Lab Exam #2 (Spring 2022)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Sustained maximal contraction of skeletal muscle due to repetitive stimulation is called _________________.
A) twitch
B) summation
C) muscle fatigue
D) recruitment
E) tetanus
E) tetanus
Which muscle cells are striated and have multiple nuclei?
A) smooth muscle
B) skeletal muscle
B) skeletal muscle
The amount of stimulus necessary to elicit a maximal response in skeletal muscle is called _________________.
A) threshold stimulus
B) suprathreshold stimulus
C) submaximal stimulus
D) maximal stimulus
D) maximal stimulus
Which procedure do we use to measure electrical activity of skeletal muscle?
A) electromyogram (EMG)
B) blood typing
C) RBC differential
D) electrocardiogram (ECG)
E) force transducer
A) electromyogram (EMG)
Contraction of a muscle leads to more minor activity in the antagonist muscle. This process is called _________________.
A) recruitment
B) coactivation
C) conduction velocity
D) summation
E) visual feedback
B) coactivation
In one of the muscle contraction labs, we measured the effects of brief rest, visual feedback, and verbal encouragement on grip force.
A) True
B) False
A) True
The speed at which an electrical impulse travels along a nerve, measured in m/s, is called the contraction strength.
A) True
B) False
B) False
What is another name for red blood cells?
A) leukocytes
B) hemoglobin
C) erythrocytes
D) antigens
E) WBCs
C) erythrocytes
Oxygen is transported in the blood.
A) True
B) False
A) True
Reduced oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood is called _________________.
A) agglutination
B) jaundice
C) inflammation
D) fatigue
E) anemia
E) anemia
The average volume of a red blood cell is called mean corpuscular volume (MCV).
A) True
B) False
A) True
In the blood, the cell fragments involved in blood clotting are called _________________.
A) white blood cells
B) antigens
C) antibodies
D) platelets
E) red blood cells
D) platelets
The process of listening to the sounds of the body is called auscultation.
A) True
B) False
A) True
During auscultation of blood pressure, when the Korotkoff sounds are first heard, _________________ blood pressure is measured.
A) diastolic
B) pulse
C) mean arterial
D) systolic
D) systolic
"Lub" and "dub" are the heart sounds.
A) True
B) False
A) True
Where is the radial pulse measured?
A) at the heart
B) at the elbow
C) at the wrist
D) in the upper arm
C) at the wrist
What equipment did we use to measure finger pulse?
A) cardiomicrophone
B) isolated stimulator
C) sphygmomanometer
D) stethoscope
E) pulse transducer
E) pulse transducer
Which of the following increases heart rate?
A) parasympathetic nervous system
B) sympathetic nervous system
C) somatic nervous system
B) sympathetic nervous system
Connections between arteries supplying the same tissue or organ are called _________________.
A) vasoconstriction
B) venous valves
C) agglutination
D) arterial anastomoses
D) arterial anastomoses
Briefly explain the difference between a muscle fiber and a muscle fascicle.
Muscle fiber: consist of a single muscle cell, helps to control the physical forces within the body
Muscle fascicle: bundle of muscle fibers, provides pathways for the passage of blood vessels and nerves
In Lab 6, how did we cause muscle fatigue to occur in the volunteer? Besides the PowerLab and LT Lab Station, what piece of equipment was used to elicit and measure muscle fatigue, and what did the volunteer do to cause muscle fatigue?
- We caused muscle fatigue to occur from previous muscle contractions.
- A force transducer was used to elicit and measure muscle fatigue.
- The volunteer gripped the force transducer as hard as they could in a given amount of time to cause muscle fatigue.
In the hematology lab, you measured hematocrit in a sheep blood sample. Define hematocrit and then briefly explain the methods you used to measure hematocrit.
- Hematocrit: ratio of volume of packed RBCs to total blood volume
- Using blood from a sheep sample, after the hematocrit tube has been centrifuged, we analyzed it using a hematocrit reader to determine the hematocrit reading.
If you were looking at white blood cells through a microscope, how would you recognize a monocyte? Briefly describe its appearance.
- Monocyte: large cell with pale cytoplasm and indented nucleus
If a person with Type B blood is given a transfusion of Type A blood, agglutination occurs. Explain why this agglutination occurs.
The agglutination indicates that the blood has reacted with a certain antibody and is therefore not compatible with blood containing that kind of antibody.
How does a sphygmomanometer work?
- It stops blood flow in the brachial artery.
- Then decreasing the pressure in the cuff allows blood flow to resume when cuff pressure matches systolic pressure. Now we hear loud, tapping Korotkoff sounds.
- The Korotkoff sounds stop when the pressure in the cuff matches diastolic pressure, as the pressure in the cuff continues to decrease.
How does the position of the volunteer's arm affect the measurements of blood pressure? Describe how the pressure measured for these two conditions differs from the pressure measured when the arm is at heart level: 1) arm hanging at side, 2) arm above head.
- BP depends on arm position because as hydrostatic pressure changes, the pressure gradient changes (increases or decreases).
- Arm at heart level: regular BP
- Arm hanging at side: hydrostatic pressure & BP are in the same direction towards the finger --> increases systolic pressure
- Arm above head: hydrostatic pressure and blood pressure are in OPPOSITE directions --> decreases the systolic pressure
What is the effect of whole-body moderate exercise on heart rate and on the R-R interval of the electrocardiogram (ECG)? Specifically, how does heart rate change during exercise compared to before exercise? How does the R-R interval immediately after exercise compare to the R-R interval before exercise? You can simply state whether each of these measures increases, decreases, or stays the same, and you don't have to provide the physiological reasons.
