Schizophrenia (Psychology)
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Describe what is meant by the terms positive and negtaive symptoms with examples
Positive refers to the addition of certain behaviours. For example, hallucinations, delusions, of grandeur, or of control and insertion of thoughts are all positive
Negative refers to the removal of certain baheviours. For example, poverty of speech, withdrawal from society and flattering of mood are all negative.
Evaluate the Freeman et al study
(-) The sample used was non-clinical sample. While this findings are of interest in terms of the use of the VR, there is no way of knowing whether it would work the same way with the clinical sample. Patients diagnosed with persecutory ideation issues may not be able to cope with VR setting or willingly participate in VR therapy
(-) The sample used was small and very specific. Participants used were students and staff in a prestigious London-based university so this may not necessarily represent the general public and definitely does not represent clinical sample. Therefore, there may be limited generalisability and applicability
(+) The procedure used in the study was clear and standardised. The situation used in the VR setting and all of the measures were clearly outlined, so other researchers can replicate the study to test it for reliability
(+) The study may have good application in therapeutic setting. Using VR to understand the persecutory thoughts of people diagnosed with schizophrenia and related disorders could be the way to create better treatment regimes and therapies for these patients
For ICD-11 describe the diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia.
To indicate schizophrenia there has to be 2 of the listed symptoms for most of the time for at least one month. One of the symptoms must come from the first four on this list
Persistent delusions - these can be grandiose (being grand or impressive) or persecutory (patients thinking someone intends to harm them)
Persistent halucinations - these are mainly auditory
Disorganized thinking - if severe, the person’s speech may become very incoherent
Experiences of influence, passitivy, or control - feeling that thoughts are not controlled by oneself
Negative symptoms - these include flattening of emotion, alogia (paucity of (very little) speech), avolition (lack of motivation), asociality (not social), and anhendonia (inability to feel pleasure)
Diorganized behaviour that impedes goal-based activities
Psychomotor disturbance - these include catatonia, agitation, posturing, waxy flexibility, negativism, mutism and stupor.
These symptoms are not caused by organic problems or substance abuse including when on treatment for substance abuse.
Describe the participants in the study Freeman et al (2003)
A total of 24 participants were recruited
All had no history of mental illness
Volunteer sample from Univerity College London.
21 participants were students
There was an equal number of males and females
Consent was taken from all participants
Nothing was revealed about the task being linked to persecutory thoughts.
Describe the aim and hypothesis of the study Freeman et al (2003)
The aim of this explarotary study was to investigate whether people without any mental health disorder diagnosis have thoughts of persecutory ideation in a VR setting.
The researchers also wanted to investigate whether there are any cognitive factors that can predict persecutory ideation in a VR setting.
Describe the context, main theories, and explanations of the Freeman et al study.
The use of virtual reality in clinical psychology is based around the assumption that people will react in the same way in the VR setting as they would in the real world.
Using VR has been successful in treating a range of phobias. However, there has been limited exploration as to whether avatars (the people you meet and interact with in VR sessions) can trigger persecutory ideation.
As VR environments and avatars can be controlled, this tool could be useful to clearly identify what triggers persecutory ideation in patients diagnosed with schizophrenia.
Persecutory ideation is when a person has distorted belief that mean they cannot recognize what is reality and what is not reality
Describe the procedure of Freeman et al study
All participants were allowed some time to explore the VR setting. Once they had got used to the VR equipment, participants were instructed to explore the room (a library but never referred to as this) and form some impression of the avatars in there with them, including what they think about the participant. A total of 5 avatars was used in the study
Sometimes the avatars showed potentially ambiguous behaviour such as smiling, chatting to each other, or looking around the room or at the participant. After 5 minutes, the participant was told to leace the VR setting.
The participants were in 2 groups, one half completed a set of measures before and after the VR experience. The other half completed the same measures, but only after the VR experience.
This was to account for the possibility that the idea of persecutory thoughts being tested was primed from the measures.
Which measures were taken in Freeman et al study?
The Brief Symptom Inventory (BSI) was used.
Paranoia Scale was used
The Spielberger State Anxiety Questionnaire was completed
VR-paranoia was measured. The research team created a measure of the feelings of paranoia in the VR setting. It measures VR-Persecution, VR-Reference, and VR positive feelings
A semi-structured interview and observer rating of persecutory ideation took place. The participants were asked about their experiences in the VR setting. It was video recorded, and an observer then watched it to rate whether there were any signs of persecutory ideation.
A sense of presence questionnaire was completed. This measured the participant felt in the VR setting.
