores of a lean 70-kg man
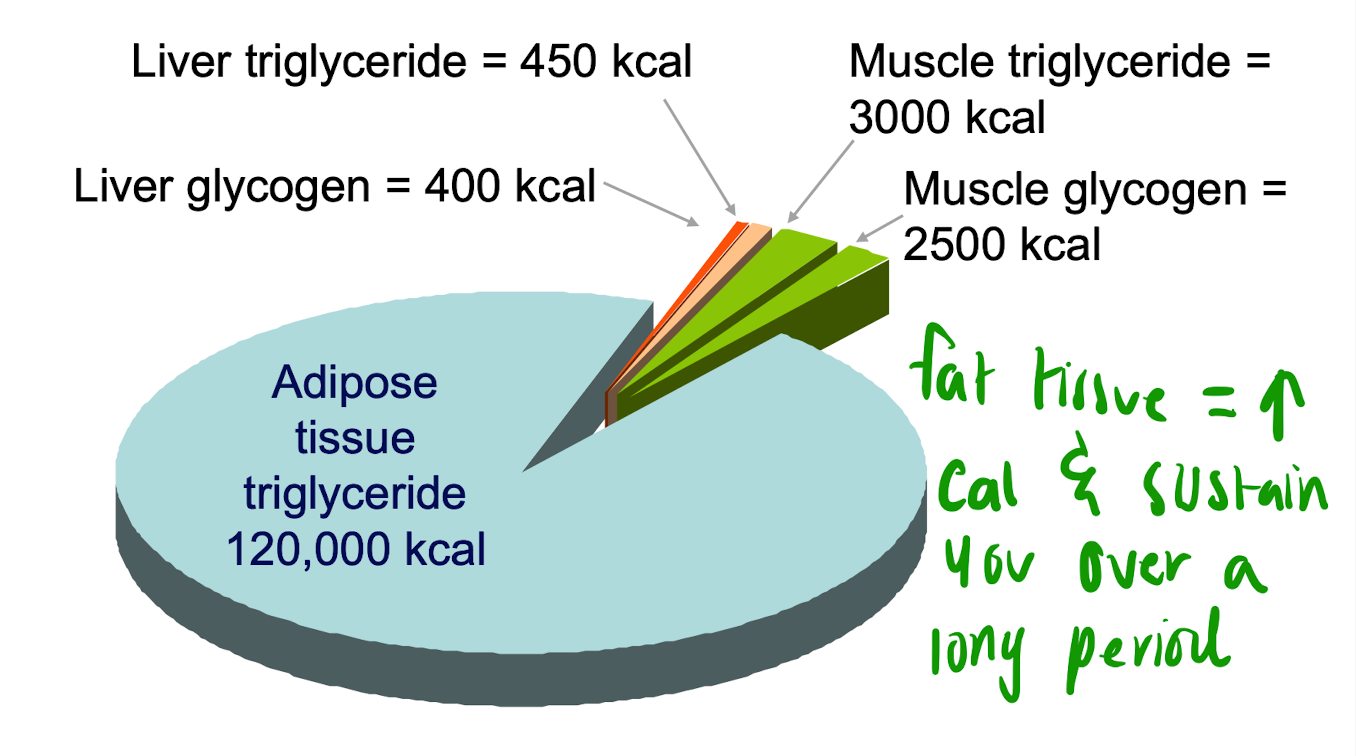
49
New cards
Obesity Paradox
* obesity survived longer because of metabolic reserves
50
New cards
Average weight gain per year
1\.8 - 2 ibs per year
51
New cards
What signals are reponsible for satiety messengers to brain
* Hunger - Grehlin
* Full - Leptin
* Full - Leptin
52
New cards
Prader-Willi
Excess Ghrelin
* increased hunger and food consumption
* obesity
* does not shut off
* no meds
* increased hunger and food consumption
* obesity
* does not shut off
* no meds
53
New cards
Satiety Hormone - Leptin
* regulating appetite (decrease) and increase metabolism
54
New cards
Deficiency of leptin in humans
* rare
* normal weight at birth
* constant hunger with chronic extra eating (hyperphagia)
* hoarding food, eating in secret
* normal weight at birth
* constant hunger with chronic extra eating (hyperphagia)
* hoarding food, eating in secret
55
New cards
Leptin Resistance
* people with obesity have higher leptin level
* signal not receive
* increased food intake
* signal not receive
* increased food intake
56
New cards
Gut satiety hormones
* released in intestines in response to food and goes to the brain to decrease urges to eat
* high fibre diets stimulate greater gut hormone production = bulk travels through intestines
* people with obesity secrete less appetite reducing gut hormones
* given injections to be broken down in stomach
* high fibre diets stimulate greater gut hormone production = bulk travels through intestines
