BIO120 TISSUES
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
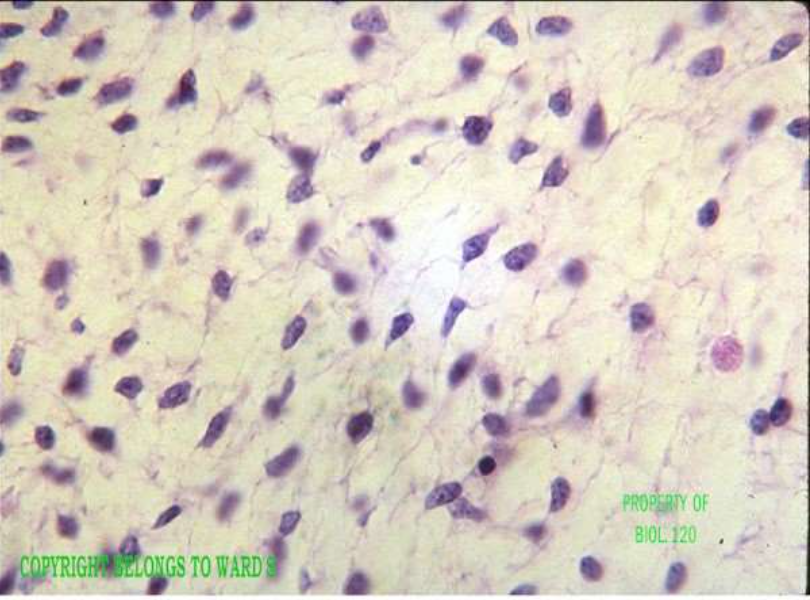
connective: embryonic mesenchyme: mesenchyme
function: give rise to all other connective tissue
location: mostly in embryo
connective: embryonic mesenchyme: mesenchyme
function: give rise to all other connective tissue
location: mostly in embryo
loose connective: areolar:
function: wrap and cushion organs
location: under epithelia of body
loose connective: areolar:
function: wrap and cushion organs
location: under epithelia of body
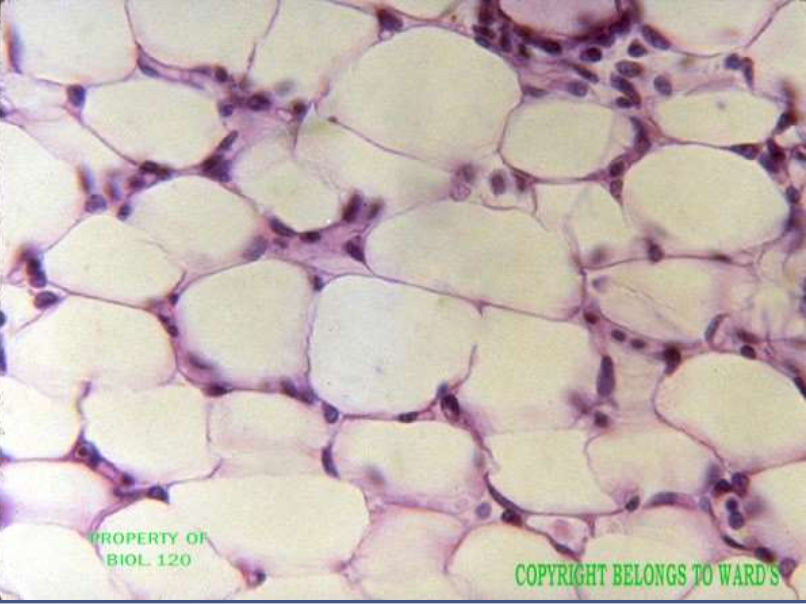
loose connective: adipose:
function: reserves energy by insulating against heat loss
location: under skin, within abdomen, in breast
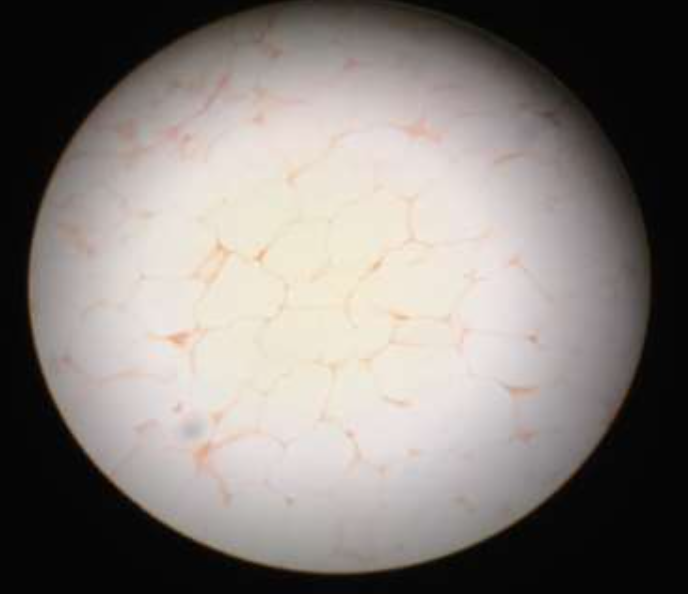
loose connective: adipose:
function: reserves energy by insulating against heat loss
location: under skin, within abdomen, in breast
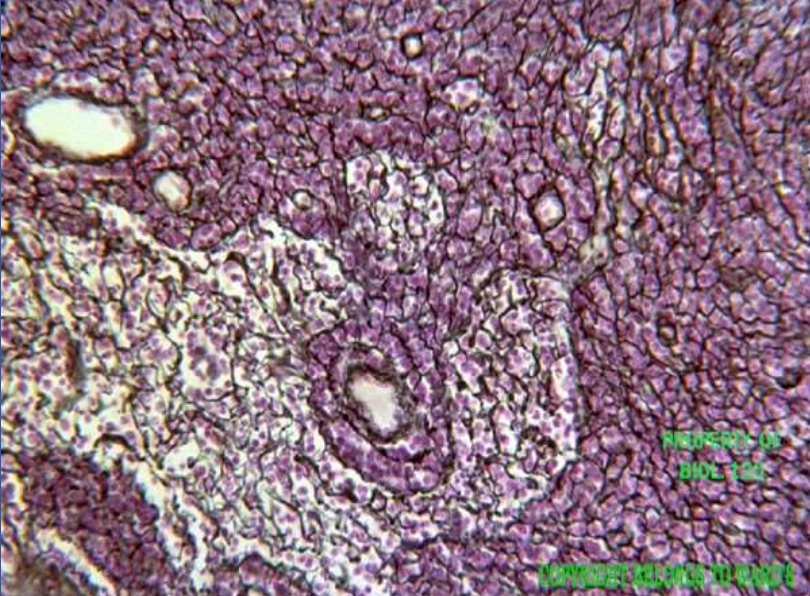
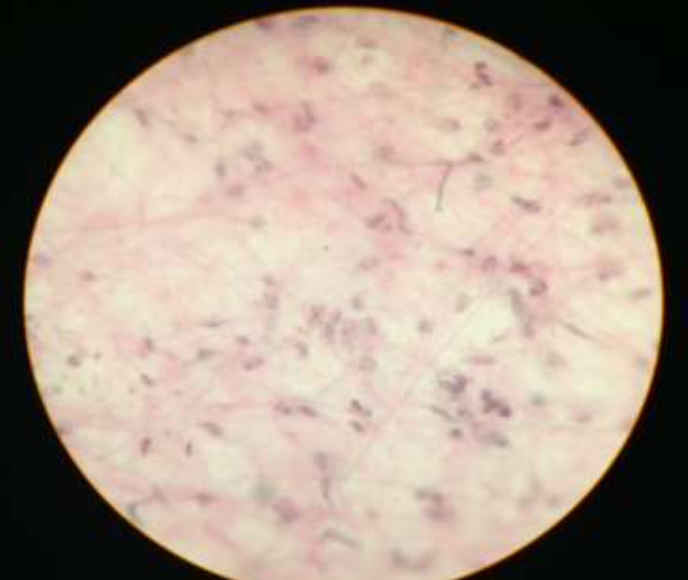
loose connective: reticular:
function: its fibers support white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages
location: in lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, bone marrow, and spleen)
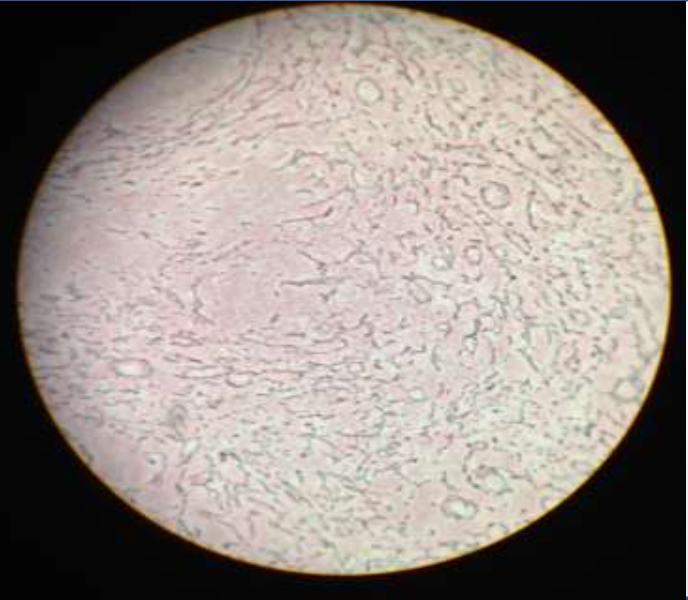
loose connective: reticular:
function: its fibers support white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages
location: in lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, bone marrow, and spleen)
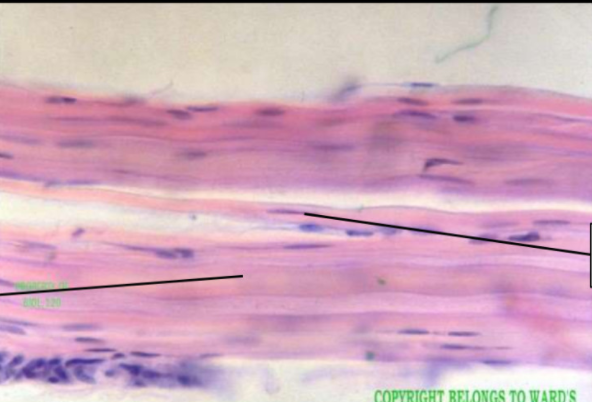
dense connective: dense regular connective tissue
function: withstands tensile stress in one direction; attaches muscles to bones, muscles to muscles, bones to bones
location: tendons and ligaments
dense connective: dense regular connective tissue
function: withstands tensile stress in one direction; attaches muscles to bones, muscles to muscles, bones to bones;
location: ligaments and tendons
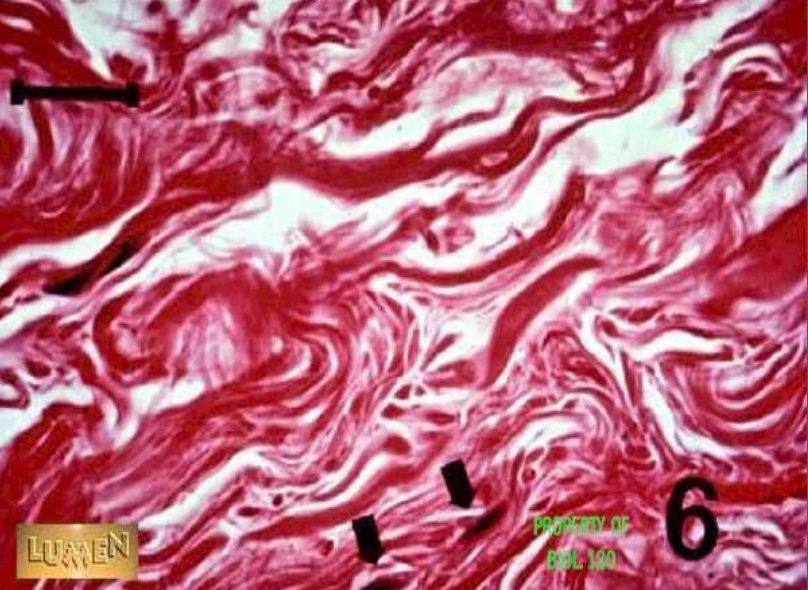
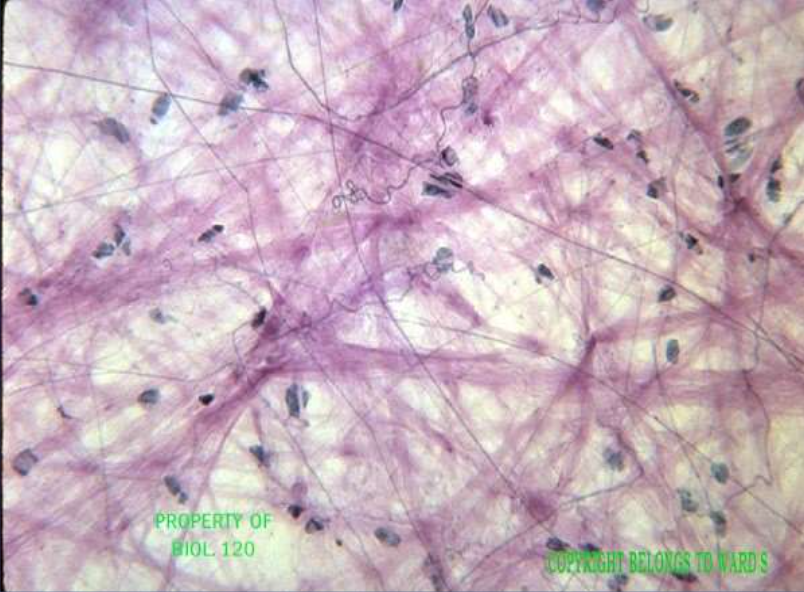
dense connective: dense irregular connective tissue
function: withstand tensile stress exerted in many directions
