Exam 2: CH13-22
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Define the function of biotechnology. Which of these is correct?
It is used to artificially create biological products using recombinant DNA technology.
All but one
It is used to make insulin.
It is used to produce food products.
It is used to naturally create biological products using recombinant DNA technology.
All but two
All but one
The charging of tRNAs is carried out by a set of enzymes called ________ synthetases.
ribozymes
aminoacyl-tRNA
aminoacyl-tRNA
TATA box is found in all microorganisms. Specify where it is located in a fungal promoter?
It is located within 70 nucleotide bases away from a gene start codon (AUG).
It is located within ~30 nucleotide bases away from a gene start codon (AUG).
It is located within 50 nucleotide bases away from a gene start codon (AUG).
It is located 100 nucleotide bases away from a gene start codon (AUG).
It is located within ~30 nucleotide bases away from a gene start codon (AUG).
The role of the Hin recombinase is to recombine specific segments of flagellin genes in Salmonella enterica.
True/False
True
Fill in the blank (Use only these keys below to fill in the blanks)
(stop codon, histones, linear, western blots, nucleosome, molecular weights, negatively charged proteins, response regulator, type II, activators, ultraviolet light, sensor kinase, repressors, phosphate)
Pyrimidine dimer is produced by [ ].
Ultraviolet light
The process of moving a genetic element within or between DNA molecules is transposition.
True/False
True
Distinguish PCR and colony PCR. Use one of these keys to fill in the blanks: Colony PCR; PCR
[A] requires the extraction of intracellular DNA. Hence, [B] is a rapid technique in relative to the other kind.
[A] PCR [B] Colony PCR
Fill in the blank (Use only these keys below to fill in the blanks)
(stop codon, histones, linear, western blots, nucleosome, molecular weights, negatively charged proteins, response regulator, type II, activators, ultraviolet light, sensor kinase, repressors, phosphate)
[A] prevent transcription, whereas [B] stimulate transcription.
[A] Repressors [B] activators
A consensus sequence of any genetic element is the sequence with the most likely amino acid (or amino acids) at each position.
True/False
False
Fill in the blank (Use only one of these keys below to fill in the blank(s))
(stop codon, histones, linear, western blots, nucleosome, molecular weights, negatively charged proteins, response regulator, type II, activators, ultraviolet light, sensor kinase, repressors, phosphate)
Eukaryotic chromosomes are [A], contained within a nucleus, and they contain DNA associated to a core of histone proteins called the [B].
[A] linear [B] nucleosome
Metagenomics is the use of modern phenotypic techniques such as next-generation DNA sequencing to study microbial communities directly in their natural environments, without the need to culture the microbes in the laboratory.
True/False
False
CRISPR-Cas9, a prokaryotic defense mechanism, is a powerful emerging tool in biotechnology Which one of the following statements is true about it?
introducing insertions, deletions, or sequence modifications into a given genome with CRISPR-Cas9.
marking a defective gene with antibiotic resistance.
introducing insertions, deletions, or sequence modifications into a given genome with CRISPR-Cas9.
Fill in the blank (Use only these keys below to fill in the blanks)
(stop codon, histones, linear, western blots, nucleosome, molecular weights, negatively charged proteins, response regulator, type II, activators, ultraviolet light, sensor kinase, repressors, phosphate)
The importance of the [ ] UAG is that it tells the ribosome to stop translating the mRNA.
stop codon
Fill in the blank (Use only these keys below to fill in the blanks)
(stop codon, histones, linear, western blots, nucleosome, molecular weights, negatively charged proteins, response regulator, type II, activators, ultraviolet light, sensor kinase, repressors, phosphate, 42, 100)
Heat-shock transformation requires a warm temperature at [ ]°C.
42
In order to transfer, an F factor must have which of the following?
oriV and its own DNA polymerase
oriT and tra genes
oriT and tra genes
One application of Gram stain is detecting the presence of a specific microbe, such as the pathogen E. coli O157:H7 in a complex environment.
True/False
False
A transferable plasmid contains all the genes needed for pilus formation and DNA export.
True/False
True
Synthetic biology uses bacterial cells and their indigenous genetic materials.
True/False
False
Fill in the blank (Use only these keys below to fill in the blanks)
(stop codon, histones, linear, western blots, nucleosome, molecular weights, negatively charged proteins, response regulator, type II, activators, ultraviolet light, sensor kinase, repressors, phosphate)
A transmembrane [ ] protein senses an environmental condition outside Gram-positive bacteria or in the periplasm of a(n) Gram-negative bacteria.
sensor kinase
Which of the following forms of transposition specifically describes the transfer of DNA from one cell to another?
nonreplicative
conjugative
conjugative
Some microbes use gene regulation to periodically change their appearance, in a process called
phase variation.
sporulation.
phase variation
Phase variation in Salmonella enterica involves specialized transduction.