* people with obesity secrete less appetite reducing gut hormones
* given injections to be broken down in stomach
57
New cards
Volumetric - Energy Density
* choose lower calorie foods that fill you up
58
New cards
Fibre Pills
* Throught: decrease index of food and increase satiety
* Results: no significant effects on BW
* reductions for total and LDL cholesterol
* diarrhea and abdominal bloating
* Results: no significant effects on BW
* reductions for total and LDL cholesterol
* diarrhea and abdominal bloating
59
New cards
social factors that influence food intake
* portion size
* taste
* ads
* variety
* plate size
* availability
* taste
* ads
* variety
* plate size
* availability
60
New cards
Fat burning zone
* does not exist
61
New cards
weight loss success rate
* 9 out of 10 adults who have tried to lose weight have attempted to do so on their own through diet and exercise
* \~50% of those who have ever used diet or exercise methods to lose weight report having done so at least 5 different times throughout their lives
* 20% of Americans with obesity have made 20 or more attempts to lose weight through diet or exercise methods
* 95% of people will not maintain reduced weight
* \~50% of those who have ever used diet or exercise methods to lose weight report having done so at least 5 different times throughout their lives
* 20% of Americans with obesity have made 20 or more attempts to lose weight through diet or exercise methods
* 95% of people will not maintain reduced weight
62