location: dermis of skin
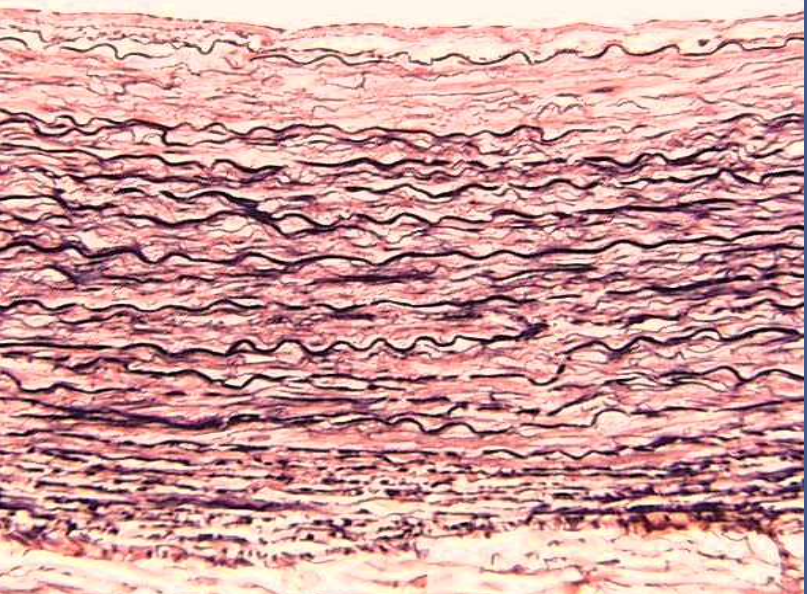
dense connective: elastic
function: allows recoil of tissue following stretching
location: walls of large arteries
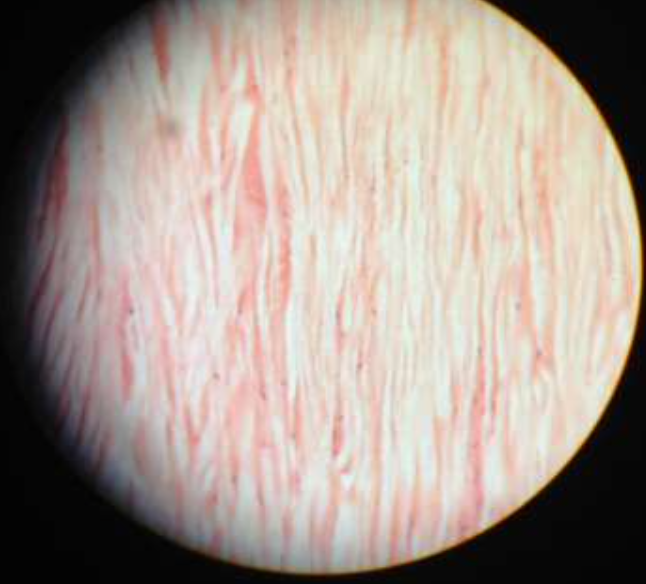
dense connective: elastic
function: allows recoil of tissue following stretching
location: walls of large arteries
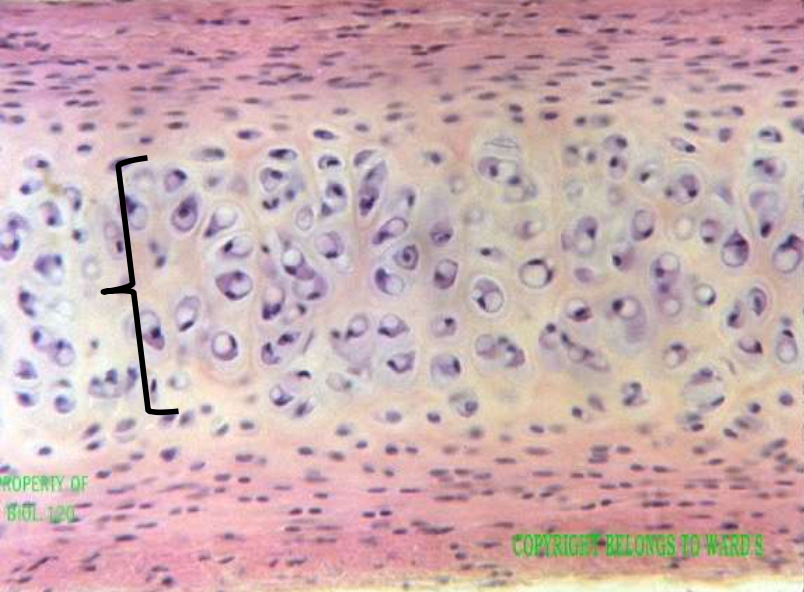
cartilage: hyaline
function: cushions, resists compressive stress
location: nose, trachea
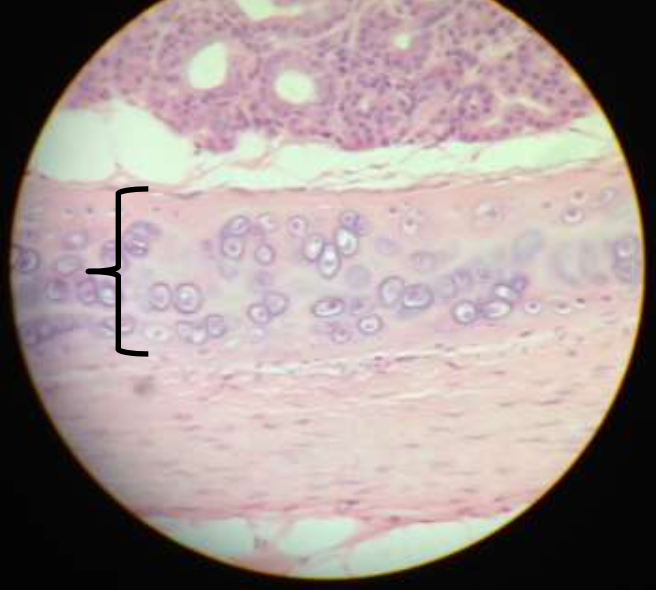
cartilage: hyaline
function: cushions, resist compressive stress
location: nose, trachea
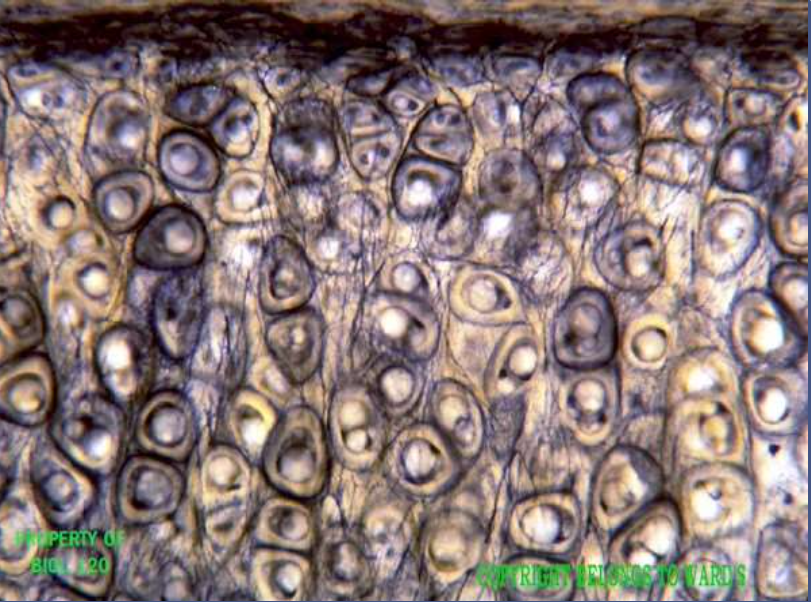
cartilage: elastic
function: maintains shape of structure while allowing flexibility
location: external ear, epiglottis
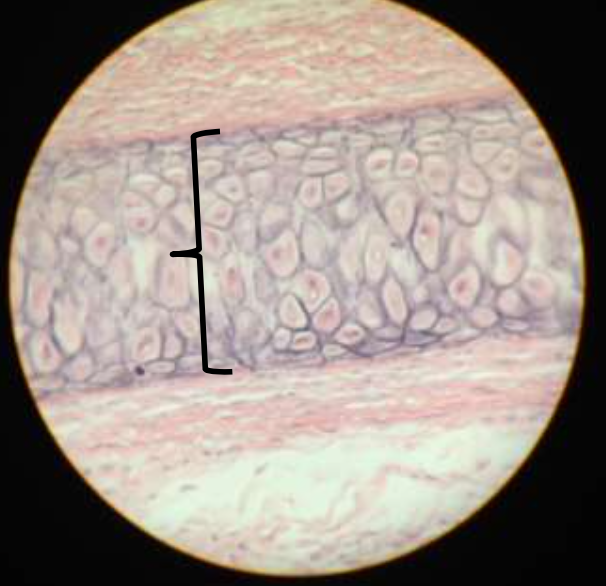
cartilage: elastic
function: maintains shape of structure while allowing flexibility
location: external ear, epiglottis
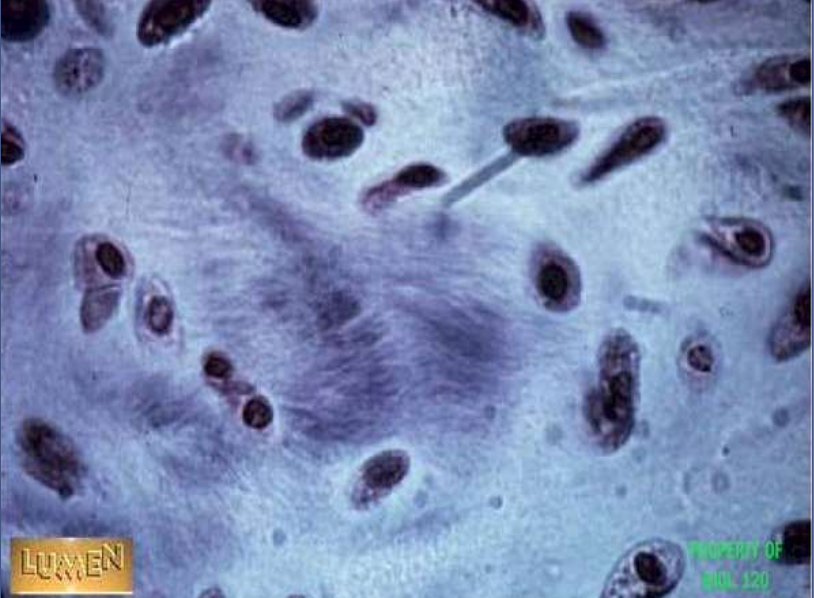
cartilage: fibrocartilage
function: tensile strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock
location: discs of knee joint
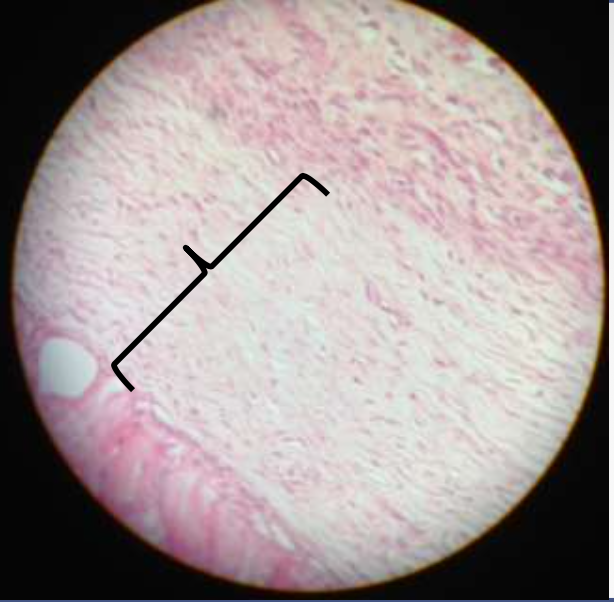
cartilage: fibrocartilage (white fibrocartilage)
function: tensile strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock
location: discs of knee joint
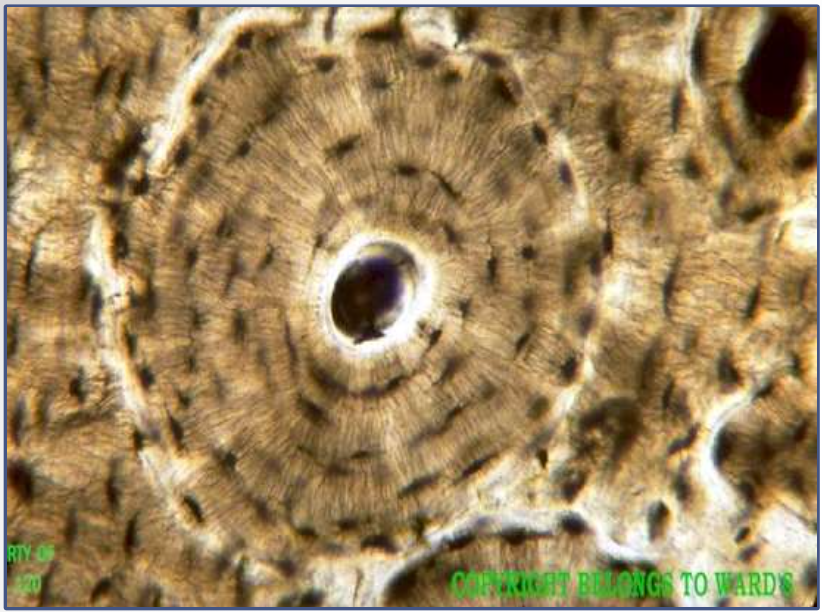
bone:
function: supports and protects, stores calcium
location: bones
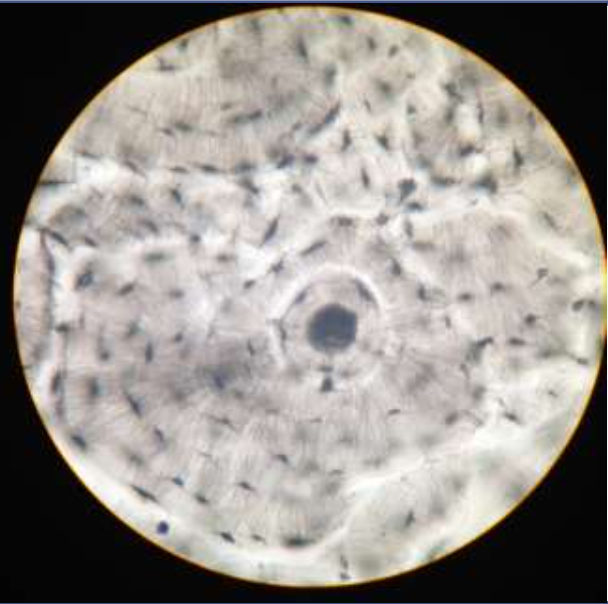
bone:
function: supports and protects, stores calcium; the marrow inside bones is the site for blood cell formation
location: bones
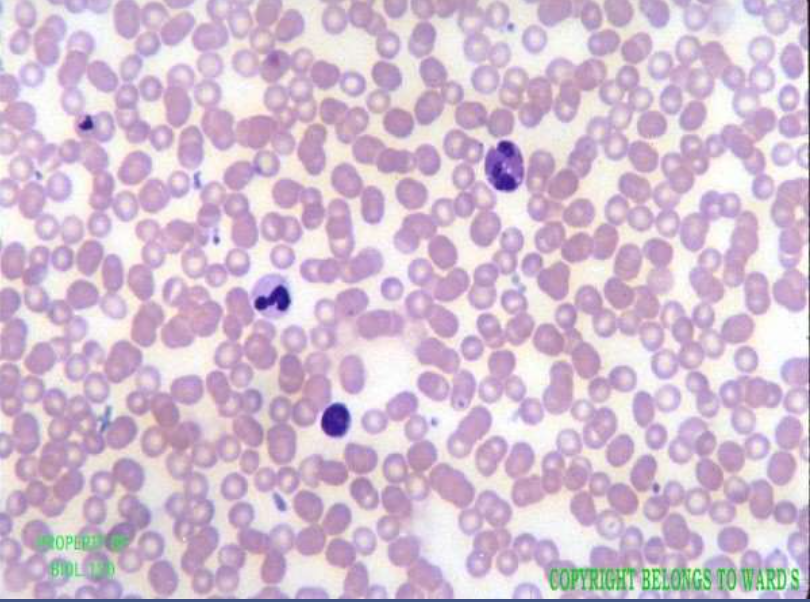
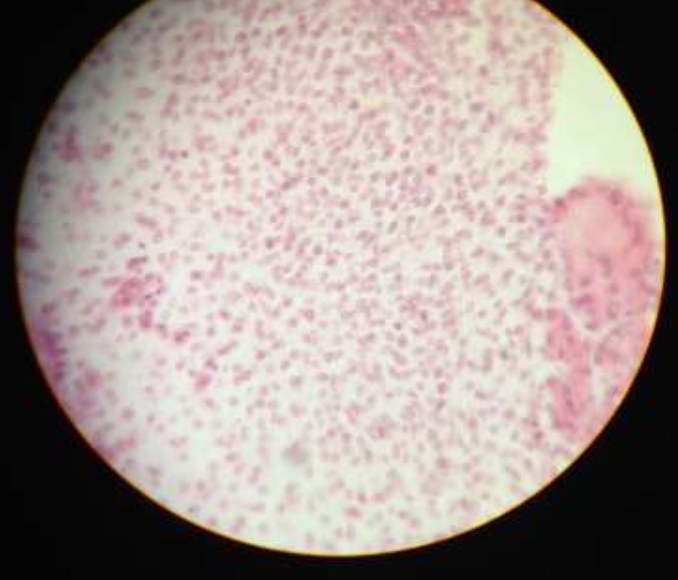
blood:
function: transport respiratory gases, nutrients, and wastes
location: inside blood vessels and the heart
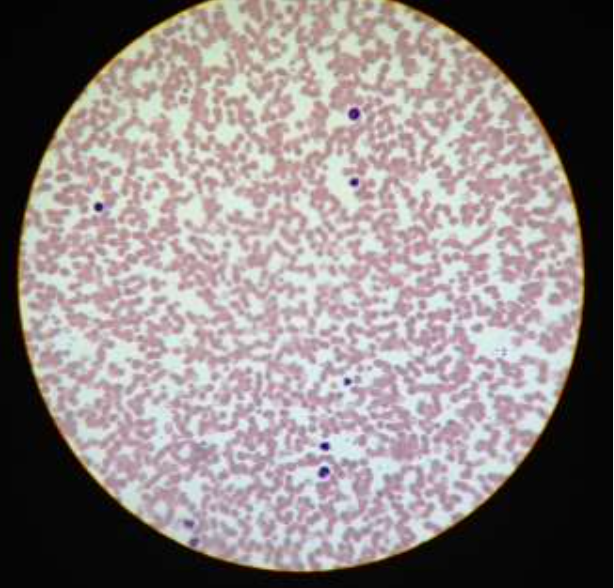
blood:
function: transport respiratory gases, nutrients, and wastes
location: inside blood vessels and the heart
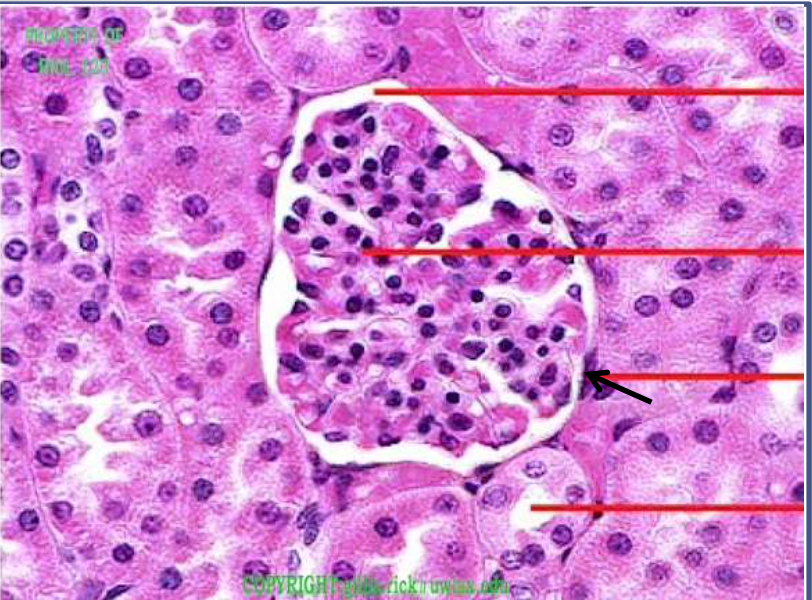
epithelium: simple squamous (bowman's capsule from kidney)
