module 10
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
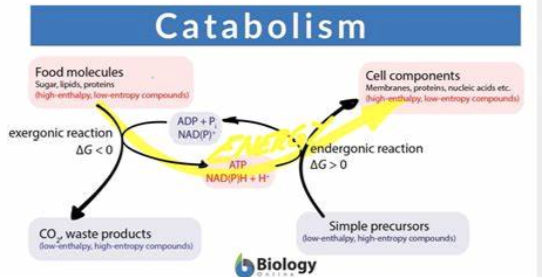
Catabolism
the breakdown of compounds.
Releases energy.
Provide building blocks.
Anabolism
building of compounds
Requires energy
Use up building blocks
Metabolism
sum of all chemical reactions within a living organism
Coenzyme
organic molecule (non-protein) might be required
vitamins
Cofactor
inorganic molecule (non-protein) might be required
minerals
Apoenzyme
protein (main part)- may act on its own (depending on the enzyme)
Allosteric site
noncompetitive substrate inhibition; causes active site to change shape
Active Site
Competitive substrate inhibition-where the substrate binds, and the shape of the cell is essential
Dehydrogenation
movement of a hydrogen atom and an electron
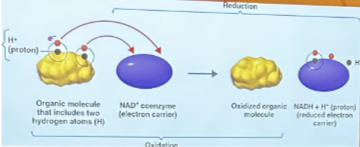
Oxidation
reduction reactions, lose an electron
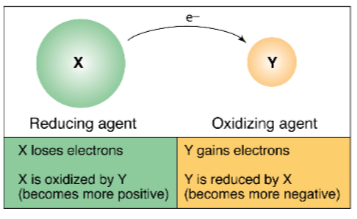
Reduction
gain an electron
What is an enzyme (define it; two things)?
An enzyme is the metabolism of the cell. It is a catalyst, and most are protein.
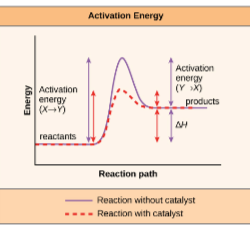
What is the function of an enzyme?
· Lowers activation energy (Catalyst)
· Bind to reactant molecules
· Ease chemical bond breaking/forming
How is an enzyme named?
· Always ends in ase
· Named for purpose
List and describe three ways of expression or production of enzymes?
· Constitutive (Produced constantly/same activity)
· Inducible (Environment causes increased production)
· Repressible (Environment causes decreased production)
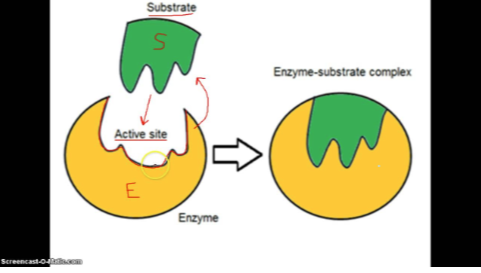
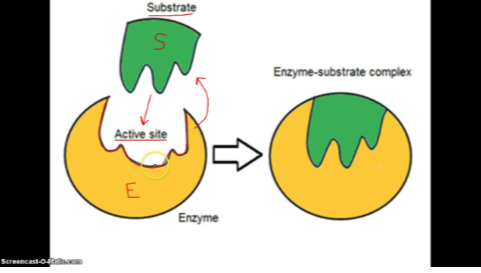
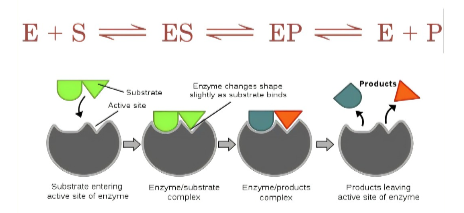
What is the mechanism of action in an enzyme?