The R-R interval decreases because heart rate increases during exercise.
In Lab 5, you used an isolated stimulator to stimulate skeletal muscle to study twitch, summation, and recruitment. Define these three terms and explain the type of stimulation used to cause each of these processes to occur in the volunteer. You don't have to provide the physiological explanation for these processes. You can make a list instead of writing a paragraph.
- Twitch: a single muscle contraction from a single stimulus
- Summation: gathering of several motor units in order to create a strong contraction; leads to tetanus
- Recruitment: rapid stimulation that does not allow a muscle to completely relax, thus creating a increased force
Electrical stimulation, also known as electromyography (EMG) stimulation is a form of stimulation that is used to elicit twitching, summation, and recruitment of muscle fibers to help detect neuromuscular abnormalities.
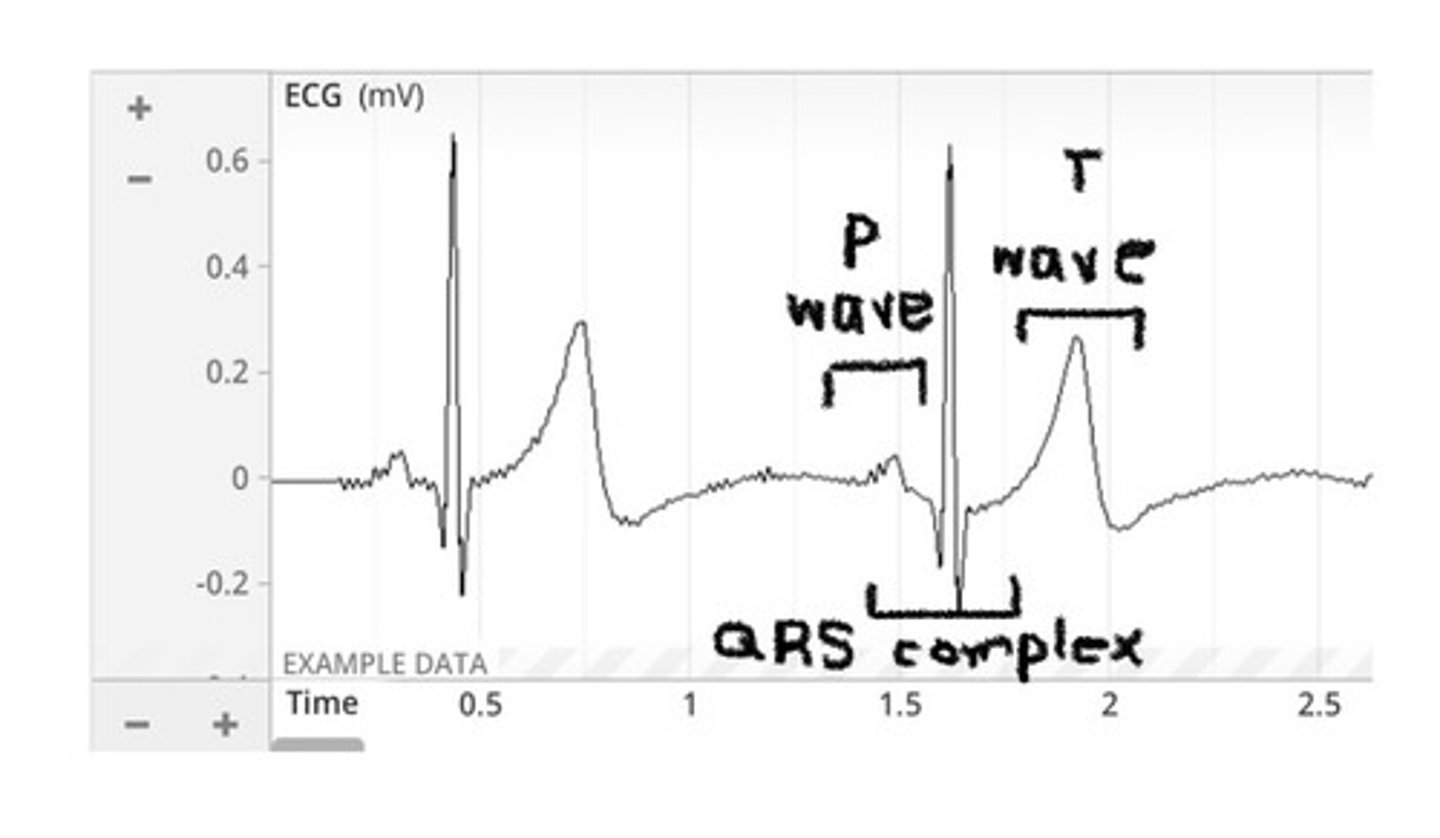
In Lab 9, you recorded the electrocardiogram (ECG). Below is a typical ECG trace measured during rest, showing two cardiac cycles. In one cycle only, label the three waves (or complexes) you have learned about in lab. Then, state the electrical events that occur during each of these three waves (or complexes), and whether each of these electrical events results in muscle contraction or relaxation. You don't have to discuss pressure changes or heart sounds, just the electrical activity and resulting change in cardiac muscle.
- P wave: atrial depolarization --> contraction
- QRS complex: ventricular depolarization --> contraction
- T wave: ventricular repolarization --> relaxation