function: allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration
location: in bowman's capsule of the kidney, alveoli of the lungs
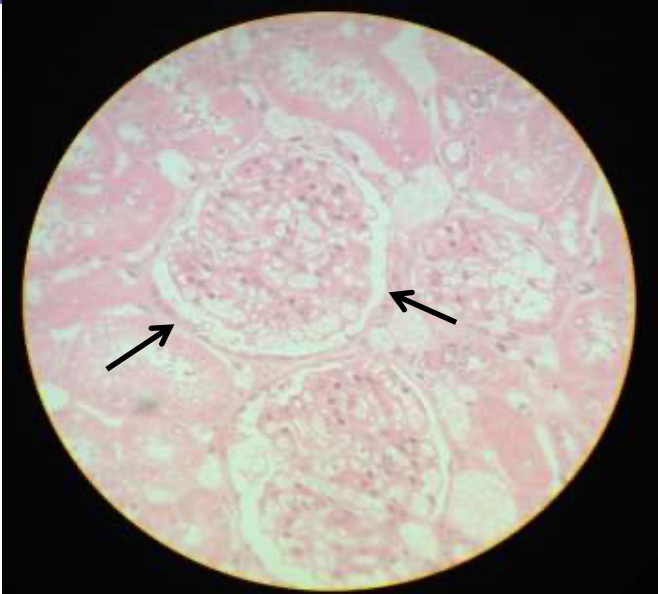
epithelium: simple squamous (bowman's capsule from kidney)
function: allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration
location: in bowman's capsule of the kidney, alveoli of the lungs
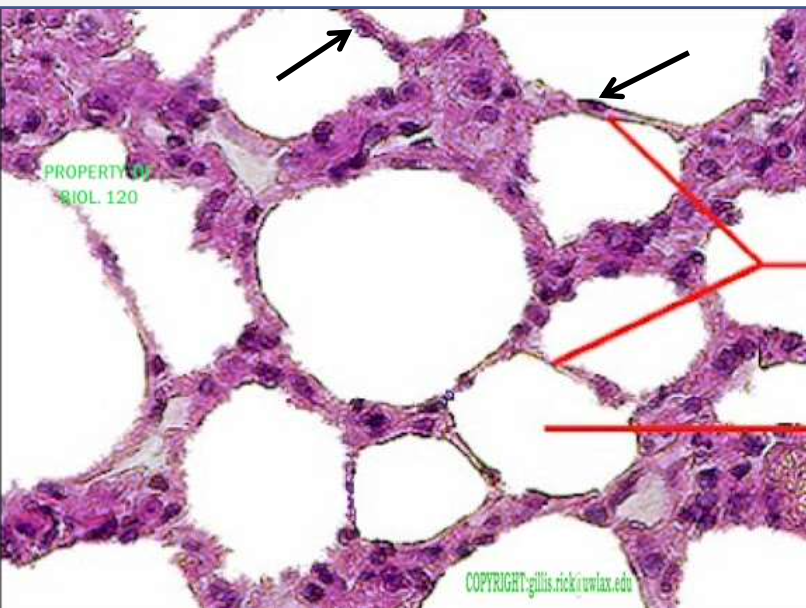
epithelium: simple squamous (alveoli from lungs)
function: allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration
location: in bowman's capsule of the kidney, alveoli of the lungs
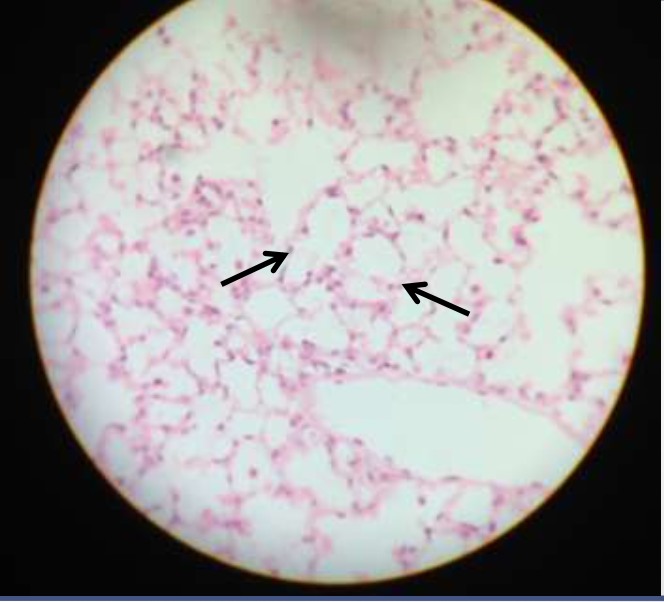
epithelium: simple squamous epithelium (alveoli from lungs)
function: allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration
location: in bowman's capsule of the kidney, alveoli of the lungs
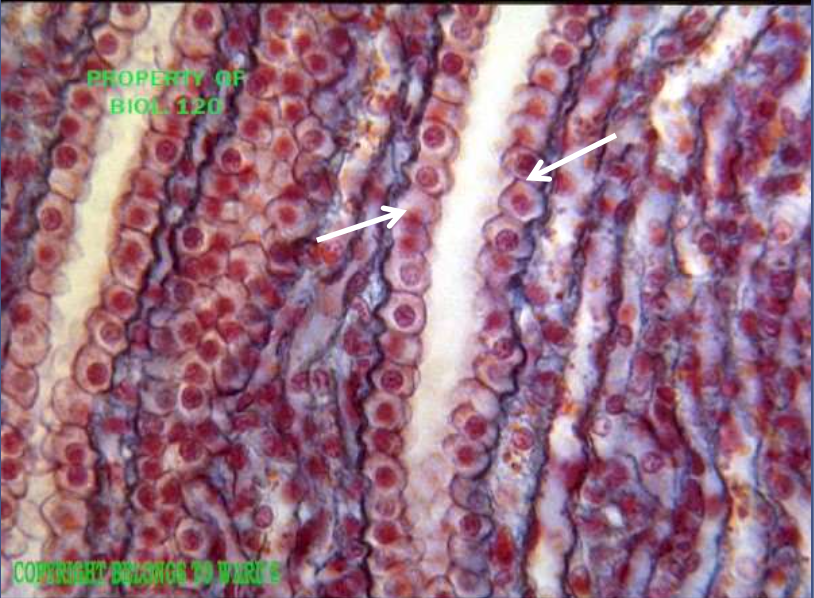
epithelium: simple cuboidal epithelium
function: absorption and secretion
location: kidney tubules, ovary surface
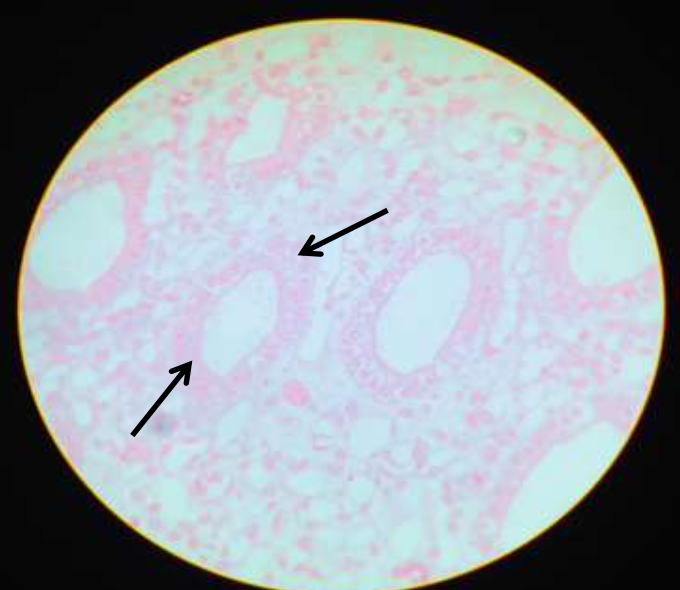
epithelium: simple cuboidal epithelium
function: secretion and absorption
location: kidney tubules, ovary surface
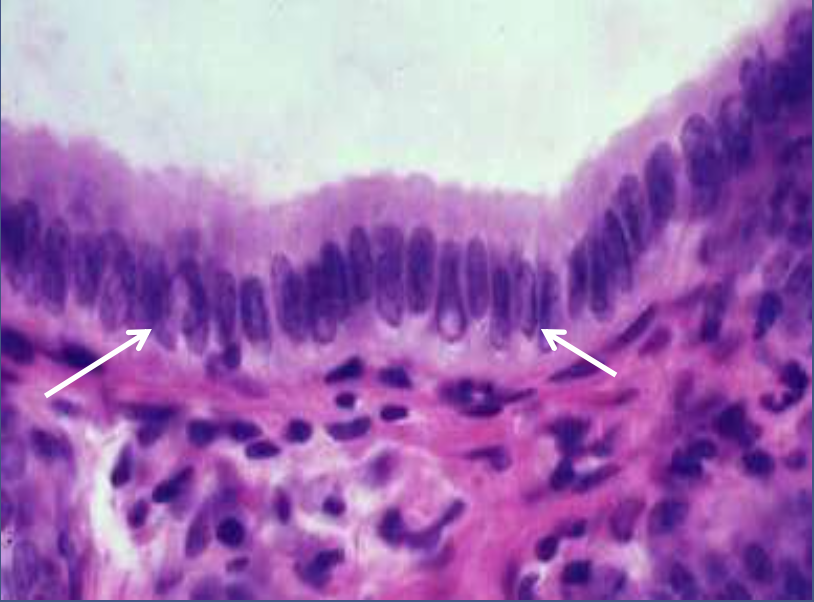
epithelium: (ciliated) simple columnar epithelium
function: secretion of mucus, and to propel mucus
location: digestive tract
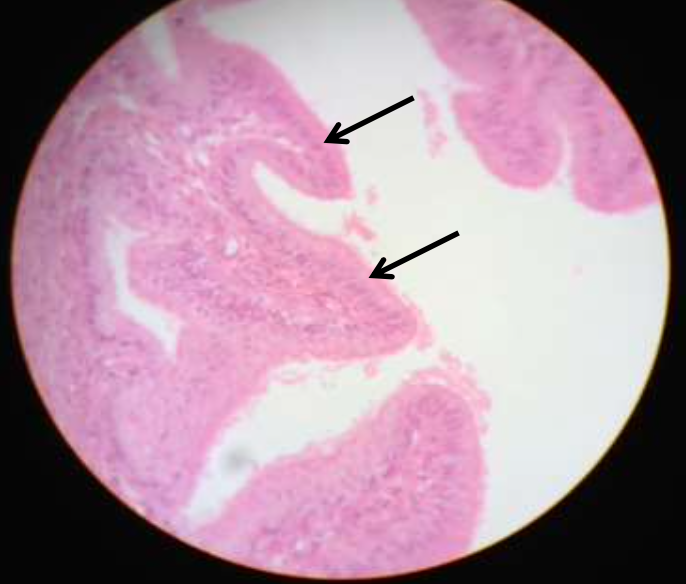
epithelium: (ciliated) simple columnar epithelium
function: secretion of mucus and propelling of mucus
location: digestive tract
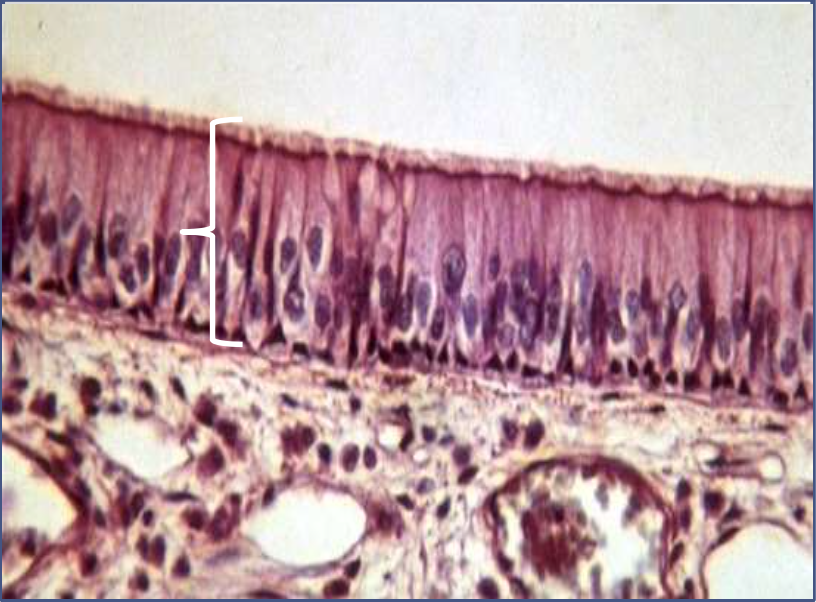
epithelium: (ciliated) pseudostratified columnar epithelium
function: secretion of mucus, pushing of mucus
location: trachea
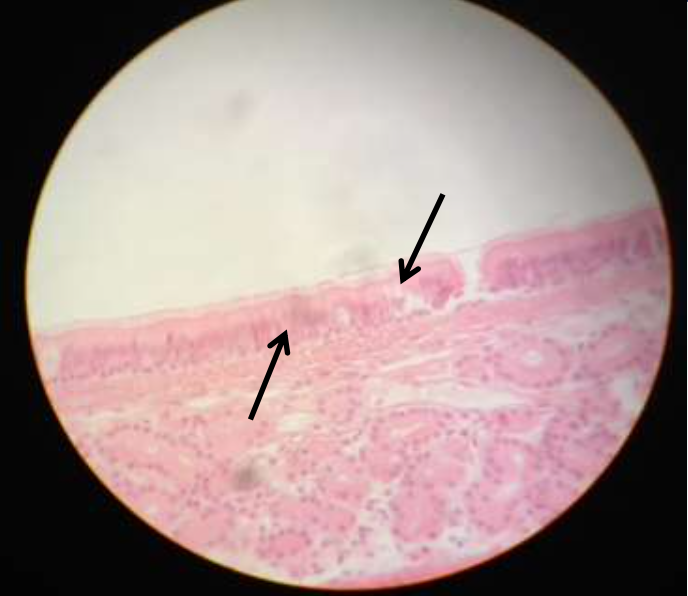
epithelium: ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
function: secretion of mucus, pushing of mucus
location: trachea
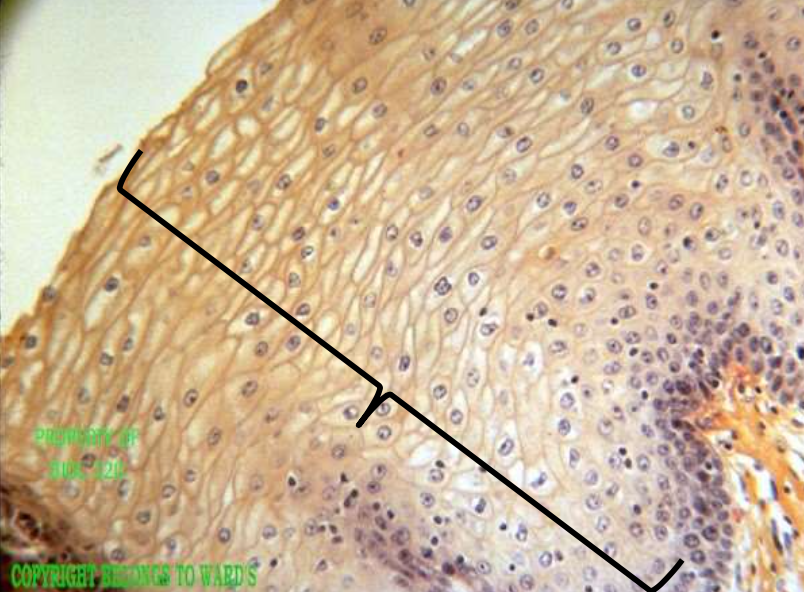
epithelium: stratified squamous epithelium
function: protects underlying areas
location: mouth, vagina
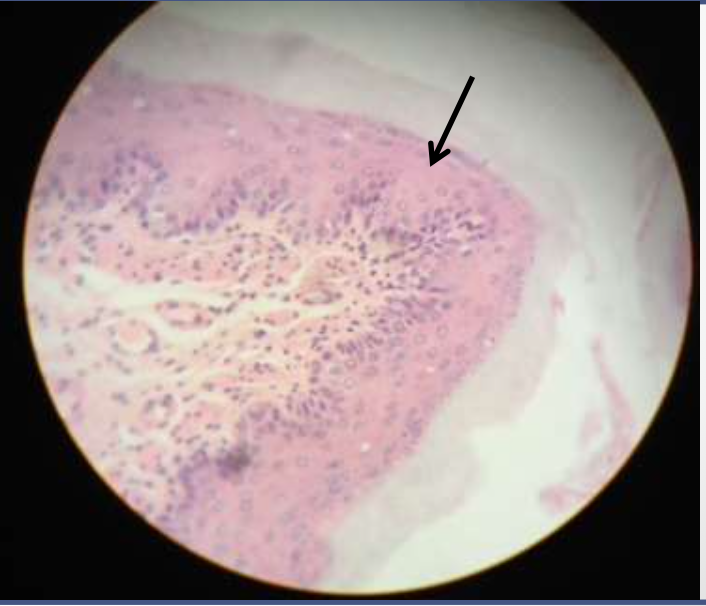
epithelium: stratified squamous epithelium
function: protects underlying areas
