ART 111 Exam 2-SIUE-Prof. Danny Holder
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
media or mediums
the materials artists use to make art
drawing
any implement running over a surface leaving a race of gesture - making marks.
dry media
metal point/graphite/charcoal/pastels/chalk
wet media
ink applied with a pen or a brush
sketch, plans or studies, finished works
3 categories of drawing
sketch
a visual notation of an idea
study or plan
a preparatory drawing done with the intent to execute in a different media (sometimes the final version)
finished work
a drawing that makes a complete finished statement (in the view of the artist)
stylus
metal made into a rod with a point on one end
metal point or silver point
done on a prepared ground. cannot erase
graphite
soft creates dark marks while hard creates light marks. can be smudged to create tone
charcoal
carbon - can also be smudged
tooth
the texture and softness of the paper which allows the media being used to stick or stay on the surface
fixative
a chemical spray that fixes or attaches the medium to the paper
pastels
colored chalk
reed pen or quill pen
different types of pens
it cannot be erased
disadvantage of ink
using a "wash" or ink diluted with water
how can tone be created with ink
encaustic, fresco, tempera, oil, acrylic, watercolor, gouache
7 categories of types of painting
encaustic
pigment mixed with a wax
fresco
pigment mixed with limewater and plaster
tempera
pigment mixed with egg yolk
oil
pigment mixed with linseed oil
acrylic
pigment mixed with plastic
watercolor
pigment mixed with water
gouache
watercolor with white chalk
buon fresco
applied while the plaster is wet
fresco secco
applied after the plaster has dried
paint on walls
purpose of fresco
dries quickly
disadvantage of encaustic
lasts long, vibrant, luminous
advantage of encaustic
not permanent and dries in 24 hours
advantages of fresco
tempera
can be applied translucent or opaque
gesso
applied to painting surface before the paint (primer)
very permanent since egg yolk dries very hard
advantage of tempera
slow process because there is a lot of layers.. and some colors do not mix with egg yolk
disadvantage of tempera
oil painting
which is the most versatile of all the mediums of painting
acrylic dries faster, easier to clean up, not as messy, and can paint on paper unlike oil
advantages/disadvantages of acrylic vs oil
really isn't a white pigment for watercolor
disadvantage of water color
the paper
what is the white parts of paintings using water color?
makes it more opaque
what does the white chalk do it gouache
powdered form
how does pigment start?
vehicle/medium/binder
what is the thing called that you mix with the pigment to create the different types of painting
support
the surface that pigment mixed with a binder is applied too
true
support is usually primed first (t or f)
relief printing
created by removing part of the matrix and the print is created by what is left behind
woodcuts or linocuts
color prints made by producing multiple blocks - one for each color and printed one color at a time
registration
aligning the blocks onto the paper
matrix
the original surface that the image is made on
limited edition prints
prints signed and numbered by the artist and produced in "limited" numbers
open edition prints
prints are not signed or numbered
relief, intaglio, lithography, silkscreen or serigraph, monoprints
5 processes of printmaking
intaglio
images are made by what is cut away from matrix, not by what is left behind
engraving
intaglio on either wood or metal, the tool is pushed across the surface
drypoint
intaglio type; tool is dragged across surface to create lines, NOT pushed, line is not as sharp as engraving, not as clean as engraving lines
etching
intaglio type; lines are created chemically in engraving, incised lines are created by force, metal
lithography
meaning "stone-writing" planographic method meaning that the matrix remains flat. It is only possible bc grease and water don't mix, created originally on flat pieces of limestone
silkscreen
process is like creating a stencil. areas the artist does not want printed are masked out, ex. tshirts
monoprint
you usually get only one good image. Image is created on any flat surface using ink or paint then paper or any other material is place on top- pressure is applied to transfer the image from original surface (matrix) to new surface bc no method has been created to preserve image multiple images are not possible.
