part 2 spcon module 3
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
WHAT CONDITION IS THIS?
● Chronic multi-system disease
● Wide range of articular and extraarticular findings
● Unknown cause
● Inflammatory process
● Immune response
● Genetic
● Characteristic feature: persistent inflammatory synovitis (usually peripheral, symmetric involvement)
RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
In RA, what is the s ite of primary effect?
SYNOVIAL LINING OF JOINTS
In RA,
○ Gene product of Class II MHC (major histocompatibility complex)
○ One of the major genetic factors in etiology
○ Seen in 70% of patients
● HLA-DR4
In RA, this is the consequence of massive infiltration of immune cells (T lymphocytes) into the synovial fluid
Joint inflammation –
In RA, this is the predominant infiltrating cell
– T lymphocyte
What is the hallmark of RA?
SYNOVIAL INFLAMMATION
○ Cartilage destruction
○ Bone erosions
○ Changes in joint integrity
In RA, what associating deformity is this?
radial deviation at the wrist with ulnar deviation of digits often with palmar subluxation of proximal phalanges
Z deformity -
In RA, what associating deformity is this?
hyperextension of PIP jt with flexion of DIP
Swan-neck deformity –
In RA, what associating deformity is this?
flexion of PIP and extension of DIP jt
Boutonniere deformity
In RA, enumerate the extraarticular manifestations
rheumatoid nodules
rheumatoid vasculitis
pleuropulmonary manifestations
In RA, what extraarticular manifestation is being defined?
■ 20-30%
■ Found on periarticular structures, extensor surfaces, or other areas subjected to mechanical pressure
■ Common location: olecranon bursa, proximal ulna, achilles tendon, occiput
■ Found in patients with (+) RF
■ Central zone of necrotic material including collagen fibrils, cellular debris, noncollagenous filaments
■ Middle zone of palisading macrophage
■ Outer zone of granulation tissue
RHEUMATOID NODULES
In RA, what extraarticular manifestation is being defined?
■ Seen with high titer of RF, severe RA
■ Most aggressive form
■ Polyneuropathy, cutaneous ulceration and dermal necrosis
■ Digital gangrene
■ Visceral infarction
■ Myocardial infarction
RHEUMATOID VASCULITIS
In RA, what extraarticular manifestation is being defined?
■ Pleural disease
■ Interstitial fibrosis, pneumonitis
■ Pleural effusion (fluid with low levels of glucose)
○ Neurologic manifestations is rare
Pleuropulmonary manifestations
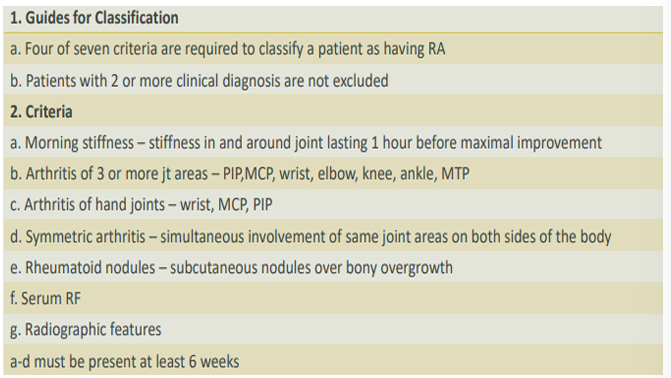
Recite the 2019 Classification Criteria for RA

In RA,
Leiden prediction rule:
<4 points
100% of not developing RA
In RA,
Leiden prediction rule:
≤6 points
92% chance of not developing RA
In RA,
Leiden prediction rule:
≥8 points:
84% chance of RA development
In RA,
Leiden prediction rule:
≥11 points:
100% chance of RA development
In RA, this medication controls the symptoms and inflammatory processes. It is also rapid and effective in mitigating symptom
aspirin and nsaids
In RA, this medication suppresses signs and symptoms of inflammation. it also retards the development and progression of bone erosions
low dose oral glucocorticoids
In RA, this medication decreases elevated levels of acute phase reactants. it also modifies destructive phase of the disease
Disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDS)
In RA, this medication is transient relied when systemic medica approach fails
intraarticular glucocorticoids