location: mouth, vagina
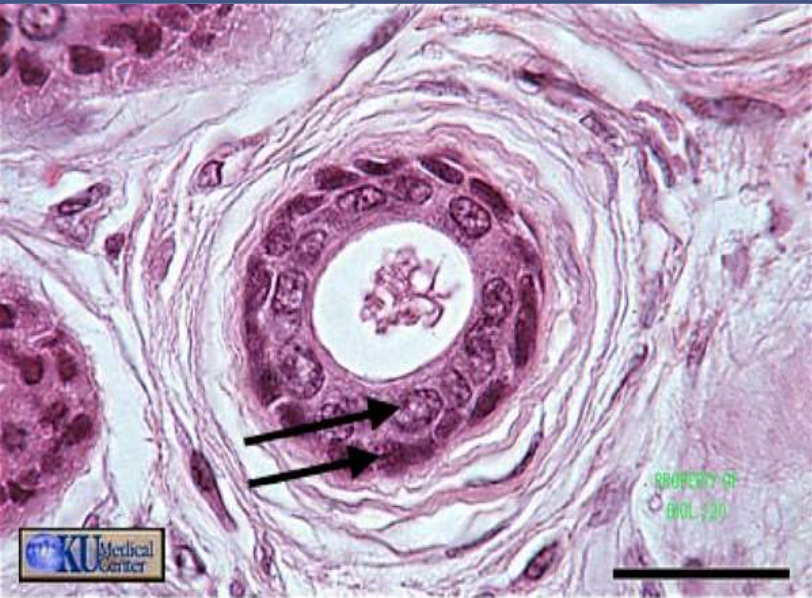
epithelium: stratified cuboidal epithelium
function: protection and secretion
location: male urethra
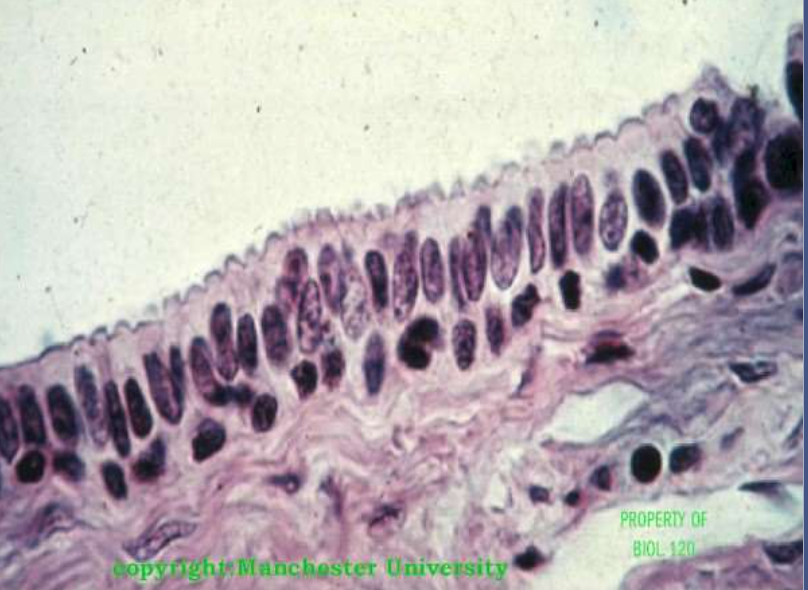
epithelium: stratified cuboidal epithelium
function: protection and secretion
location: male urethra
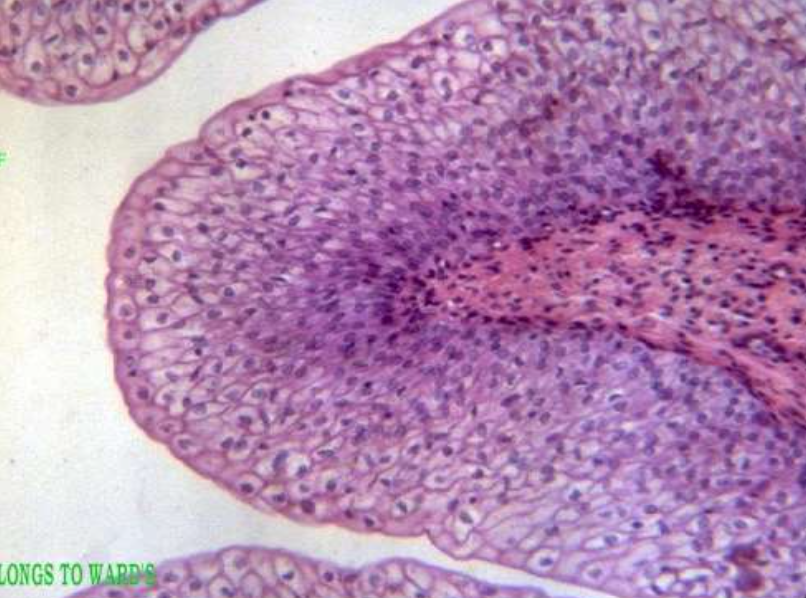
epithelium: transitional epithelium
function: stretches bladder
location: urinary bladder
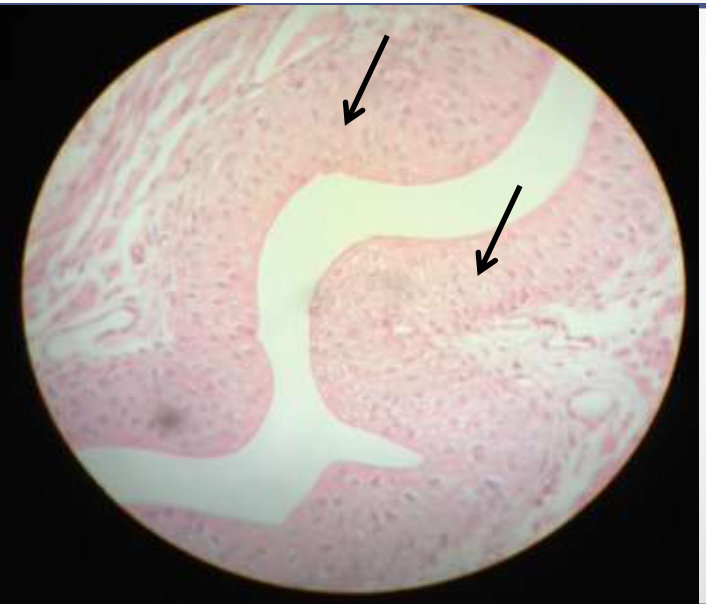
epithelium: transitional epithelium
function: stretches bladder
location: urinary bladder
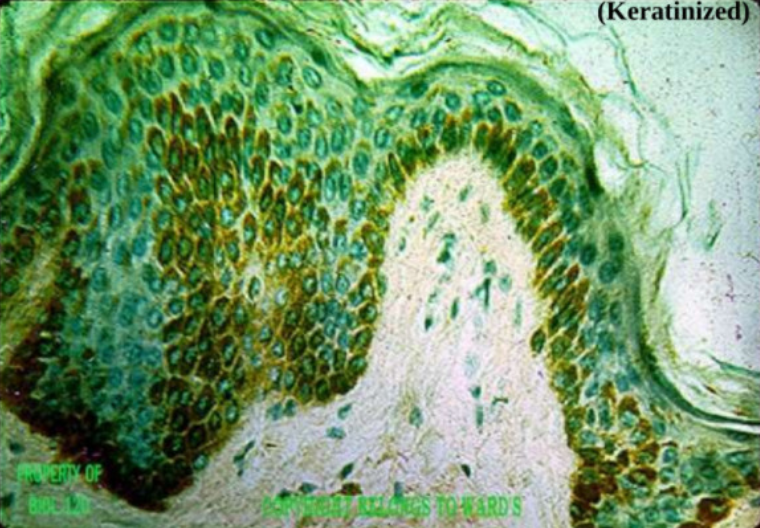
epithelium: stratified squamous epithelium (keratinized)
function: protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion
location: epidermis of skin
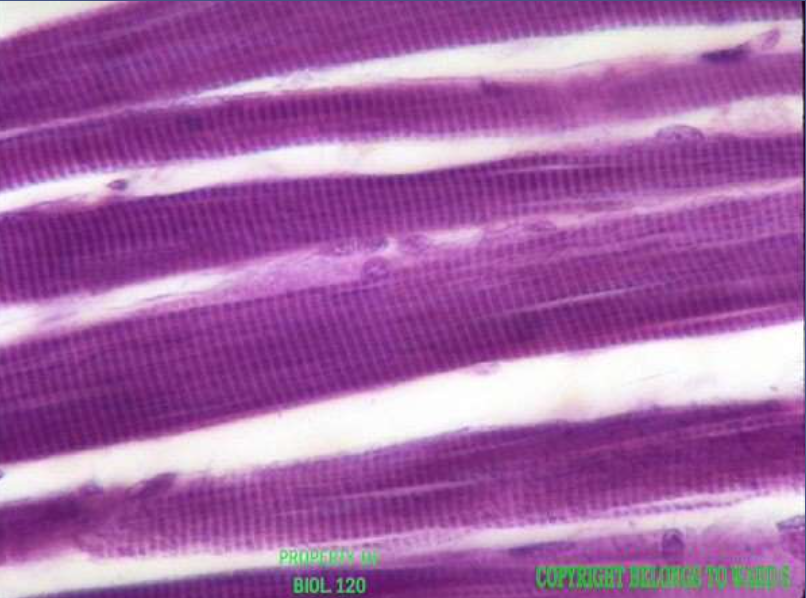
muscle: skeletal muscle
function: voluntary movement, locomotion, facial expression
location: attached to bones or skin
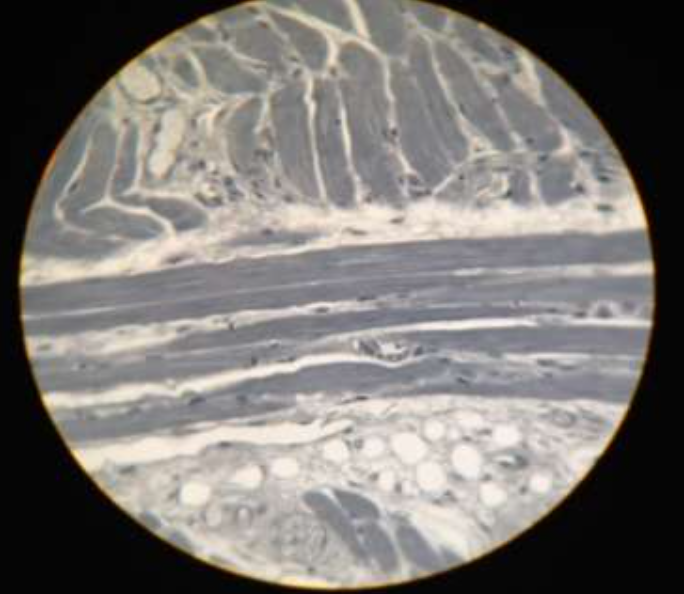
muscle: skeletal muscle
function: voluntary movement, locomotion, facial expression
location: attached to bones or skin
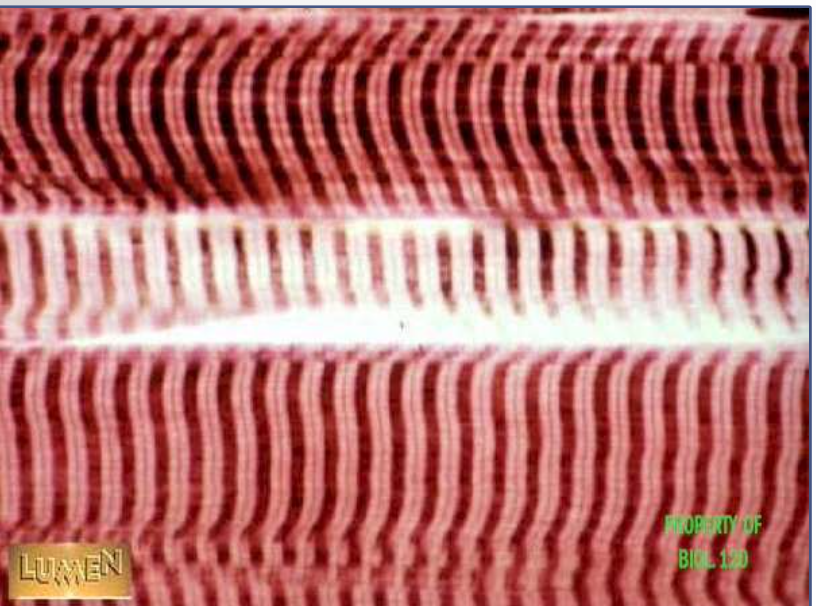
muscle: skeletal muscle
function: voluntary movement, locomotion, facial expression
location: attached to bones or skin
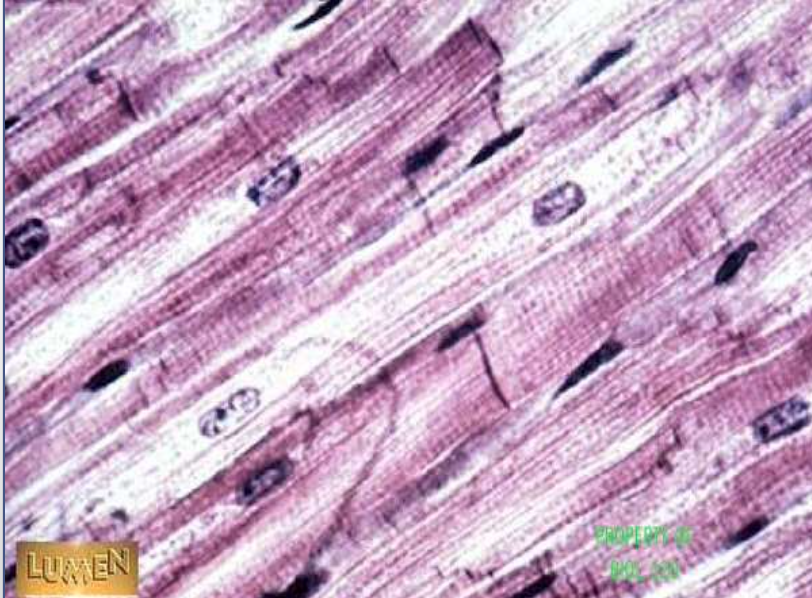
muscle: cardiac muscle
function: involuntary propelling of blood into circulation
location: walls of the heart
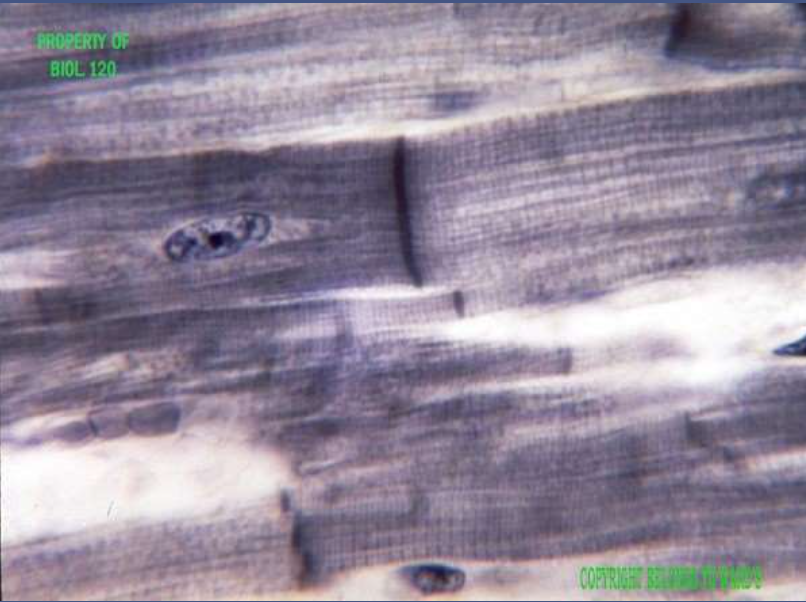
muscle: cardiac muscle
function: involuntary propelling of blood into circulation through blood vessels
location: walls of the heart
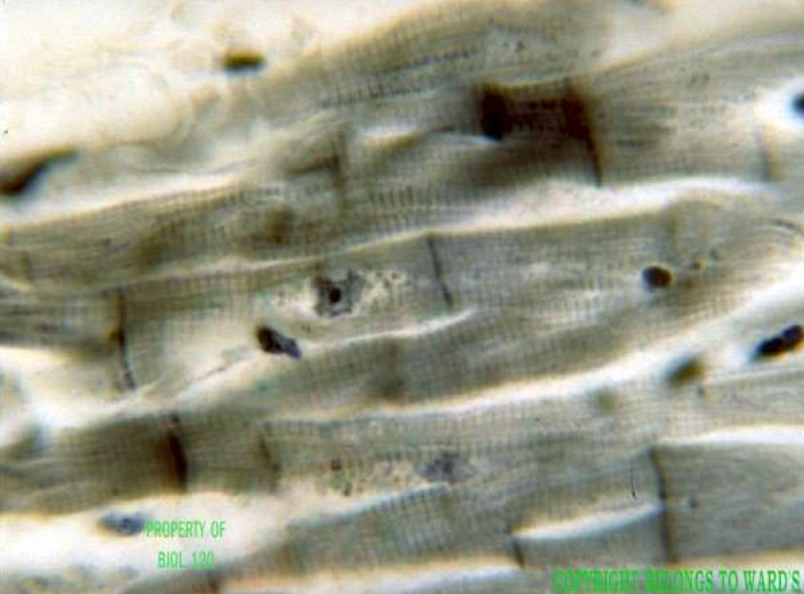
muscle: cardiac muscle
function: involuntary propelling of blood into circulation through blood vessels
location: walls of the heart
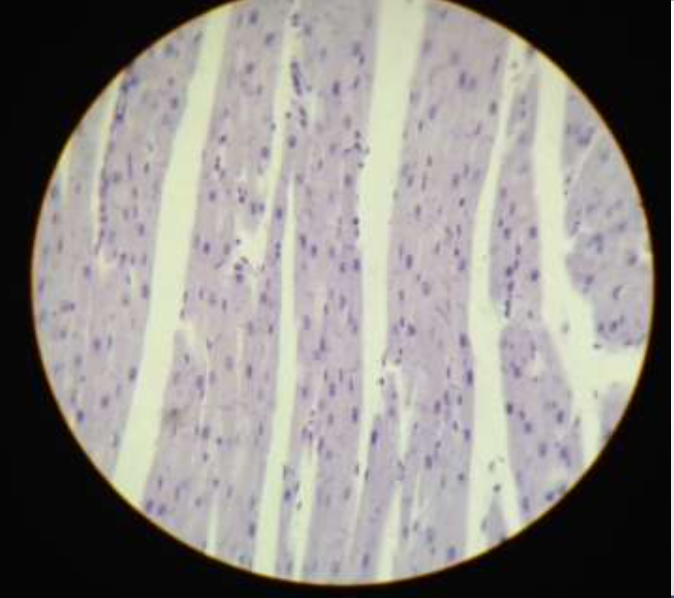
muscle: cardiac
function: involuntary propelling of blood into circulation through blood vessels
location: walls of the heart
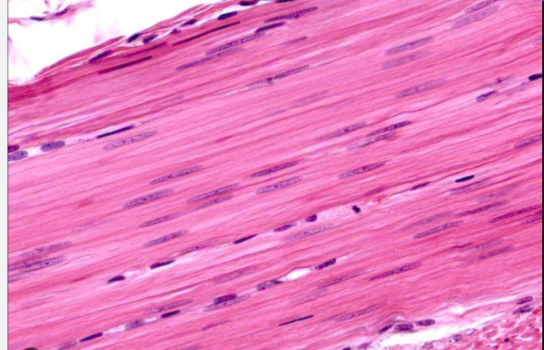
muscle: smooth muscle
function: involuntary propelling of substances along passageways
