Chem 120 Lecture 6 - Chapter 9: Nature of Energy
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Energy
Capacity to do work/produce heat
Surroundings
Anything outside rxn
Also the universe outside of the system.
System
Studying part of the universe.
Will be considered as R and P
PV Work units
101.3 J = L x atm
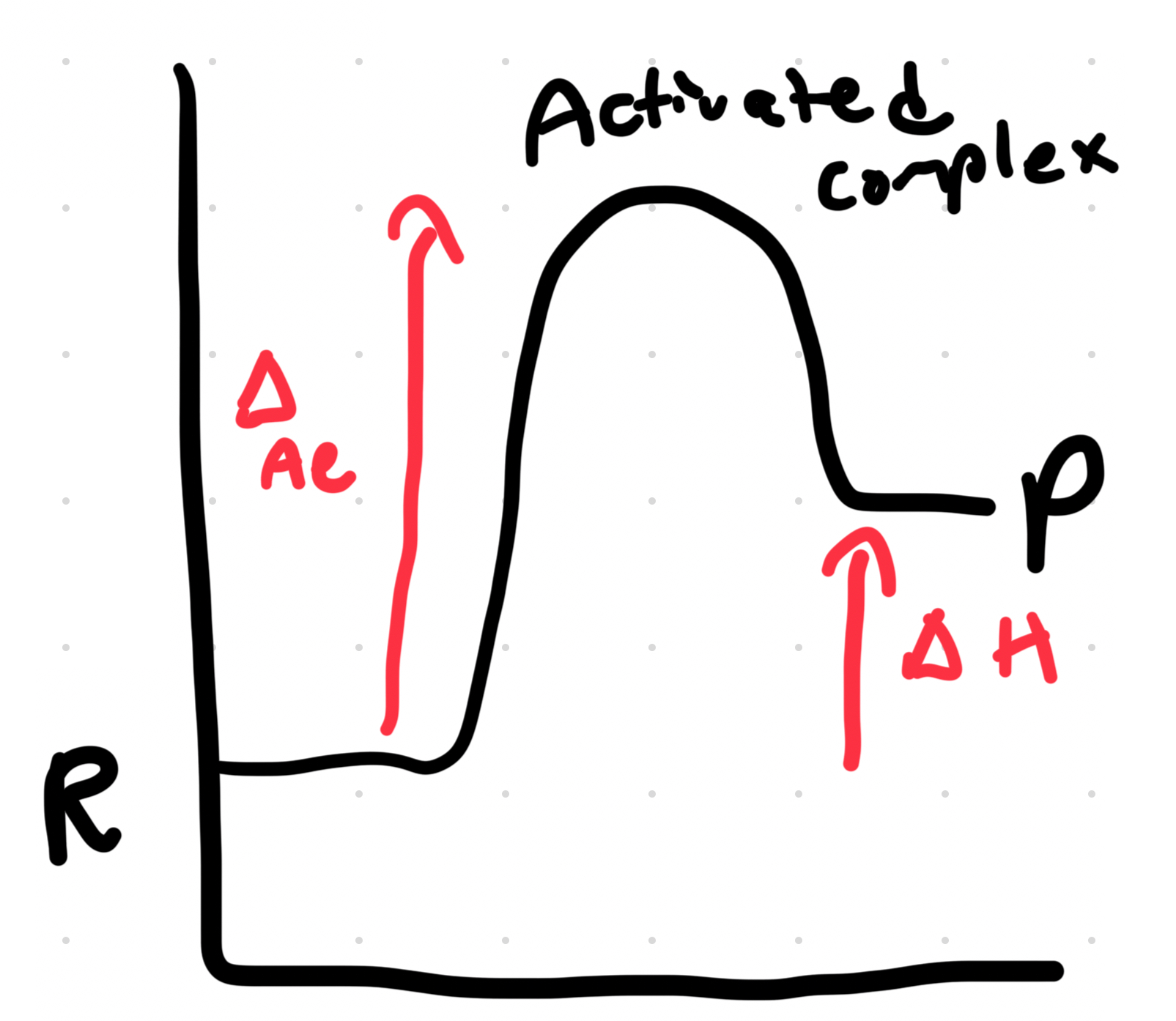
Exothermic Reaction
Energy coming out of the system.
HOT!!!
