Physics - OCR Gateway GCSE Physics (9-1) P3
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
A property of a particle that can be positive or negative
Charge
Atoms are neutral overall
Why we do not normally see effects of charge
The charge that insulating objects acquire because of transfer of electrons
Static electricity
Rub two insulators together to transfer electrons from one insulator to the other, leaving positive charges behind because they do not move, resulting in one insulator with more electrons than the other.
How to produce static electricity
The breakdown of air that discharges a charged object
Spark
They exert forces of attraction on one another
What happens to oppositely charged objects when not in contact
They exert forces of repulsion on one another
What happens to same charged objects when not in contact
A region of space around a charge where another charge will feel a force
Electric field
What the direction of the field lines represent
The direction of the force of on a positive charge
The rate of flow of charged particles
Current
Using a cell, a battery, or a power supply, and a complete circuit
How to make a current flow
Current (A) = Charge (C) / Time (s)
Equation for current
From the positive terminal of the battery to the negative terminal
The conventional direction of electric current on a circuit diagram
From the negative terminal of the battery to the positive terminal
The direction of electron flow on a circuit diagram
The same
The current everywhere in a single closed loop
A difference in electrical potential produced by the separation of charge
Potential difference
Potential difference (V) = Energy transferred (J) / Charge (C)
Equation for potential difference
Cell/battery
What the symbol represents

Voltmeter
What you measure potential difference with
Longer side
Which side of the cell symbol is the positively charged side
Yes
If there is potential difference if voltmeter was set on both sides of a cell
No
If there is potential difference if voltmeter was set on two points on a wire with nothing in between
The method of transferring energy from chemical stores to electrical components
Electrical working
Bulb
What the symbol represents
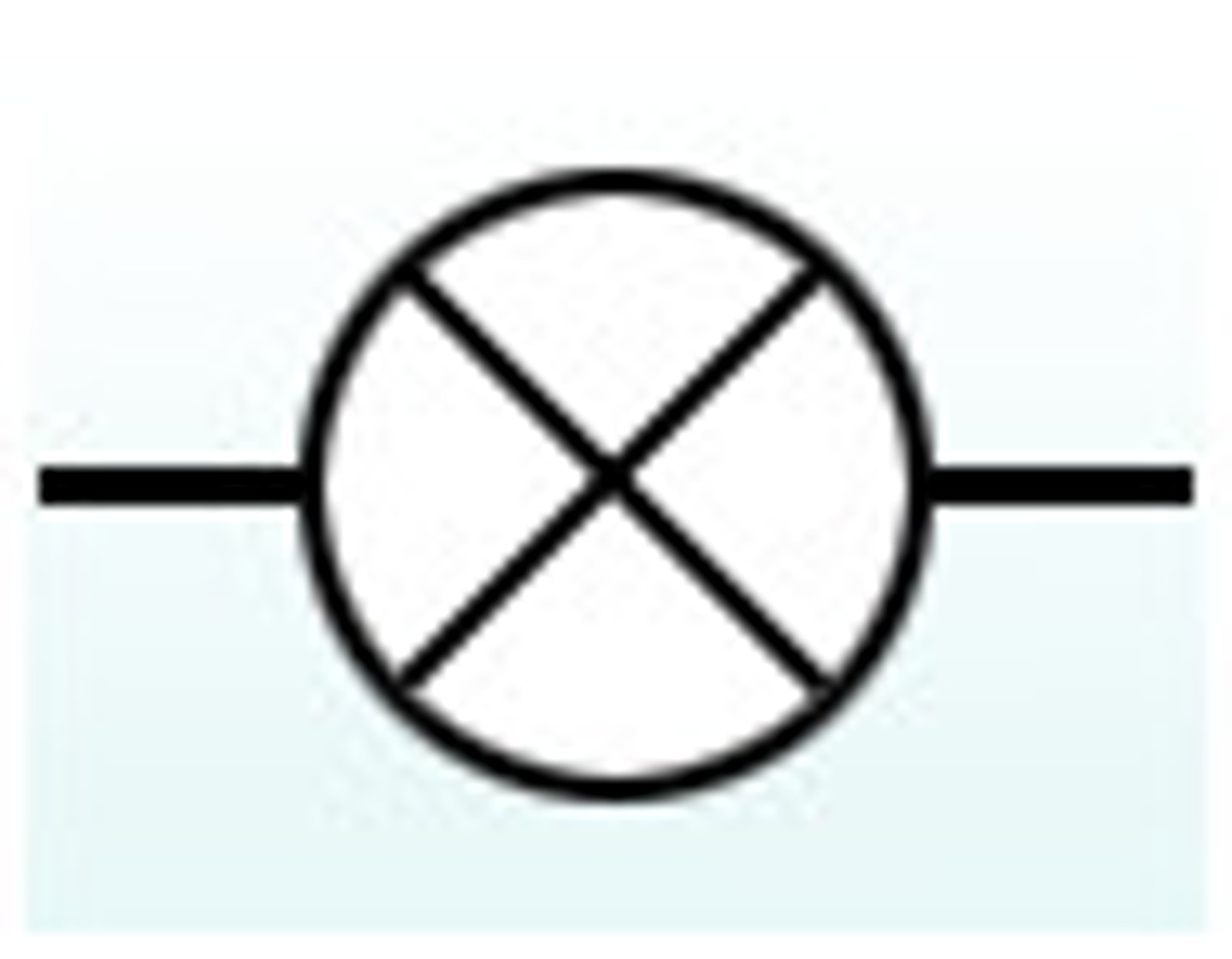
Voltmeter
What the symbol represents

What you measure the current of a circuit with
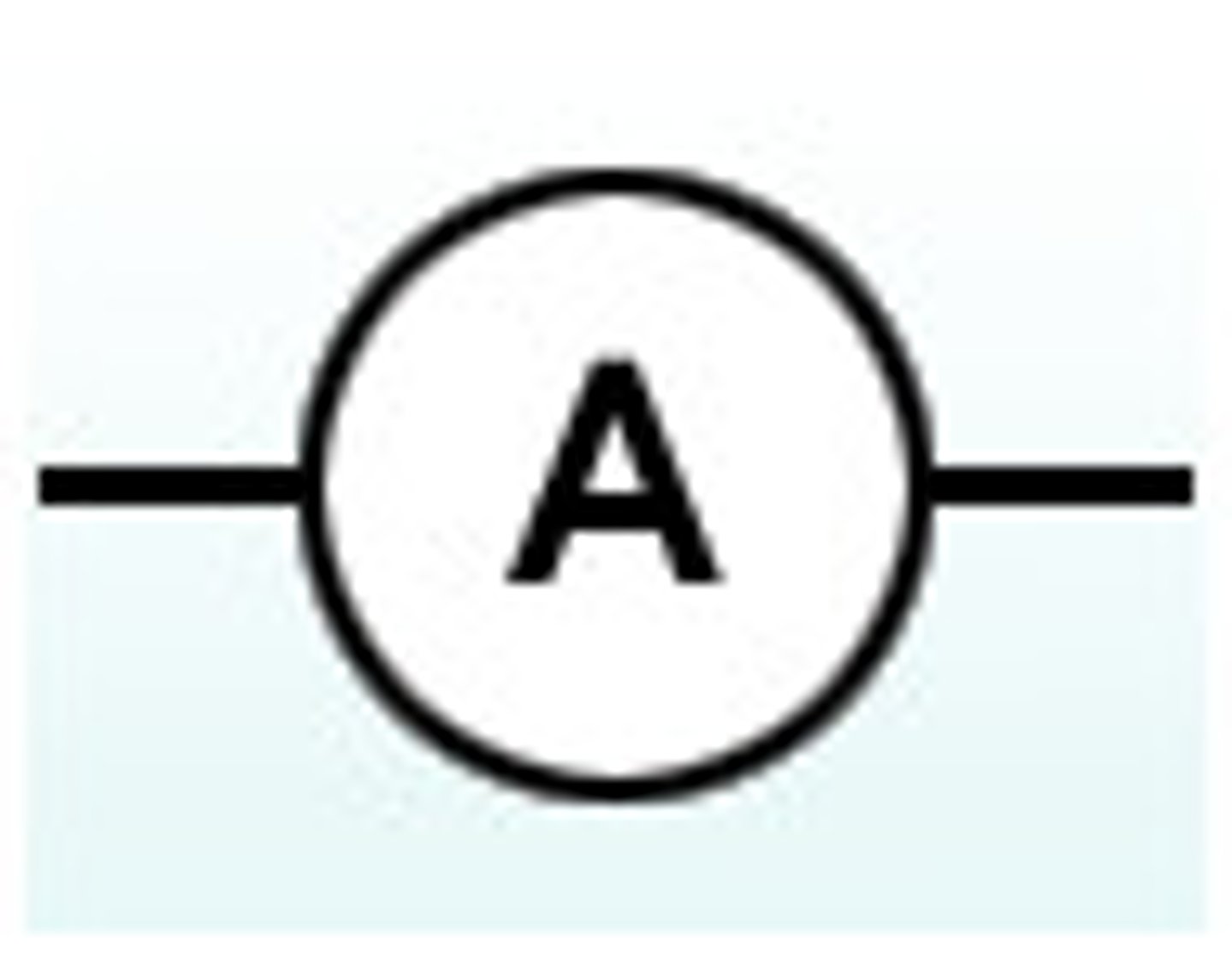
Ammeter
Ammeter
What the symbol represents
A circuit with one loop
Series circuit
Parallel circuit
A circuit with multiple loops
Resistance (Ω) = Potential difference (V) / Current (A)
Equation for resistance
Potential difference and resistance
What the current in a circuit depends on
A circuit component which has a resistance that depends on temperature
Thermistor
What happens if you put a thermistor in cold water then heat the water up
The resistance of the thermistor decreases
A circuit component which has a resistance that depends on temperature
Thermistor
What happens if you put a thermistor in cold water then heat the water up
The resistance of the thermistor decreases