location: blood vessels
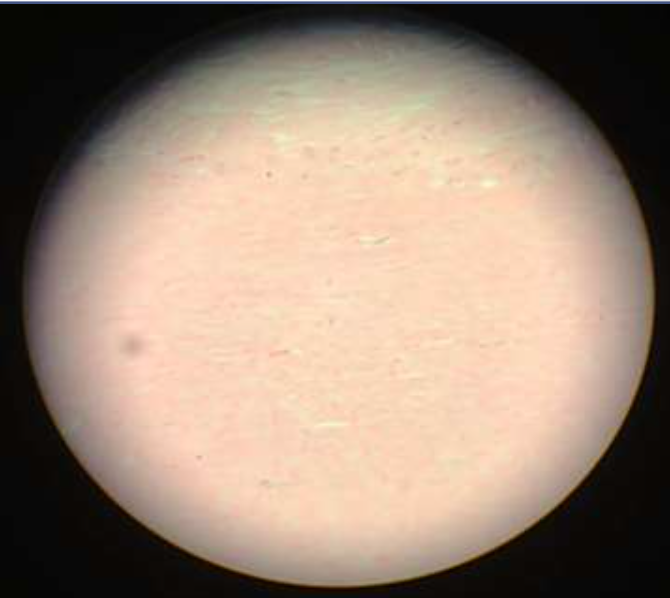
muscle: smooth muscle
function: involuntary propelling of substances along passageways
location: blood vessels
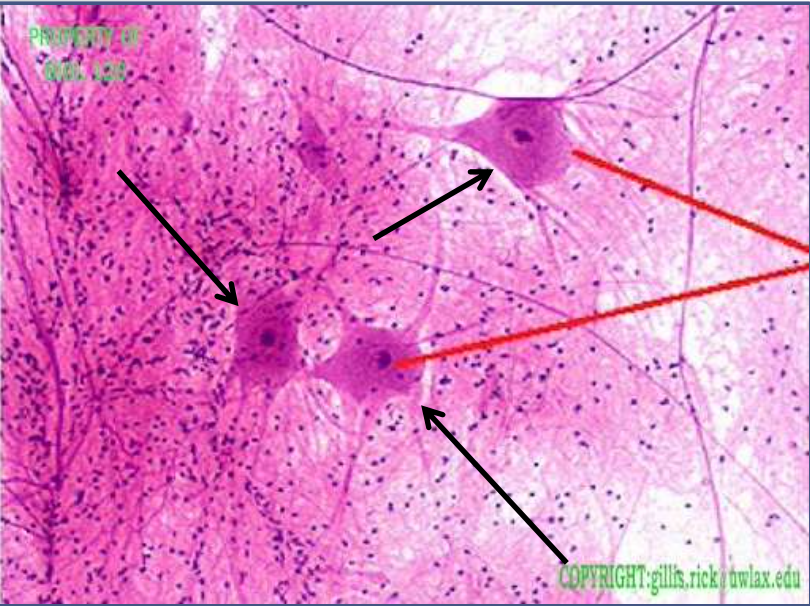
nervous: multi-polar motor neuron
function: transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors to effectors
location: in the brain, spinal cord, and nerve/tracts
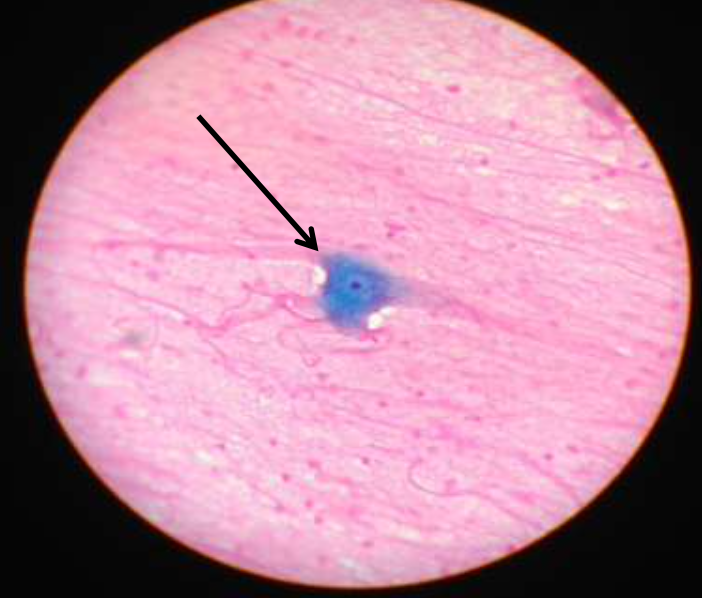
nervous: multi-polar motor neuron
function: transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors to effectors
location: in the brain, spinal cord, and nerve/tracts
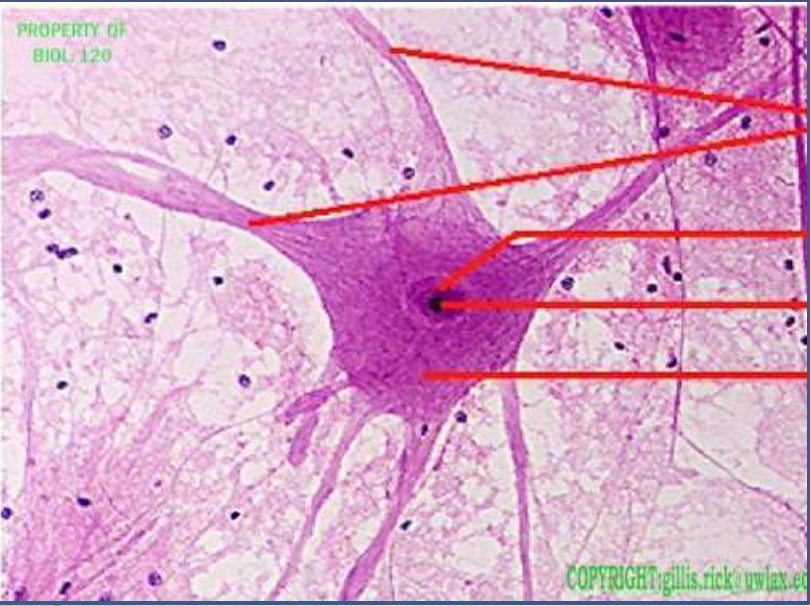
nervous: multi-polar motor neuron
function: transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors to effectors
location: in the brain, spinal cord, and nerve/tracts
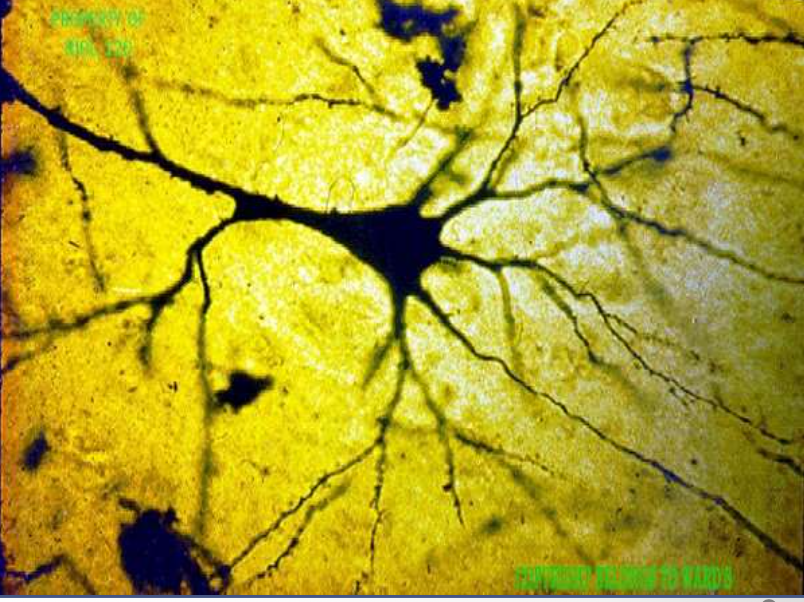
nervous: pyramidal neuron
function: transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors to effectors
location: in the brain, spinal cord, and nerve/tracts
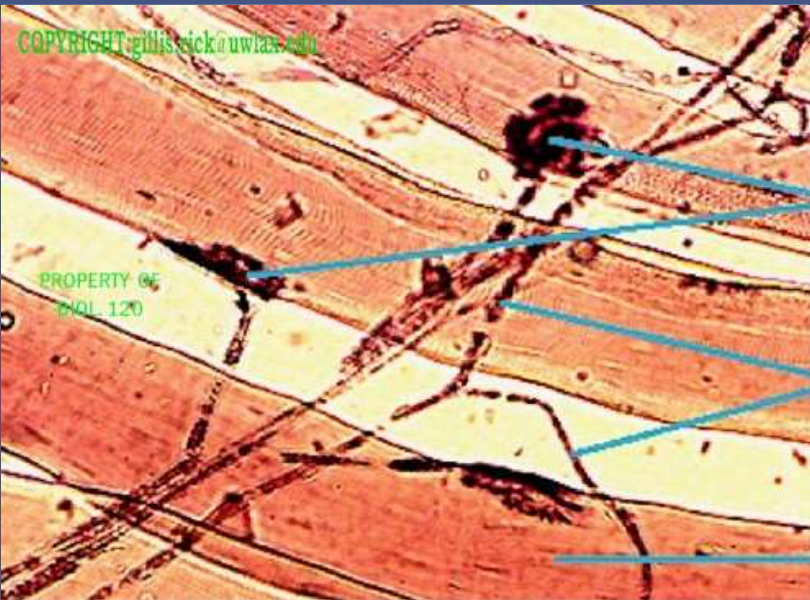
muscle + nervous : skeletal muscle and neuron
function: nerve impulses lead to muscle contraction
location: neuromuscular junction
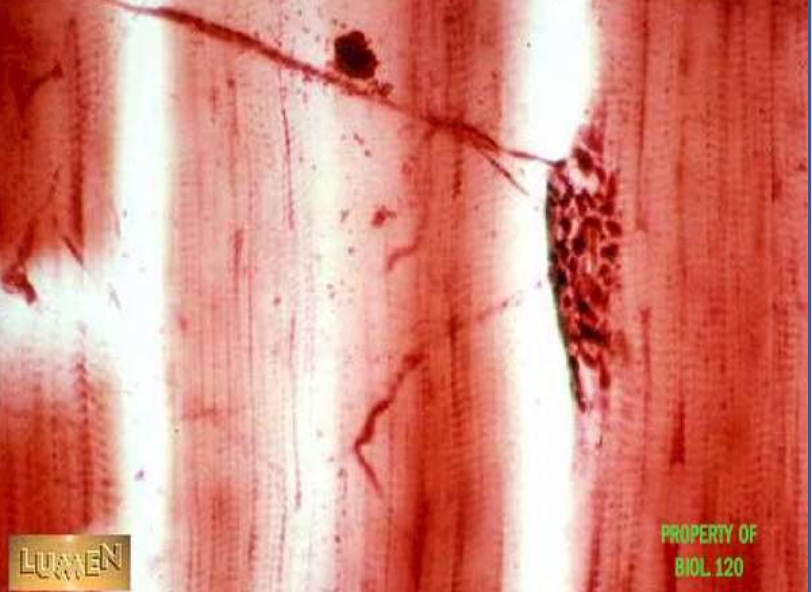
muscle + nervous : skeletal muscle and neuron
function: nerve impulses lead to muscle contraction
location: neuromuscular junction
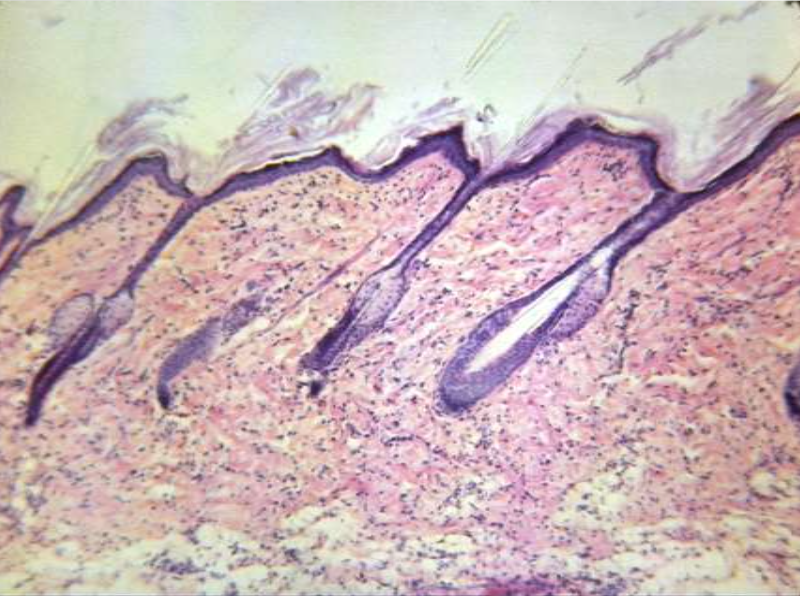
integument (skin), epidermal, dermal:
function: protection from surroundings; mechanical, thermal, chemical, bacteria. protects against losing water, produces vitamin D, protect against UV rays from sun
location: outer layers of body
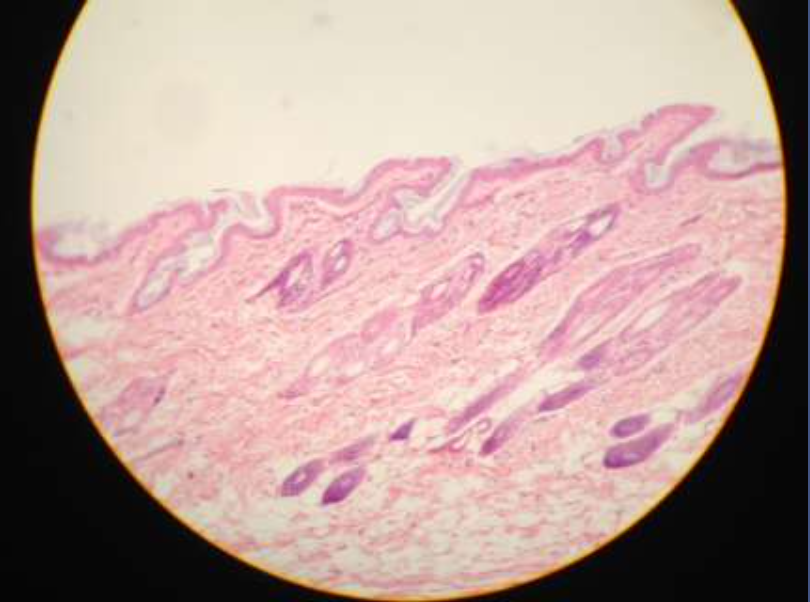
integument (skin), epidermal, dermal:
function: protection from surroundings; mechanical, thermal, chemical, bacteria. protects against losing water, produces vitamin D, protect against UV rays from sun
location: outer layers of body
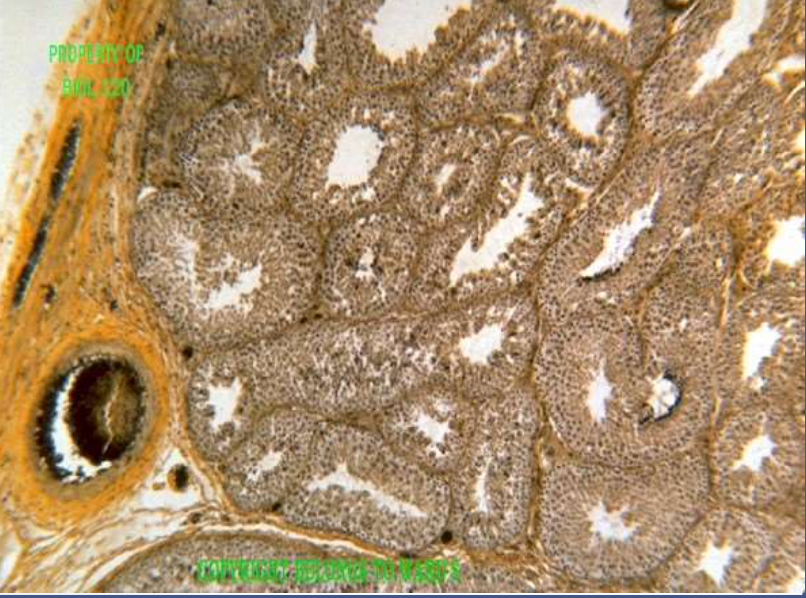
structure: seminiferous tubules
function: produce sperm, the male gamete
location: testis
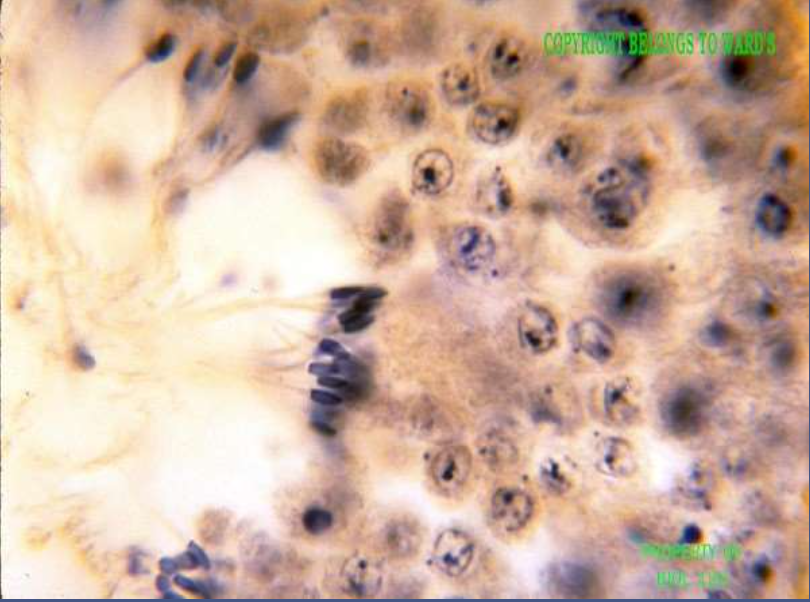