planographic
method meaning that the matrix remains flat. it is only possible bc grease and water don't mix
subtractive and additive
2 types of sculpture
subtractive (carving)
carving for example where artists start with a material and removes unwanted material to achieve final form - example, stone - no undoing
additive (modeling, casting, constructed, assemblage)
material is built up into a final form (type of sculpture)
sculpture in the round
you can walk around the sculpture, multiple vantage points
low relief or BAS relief
suddenly projected sculpture
high-relief
deeper projected sculpture
armatrue
the skelaton
modeling
an additive process. taking a soft pliable material and building/shaping it into a form
lost wax casting
process to turn soft material like clay or wax into a more permanent material like metal. molded into wax and then covered with clay, then fired (melting away the wax and hardening the clay), and the resulting hardened mold is filled with molten metal
constructed sculpture
artists take a material and bend, cut, twist, reshape it into new forms
assemblage sculpture
takes found materials or objects and puts them together to create new forms
mixed media
20th century phenomena which grew out of the practice of collages. artists way to break down barriers between the traditional mediums of drawing/painting/sculpture
installations
incorporate sculptureal forms into an interior space
earthworks
incorporates exterior space into the work. example: stonehenge
performance art/body art
the artists body and the actions of the artist become the work
daguerreotype
one of the earliest forms of photography made on copper plate polished with silver
solarization
the technique used by a photographer who was experimenting with or manipulating the developing process so that the printed photographs had areas that printed in reverse in terms of the darks and lights.
Camera obscura
a small hole on the side of a light-tight room that admits a ray of light that projects a scene, upside down, directly across from the hole onto a white wall
Louis Daguerre
teamed with Niepce to refine the process of camera obscura then took over when Niepce died, created daguerreotype
Joseph Niepce
produced the first known photograph
D.W. Griffith
Birth of a Nation (beginning of the way we film today) created "Narrative Editing" which was very controversial
Orson Welles
"Citizen Kane" invented fade in/fade out and the use of time other than linearly. like in Citizen Kane, it starts at the end of his life rather than the beginning
zoogyroscope
device that projects a series of the images.. it has a wheel and a crank to spin the wheel to see the image through a view finder, origin of modern film
stroboscopic motion
still images projected rapidly to represent the illusion of movement. 22-26 frames per second in a film