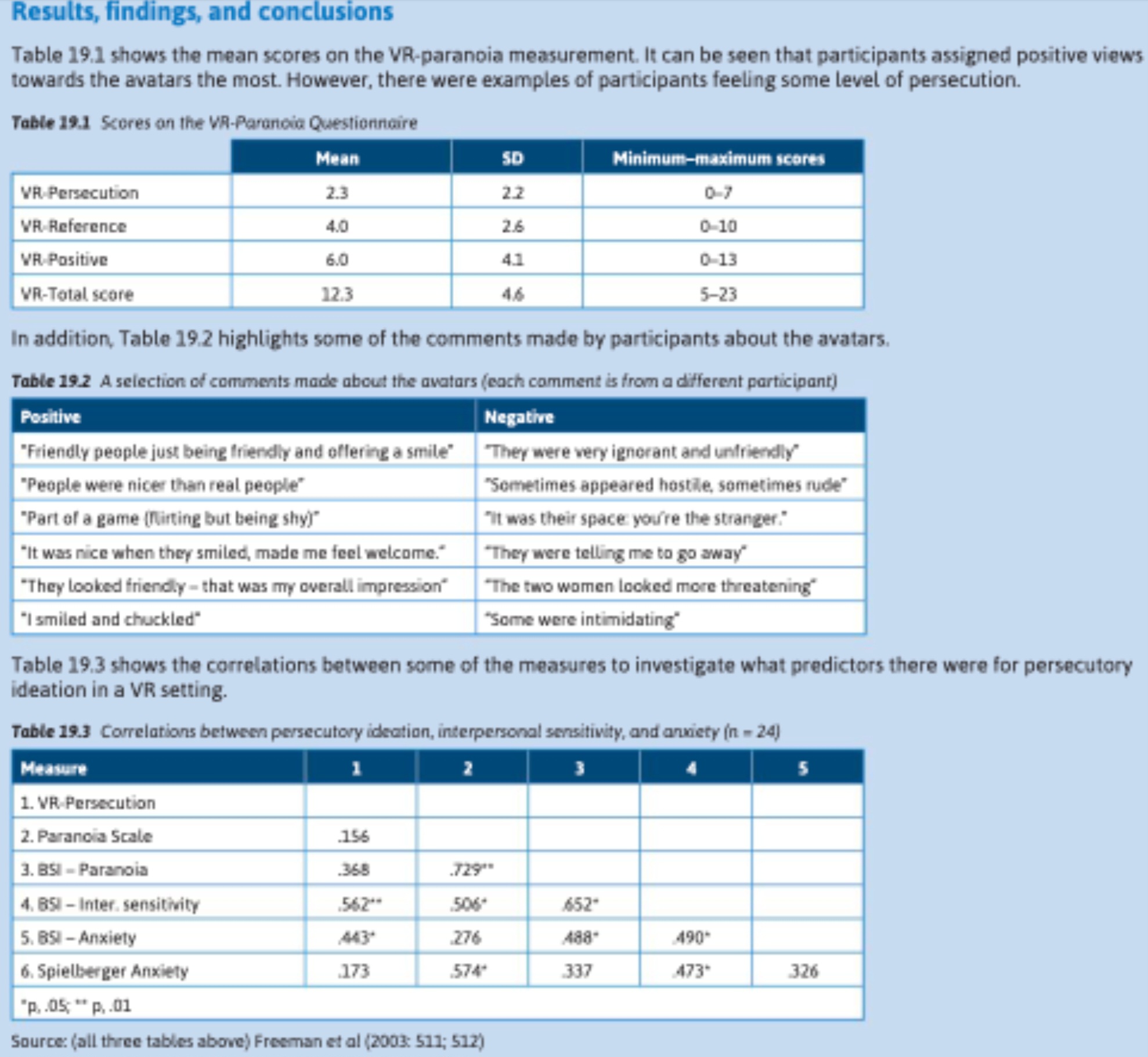
What are the results of the Freeman et al study?
Participants assigned positive views towards avatars the most. However there were examples of participants feeling some level of persecution.
Table 19.3 shows the correlation between some of the measures to investigate what predictors there were for persecutory ideation in a VR setting.
Therefore, this study does provide evidence that people attribute mental states to avatars in a VR setting, and so will be useful when exploring what triggers persecutory ideation in patients diagnosed with schizophrenia.
Describe the Biological explanation of schizophrenia (Genetic)
Reviews conducted by Gottesman and Shields appear to be the ones quoted the most in the field. This review looked at adoption, twin and family studies to see whether there was a potential genetic component to schizophrenia
WIth studies of twins, researchers can examine monozygotic twins (MZ identical) and dizygotic twings (DZ non-identical) to test whether a genetic component is seen because the monozygotic twins share 100% genetic material. Therefore if the prevelance of schizophrenia is higher in MZ twins (when both twins have been diagnosed with schizophrenia) this could point towards a genetic component. Five twins formed the review and results are shown below.
The difference between the pairwise concordance rate and probandwise concordance rate is highlighted by Gottesman and Shields as ‘… the paiwise rate expresses the degree of concordance as the percentage of all pairs in which both twins are schizophrenic, given a specifified sample of twin pairs which at least one twin schizophrenic. The probandwise rate is the percentage of independently ascertained schizophrenic twins (the probands)‘ who have a schizophrenic co-twin
Simply:
• Pairwise concordance rate:
The percentage of twin pairs in which both twins have schizophrenia, out of all twin pairs where at least one twin is affected.
• Probandwise concordance rate:
The probability that the co-twin of a schizophrenic individual also has schizophrenia, making it a better estimate of individual genetic risk
Proband - the schizophrenic twin
Independently ascertained:
Each diagnosed twin counts as a separate starting point (proband) and then the researchers ask ”Does this proband's co-twin also have schizophrenia?”
Results:
The overall results do point towards