New cards
Gilosis
* scar tissue in hypothalamus
* causes chronic obesity
* set point theory
* causes chronic obesity
* set point theory
63
New cards
are a little bit less
stores more fat overtime
64
New cards
weight loss with increases in skeletal muscle work efficiency
becomes more effective
65
New cards
PA and choice
due to genetics some people enjoy physical activity
66
New cards
Decreases in energy balance with weight loss
1. immediate, thermic effect on metabolism (digestion, transport, storage)
2. Changes in body com
1. weight loss, bm, skeletal muscle mass is loss and RMR goes down
3. Decreases RMR
1. excessive cal consumption RMR increase by 10-15%
2. servere cal restriction causes RMR to decrease (over 2-3 weeks = 20-30%)
3. decrease is more than expected given body comp changes
4. Increase energy efficiency
67
New cards
Successful Weight loss maintenance
cal consumption - 1400 kcal
exercise expenditure - 400 kcal
non-exercise activity- 1000 kcal
exercise expenditure - 400 kcal
non-exercise activity- 1000 kcal
68
New cards
physiological consequences of repeated cycles of weight loss and weight gain
Increased:
* preference for dietary fat
* efficiency of fuel utilization
* ratio of total fat and lean mass
* redistribution of fat to abdominal area
* CHD and cancer risk factors
Decrease
* metabolic rate
* preference for dietary fat
* efficiency of fuel utilization
* ratio of total fat and lean mass
* redistribution of fat to abdominal area
* CHD and cancer risk factors
Decrease