structure: lumen of seminiferous tubules
function: produce sperm, the male gamete
location: testis
structure: lumen of seminiferous tubules
function: produce sperm, the male gamete
location: testis
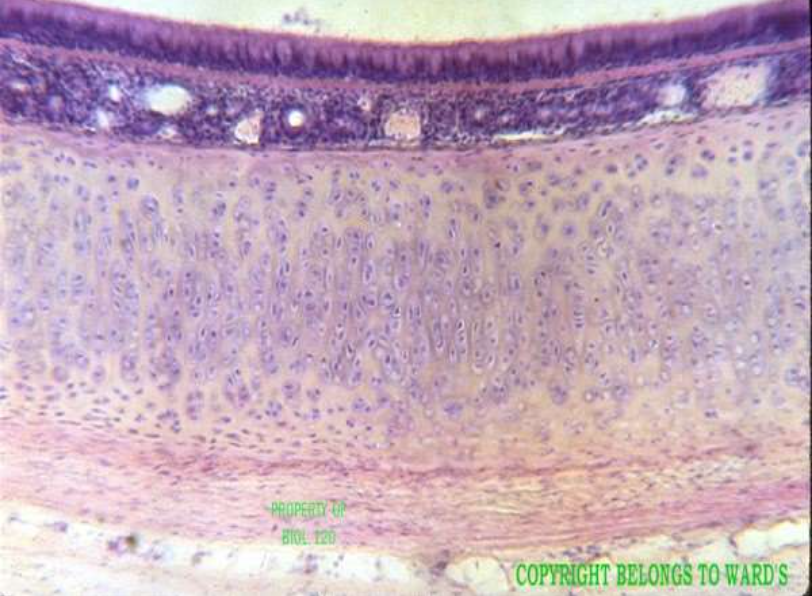
type: mucous membrane
function: line cavities and secrete mucus by goblet cells
location: trachea, digestive tract
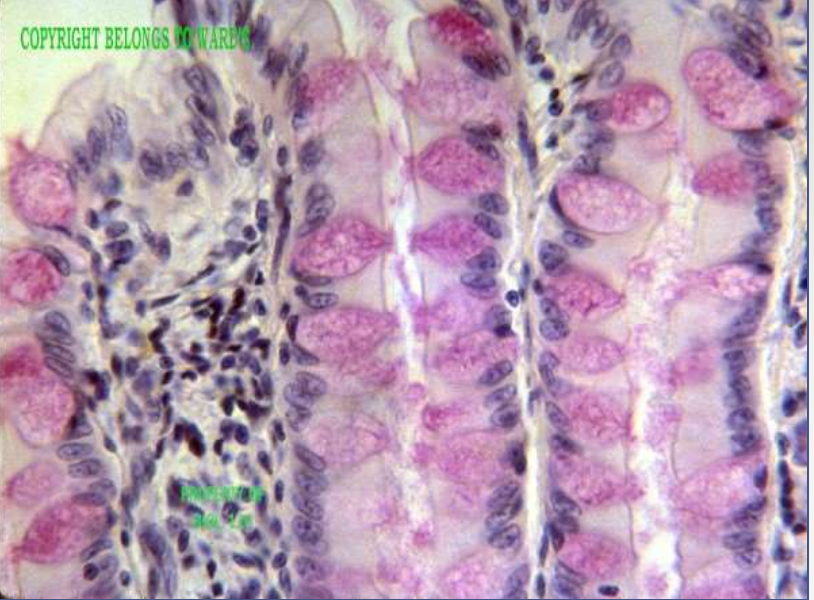
type: mucous membrane
function: line cavities and secrete mucus by goblet cells
location: trachea, digestive tract
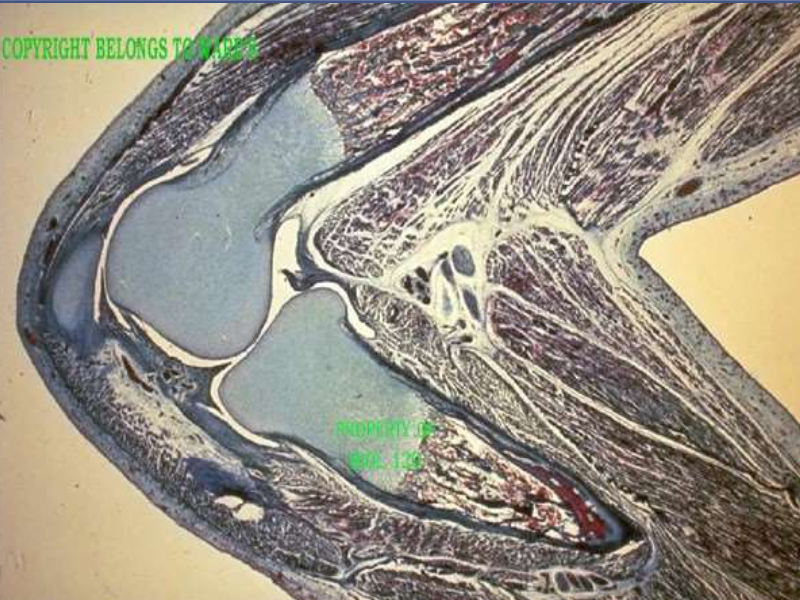
type: knee, synovial membrane
function: line cavities surrounding joints, lubricates to reduce friction
location: knees, elbows
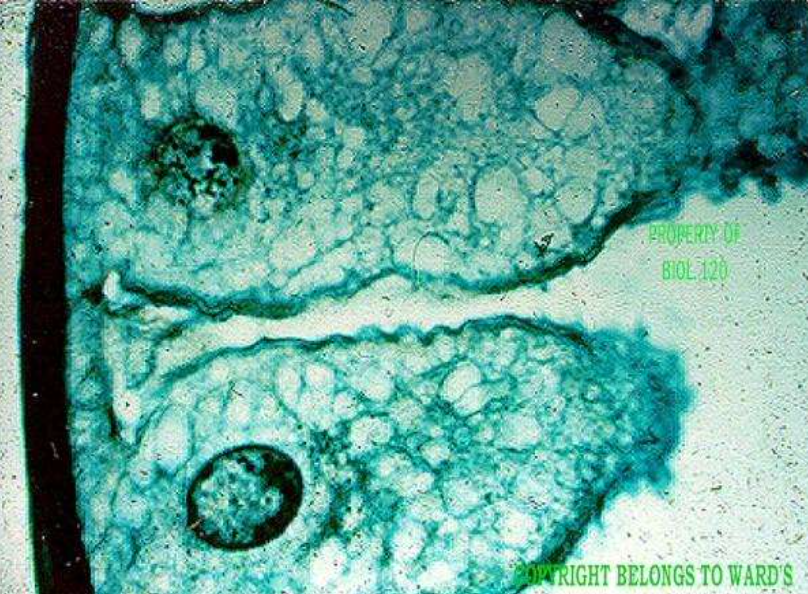
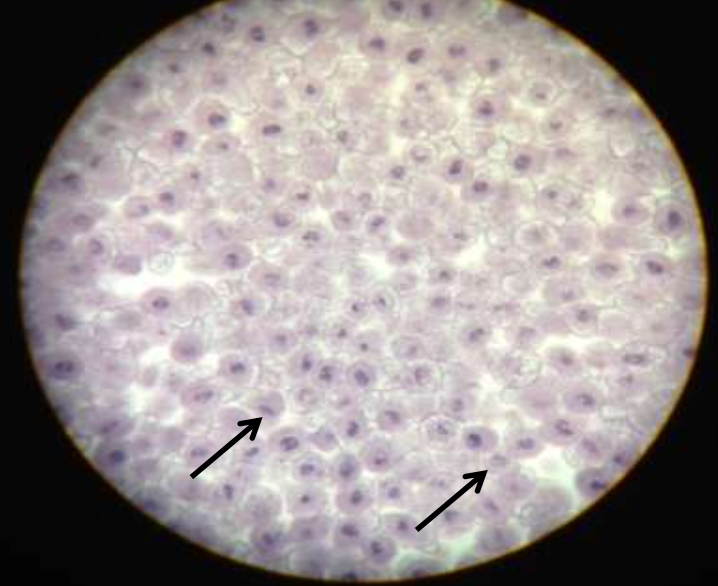
mitotic stage: interphase (not a mitotic stage)
what's happening: the cell grows, DNA is replicated
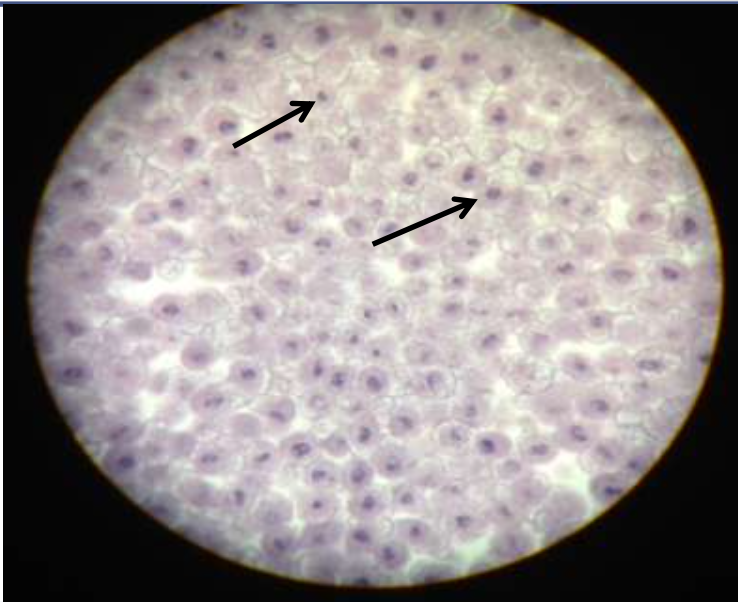
mitotic stage: interphase (not a mitotic stage)
what's happening: the cell is growing, DNA is replicated
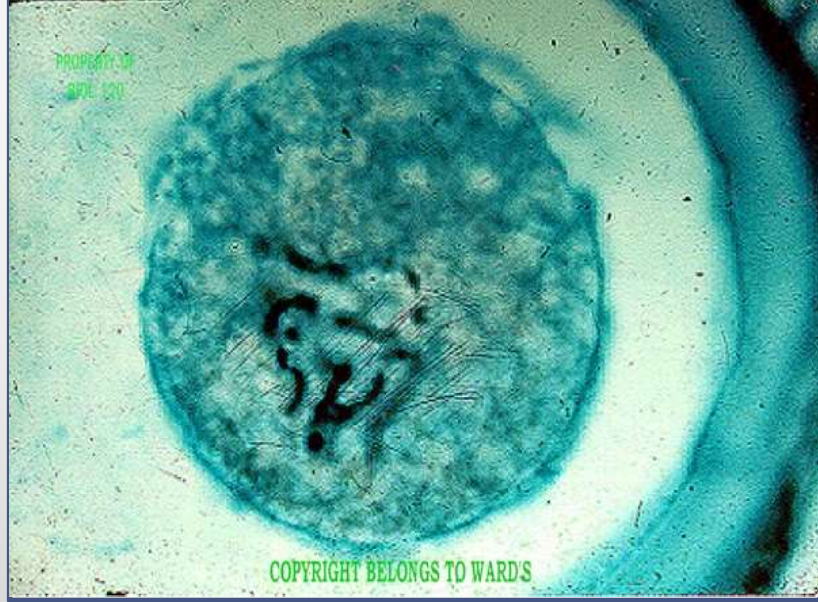
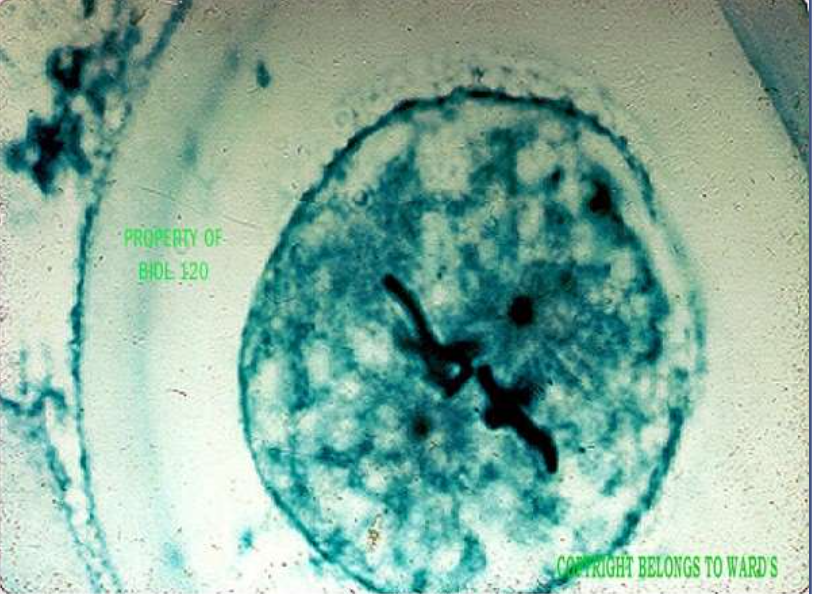
mitotic stage: prophase
what’s happening: chromosomes form, start of the mitotic spindle
mitotic stage: prophase
what’s happening: chromosomes form, start of the mitotic spindle
mitotic stage: metaphase
what's happening: replicated chromosomes line up one on top of the other (north to south) at the metaphase plate
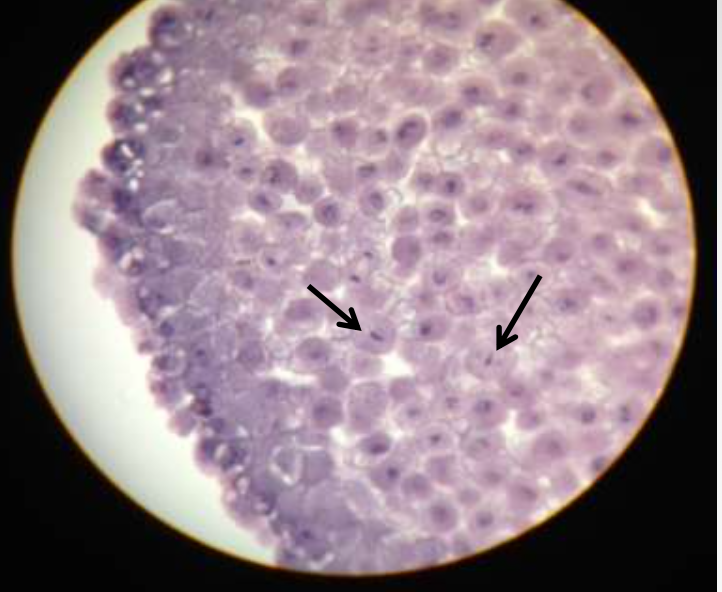
mitotic stage: metaphase
what's happening: replicated chromosomes line up one on top of the other (north to south) at the metaphase plate
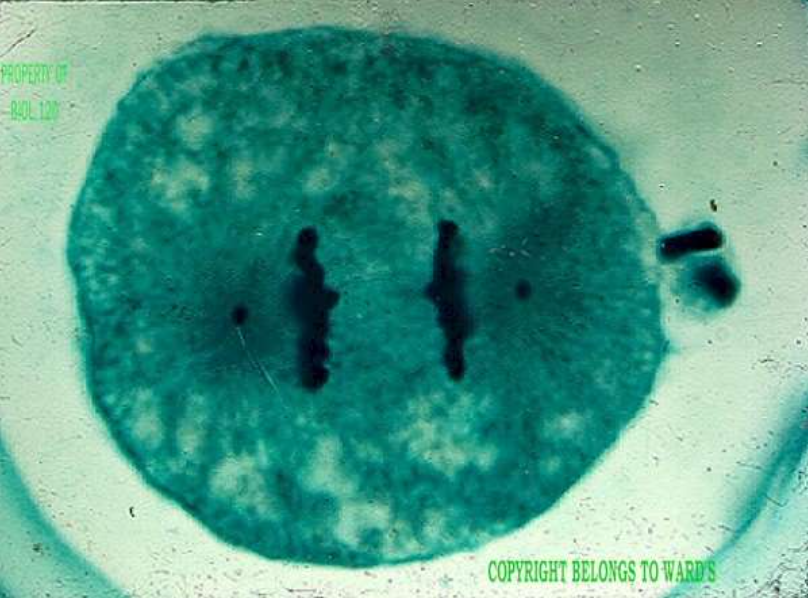
mitotic stage: anaphase
what's happening: the chromatids are pulled apart and cleavage furrow begins at the end.
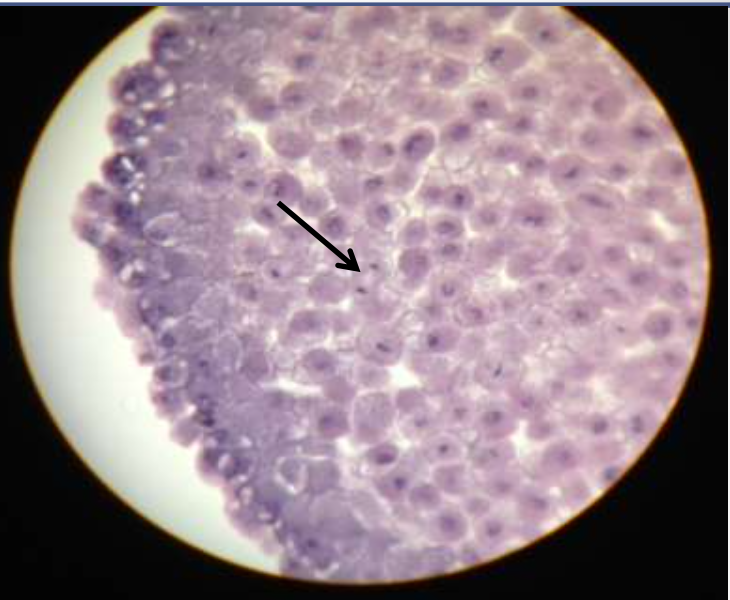
mitotic stage: anaphase
what's happening: the chromatids are pulled apart and cleavage furrow begins at the end.
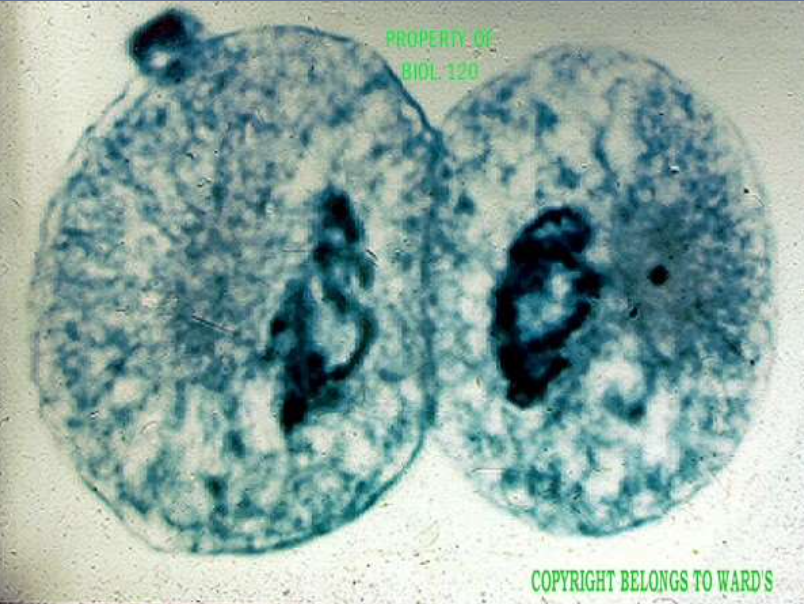
mitotic stage: telophase
what's happening: chromosomes diffuse, the nucleus begins to reform
