Anna Horgan Lectures
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Define chromatography
physical method of seperation in which the components are distributed between TWO phases
what’s the mobile phase
a liquid which percolates through the
what’s the stationary phase?
column packing material
what’s the Rf value
retardation factor
distance travlled by component/distance travelled by solvent
describe the solvent set up in HPLC
degassing
dust removal
several reservoirs
gradient/isocratic
descrive gradient elution
change in solvent composition
may be contanstly changing or changing in a stepwise manner
why is degassing needed
avoids band spreading
avoids the detector detecting gas bubbesw
why is dust removal needed
protects the column from clogging
protects the pump
detection interference
band spreading
what are the solvents used for reversed phase lc
water
methanol
polar stuff
describe the pump in hplc
constant rate
resistant to corrosion
describe the pressures in pumps
normally 400-600bar
6000psi-9000psi
in ultra high pressure systems = 1300bar
describe two types of injectors
autosampler (multiple samples)
manual
describe the physical needs of an injector
must be resistaant to high pressures of the liquid
describe the column
small particles inside cause backpressure
can be made of stainless steel/heavy wall glasss/peek tubing
how is the column protected
guard column remives particular matter
when can heavy wall glass be used
pressure below 600psi
whata is column packing made up of
alumina/silica/divinylbenzene synthetic/ ion echange resin
what does a detector do
quantative
qualatative analysis
whats the most used detetctor
uv/ visable light detector
what is the most senstive lc detetctor
fluorescence detectorwh
what’s the issue w/ fluorescence detectors
Fluorescent derivatives must be synthesized
what detector is used for lipids/proteins/polymers
refractive index
why is refractive index used for polymers
non uv absorbing
what’s the partitioning co-eff
the partitioning relationship a solute has between teh stat and mobile phase expressed as a ratio
K= Cs/Cm (the solid Cork floats on the liquid)
why do solutes have a different eluting time
each solute has a different solubility due to the stationary phase
whats dead time
time between injection point and dead point
what’s dead volume
vol of mobile phase passed through the column between injection point and dead point
what’s the retention time
time between injection point and peak MAXIMUM
what’s corrected retention volume
vol. of mobile phase passed through the column between dead point and peak maximum
(as opposed to the injection point)4444
whats the capacity factor
k’= (tr-t0) /t0
what’s t0
dead time
what happens to k’ if a compoment spends longer in the column
increased capacity factor
what’s the selectivity (a)
relative retention of two compouds
a= k’2/k’1
the larger k’ will be on the top (gay fanfic laws)
in gc what is the mobile phase
a carrier gas
what is the stat phase in GC
the liquid film that coats the column filling (packed tubular)
or
the liquid film that coats the column walls (open/ capillary columns)
what happens at the GC inlet
injection point
the sample solution is vapourised amd taken to the column by the carrier gas
what are the sepating forces in GC
temperature (boiling points)
stationary phase interactions
how does seperation based on temp happen in GC
the capillary column is in an oven
oven temp increases (gradually! also called ramped)
lower b.p. components elute quicker
what happens at the base line of a chromatogram
that is the part of the chromatogram where only the mobile phase is emerging from the column (analytes stuck in the column due to interactions)
how to calculate flow rate
dead volume= flow rate * dead time
retention volume= flow rate* retention time
what do sharp, symmetrical peaks represent
a good seperation
what’s column efficiency
a measure of how good the stat phase is able to seperate components
what are theoretical plates
a measure of how efficient the column is
what’s plate height
HEPT (height eq. to one plate) = lenght of column/ no. of theoretical plates
(how wide the plate is, smaller the plate the more specific seperation)
give the equation for Neff
5.54( tr/ FWHM)²
give the van deemter eq and describe what it does
height eq of one plate= A + B / u+ Cu
describes the factors that impact peak broadeining (what things will make the column less efficient)
what’s eddy diffusion
the column is packed therefore each molecule will take a different path towards the end of the column
different path will take different amounts of time
what’s longitudal diffusion
the conc. of the analyte is the highest in the centre of the column
diffusion to the edges takes time
how to decrease longitudal diff
increase the velocity of the mobile phase
→ decreasing the time spent in column decreases the longitudal diffusion
what’s resistance to mass transfer
the analyte with a strong affinity to the stationary face will stay behind while the analyte that is in the mobile phase will zoom past it
this broadens the band especially badly when the velocity of the mobile phase is high
what causes resistance to mass transfer
the analyte takes time to equilibrate between mobile and stat phase
draw a van deemter plot
the optimum velocity is the x variable of the min point
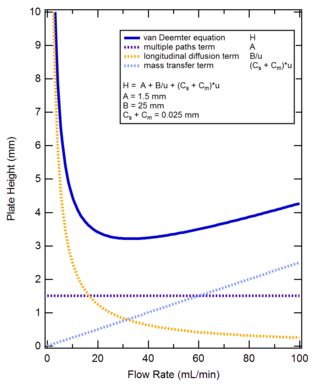
which term in the equasion is independent of velocity
eddy diffusion
random paths will occur at different speeds