True/false
False
Both codons and anticodons are complementary DNA sequences.
True/False
False
Supercoiling in bacteria is typically introduced by enzymes called
gyrases.
polymerases.
Gyrases
Which probing technique detects DNA immobilized on a membrane using labeled DNA fragments?
Southern blot
Northern blot
Southern blot
Many infectious bacteria have regions of DNA coding for virulence factors. These regions are called pathogenicity islands.
True/False
True
Fill in the blank (Use only these keys below to fill in the blanks)
(stop codon, histones, linear, western blots, nucleosome, molecular weights, negatively charged proteins, response regulator, type II, activators, ultraviolet light, sensor kinase, repressors, E. coli, phosphate, Mycobacterium)
Name one example of microorganism that is used in synthetic biology [ ].
E. coli
Where can you locate a gene within a full genome?
It doesn't have a promoter.
It is located adjacent to a promoter.
It is located adjacent to a promoter.
Vertical gene transfer is equivalent to horizontal gene transfer.
True/False
False
Which of the following bacteria requires artificial assistance to become competent to take up DNA?
Streptococcus
E. coli
E. coli
Bacterial cells have restriction enzymes that recognize random sequences of DNA and make double-stranded breaks within these recognition sites.
True/False
False
If a cell always need a gene for housekeeping purposes, it is
constitutive.
derepressible.
constitutive

The figure below shows subunits of a structure in a bacterial cell. This structure is
RNA polymerase.
a ribosome.
A ribosome
Define synthetic biology. Which of these is correct?
All
Some applications of that are engineered strains of microbes for antibiotic and insulin manufacturing.
All but one
Synthetic biology applies engineering principles to design and construct new biological parts for a desired purpose.
It creates GMO using DNA recombinant technology.
All
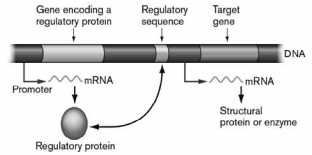
The figure below shows a regulatory being produced on the left. Based on the information in the figure, this protein must function in which of the following ways?
When glucose binds to it, the protein binds to the regulatory sequence and prevents transcription of the target gene.
In the presence of the end product of the operon, this protein will bind to the regulatory region and acts as an activator
In the presence of the end product of the operon, this protein will bind to the regulatory region and acts as an activator

Using the genetic code shown below, find the correct start and stop codons. Which of the following peptides might this message code for?
5'-GAGUUAUGCACGGGUUCUAUGUGUAG-3'
GLU-LEU-CYS-MET-GLY-SER-MET-CYS
MET-HIS-GLY-PHE-TYR-VAL
MET-HIS-GLY-PHE-TYR-VAL
Gene transfer from parent to progeny is called
horizontal gene transfer.
vertical gene transfer.
vertical gene transfer.
Define the purpose of carrying out cell culture. Which of these is correct?
It is used to store cells.
It is used to grow mixtures of cells.
It is used to grow a single type of cells.
It is used to grow a single type of cells.
Competence in Gram-positive organisms is induced by
competence factors made of peptides.
calcium and cold.
competence factors made of peptides.
All bacteria can transfer DNA to plants using its Ti plasmid.
True/False
False
The entire genetic complement of DNA in a cell of a particular organism is called
proteome
genome
genome
________ RNA polymerase and sigma factor complex is called ________.
Holoenzyme; core
Core; holoenzyme
Core; holoenzyme
Which form of control is the LEAST reversible and MOST drastic?
posttranslational control
alterations of DNA sequence
alterations of DNA sequence
The term _________________describes a polycistronic messenger RNA whose expression is under control of a promoter.
amplicon
operon
operon
Many restriction enzymes recognize palindromic sequences on double-stranded DNA. Among the following, which is a palindromic sequence?
5'-GGATCC-3'
3'-CCTAGG-5'
5'-GATTACCTAGG-3'
3'-CCTAGGTAATC-5'
5'-GGATCC-3'
3'-CCTAGG-5'
Fill in the blank (Use only these keys below to fill in the blanks)
(stop codon, histones, linear, western blots, nucleosome, molecular weights, negatively charged proteins, response regulator, type II, activators, ultraviolet light, sensor kinase, repressors, phosphate, type IV)
A difference between type II restriction enzyme and type I or type III restriction enzymes is that [ ] enzymes cut at the recognition sequence rather than elsewhere.
type II
One benefit of operons in bacteria is that they
allow for alterations in DNA sequence by flipping promoters around.
allow for coordinated gene expression of related genes on one mRNA controlled by one promoter.
allow for coordinated gene expression of related genes on one mRNA controlled by one promoter.