* metabolic rate
69
New cards
Prescription weight loss drugs
* Xenical
* Saxenda
* Saxenda
70
New cards
Prescription weight loss drugs - Bupropion/naltrexone combo
* Bupropion - depression and smoking
* Naltrexone - opioid/alcohol dependence
* appetite suppressant
* 8.1% WL
* $250/month
* Naltrexone - opioid/alcohol dependence
* appetite suppressant
* 8.1% WL
* $250/month
71
New cards
Semaglutide (wegovy)
* injectible for GLP-1 hormone
* Approved in Canada and USA
* 15% WL
* $1627 per month
* Approved in Canada and USA
* 15% WL
* $1627 per month
72
New cards
How much wright do most people lose with these meds
* Xenical (orislate)
* 3%
* Contrave (naltrexone and bupropion)
* 8.1
* Saxenda (liraglutide)
* 8
* Wegovy (semaglutide)
* 15
* 3%
* Contrave (naltrexone and bupropion)
* 8.1
* Saxenda (liraglutide)
* 8
* Wegovy (semaglutide)
* 15
73
New cards
Gastic surgery
* target food intake (size of stomach) or absorption (length of intestine)
* covered by OHIP
* covered by OHIP
74
New cards
surgical weight loss and mortality risk
* 89% reduction in risk of death over 5 years
* 77% of weight management patients are not interested in bariatric surgery
* 77% of weight management patients are not interested in bariatric surgery
75
New cards
weight times for weight loss surgery
* can range from a couple months up to 15 years
76
New cards
Hormonal changes with bariatic surgery
* unless you change physiology, nothing will change
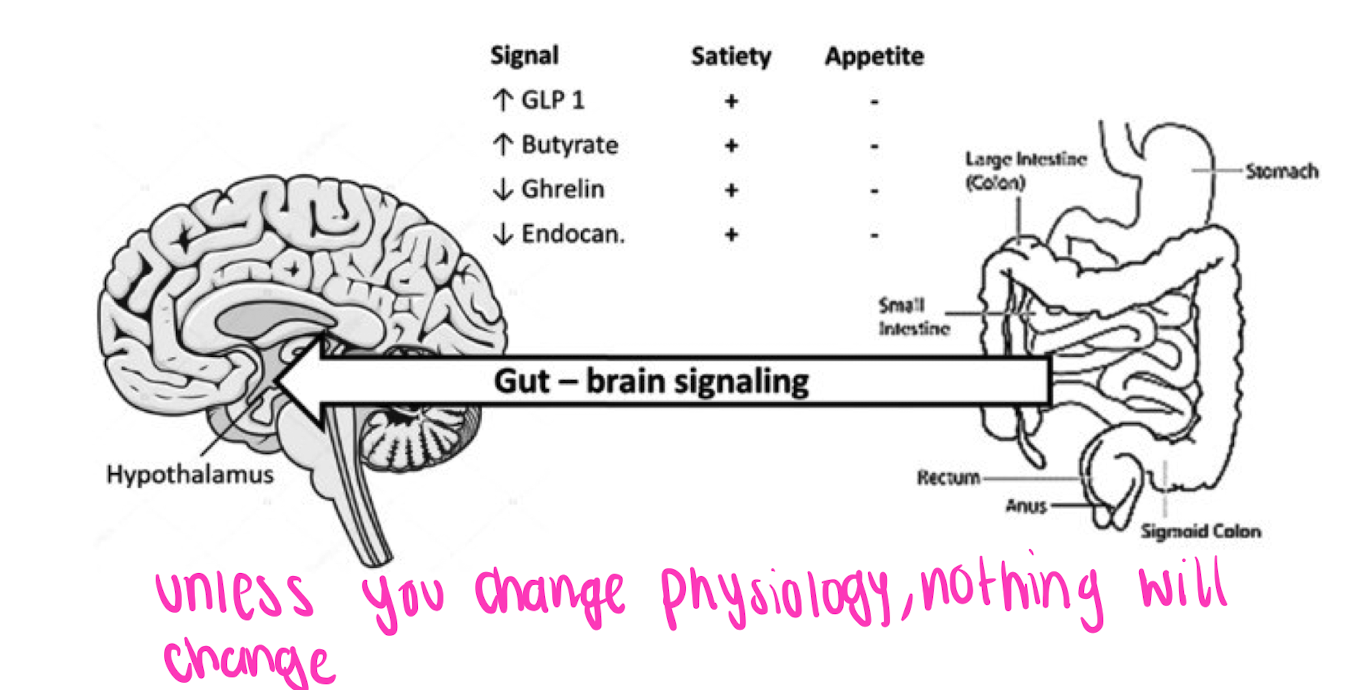
77
New cards