Narrative editing
takes a lot of pictures from different angles and puts them together
comedy, propaganda, satire, social commentary, fantasy, and symblism
6 categories of film
topography
architecture that has the features of the local environment
technology
architecture that has materials and knowledge available at a given time in history
topography and technology
two factors of architecture
shell and skeleton and skin
two systems of architecture
shell
one material provides support and acts as outer covering
skeleton and skin
one material provides support and a different material provides the outer covering
load bearing, lintel and post, arches and domes, cast iron construction, suspension, frame construction, steel and reinforced concrete
7 forms of construction
load bearing
stacking materials, ex. pyramid or sizzorots
lintel and post
a system of building in which two posts support a crosspiece that spans the distance between them

arches and domes
much stronger than post and lintel weight gets distributed outward
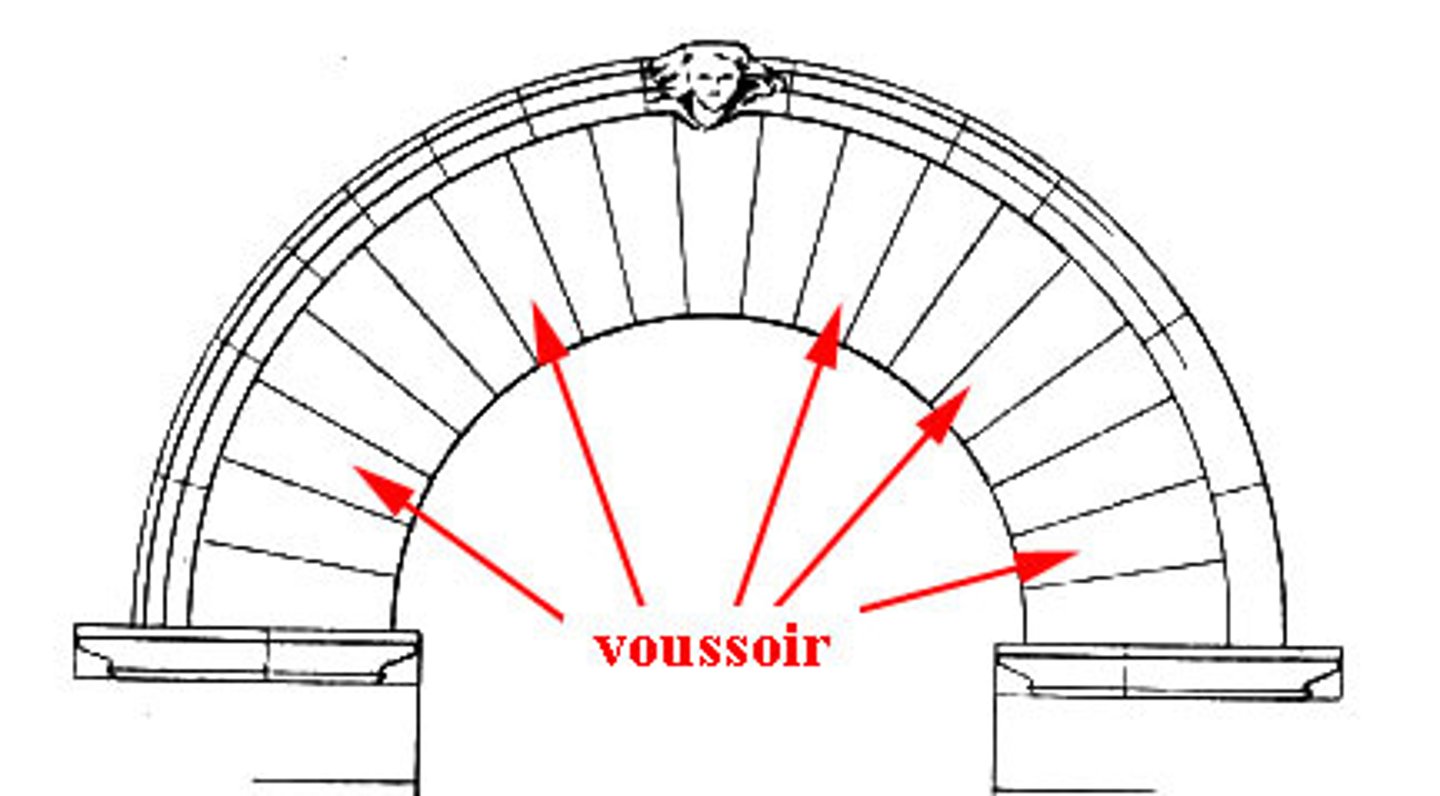
voussoir
wedges in an arch
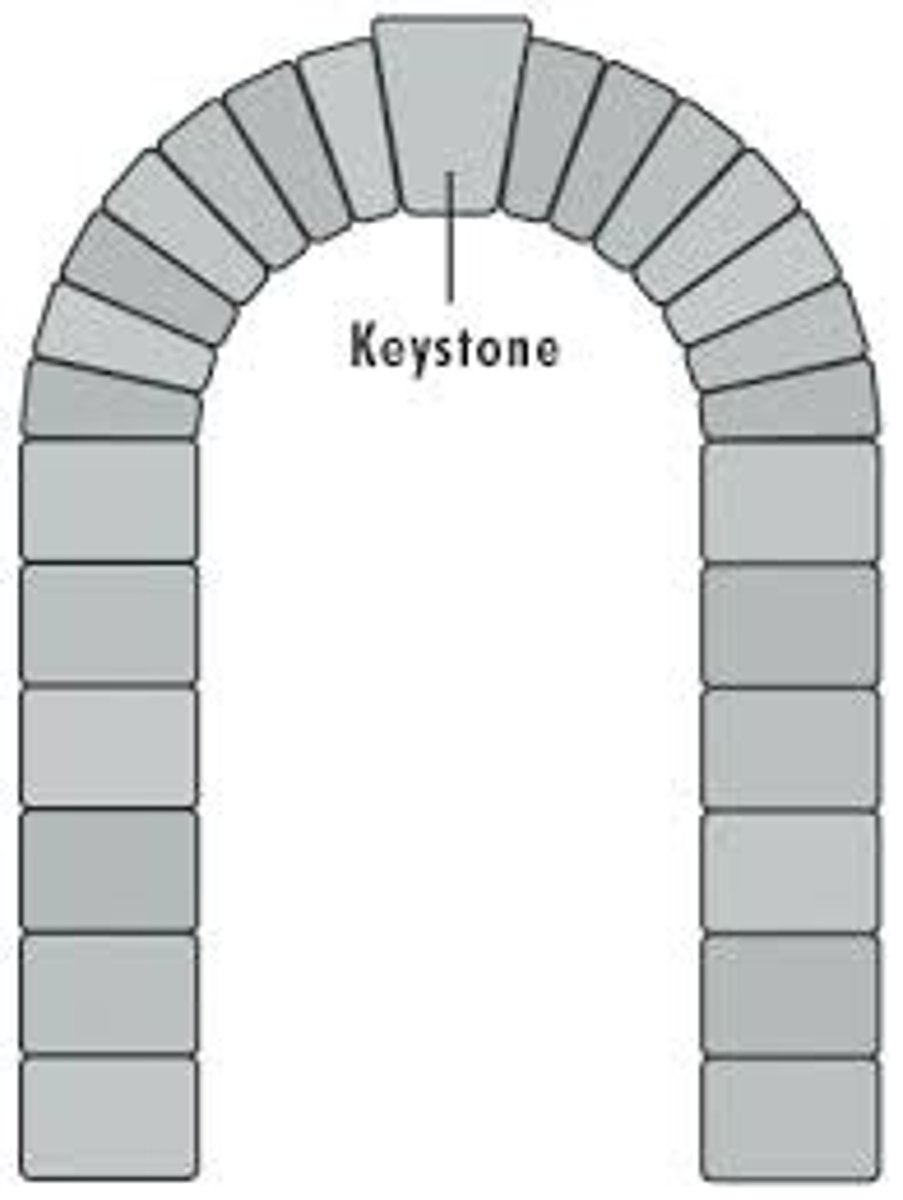
keystone
piece directly in the center of an arch
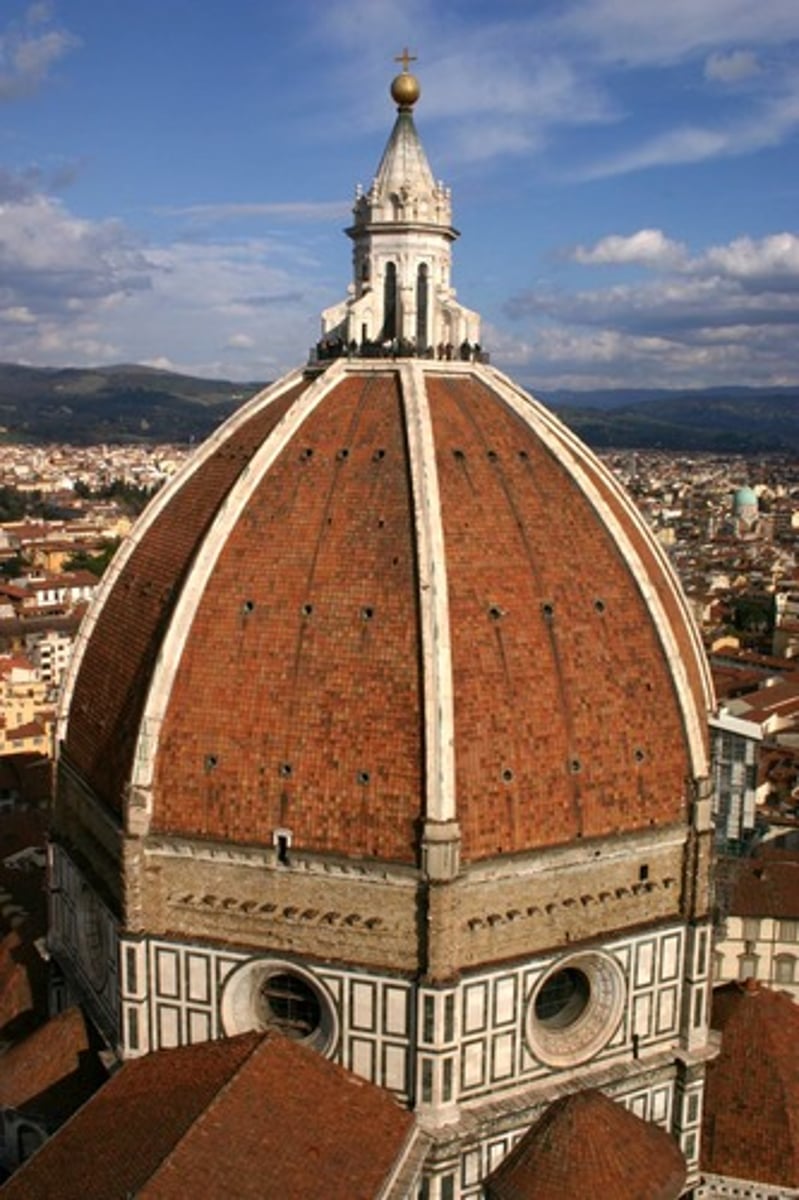
dome
arch in 360 degrees

pointed arch
an arch that is not semicircle but rises more steeply to a point at its top