1. Active site (substrate bind)
2. Form Enzyme (substrate complex)
3. Substrate transferred to products
4. Products released
5. Enzyme is recycled
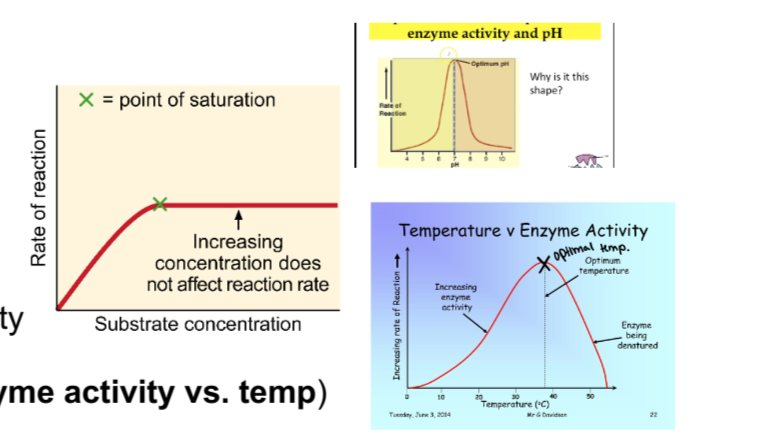
What factors influence enzyme activity and why?
Temperature
Low temp- molecules move more slowly, the enzyme becomes rigid
High temp- protein denatures or unfolds because noncovalent (and hydrogen) bonds are broken
pH- high (H+) or (OH-)
extreme pH can cause enzymes to denature
substrate concentration
saturation-all active sites are filled with substrate
inhibitors
Competitive
non competitive
Compare and contrast the two types of inhibitors (be specific)?
Competitive
Binds the active site
Does not undergo any reaction or change (the enzyme)
Irreversible- inhibitor binds and never leaves, reversible- inhibitor binds and leaves and binds and leaves
Antimicrobial agent sulfanilamide
Noncompetitive
Binds the allosteric site- some other place on the enzyme
Causes active site to change shape
Can be reversible or irreversible
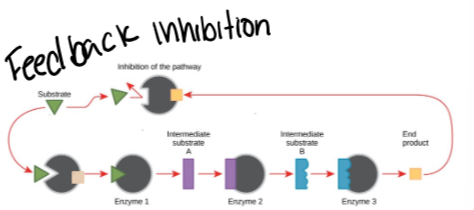
Feedback inhibition- an end product in a series of reactions inhibits the first enzyme in the series.
Keeps the cell from wasting resources
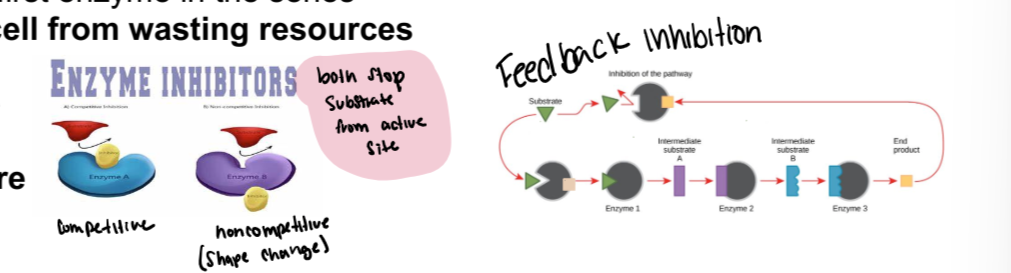
What is feedback inhibition?
An end product in a series of reactions inhibits the first enzyme in the series.
Understand concepts and parts concerning a hypothetical metabolic pathway.