top reasons for not being interested in bariatric surgery
* feat of other complication
* don’t need surgery to lose weight
* fear of surgery
* pain
* cost
* don’t need surgery to lose weight
* fear of surgery
* pain
* cost
78
New cards
health care professionals do not listen
* late diagnosis
* told not to eat as much
* told not to eat as much
79
New cards
weight loss products
* a scam
80
New cards
Anorexia Nervosa
* body image distortion
* extremely low body weight
* fear of gaining weight
* see themselves as larger
* more common in women
* excessive eercise
* misuse of laxatives, dirt aids
* self-induced vomiting
* extremely low body weight
* fear of gaining weight
* see themselves as larger
* more common in women
* excessive eercise
* misuse of laxatives, dirt aids
* self-induced vomiting
81
New cards
Anorexia Nervosa - signs and symptoms
* insomnia
* weight loss
* abdominal pain
* anaemia
* disguise body
* denies hungerv
* weight loss
* abdominal pain
* anaemia
* disguise body
* denies hungerv
82
New cards
Anorexia Nervosa consequences
* heart problems - consumes body mass
* anaemia
* kidney stones
* lack of periods
* higher risk for miscarriage
* high death rate
* anaemia
* kidney stones
* lack of periods
* higher risk for miscarriage
* high death rate
83
New cards
Bulimia Nervosa
* periods of food restirctions then binge eating cycle
* lack of control of what they are eating - feeling
* normal or overweight
* 1-3% of pop
* 90% cases are female
* lack of control of what they are eating - feeling