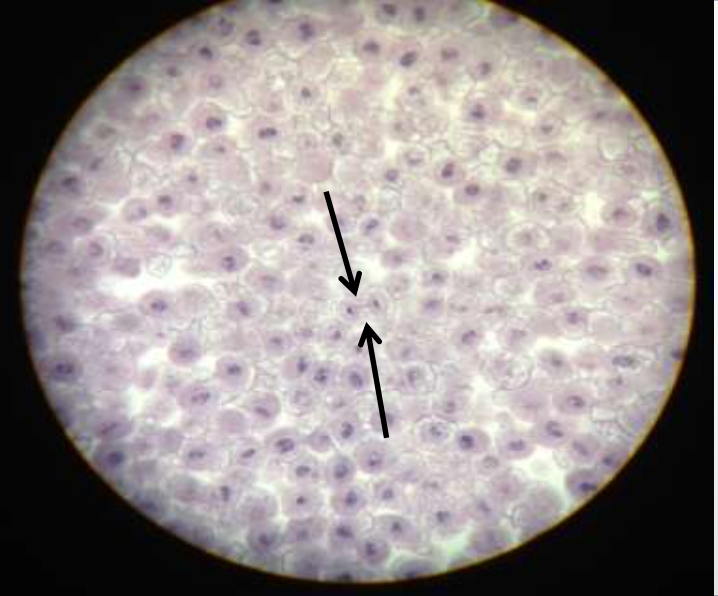
mitotic stage: telophase
what's happening: chromosomes diffuse, the nucleus begins to reform
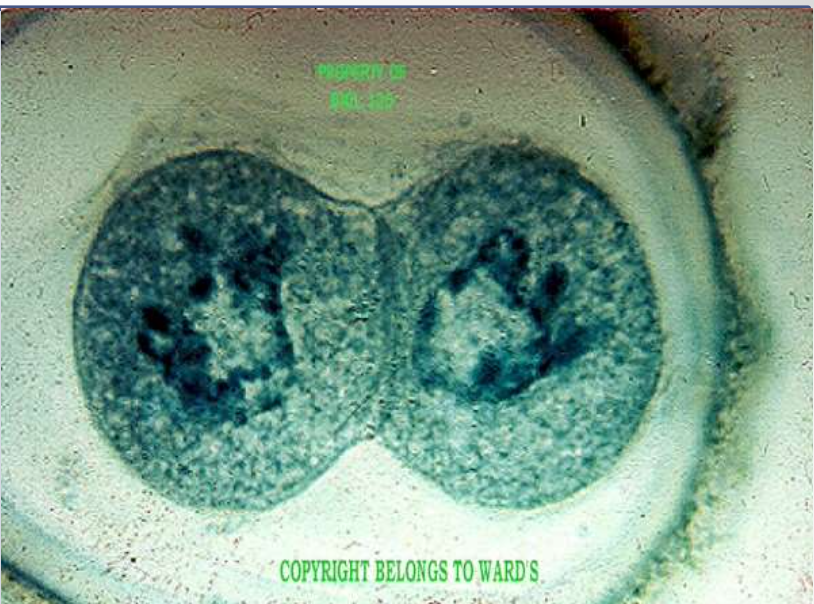
mitotic stage: cytokinesis (not a mitotic stage)
what's happening: cytokinesis is the physical process of cell division, which divides the cytoplasm of a parent cell into two daughter cells
connective tissue: embryonic connective tissue
function: give rise to all other connective tissue
location: mostly in embryo
loose connective tissue: adipose connective tissue
function: provides reserve fuel, insulates against heat loss, supports and protects organs
location: under skin, within abdomen, in breast
loose connective tissue: areolar connective tissue
function: wrap and cushion organs
location: under epithelia of body
loose connective tissue: reticular connective tissue
function: its fibers support white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages
location: in lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, bone marrow, and spleen)
dense connective tissue: dense regular connective tissue
function: withstands tensile stress in one direction; attached muscles to bones, muscles to muscles, bones to bones
location: tendons and most ligaments
dense connective tissue: dense irregular connective tissue
function: withstands tensile stress in many directions
location: dermis of skin
dense connective tissue: elastic dense connective tissue
function: allows recoil of tissue following stretching
location: walls of large arteries
what are the 6 connective tissue propers?
adipose, areolar, reticular, dense regular, dense irregular, and elastic
cartilage: hyaline
function: cushions, resist compressive stress
location: nose, trachea
cartilage: elastic
function: maintains shape of structure while allowing flexibility
location: external ear, epiglottis
cartilage: fibrocartilage
function: tensile strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock
location: discs of knee joint
bone
function: supports and protects, stores calcium and fat; the marrow inside bones is the site for blood cell formation