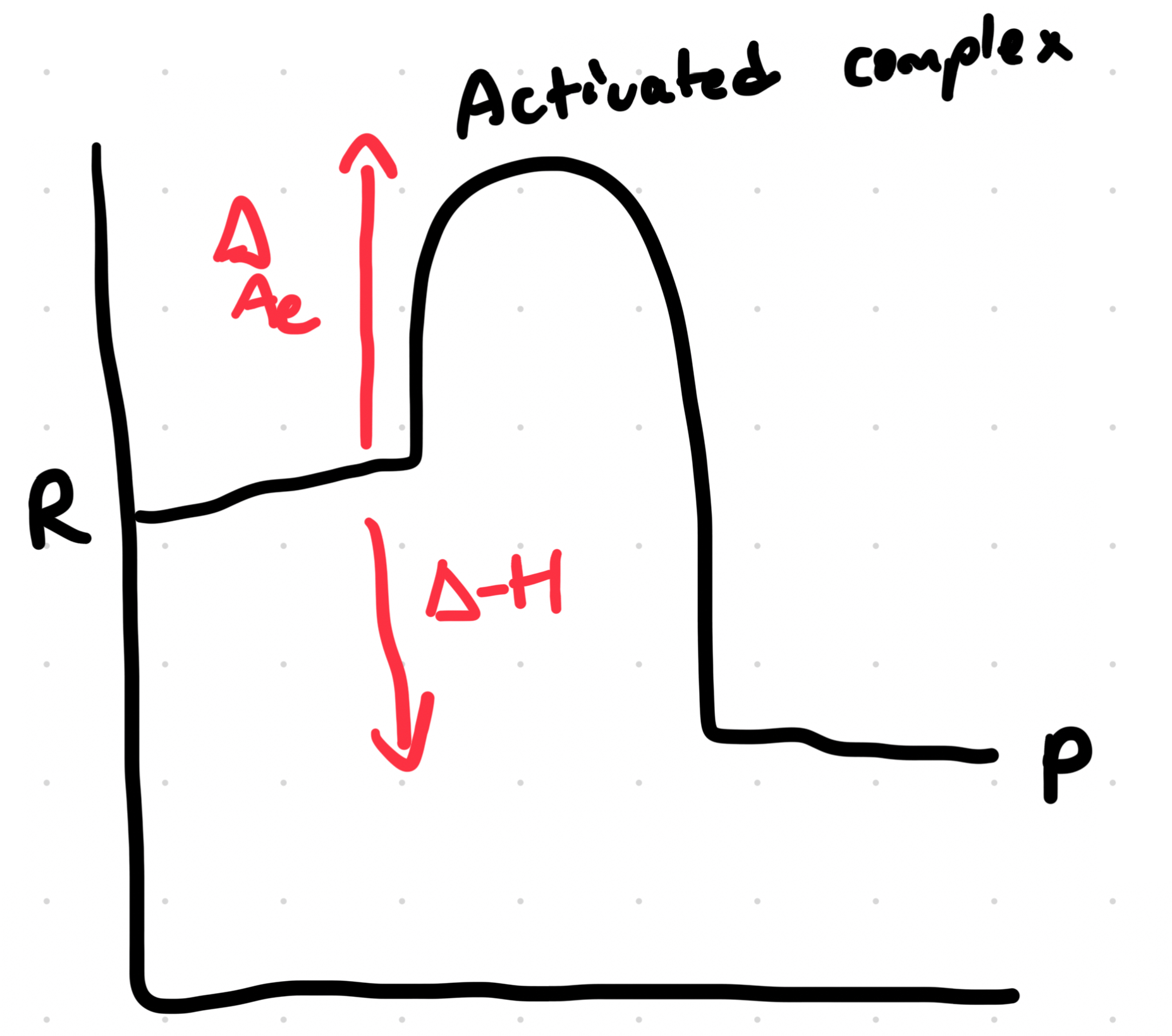
Endothermic Reaction
Energy going into the system
COLD!!!
Potential Energy (PE)
Energy due to the position (mgh)
Kinetic Energy (KE)
Energy due to the objects motion (1/2 m v²)
PV Work
Work that results a change in V
Work also done on surroundings.
PV Work Formula
W = -P (change in V)
Internal Energy
The total energy of the system and the sum of PE + KE.
The change of the system = heat + work.
Internal Energy Formula
E = q + w
E = Change in the internal energy system
q = heat
w = work
What does q stand for?
The heat:
If -q = heat goes outside
If q = heat comes inside
Enthalpy
The measure of heat energy in a system at constant pressure. It includes the internal energy of a substance and the work done on or by the system.
Change in H Formula
H = (Qp = E + P x (V))
H = 5/2n x R x (change in T)
Change in Enthalpy Formula
H = n x Cp x T
H = change in heat
n = moles
Cp = Heat capacity with constant pressure
t = temperature (Use C)
Change in H in Endothermic Reaction
H + R —> P
Change in H in Exothermic Reaction
R —> P + H
Heat Flow of Ideal Gas at const V Formula
Qv = n x Cv x T = (Change in E)
Heat Flow of Ideal Gas at const P Formula
Qp = n x Cp x T = (Change in H)
State Functions
Property of system that depends on present state.
Examples of State Functions
Q and W are not state functions but E and H are state functions.
Molar Heat Capacity
Energy must change both translational energy to provide work gas does.
Substance defined as the energy needed to raise T by 1 K.
Molar Heat Capacity for constant v formula
Cv = 3/2 R
Molar Heat Capacity for constant p formula
Cp = Cv + R
Cp = 5/2 R
KE Average Formula
____= 3/2 R x T
Heat Flow Expression for constant v
Qv = nCv x T
T = Celcius NOT K
Heat Flow Expression for constant p
Qp = nCp x T
T = Celcius NOT K
How do you change the KE?
By changing the Temperature using the KE = 3/2 R x T formula
Average Transitional Energy
Energy of ideal gas by change of temp
Average Transitional Energy Formula
E = 3/2 R x T
Calorimetry
The measurement of heat transfer in a system. It helps determine the specific heat capacity or energy content of substances from chemical reactions.
If a system consists of 1 mol, what is it?
Molar Heat Capacity
Calorimetry Formula
Qrxn = -mCs x T
How does System and Surrounds affect Calorimetry?
System = Solid
Surrounds = Water
Calorimeter
Used to measure heat.
Standard Enthalpies of Formation: H Formula
Hrxn = Hf(products) - Hf(reactants)
Standard State in Condensed State
Pure Liquid/Solid
Standard State for Gas Pressure
1 atm
Substance in Solution of Standard States.
1 M at applied Pressure of 1 atm
Hess’s Law
The overall enthalpy change of a reaction.
Balancing formulas to find the change in H
Hess’s Laws Calulations
H must be reversed if rxn switches sides.
H must be multiplied to the same coefficients of rxn numbers.
From R → P, enthalpy = same either when rxn takes 1 or multisteps.
What is the best P and T where the gas behaves most ideally?
P = 0.5 atm T = 100 C