* normal or overweight
* 1-3% of pop
* 90% cases are female
84
New cards
Bulimia Nervosa signs and symptoms
* weight change
* tooth pain
* swelling in cheeks and jaw
* dehydration
* tooth pain
* swelling in cheeks and jaw
* dehydration
85
New cards
Differences between anorexia and bulimia
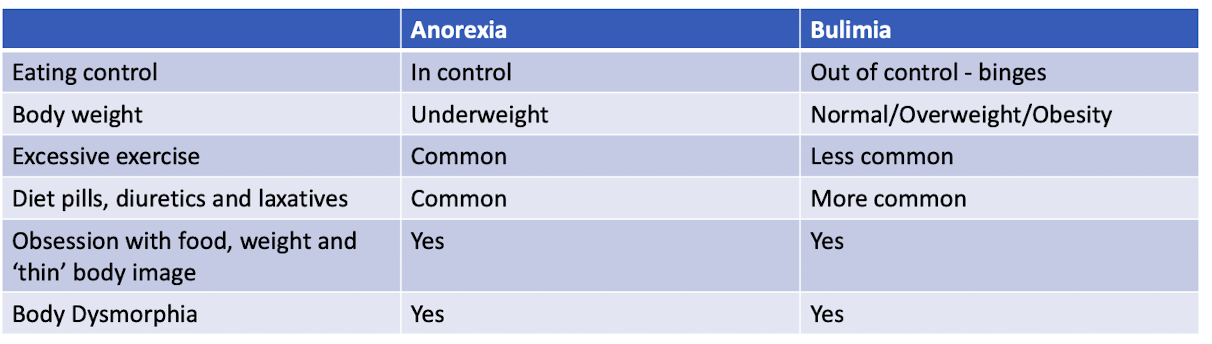
86
New cards
eating disorders - deadliest mental health condition
* depression shortens life by 10 years
* Anorexia
* age of death = 36 years
* 16 years from disorder to death
* BN
* age at death = 42 years
* 19 years from disorder to death
* Anorexia
* age of death = 36 years
* 16 years from disorder to death
* BN
* age at death = 42 years
* 19 years from disorder to death
87
New cards
Risk factors of eating disorders
* genetics
* body dissatisfaction
* low self-esteem
* personality traits
* influence of social media
* body dissatisfaction
* low self-esteem
* personality traits
* influence of social media
88
New cards
eating disorders in athletes
* 0-19% in males
* 6-45% in females
* 6-45% in females
89
New cards
Chisty Henrich
* told to lose weight because she was too fat
* age 16, 147cm, 93ibs, 19.8 kg/m^2
* died at age 22 - 13.0 kg/m^2
* age 16, 147cm, 93ibs, 19.8 kg/m^2
* died at age 22 - 13.0 kg/m^2
90
New cards
treatment for eating disorder
* accept the have a problem
* nutritional therapy
* psychotherapy
* support groups
* medicine
* nutritional therapy
* psychotherapy
* support groups
* medicine
91
New cards
recovery eating disorder
* most patients will replase