location: bones
blood
function: transport respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes
location: inside blood vessels and the heart
epithelial tissue: simple squamous epithelium (bowman’s capsule from kidney)
function: allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration
location: in bowman's capsule of the kidney, alveoli of the lungs
epithelial tissue: simple squamous epithelium (alveoli from lungs)
function: allows passage of materials by diffusion and filtration
location: in bowman's capsule of the kidney, alveoli of the lungs
epithelial tissue: simple cuboidal epithelium
function: secretion and absorption
location: kidney tubules, ovary surface
epithelial tissue: ciliated simple columnar epithelium
function: secretion of mucus, propelling of mucus
location: digestive tract
epithelial tissue: ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
function: secretion of mucus, propelling of mucus
location: trachea
epithelial tissue: stratified squamous epithelium
function: protects underlying areas
location: mouth, vagina
epithelial tissue: stratified squamous epithelium (the green one)
function: protects underlying tissues in areas subjected to abrasion
location: epidermis of skin (keratinized)
epithelial tissue: stratified cuboidal epithelium
function: protection and secretion
location: male urethra
epithelial tissue: transitional epithelium
function: stretches bladder
location: urinary bladder
muscle tissue: skeletal muscle tissue
function: voluntary movement, locomotion, facial expression
location: attached to bones or skin
muscle tissue: cardiac muscle tissue
function: involuntary propelling of blood into circulation through blood vessels
location: walls of the heart
muscle tissue: smooth muscle tissue
function: involuntary propelling of substances along passageways
location: blood vessels
nervous tissue: multi polar motor tissue
function: transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors to effectors
location: in the brain, spinal cord, and nerve/tracts