describe what happens to longitudal diffusion as velocity increases
decreases (flaccid graph line thing )
describe what happens to resistance to mass transfer as velocity increases
increases
gets worse as the mobile phase zooooms past the analyte that is has a high affinity to the stat. phase
which type of gc column has a lower hept
open tubular as no eddy diffusion happens
list all the factors that impact gc seperations
volatility of a compound
polarity of compouns
polarity of column
column temperature
flow rate of the gas
the leght of the column
A has a b.p. of 55C
B has a b.p. of 200C
Which travels faster
A, the compounds with a lower b.p. will travel faster
A is polar
B is non polar
Which travels faster
the polar will travel more slowly , especially when the column is polar as well (like attarcts like)
column a is set to 50 C
column b is set to 500 C
which tarvels faster
The column with a higher temperature will have the components move faster
What gases are used as carrier gases
Argon
Helium
Nitrogen
Hydrogen
What affects the choice of the carrier gas
Sample type
sample matrix
detector used
safety
purity
price
availibity
What does a carrier gas must be
inert
pure
compatible with detector used
in GC, where is the inlet attached
column head
how is the analyte injected
microsyringe through a rubber septum
whta happens to the analyte when injected
flash vapourisation
how is the injector temperature chosen
needs to volatilize the sample
cant decompose it
50C above b.p, of the less volatile compound
what are the types of open tubular columns
wcot
plot scot
whats plot
capilarry column with a porous layer of stationary phase
whats scot
support coated ot column
whats wcot
wall coated column ( walls coated w/ liquid stat phase)
what are the types of packed gc columnns
gls—> more common
gsc
what are packed gc columns made of
outside—> stainless steel/ glass(when it needs to be an inert column)
inside—> inert support is tighly packed
the support is coated with a thin film of liquid (3%-10% of stat phase)
what is the support made up of in the packed column
diatomaceus earth
what are the disadv. of packed columns
limited resolution (N<80.000)
long lenghts are impractical PRESSURE DROP
eddy diffusion
What are OT capillary columns made up of
out—> fused silica (inert)
in—> open tube, low resistance to flow, can get loooong lenghts (L>100m)
how is the stationary phase arranged in OT
thin , uniform liquid film that coats the wall fo the tubing
which type of column in gc is
more common
higher res
open
open tubular
What is the res of the OT
open tubing has 100,000= N
what type of column shpuld be used to analyse polar compounds
polar columns
what is the stat. phase in a polar column
CArbowax 20M (composed of polyethylene glycol stat phase)
what column should be used for non poalr compounds
non polar stat phase
—> CP Sil 5CB
dimethylpolysiloxane
why can’t the temperature be too high
high temp= fast elution time= less interaction= less seperation= broad peaks
what does the temp @ injector influence
the vapourisation of the sample
what does the temp @ column influence
the retetention time
the resolution
how is the detector selected
"based on sample matrix= everything that is present in the typical sample except for the analytes of interest
the sensitivity
what are the perfect gc detector properties
stability
reproducibility
linear response to many orders of magnitude
similar response to all analytes
temp. range from room temp to 400 C
non destructive
easy to use
short response independent of flow rate
how can we classify detectors
bulk property / solute property
destructive/ non destructive
conc. sensitive/ mass sensitive
specific / non-specific
describe bulk property / solute property
bulk= measures bulk phys property of eluent
solute= chem/phys properties unique to solute
give example of bulk property
dielectric constant
refractive index
give solute propertie example
heat of combustion
fluroresnence
describe specific detectors
higher sensitivities
only respond to selected substances
eg nitrogen phosphorous detector detects N or P
what are the advantages of GC
fast
small samples only needed (microliters/grams)high resolution
reliable
cheap
non-destructive
sensitive (ppm/ppb )
complex samples in trace amounts
organic materials caqn be anylised
disadv. of gc
olatile only (temp. max =380, analyte must have a bp below 500)
cant use w/ thermally labile samples
samples need prep sometumes
samples cant react w/ column
samples must be soluble
requires spectroscopy (MS)
samples must be stable below 400C
most common detectors are unselective→ less sensitiv
what causes the rate of the elution
the equilibrium constants of the components in the stationary and mobile phase
K= Cs/Cm (cork floats on water)
give the formula for selectivity
a= k1/k2 the larger on top
what causes peak broadening
dispersion of analyte in dead volume, connection between injector and column and between the column and detector (need to min dead volume)
column broadening - van demteer
broadening doesnt occur onky in the column!
what temp. is used for LC and why is that an advantage
room temp.
heat sensitive compounds can be analysed
what is seperation optimasation and where can it be done
LC- seperation is based on the interaction of solutes with the mobile/stat phase so you can tweak either
GC seperation is set on bioling point- cant change that
what can you seperate using
gc
lc
volatile compounds and gaseous mixtures
soluble compounds (aa, proteins, drugs, polymers, nucleic acids)