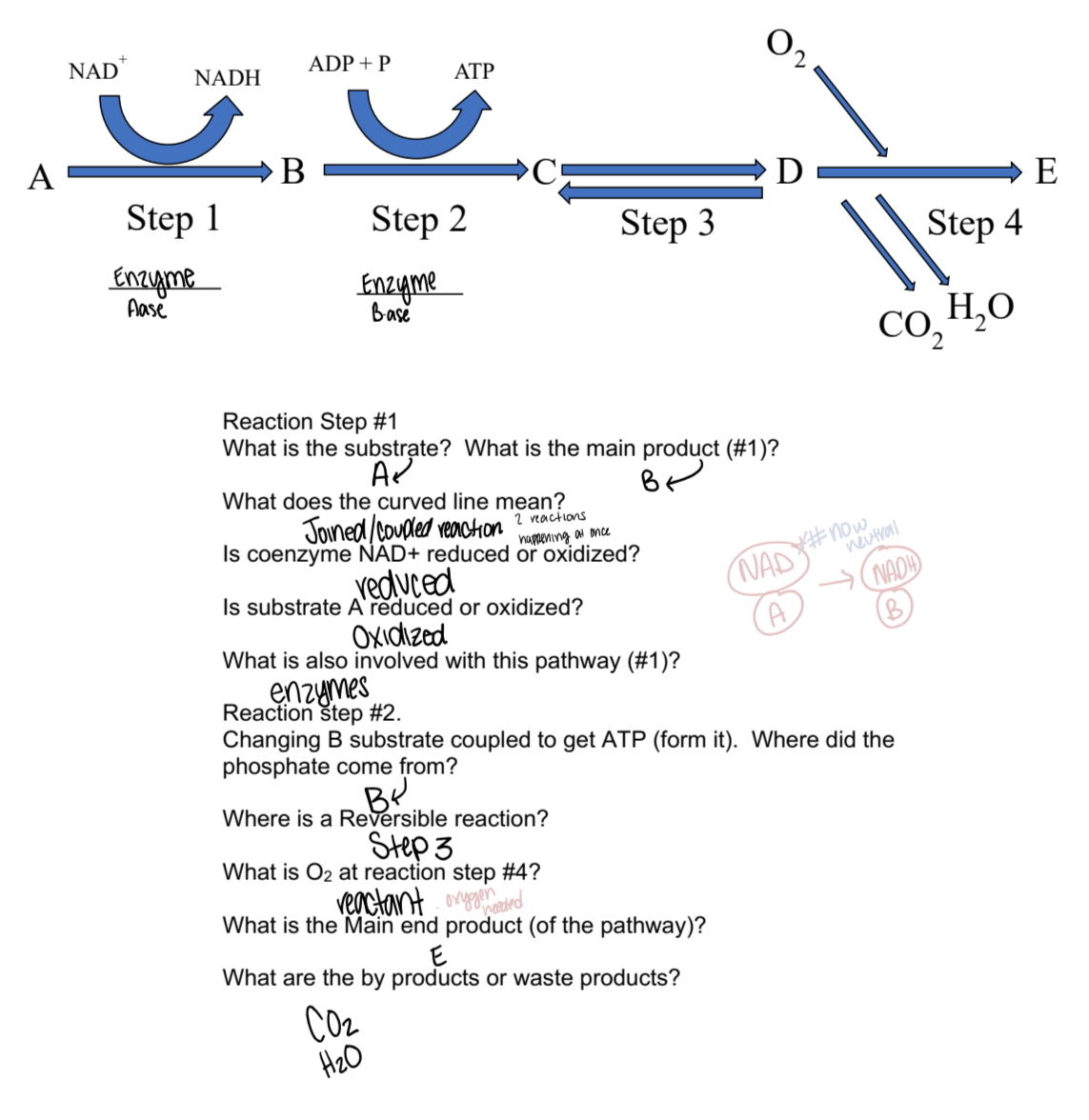
What is a coupled reaction?
It is two reactions happening at once.
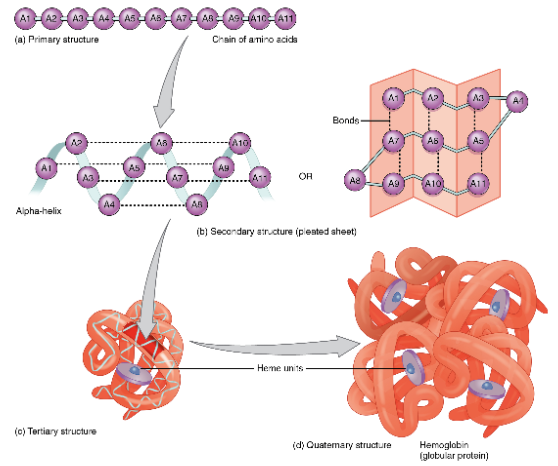
protein levels
primary
secondary
tertiary
quaternary
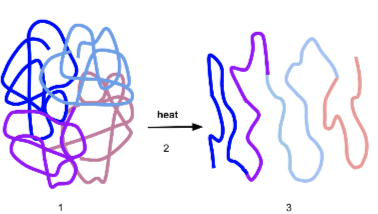
denature
loss of conformation or shape
no longer active
caused by high temp or extreme pH
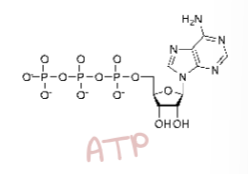
ATP