The mechanism behind slipped-strand mispairing is that
short repeats allow for slippage of DNA polymerase during replication, which leads to an out-of-frame reading sequence.
an invertible promoter slips into different reading frames.
short repeats allow for slippage of DNA polymerase during replication, which leads to an out-of-frame reading sequence.
Distinguish PCR and real-time PCR. Which of these is incorrect?
PCR allows for the detection of amplifications at the end point of the reaction
Real timePCR allows for the detection of amplifications during the early phases of the reaction.
None
Real-time allows for the detection of amplifications while the reaction is occurring.
none
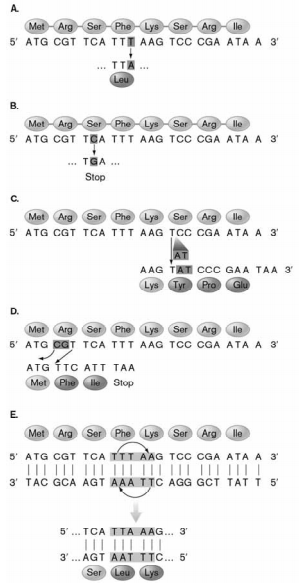
In the figure below, which type(s) of mutation(s) is/are introducing frameshifts?
C and D
A, B, and C
C and D
Phase variation is an example of
conjugation.
site-specific recombination.
site-specific recombination.
Microbial transformation can be carried out via multiple means. Which of these requires competence factors?
transduction
natural transformation.
conjugation
heat shock
natural transformation.
During conjugation, DNA pol ________ is used for replication beginning at ________.
III; oriT
I; oriV
III; oriT
E. coli is being used in order to study various agents that inhibit protein synthesis. An agent will bind the 16S rRNA of the 30S subunit and block aminoacyl tRNA from entering the ribosome. This agent is most likely related to ampicillin.
True/False
False
Enzymes that modify the supercoiling of a DNA molecule are called
primases.
topoisomerases.
topoisomerases.
A collection of genes and operons whose expression is controlled by a single protein is called a(n)
regulon.
monocistronic message.
regulon.
The value of studying a transcriptome rather than a genome is that one can get a snapshot of what genes are expressed under some conditions but not others.
True/False
True
DNA and RNA polymerases can only synthesize in the ________ direction.
3'-to-5'
5'-to-3'
5'-to-3'
All the cell’s expressed RNAs are collectively referred to as the cell’s transcriptome.
True/False
True
Distinguish a structural gene and an operon. Which of these statements is correct?
All but two
A structural gene consists of multiple operons.
All but one
An operon consists of one promoter.
A structural gene consists of multiple promoters.
An operon consists of multiple structural genes.
All but two
Phase variation in Salmonella enterica involves
chemotaxis.
gene inversion.
gene inversion.
Define and name one function of bioinformatics. Which of these is correct.
It can be used to identify gene.
It can be used to identify microorganism.
All but one
It can be used to identify protein.
All but two
All
Bioinformatics is a key tool for microbiologists because it is an interdisciplinary field that combines computer science, mathematics, and statistics.
All
Newly replicated, and consequently ________, DNA sequences are invisible to a restriction enzyme.
mutated
hemimethylated
hemimethylated
Describe quorum sensing. Which of these statements is incorrect?
It is used in the formation of biofilms.
Quorum sensing systems produce effects by accumulating a secreted small molecule called a regulatory protein.
The function of quorum sensing systems are synthesis, secretion, and extracellular accumulation of small autoinducer signaling molecules.
It is used to express virulence factors by pathogenic bacteria.
It is the process of cell-cell communication that allows bacteria to share information about cell density and adjust gene expression accordingly.
Quorum sensing systems produce effects by accumulating a secreted small molecule called a regulatory protein.
Large regions of sequence homology are required when recombining DNA molecules by ________ recombination.
transposition
general
general
A ________ mRNA is a single mRNA molecule that contains information from several contiguous genes.
cistronic
polygenic
polygenic
The process of taking a DNA template and making a complementary RNA molecule is called
transcription.
translation.
transcription.
Autoinducers regulate gene expression by
accumulating inside the cell until enough is present to bind repressor proteins and stop transcription.
diffusing out of the cell and when a critical cell density is reached, moving back in and binding to a regulatory protein to initiate transcription.
diffusing out of the cell and when a critical cell density is reached, moving back in and binding to a regulatory protein to initiate transcription.
The significance of the Shine-Dalgarno sequence is that it is the site where a RNA polymerase binds so that it can initiate translation.
True/False
False
Which RNA species is a component of the 30S subunit of the ribosome?
16S rRNA
mRNA
16S rRNA
Which of these explain why genetic code is redundant?
There is more than one kind of amino acid in proteins.
More than one codon can specify the same amino acid.
More than one codon can specify the same amino acid.