92
New cards
death - eating disorders
* males have higher mortality rate
93
New cards
ideal balanced blood sugar
* 5 mmol before meal
* 5-7 idea balanced blood sugar
* 9 mmol should go down after the meal
* 5-7 idea balanced blood sugar
* 9 mmol should go down after the meal
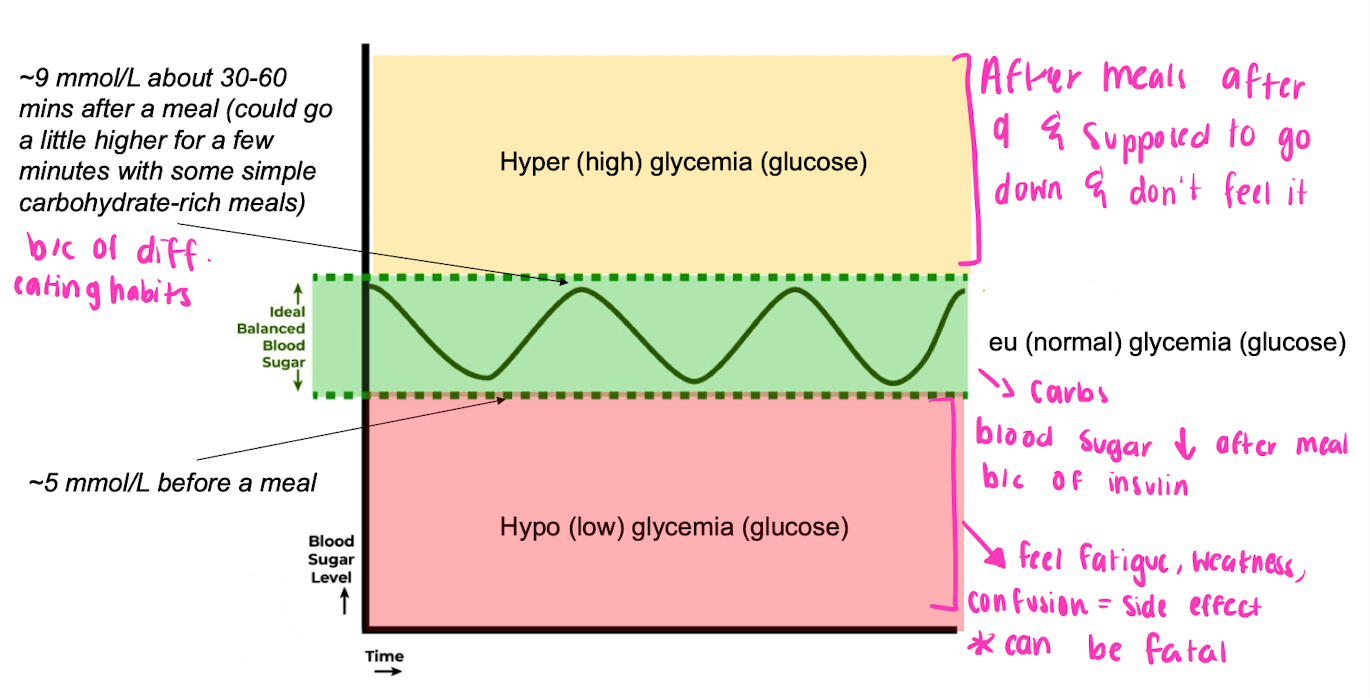
94
New cards
amount of glucose in the bloodstream
* 5 mmol before meal
* 4 grams before meal
* 7.3 grams after meal
* 4 grams before meal
* 7.3 grams after meal
95
New cards
raises blood surgar
* carbs
* illness and stress hormones
* growth and growth hormones
* hormone glucagon -→ anti insulin hormone
* illness and stress hormones
* growth and growth hormones
* hormone glucagon -→ anti insulin hormone
96
New cards
lower blood sugar
* hormone insulin
* mild to moderate PA
* mild to moderate PA
97
New cards
Insulin and Glucagon
* comes from pancreas
* glucose homeostasis is controlled by liver
* picks up chemical signals of insulin and glucagon from pancreas via portal veins
\
* glucose homeostasis is controlled by liver
* picks up chemical signals of insulin and glucagon from pancreas via portal veins
\
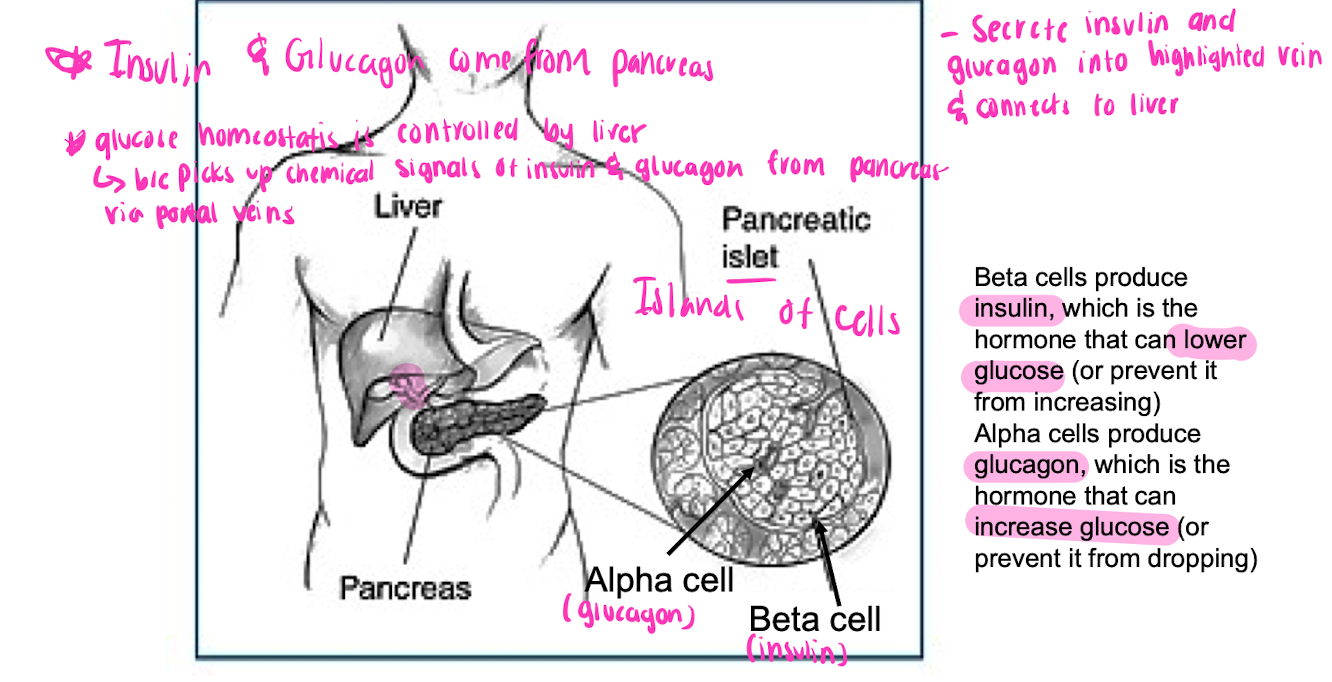
98
New cards
alpha cells
glucagon
99
New cards
beta cells
insulin
100
New cards
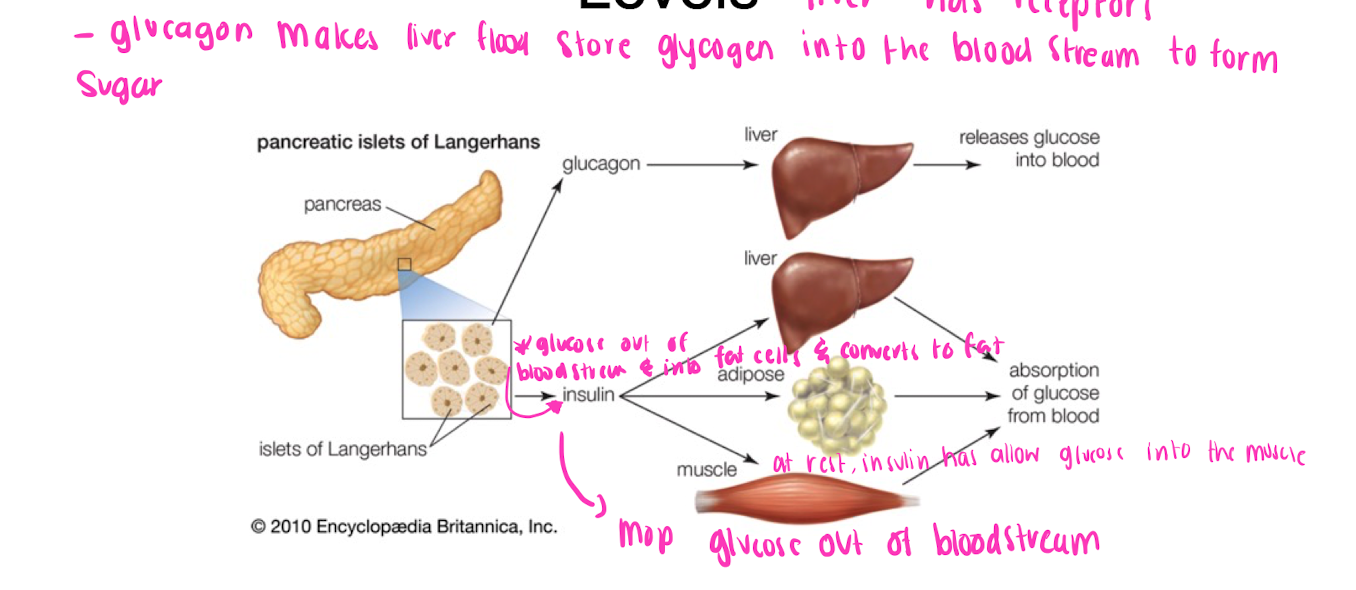
Insulin and Glucagon regulates glucose levels
* liver has receptors
* glucagon makes liver flood stored glycogen into blood stream from sugar
* glucagon makes liver flood stored glycogen into blood stream from sugar